paper 2 and 3 but all organic
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Give an equation for the preparation of 1,6-diaminohexane by the reaction of 1,6-dibromohexane with an excess of ammonia.
Br-(CH2)6-Br + 4NH3 → H2N-(CH2)6-NH2 + 2NH4Br
1,6-Diaminohexane can also be formed in a two-stage synthesis starting from 1,4-dibromobutane. Suggest the reagent and a condition for each stage in this alternative synthesis.
KCN AQEOUS ALCOHOL
lalh4 in dry ether - aqueous
justify statement that no chiral carbons
no carbon atom is attached to 4 different groups
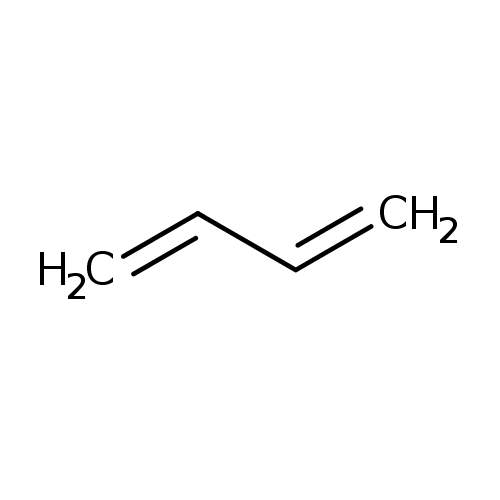
butA 1-3 DIene
when drawing the repeating unit, alway remember
the trailing bonds
why are addition polymers non bio degradable
carbon carbon bonds, cannot be hydrolysed
carbon carbon bonds, are non polar
why does alcohol have a higher boiling point than ketone
1) alcohol, has H bonds BETWEEN MOLECULES, ketone has dipole dipole intermolecular forces
2) more energy is required to overcome the H bonds
suitable reagent for the hydrolysis of a protein
CONC HCL
why was it necessary to use two different solvents
some of the amino acids did not separate, with the first solvent
some of the amino acids, have the same RF value
why can … be distinguished by high res mass spectrometry, even if same mr
the precise relative formula masses, are different
how does co2 cause global warming
c=o bonds in co2 absorb ir radiation
ir radiation EMITTED by earth, does not escape
state meaning of the term complementary in dna
A TO T
C TO G
explain why sodium borohydride reduces aldehyde, but not alkene
1) nucleophile is attracted to the delta positive carbon
2) the c double bond c is electron rich
3) the nucleophile is repelled by the c=c
name the type of compound shown by the formula RCOOK (coconut oil and KOH)
carboxylate salt
uses of carboxylate salt
SOAP, detergent surfactant
why is aqueous ethanol a suitable solvent when heating oil w KOH
acts as a MUTUAL solvent
to ensure reactants are miscible
meaning of fraction
GROUP OF HYDROCARBONS, with similar boiling points
why does co2 absorb IR radiation
c=o vibrates at the same frequency of IR
how is bioethanol produced
1a Photosynthesis (is the natural process in plants that takes CO2 from the air)
1b Fermentation (is the process used to make bioethanol releasing some CO2)
1c Combustion (is the process where bioethanol is burned and releases CO2)
equations for the formation of bioethanol
2a 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
2b C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
2c 2C2H5OH + 6O2 → 6H2O + 4CO2
environmental issues with bioethanol
deforestation, sacrifice land that could be used for fuel
loss of biodiversity habitat
fuel used in production and distribution
suitable table for the combustion practical

two disadvantages of using a glass beaker on a tripod and gauze instead of …
1) glass is a poorer CONDUCTOR than …
2) tripod and gauze would have a fixed height above the flame
3) tripod and gauze would reduce heat transfer
why is benzene more thermodynamically stable
PI electrons delocalised
reagent needed for dehydration
conc H2So4
ethanol —>ethene + water
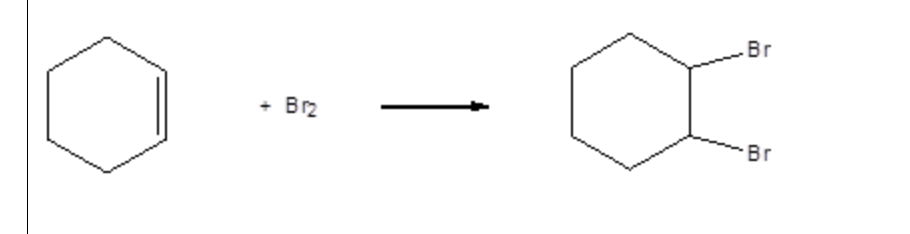
electrophilic addition equation w br2
why is fewer steps better
less energy used
better yield
why is high percentage atom economy better
less waste, less pollution
state how cfcs form chlorine atoms in the upper atmosphere
c-cl bonds broken homolytically
suggest why 1cm³ portions of the reaction mixture is added to an excess of NaHCo3
The sodium hydrogencarbonate solution neutralises the acid (catalyst)
So stops the reaction
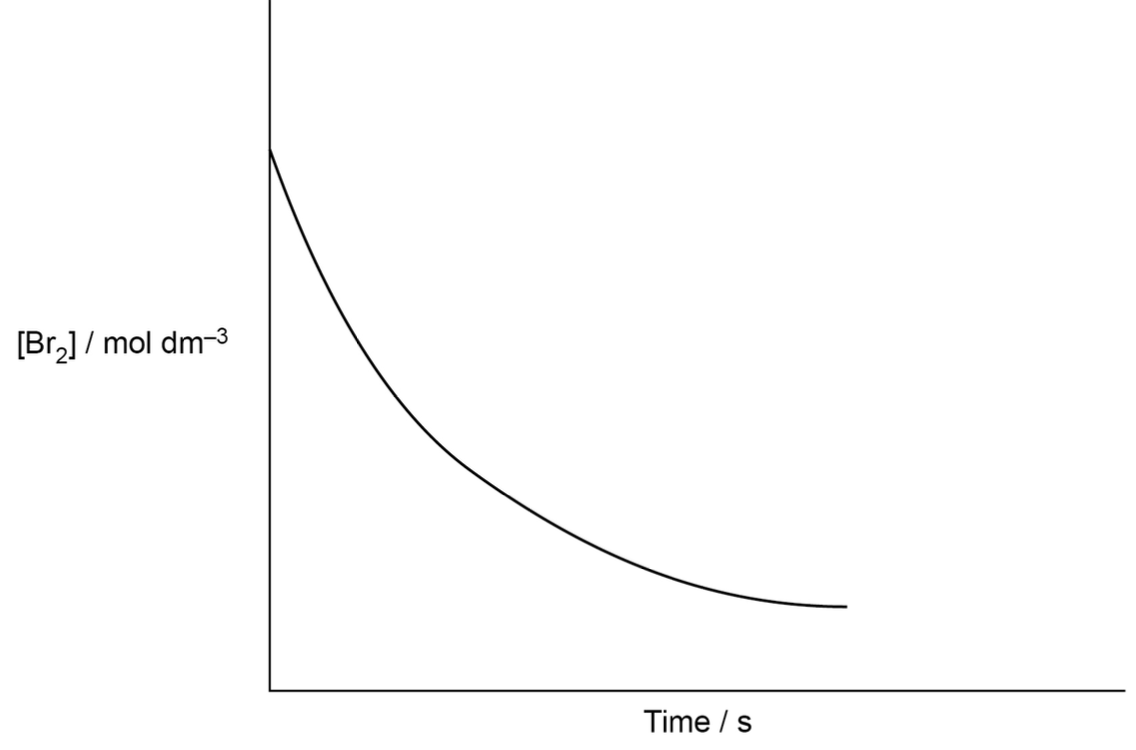
how does graph show reaction is zero order with respect to iodine
volume/time graph
The graph is a straight line / has a constant gradient
So the rate of reaction does not change as the concentration (of iodine) changes / the iodine is being used up at a constant rate.
graph that shows 0 order w respect to time
use evidence from the equation to explain why…. is the rate determining step
… contains all the species in the rate equation
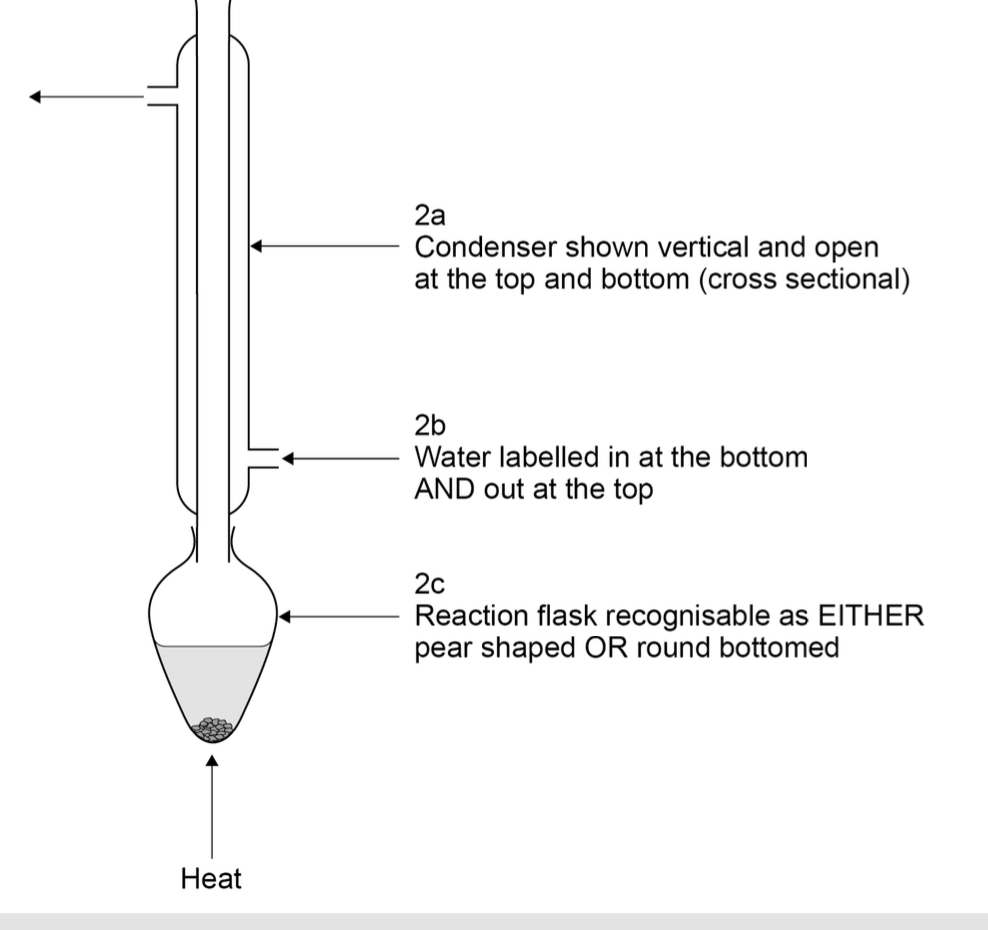
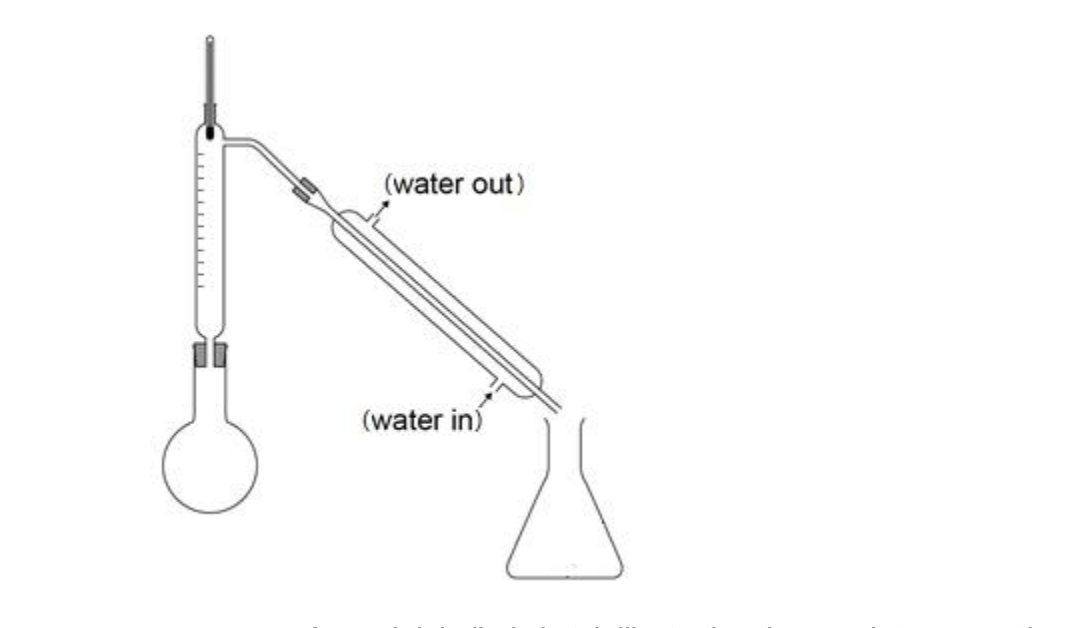
aparatus for reflux
when shaking mixture, what precaution should you take
Remove stopper/bung OR tip the funnel upside down and open
the tap
there would be a build up of pressure
equation for the formation of the electrophile for electrophilic substitution of benzene
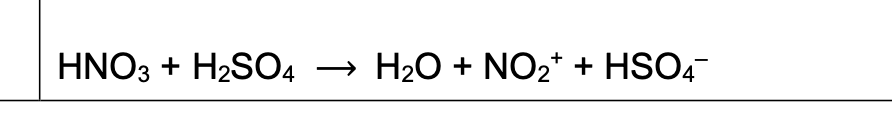
use of amine
MANUFACTURE of dyes
why would using a conical flask instead of a beaker give more accurate results
reduces loss of liquid droplets
suggest why chloroethanoic acid, is stronger than ethanoic acid
M2 Cl is an electron withdrawing group or negative inductive effect
M3 Weakens the O-H bond / increase polarity of O-H bond
how do you know… rds
ONLY LOOK AT RATE EQUATION
can say slowest step
condition for KCN nucleophilic substitution
AQUEOUS + ETHANOL
reagent and condition needed for reduction of nitrile to amine
lial4 in dry ether
acid used to acidify dichromate
sulfuric acid
why is fractional distillation preferred over simple distillation
… have similar boiling points
how would experimental enthalpy of combustion differ from data book value
it would be lower, less exothermic
incomplete combustion
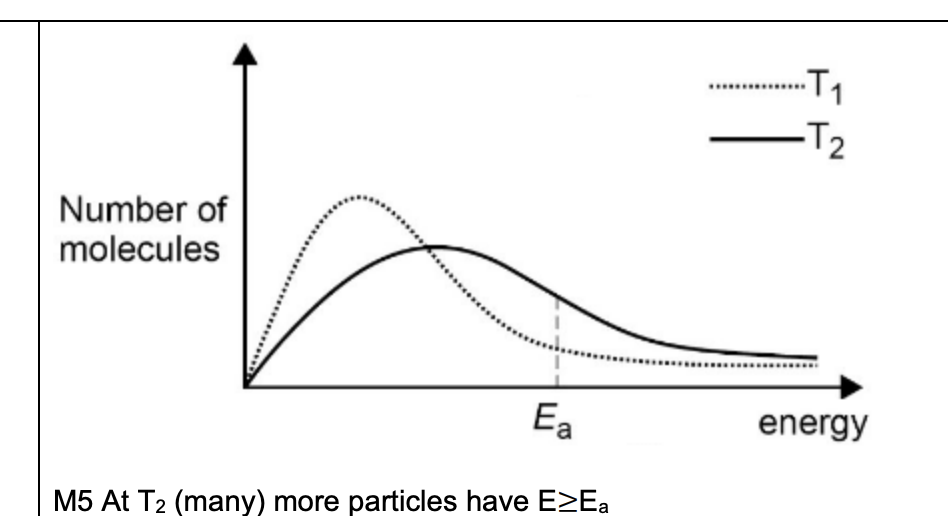
labelled maxwell boltzman cuve
when calculating q=mcdelatat what should be the unit of the mass of water
GRAMS
what is kevlar made from
benzene 1,4 dicarboxylic acid
1,4 di amino benzene
nylon 6,6
hexanedioc acid 1,4 diamino hexane
polyamide
polyester
terylene
dicarboxylic acid and diol
benzene 1,4 dicarboxylic acid ethane 1,2 diol
conditions for base hydrolysis of esters
AQUEOUS
formation of biodiesal
triester and methanol, makes glycerol and methyl esters
KOH as a catalyst
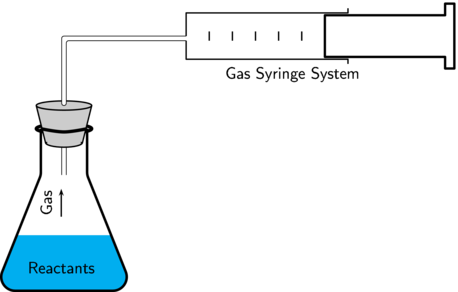
apparatus, for measuring volume of gas
why does chlorobenzene, not react with ammonia
electron rich ring or benzene or pi cloud repels nucleophile/ammonia
why is ethanoic anhydride not used in industrial synthesis
Corrosive OR forms strong acid/HCl (fumes) OR vulnerable to hydrolysis OR dangerous (to use)
KCN
AQUEOUS ALCOHOL
why is 3 aminopentane a stronger base than ammonia
lone pair on N more available, because of alkyl postive inductive effect
why is the halogenoalkane attacked by the nucleophile
bromine more electronegative than carbon
CARBON IS PARTIALLY POSITIVE
electron pair donated to the partially positive carbon
aldehyde to hydroxy nitrile
KCN & (dil) acid
fractional distillation
ozone depletion
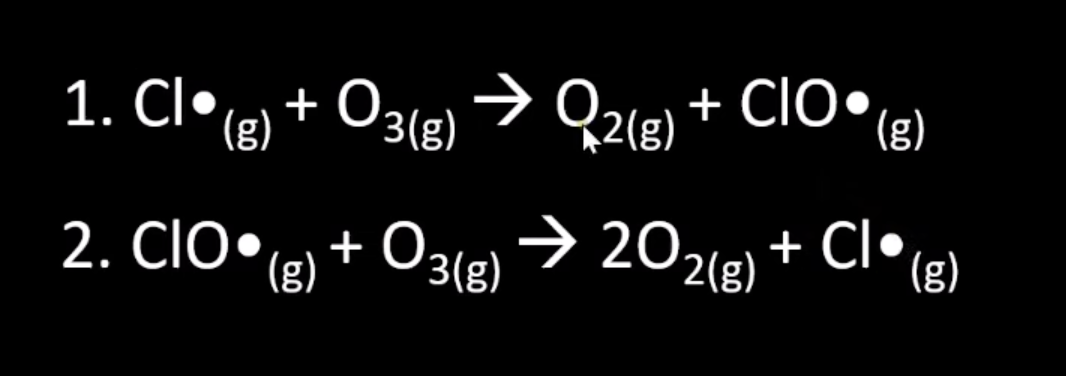
formation of electrophile no2+

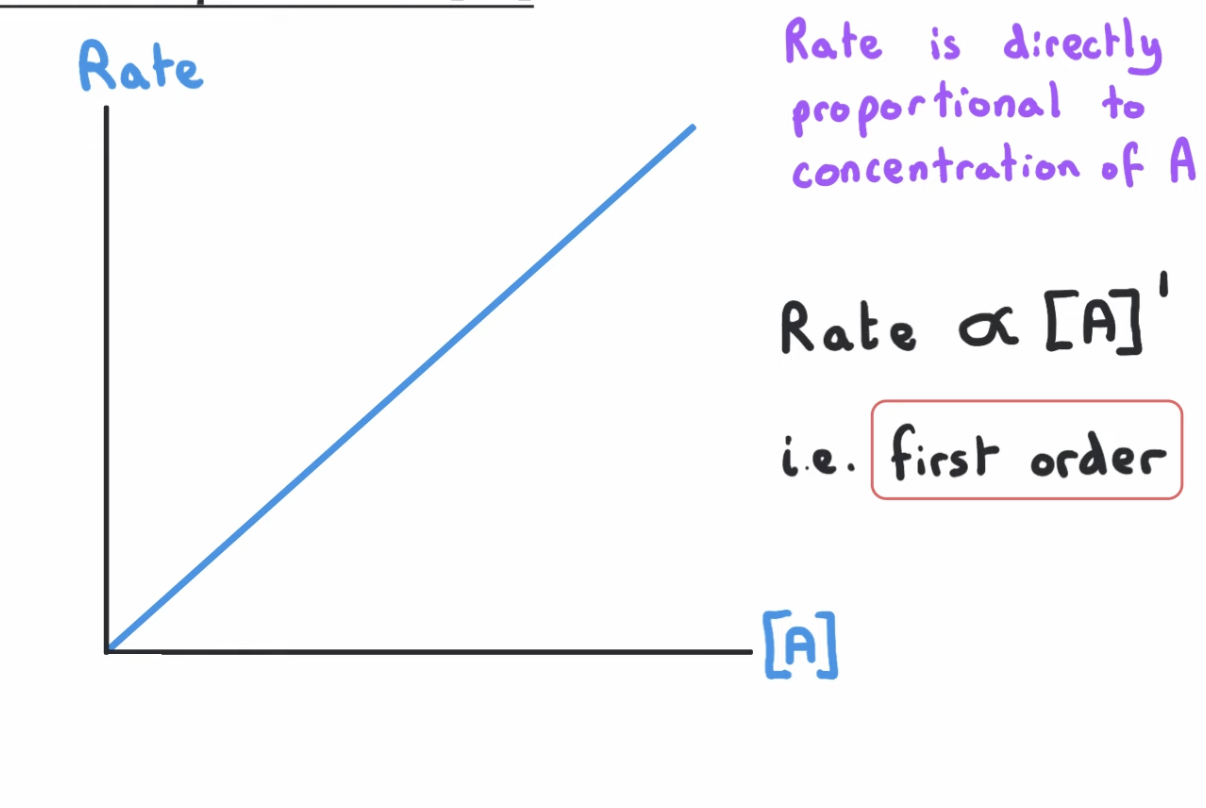
first order graph
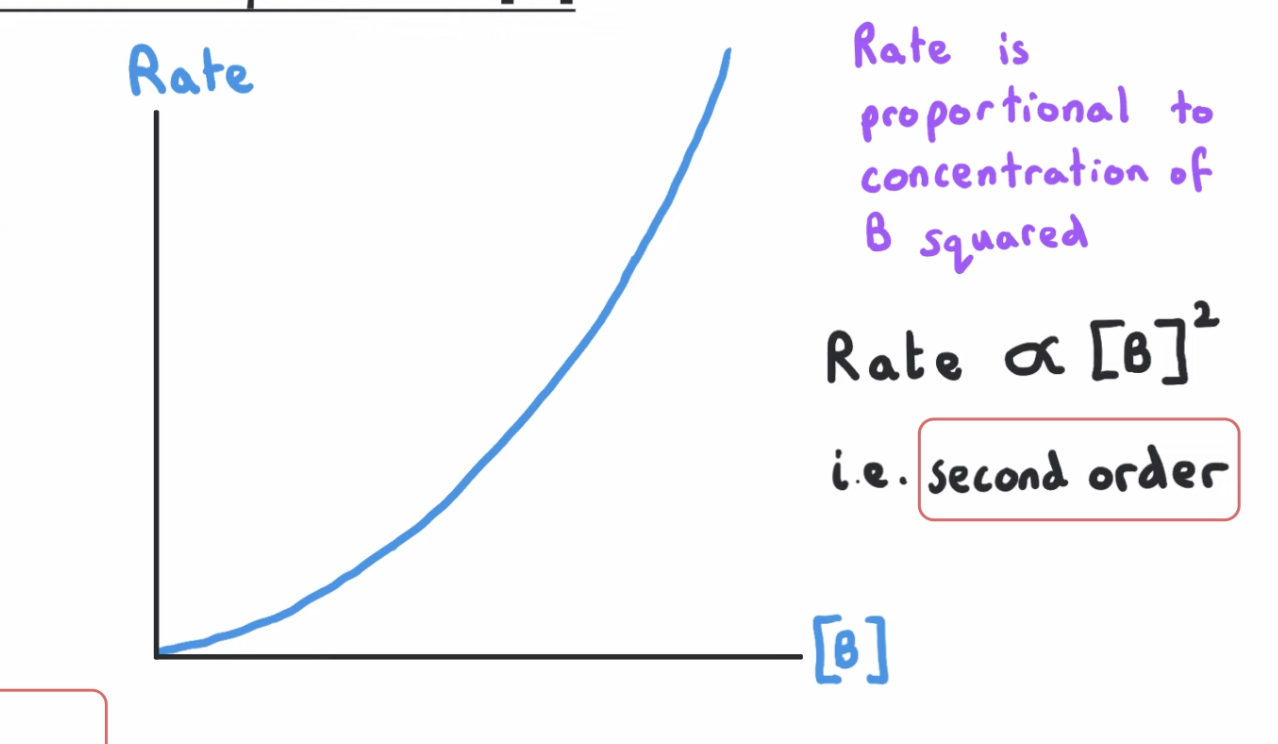
second order
0 order

why would raising temp by ten degrees have a much greater effect on the rate of reaction, than doubling conc
Reaction occurs when molecules have E≥Ea
Raising T by 10 °C causes many more molecules to have this E
Whereas doubling [E] only doubles the number with this E
boiling point of alkene ketone alcohol
alkene lowest, ketone, alcohol
which alcohols cannot be dehydrated
alcohols where the adjacent carbon, does not have any hydrogens attached to it
how do h bonds form in a protein
Nitrogen and oxygen are very electronegative Therefore, C=O and N–H are polar Which results in the formation of a hydrogen bond between O and H In which a lone pair of electrons on an oxygen atom is strongly attracted to the δ+H
why are polyesters biodegradable
Polar C=O group or δ+ C in Q (but not in P) Therefore, can be attacked by nucleophiles (leading to breakdown)
enthalpy of lattice dissociation
the enthalpy change, when one mol of a solid ionic compound DISSOCIATES FULLY into its gaseous ions
main difference of value of enthalpy of solution
HEAT GAIN FROM SURROUNDINGS
or incomplete dissolving
definition of steroisomers
1) Same molecular formula
2) Different spatial arrangement of ATOMS
why can … not experience e/z isomerism
two of the same groups on one of the C=C
quicker formation of ppt for halides and silver
carbon halogen bond strength decreases down the group
why is the reaction fastest at the start
1) high conc of reactants
2) more frequent successful collisions
why is ethanoic anhydride preferred to ethanoyl chloride in aspirin practical
1) ethanoic acid less corrosive
2) is not vulnerable to hydrolysis
why is reflux not essential when flask is heated to 85 degrees for ten mintues
boiling points are above 85 degrees
none of them will boil
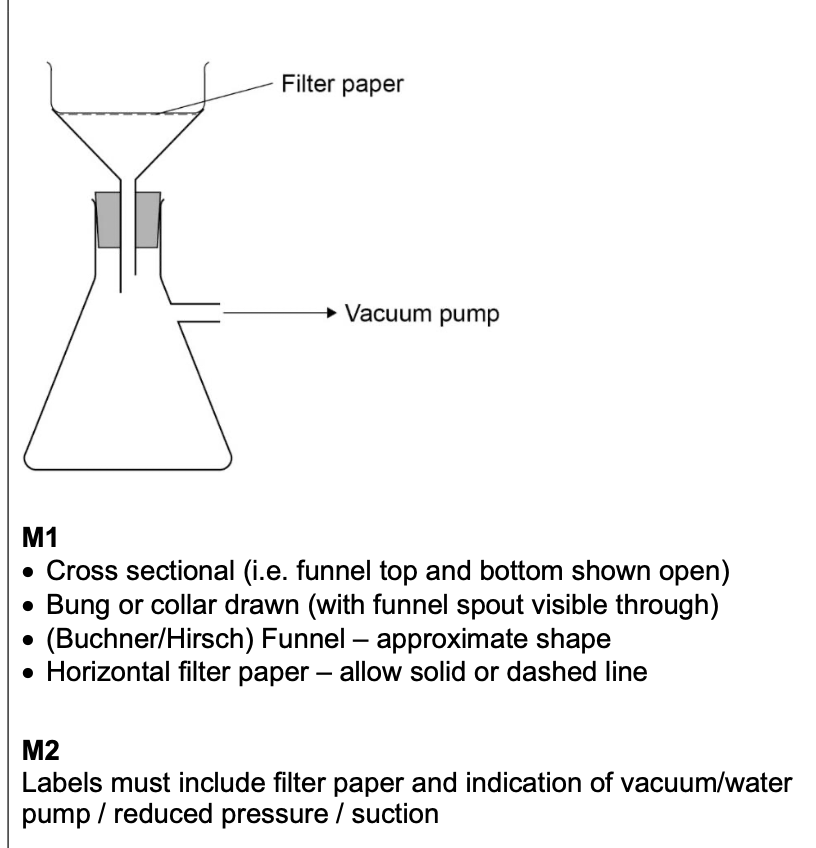
filter under reduced pressure apparatus
recrystallisation practical

how would you know if the product is impure
would melt over a larger range of TEMPERATURES
the melting point value would be lower than the data book value
why is loose cotton wool instead of leaving flask open
to avoid acid/solution/liquid
escaping
OR to avoid (acid/solution/liquid) splashing/spraying/spitting
why is loose cotton wool instead of inserting a bung
allow CO2 to escape
state how graph shows rate = k[Hcl]
straight line and through the origin
what variables can be measured to investigate rate of reaction at constant temperature
• volume of gas / CO2
• pH
• concentration of HCl/acid/H+
• conductivity
why would add NAOH dropwise around the equivalence point
as there is a large pH change (for a small addition of alkali)
how does buffer buFF Ph
M1 OH– reacts with propanoic acid OR reacts with H+
M2 EITHER
ratio of [CH3CH2COOH] to [CH3CH2COO–] remains almost
constant
why would methyl orange not be a suitable indicator to use
would not change colour at the equivalence
point
why would universal indicator not be suitable
idea of range of colours during titration /
no distinct colour change
why increase in rate of reaction when a catalyst is added at a constant temp
the PROPORTION OF SUCCESSFUL COLLISONS INCREASES
decrease in activation energy
what is formed by the acid hydrolysis of phenyl benzenecarboxylate
c6h5cooH
why are polyesters biodegradable but polyalkenes are not
polyesters: C=O
polyalkenes: (only) C−C
polyesters are susceptible to nucleophilic attack
safety precautions when filling the burette
fill bellow eye level
if toxic wear gloves
dioate in burette and manganate
colourless to pink
(not safety) why is KCN used rather than HCN
[HCN] weak
describe enthalpy of solution practical
Stage 1 Method (1a) Measures water with named appropriate apparatus (1b) Suitable volume/mass / volume/mass in range 10 – 200 cm3 /g (1c) Into insulated container / polystyrene cup (NOT just ‘lid’) (1d) Add known mass of MgCl2(s) (1e) Use of ‘before and after’ weighing method. NOT ‘added with washings’
Stage 2 Measurements (could mark from diagram) (2a) Record initial temperature (min 2 measurements) (2b) Record T at regular timed intervals for 5+ mins / until trend seen (2c) Plot T vs time
Stage 3 Use of Results (3a and 3b could come from diagram) (3a) Extrapolate lines to when solid added (to find initial and final T) (3b) Tfinal – Tinitial = ∆T / idea of finding ∆T from graph at point of addition (3c) q = mc∆T (3d) amount = mass/Mr (0.80/95.3 = 8.39 x 10–3 mol) (3e) ∆Hsoln = q/8.39 x 10–3 or in words
in graph of delta g against temperature what is the gradient
- minus deltas s
role of sulfuric acid in the formation of ketone from alcohol
OXIDISING AGENT
Role of sulfuric acid with nacl
proton donor
explain why excess of NaOH used when reacting with ester
To ensure that the ester is completely hydrolysed / to ensure all the ester reacts