L19 Principles of Sensory Systems (Imported from Quizlet)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
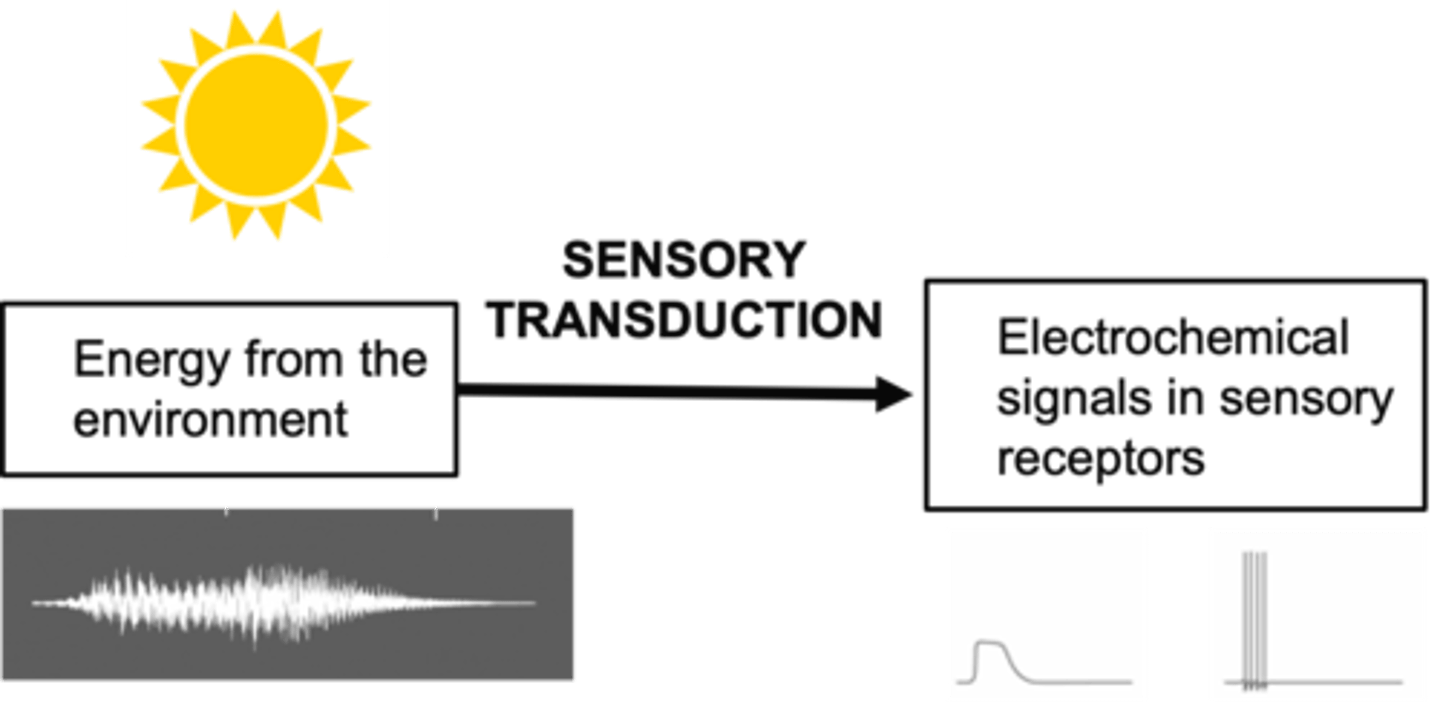
Require a physical stimulus
Must transform the stimulus into nerve impulses (done by sensory receptors in the peripheral nervous system)
Evoke a response to the signal in the form of perception of sensation (central nervous system)
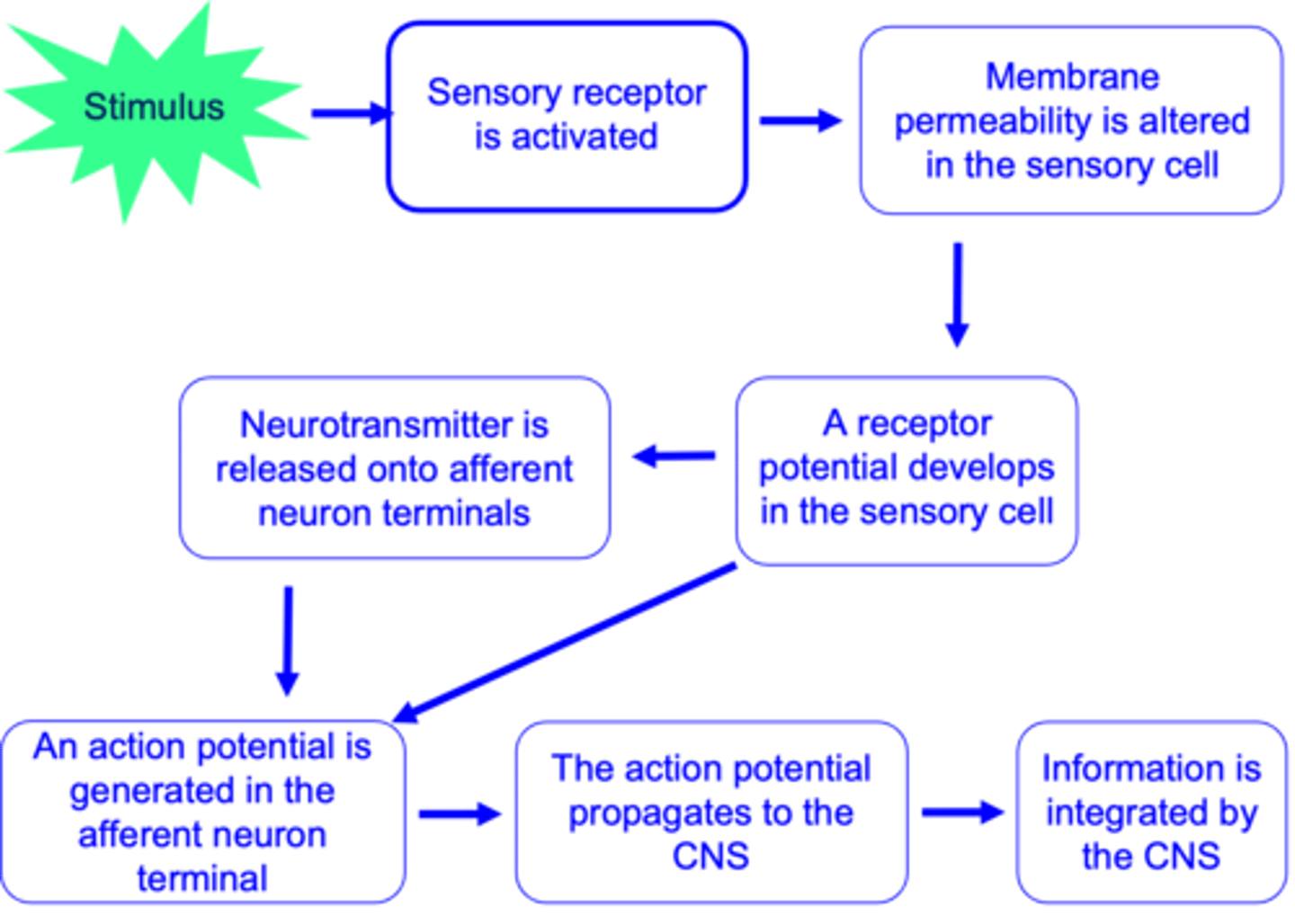
Conservation of sensory processing across systems consists of 3 common steps, what are they?
Cells, proteins
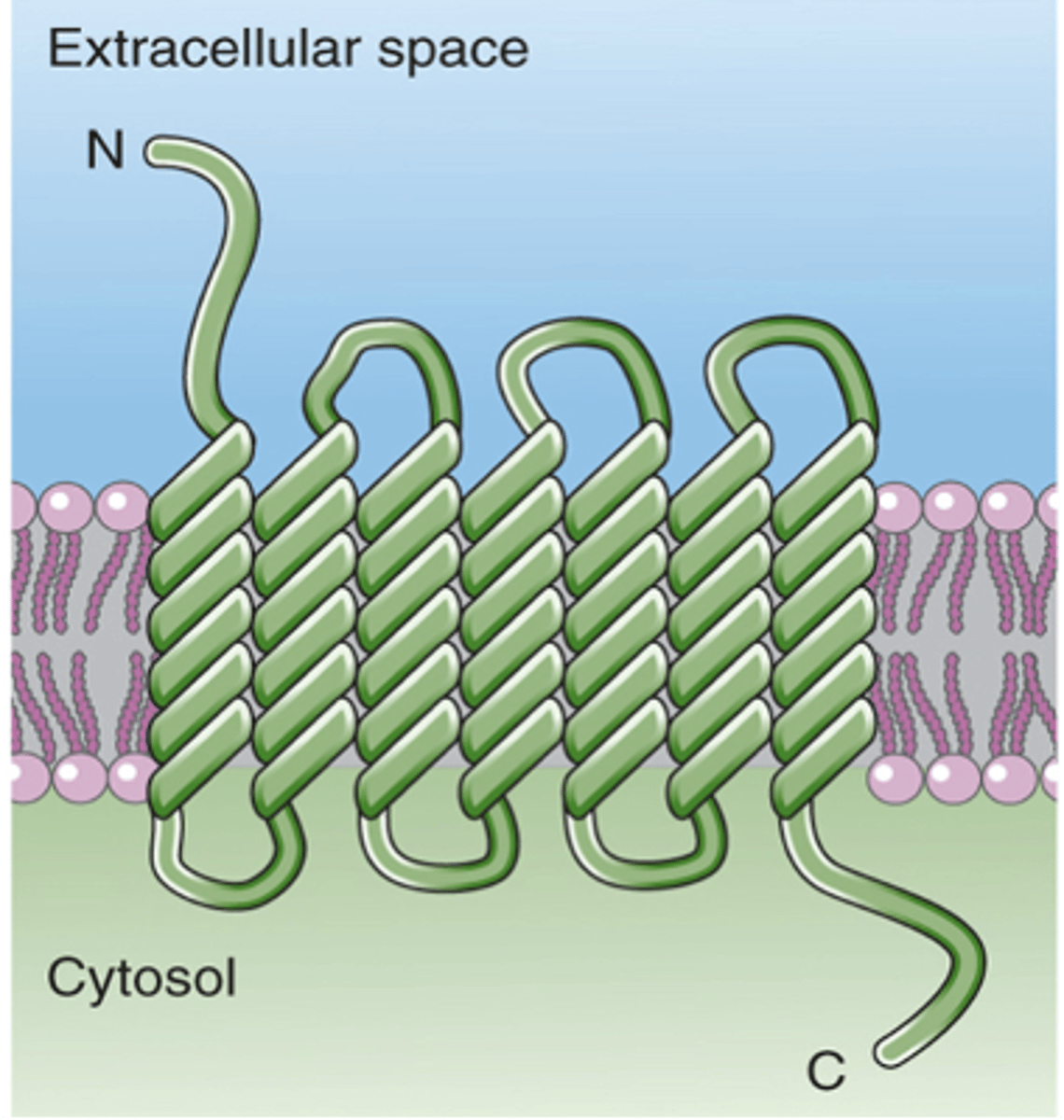
Sensory receptors are _____ not just ____________
Ion channels, G-protein coupled receptors
Many sensory receptor cells possess _____ __________ and _-_______ __________ _________ that are common to many bodily functions
G-protein coupled receptor
Is this an ion channel or G-protein coupled receptor?
Ion channel
Is this an ion channel or G-protein coupled receptor?
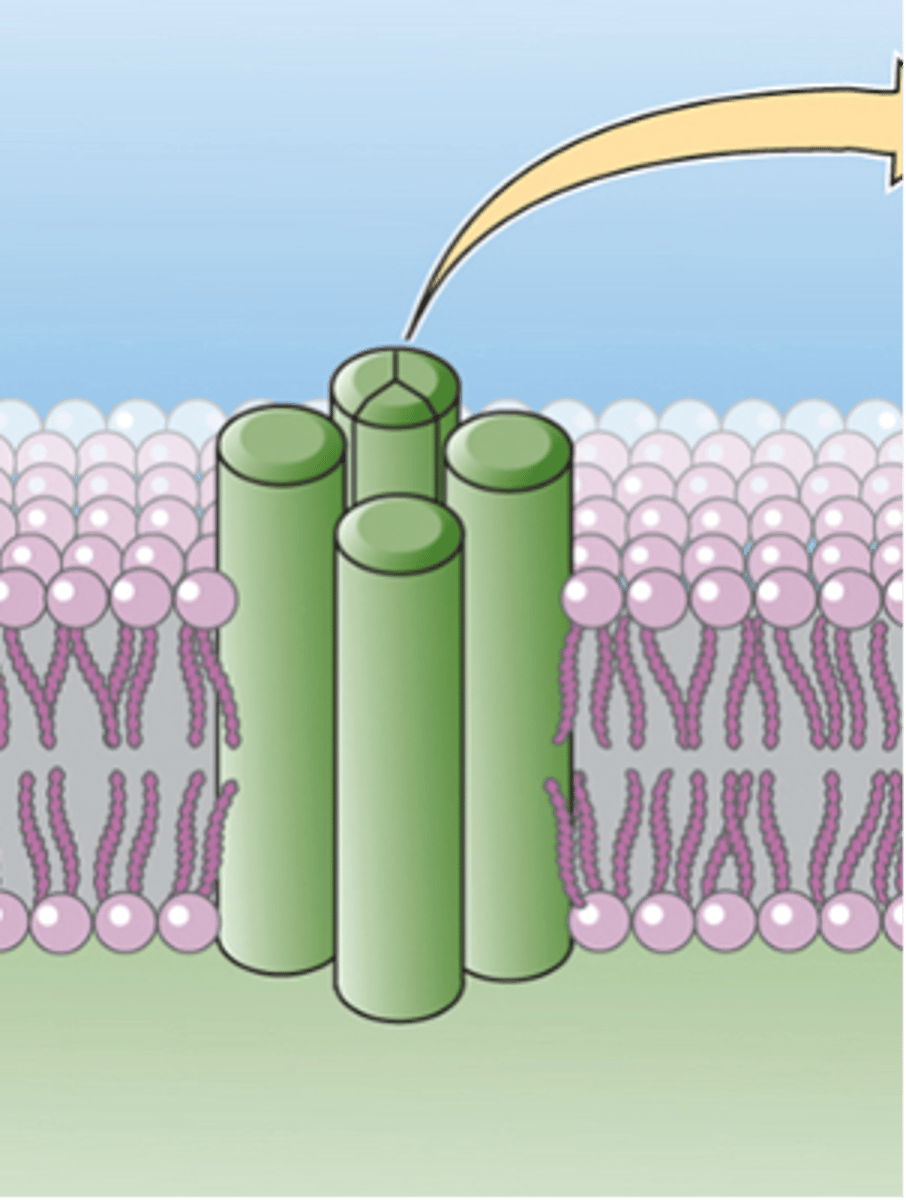
Structure, position
Specificity for sensory modalities is achieved by the _____________ and __________ of the sensory receptor
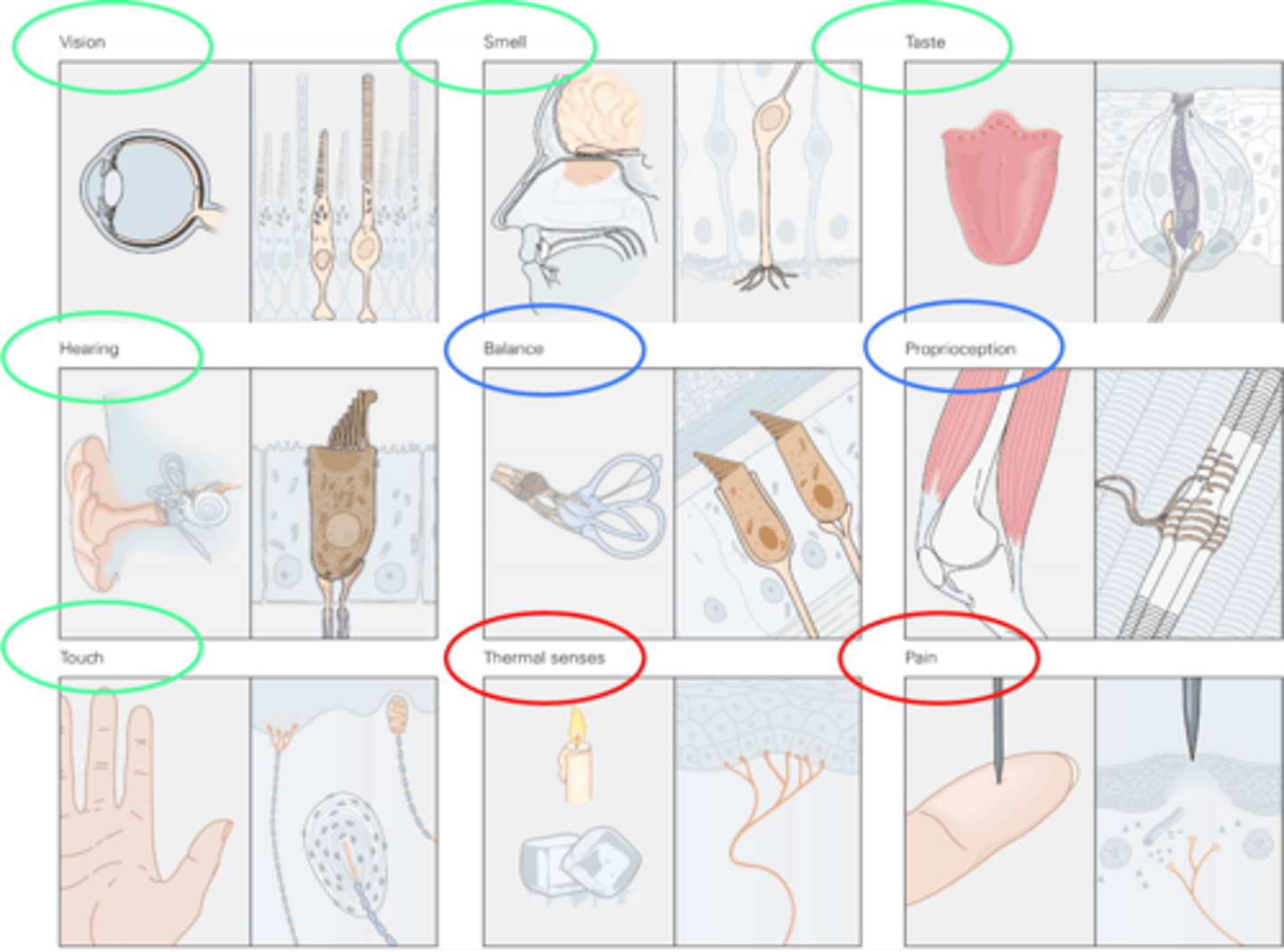
5 traditional senses (touch is removed and balance added)
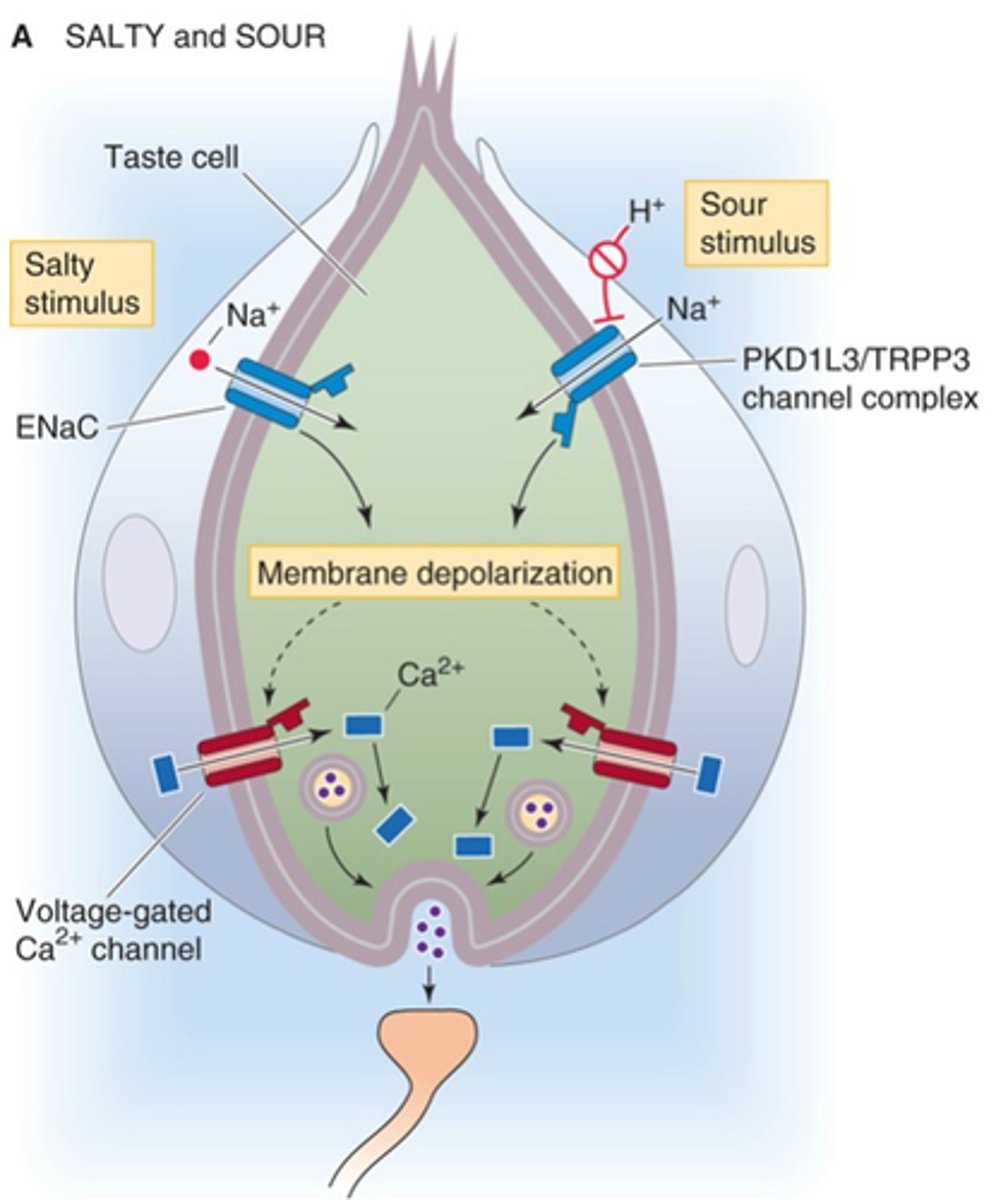
What is indicated in green in this image?
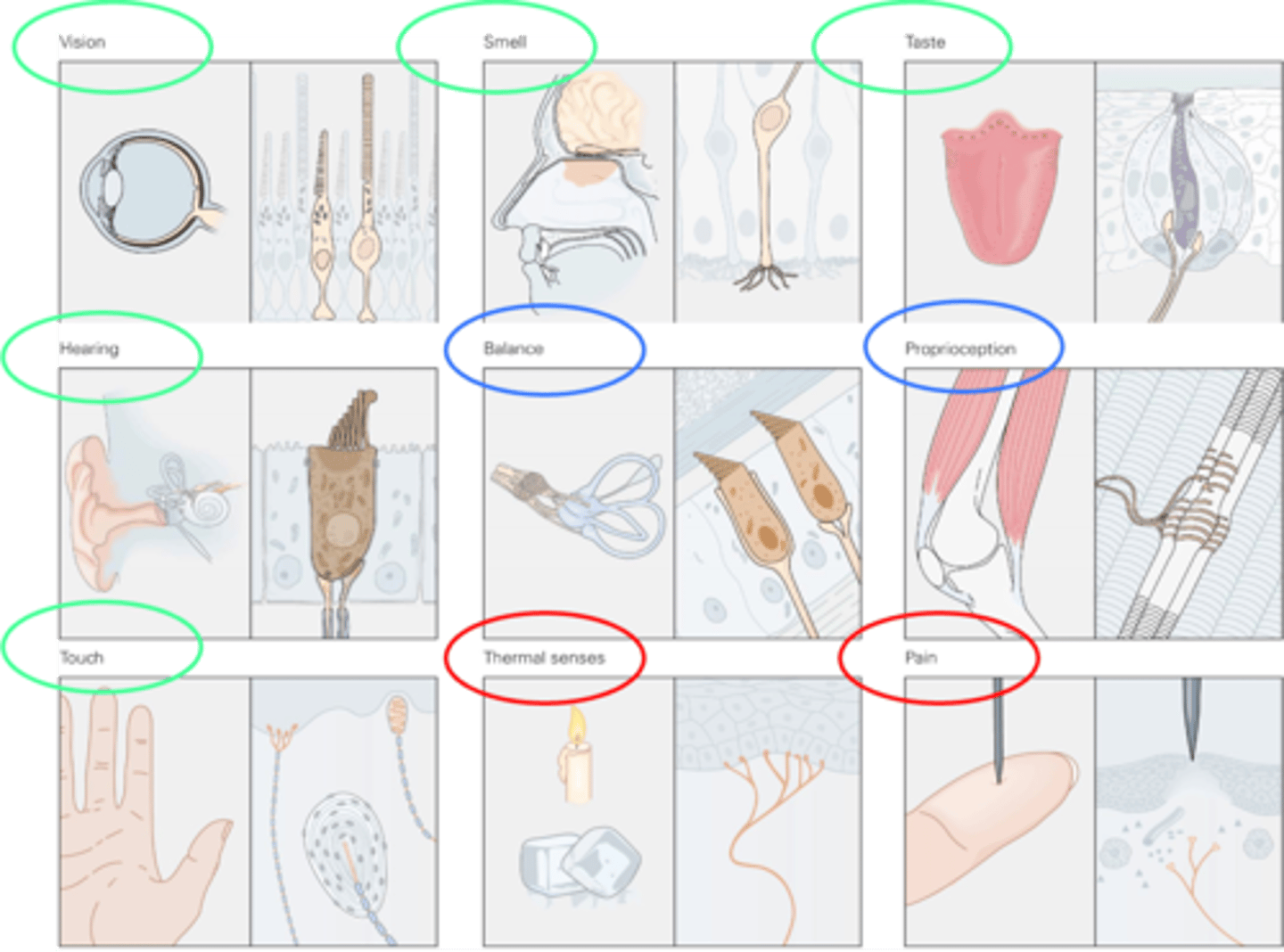
All sensory modalities
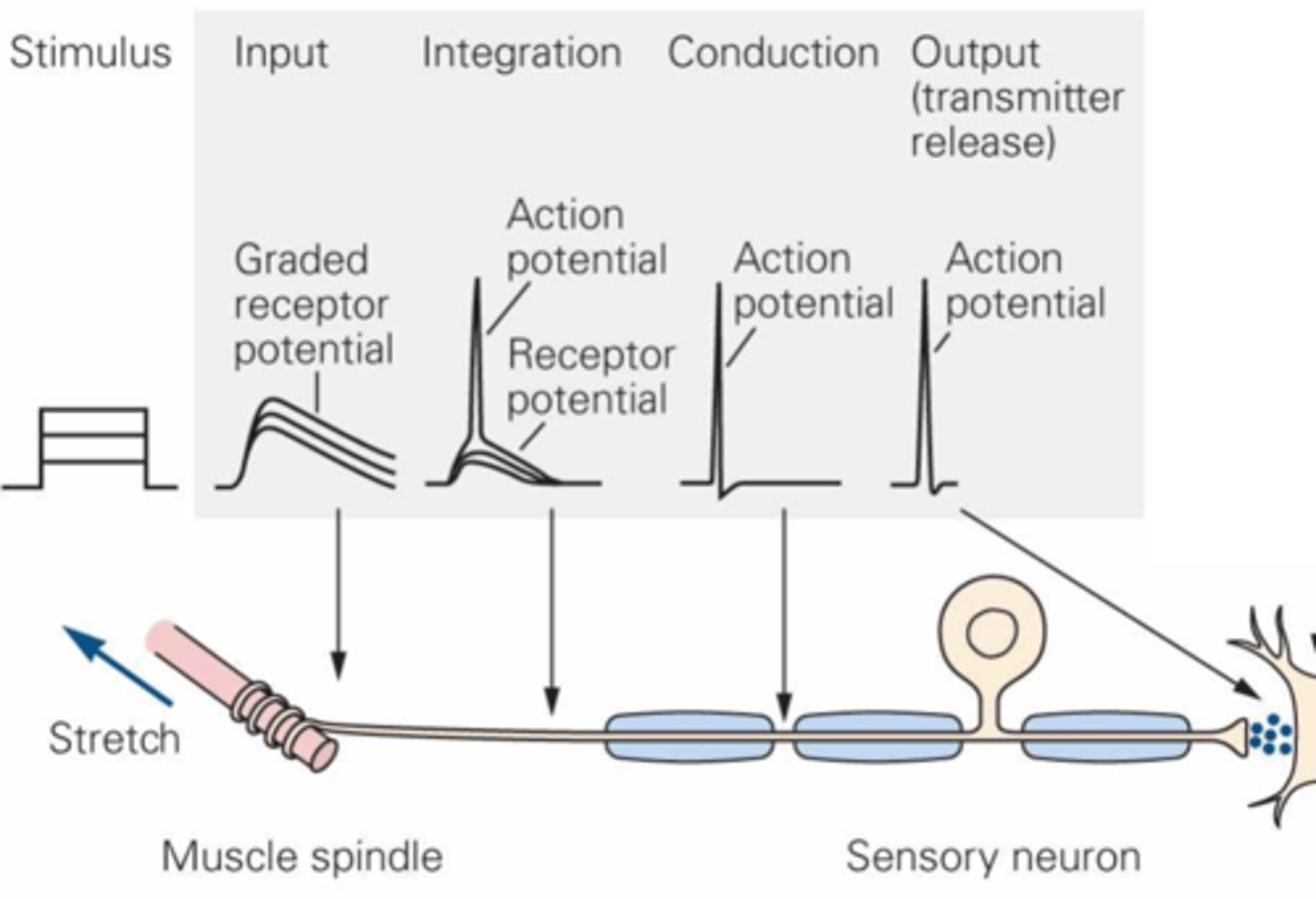
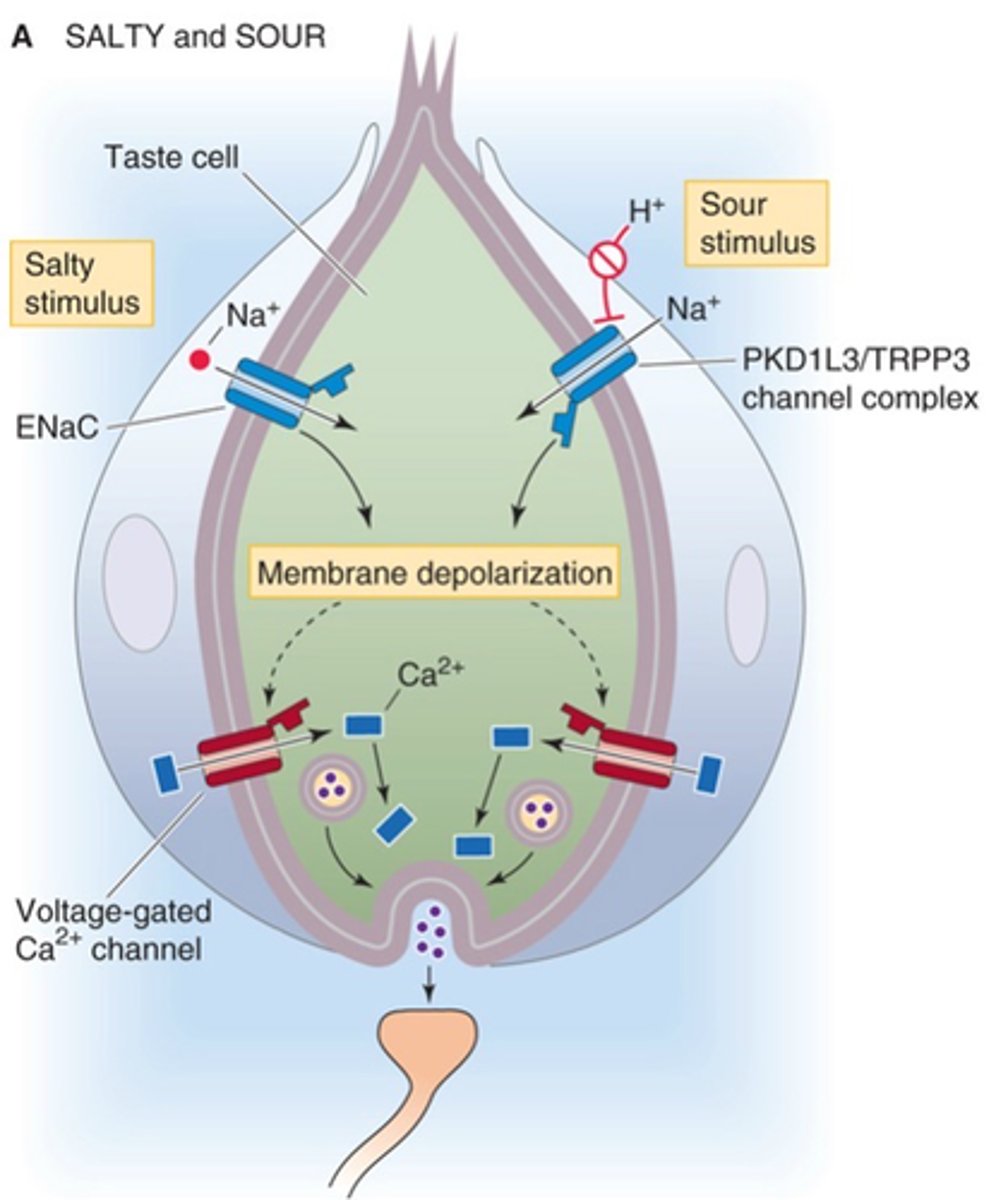
A receptor potential will cause an action potential in the afferent nerve terminal directly if the sensory cell and afferent nerve are the same thing (e.g. in the case of touch receptors)
What does the diagonal arrow indicate here?
Increase, increases in stimulus amplitude
Graded receptor potentials ___________ in size in response to ...?
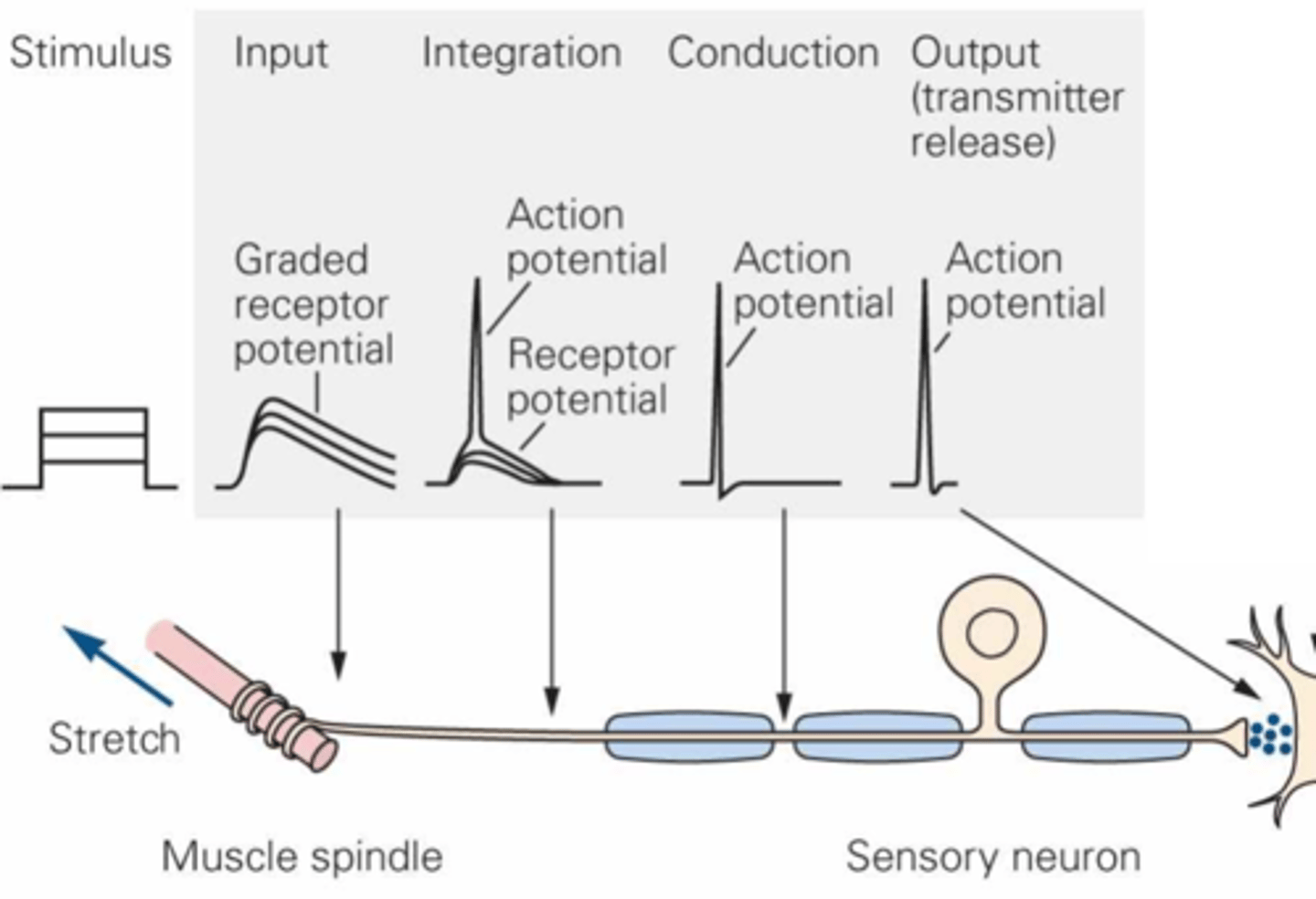
Size, threshold, activation
Action potentials are always the same ______, but have a _____________ for _____________
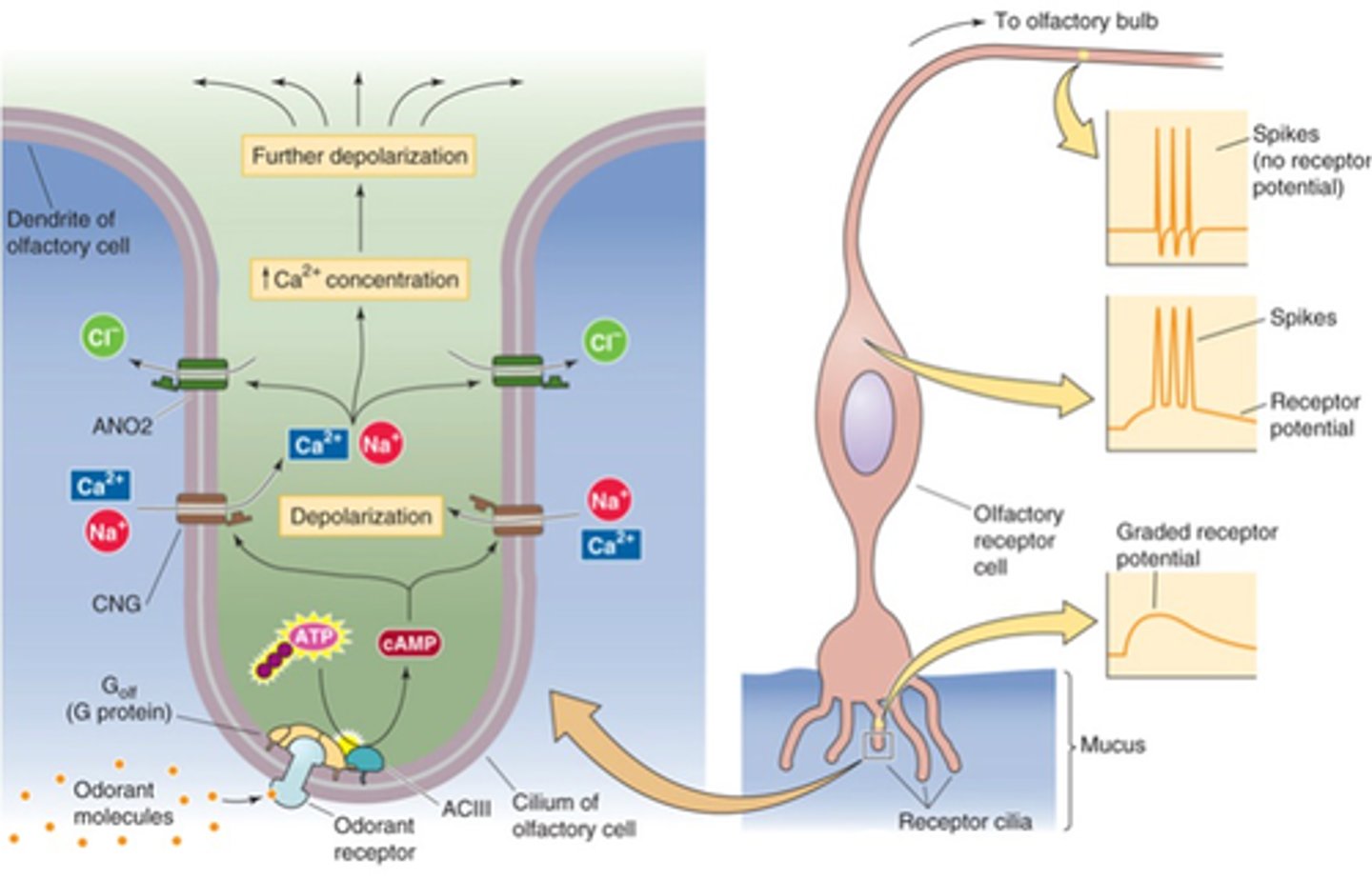
Olfactory receptors
Name an example of direct neuronal activation
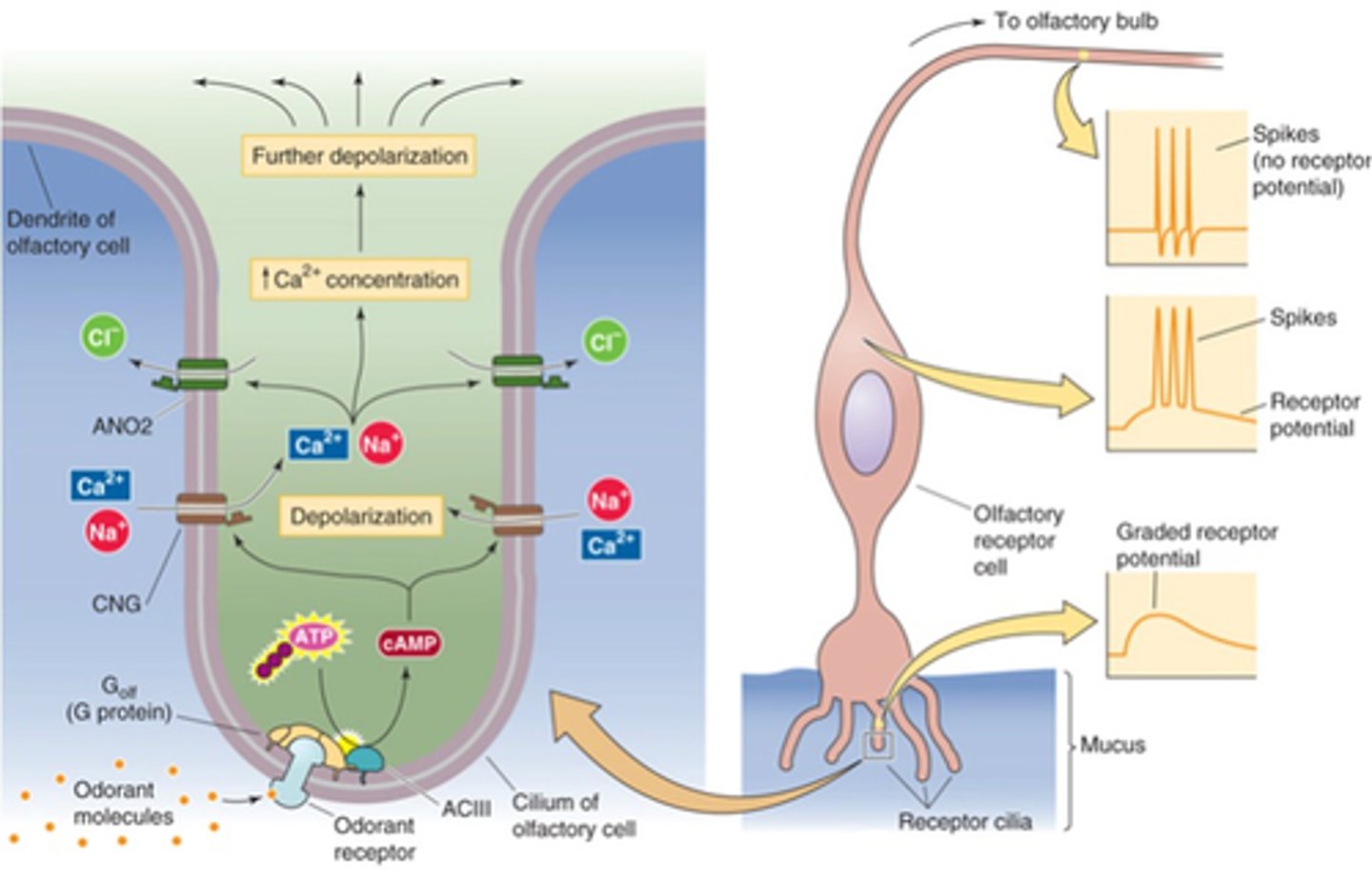
Depolarisation, graded receptor potential
Ion influx causes membrane ______________ and a ________ __________ _________ develops in a cilium
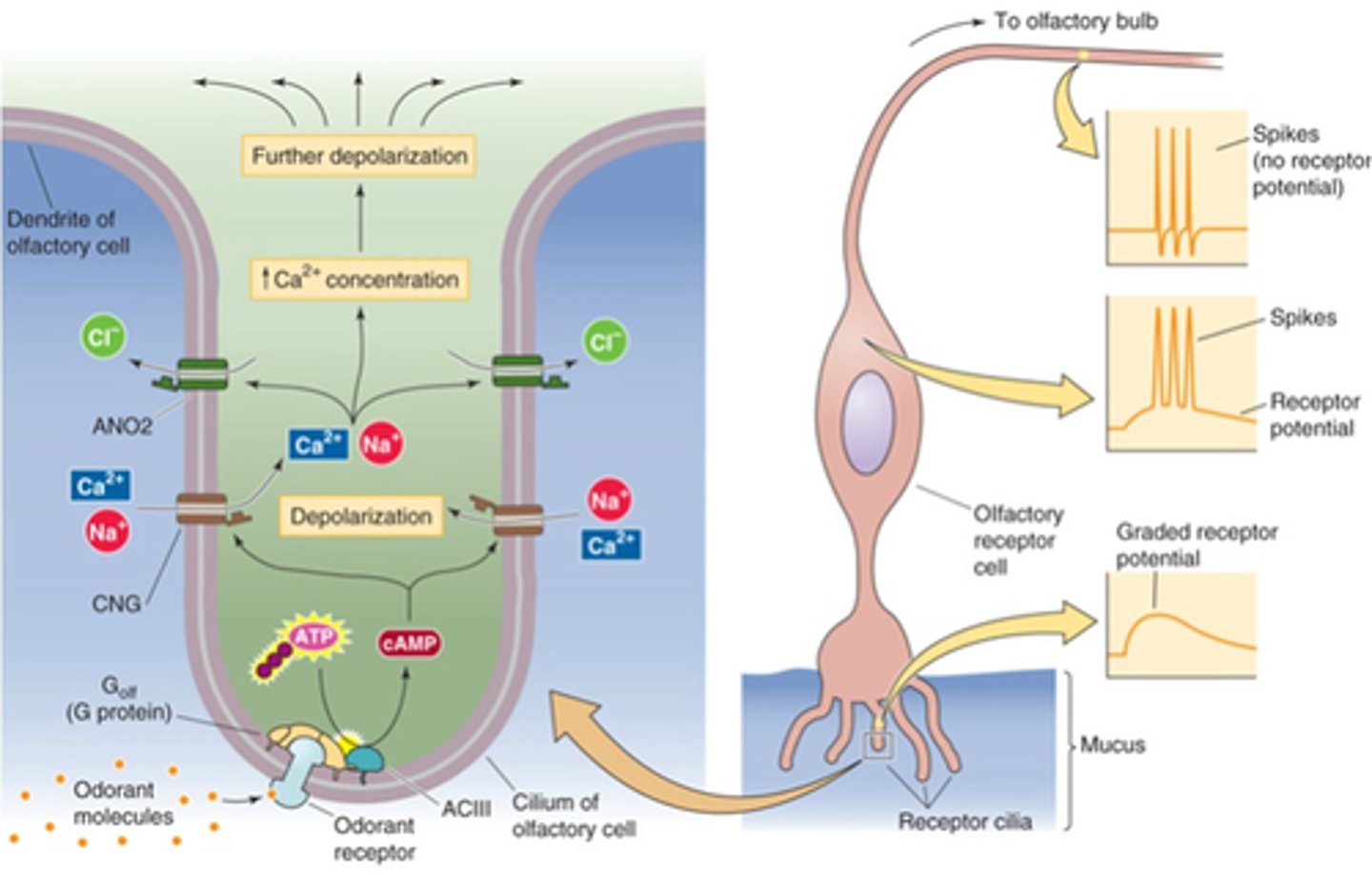
Depolarisation, action potentials
Large enough receptor potentials cause ________________ in the cell soma, triggering ________ ___________ that travel to the olfactory bulb
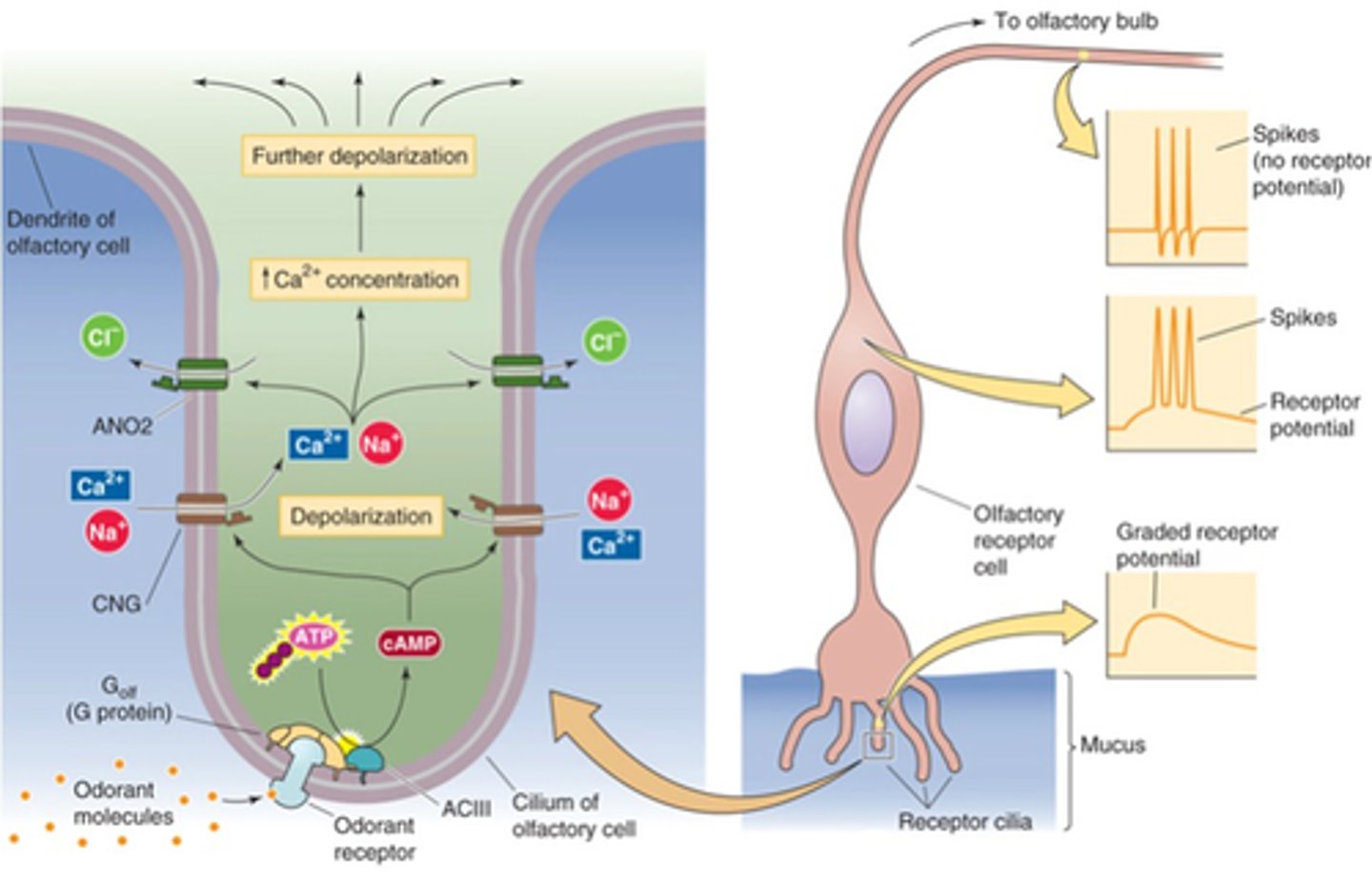
Bipolar neurons
Which broad category of neuron would the olfactory receptor cell fall into?
Taste receptors
Name an example of direct neuronal activation including synapse
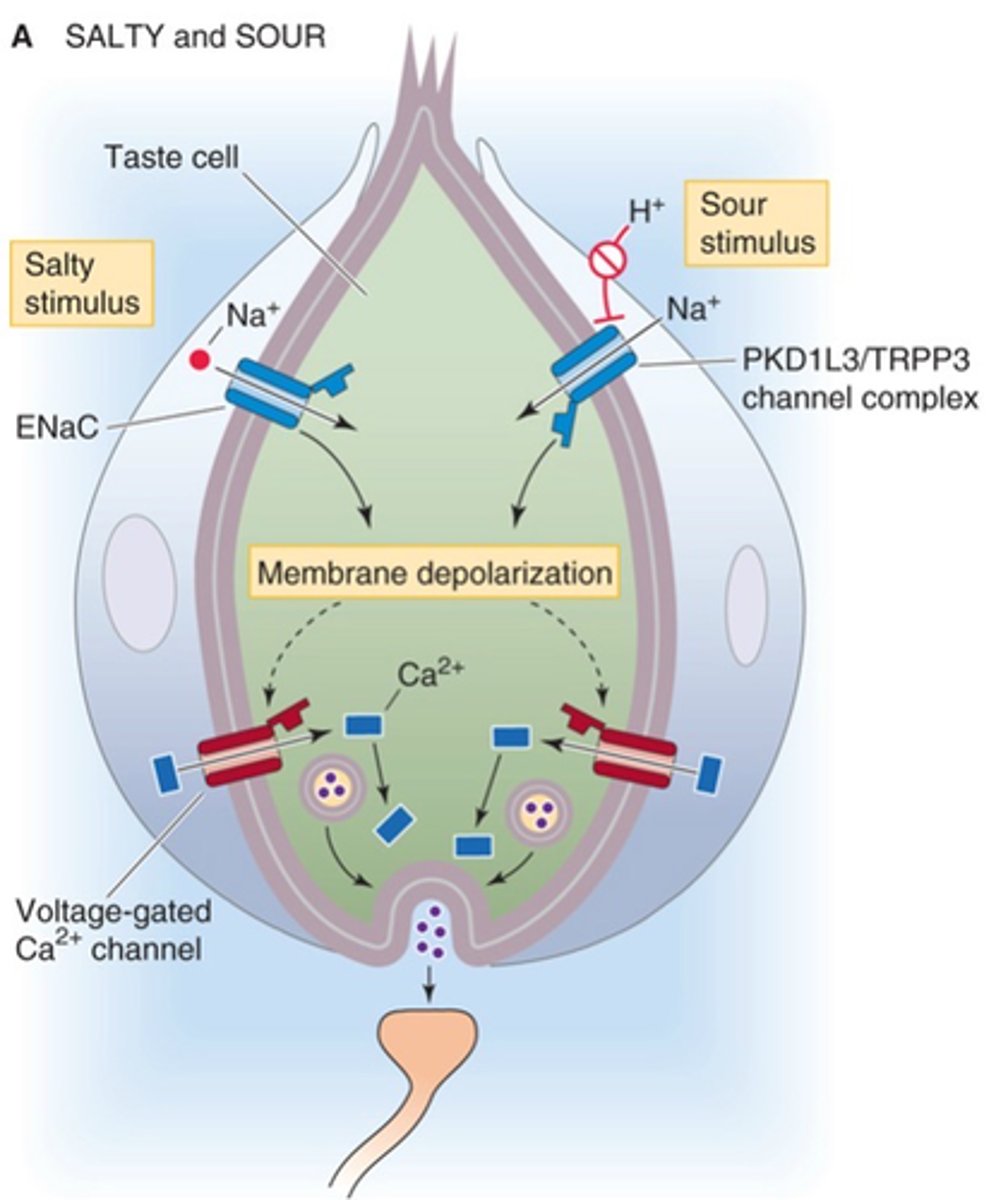
Depolarisation, graded receptor potential
Ion influx causes membrane _______________ and a __________ __________ ____________ develops
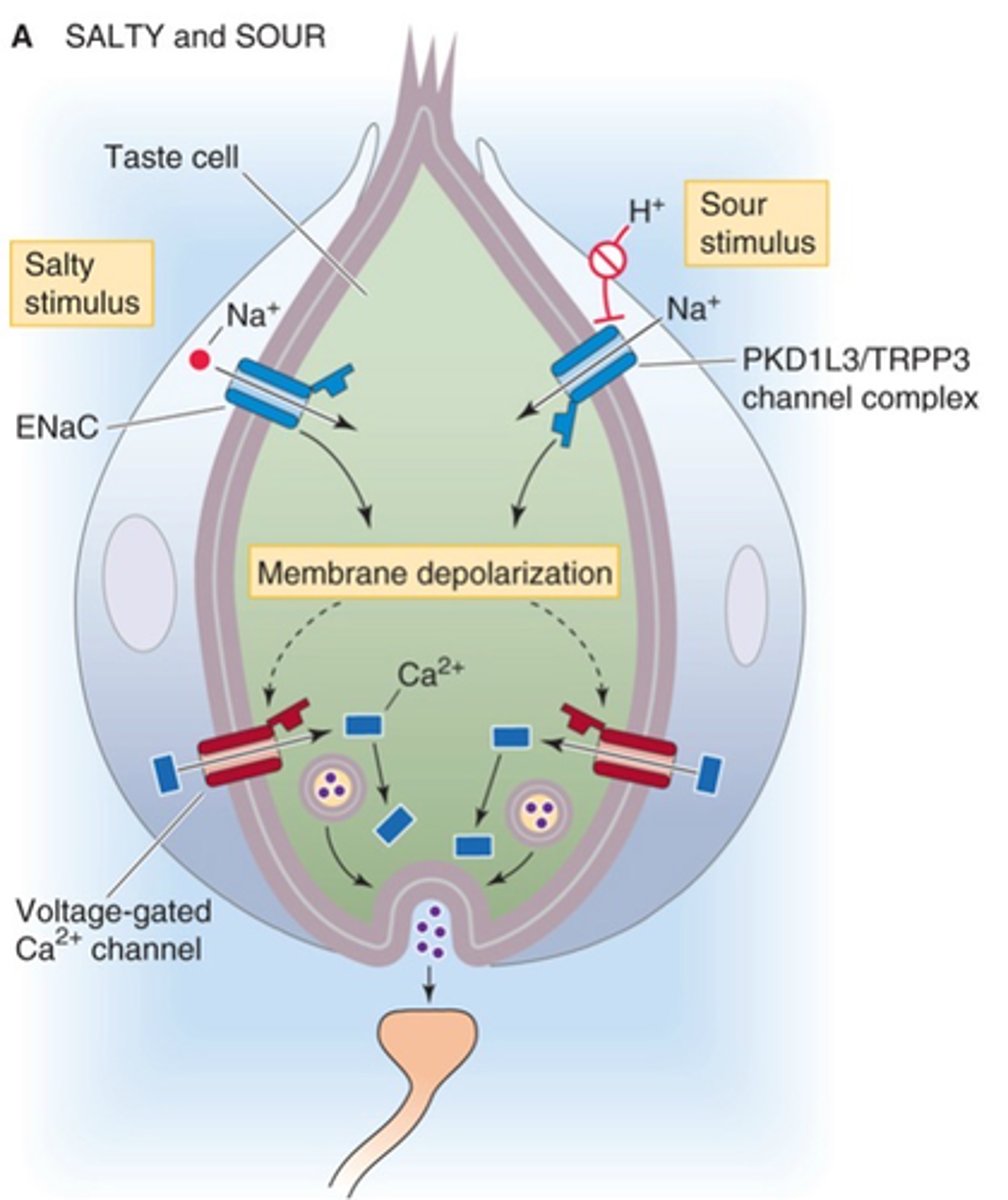
Synaptic vesicle, neurotransmitter
Initiates ____________ _______ fusion with membrane and ___________________ release
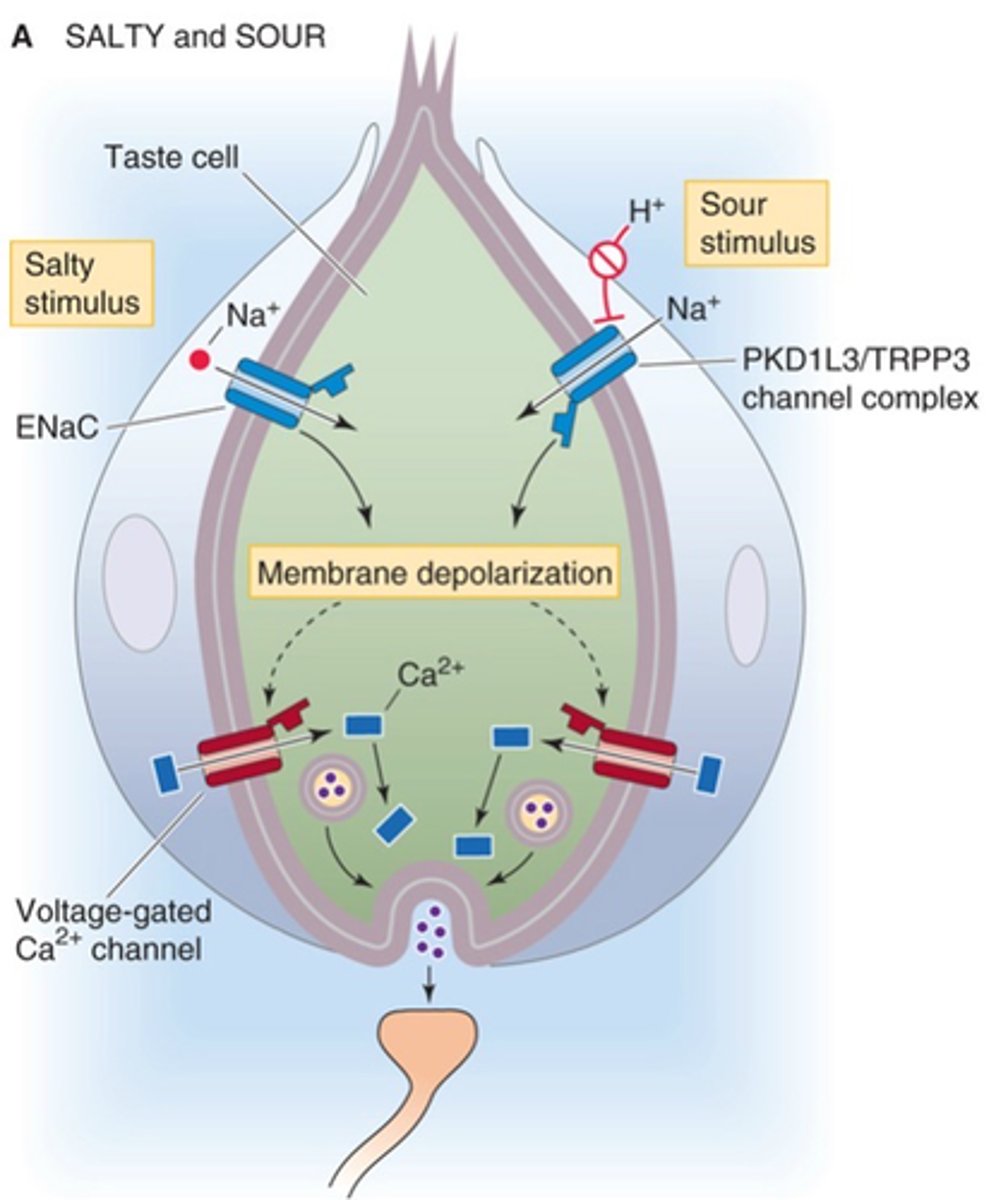
EPSP, afferent neuron
Neurotransmitte binds to postsynaptic receptors, generating an ______ in the dendrite of the ____________ __________
Action potentials
Large enough EPSPs generate what?
Graded receptor potentials
All sensory receptor cells respond with ...?

Primary afferent neurons, neurotransmitters
Sensory receptor cells can also be the ___________ _________ _________ or can release __________________ on to primary afferent neurons
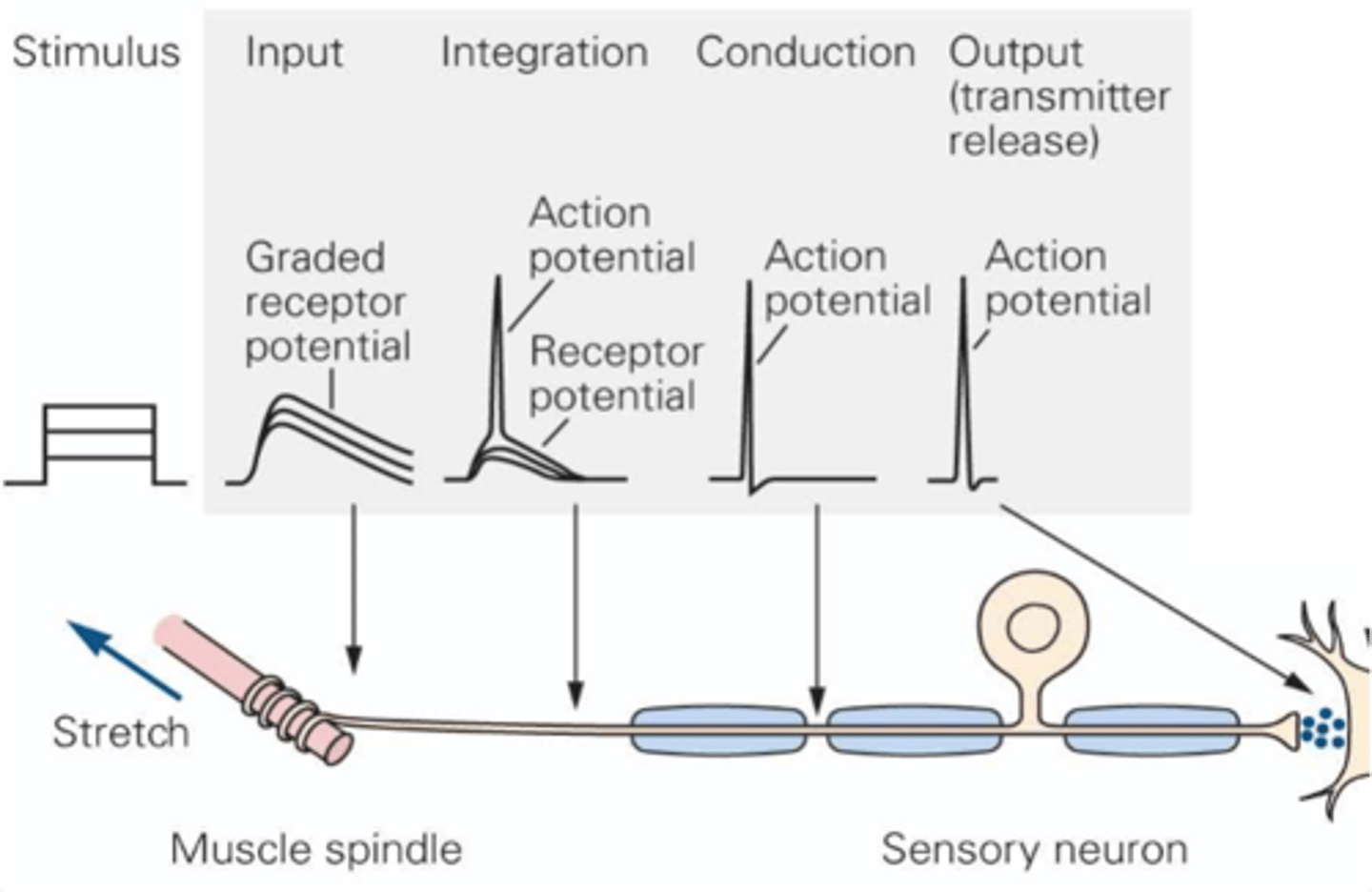
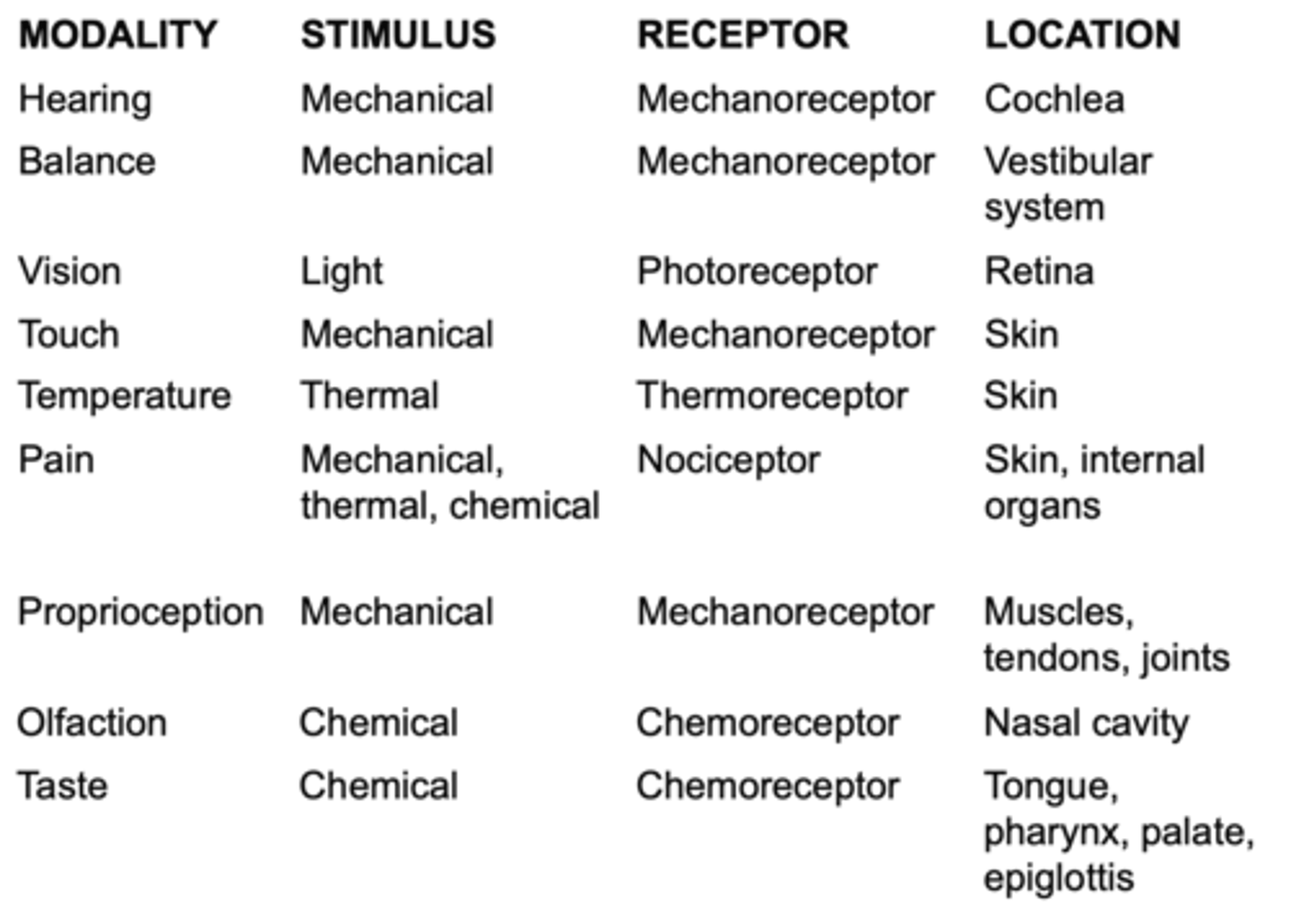
Modality, location, intensity, timing
Sensory receptors can convey 4 types of information, what are they?
The labelled line code
Stimulus modality is coded by what?
One, stimulus energy
The receptor is selective for ____ type of ___________ ______
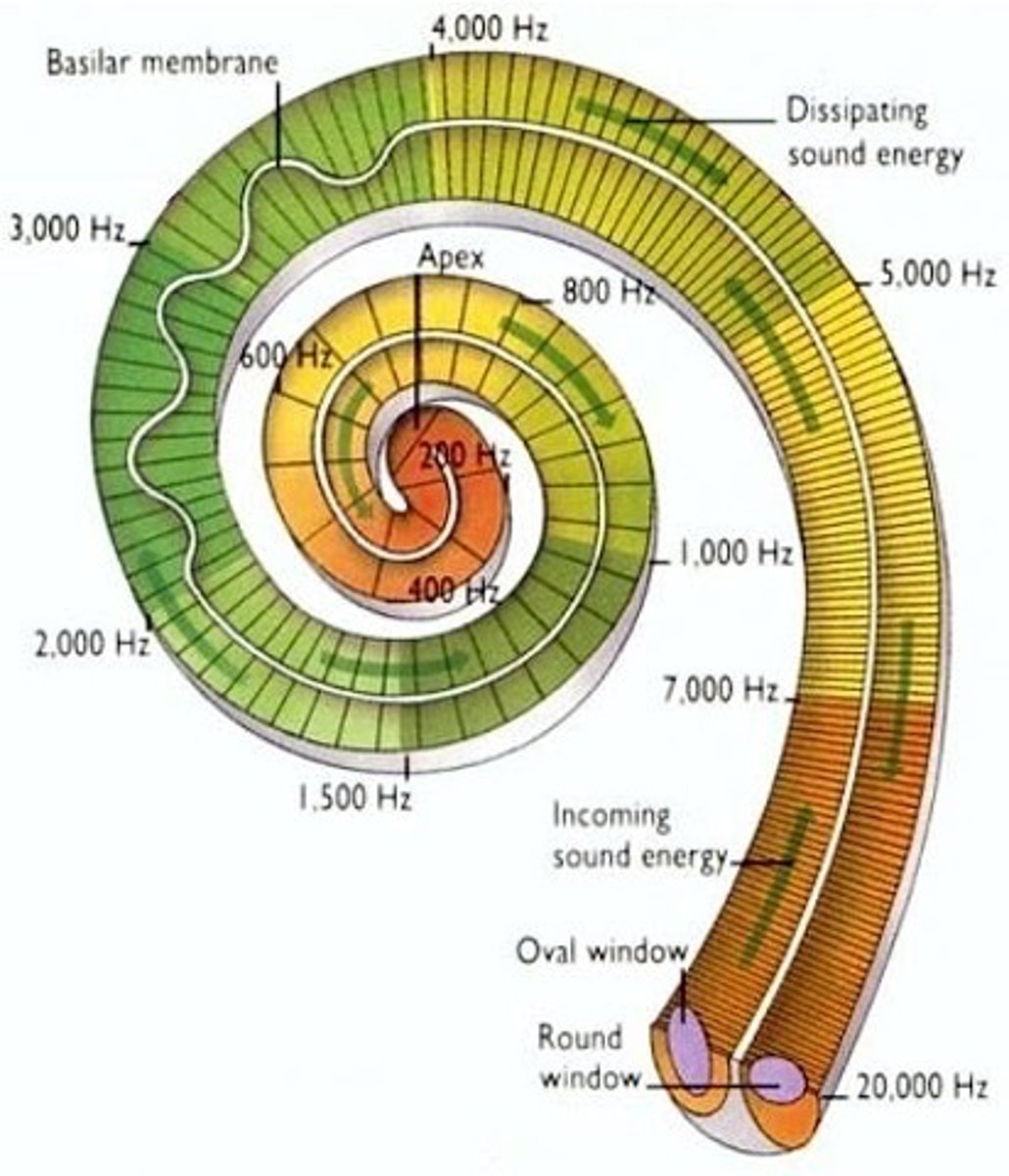
Modality specific line of communication
The axons of the receptor/associated afferent neuron acts as a _________ _________ _______ ____ ________________
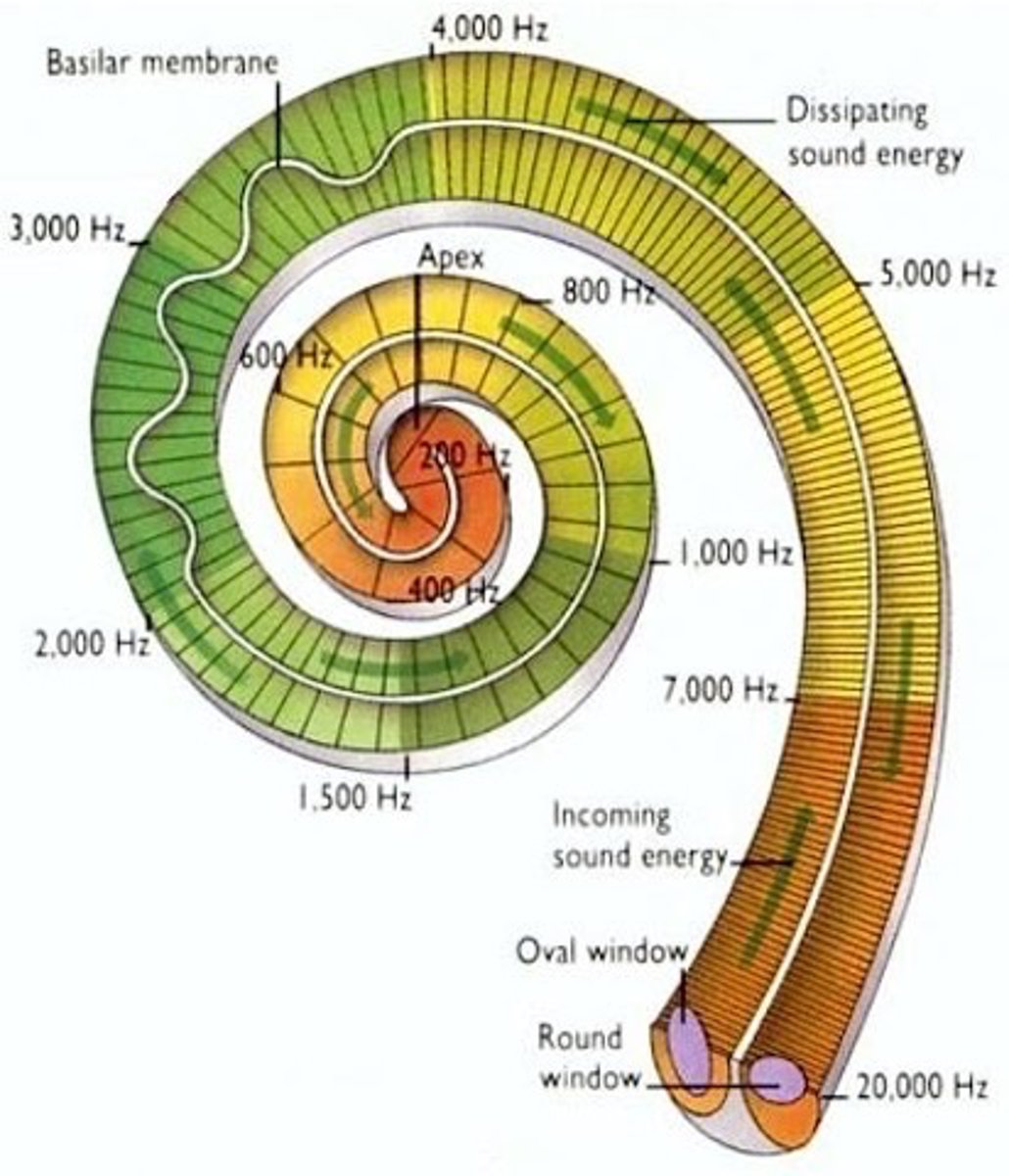
Connections, CNS
Axons from these neurons make ___________ with specific areas in the _____
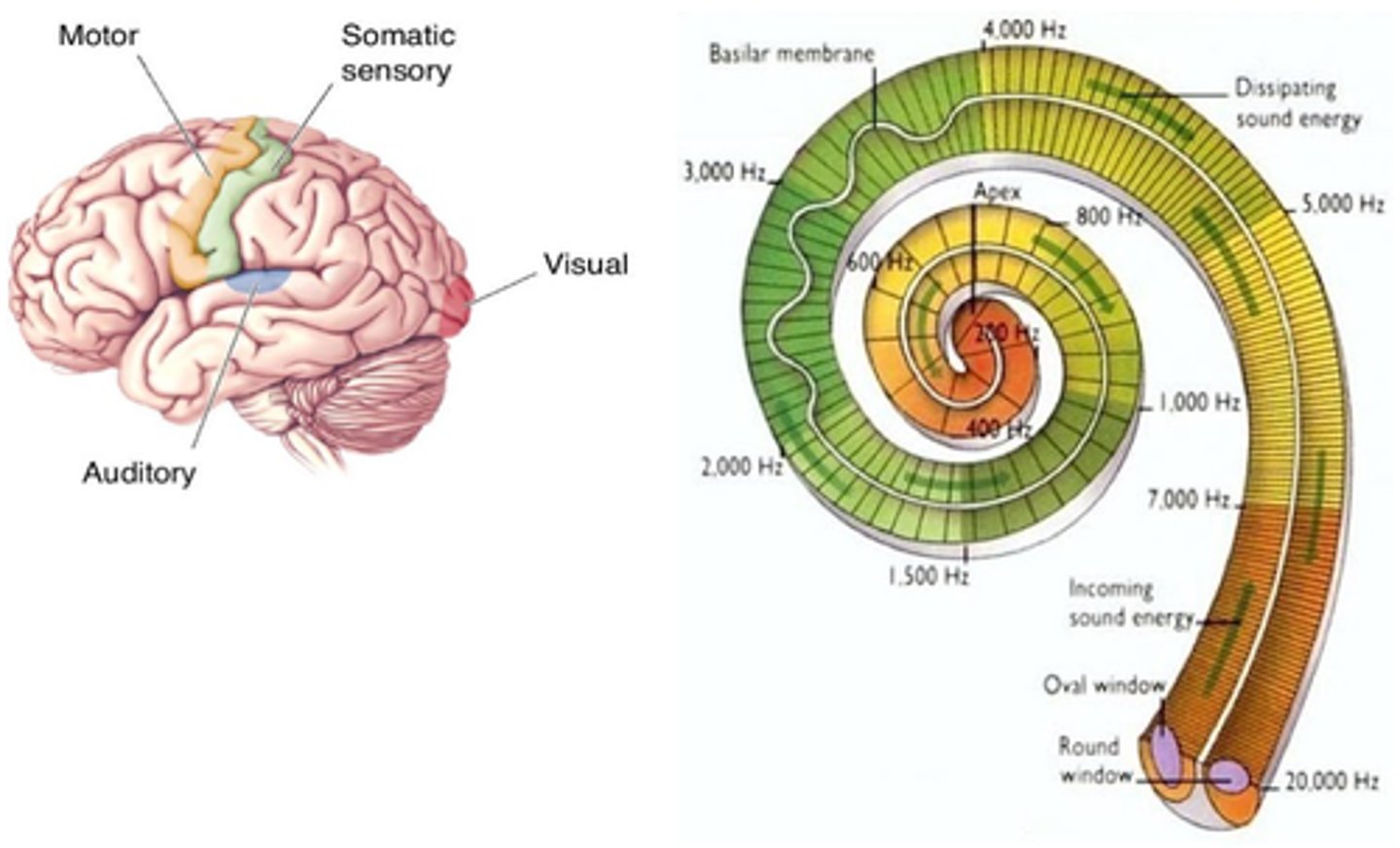
Perception of the associated sensation
Stimulating afferent neurons electrically leads to what?
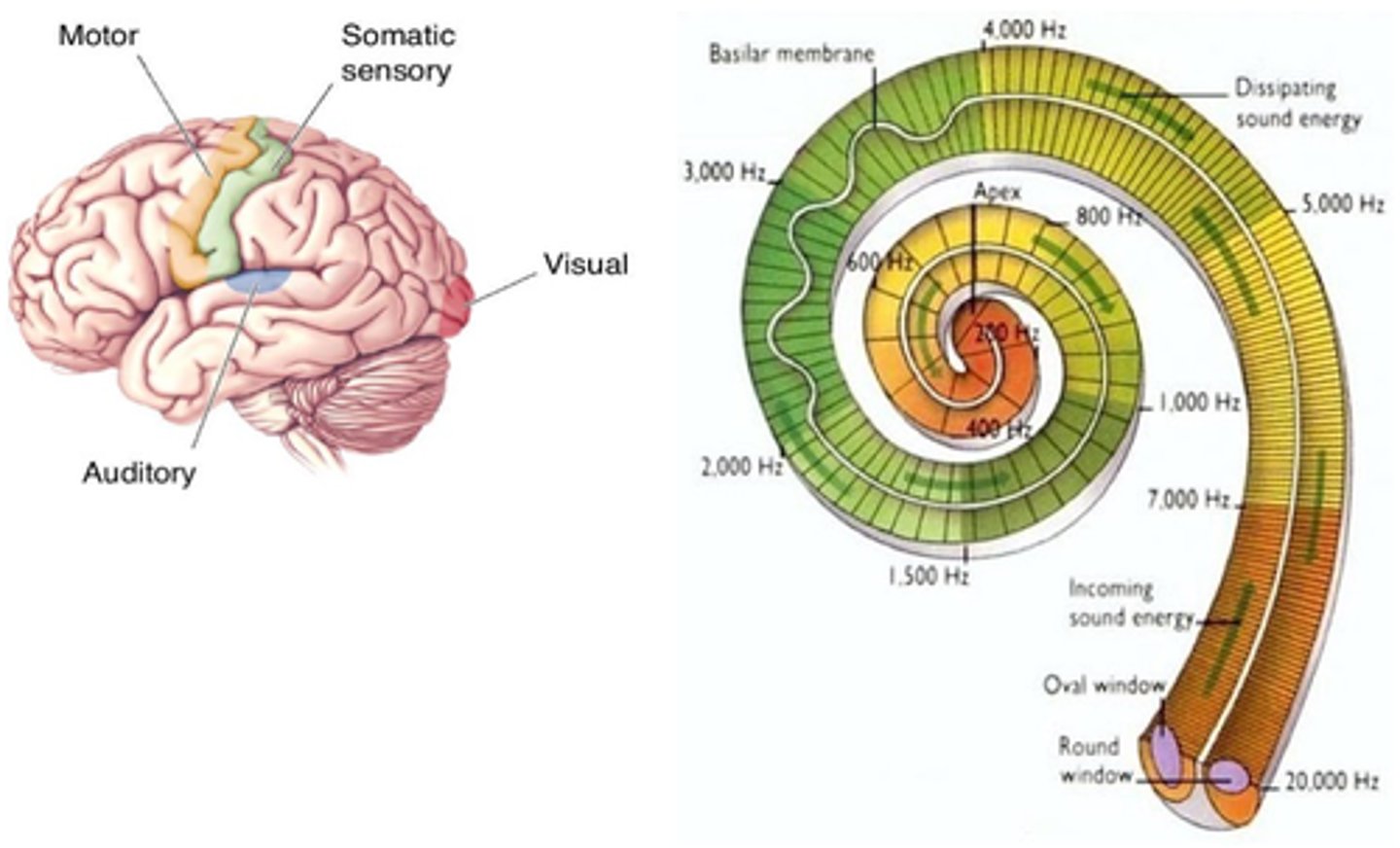
Synaesthesia
The labelled line code is faulty in ...?
The stimulus
Spatial arrangement of activated receptors within a sense organ gives information about ...?
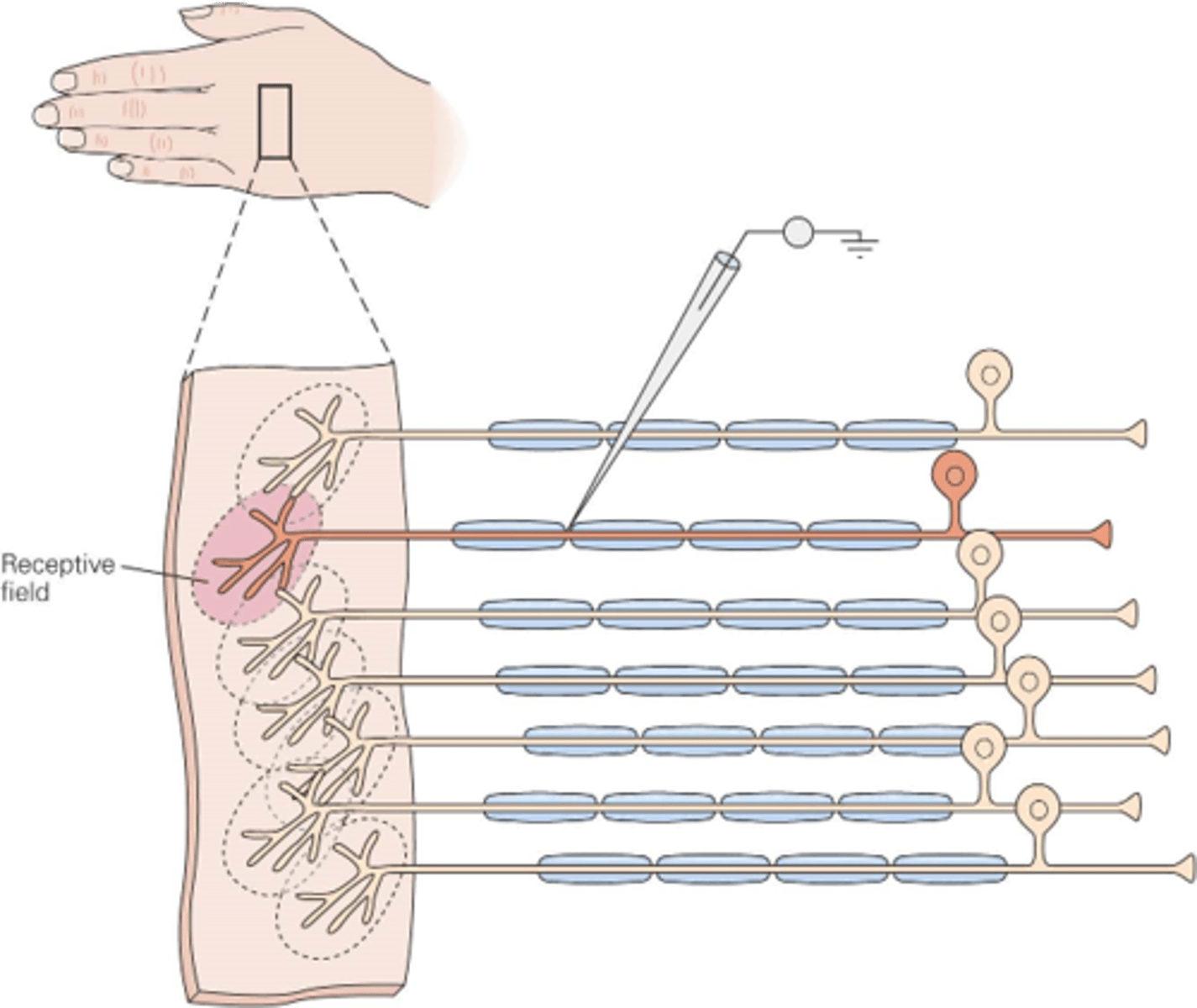
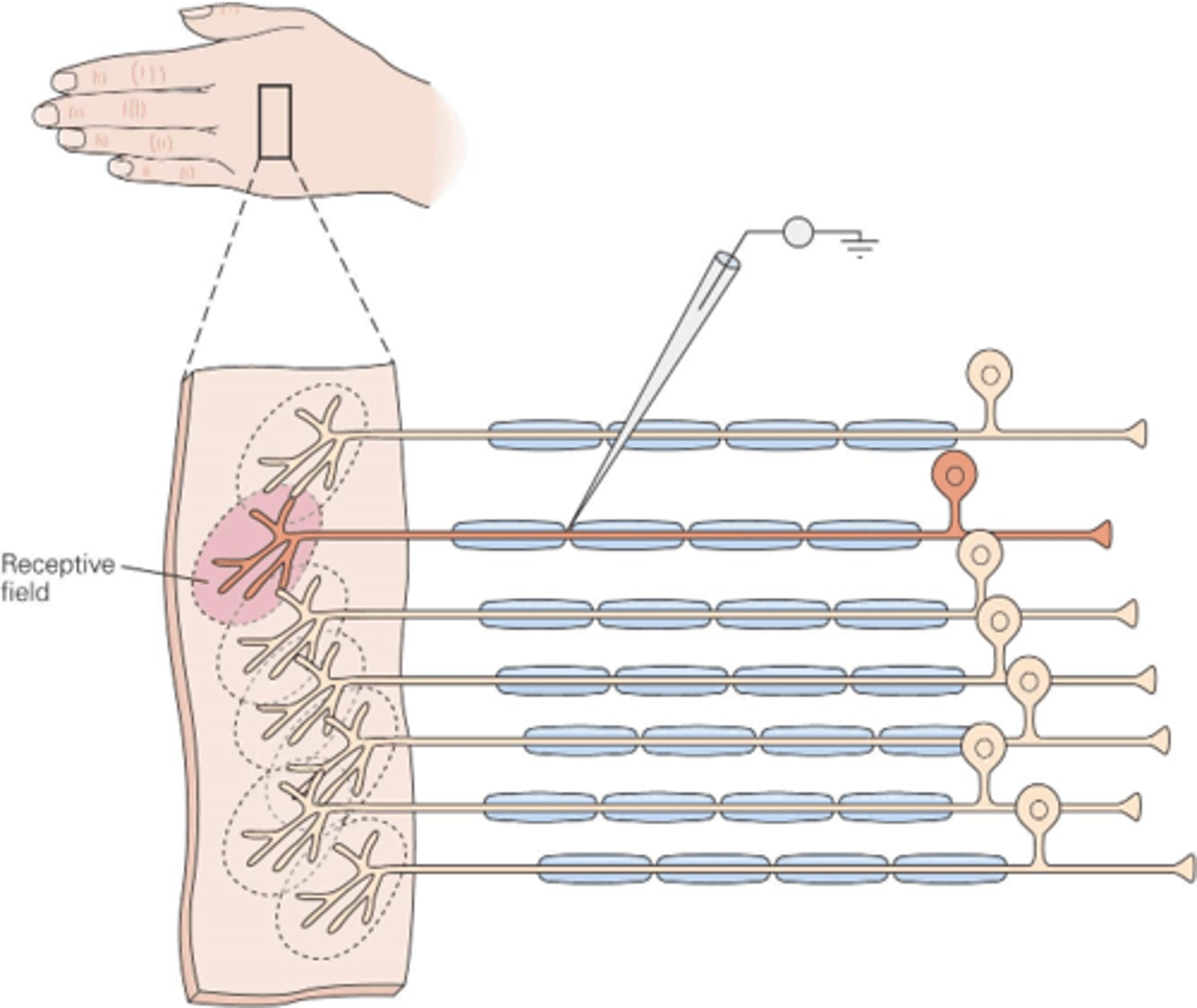
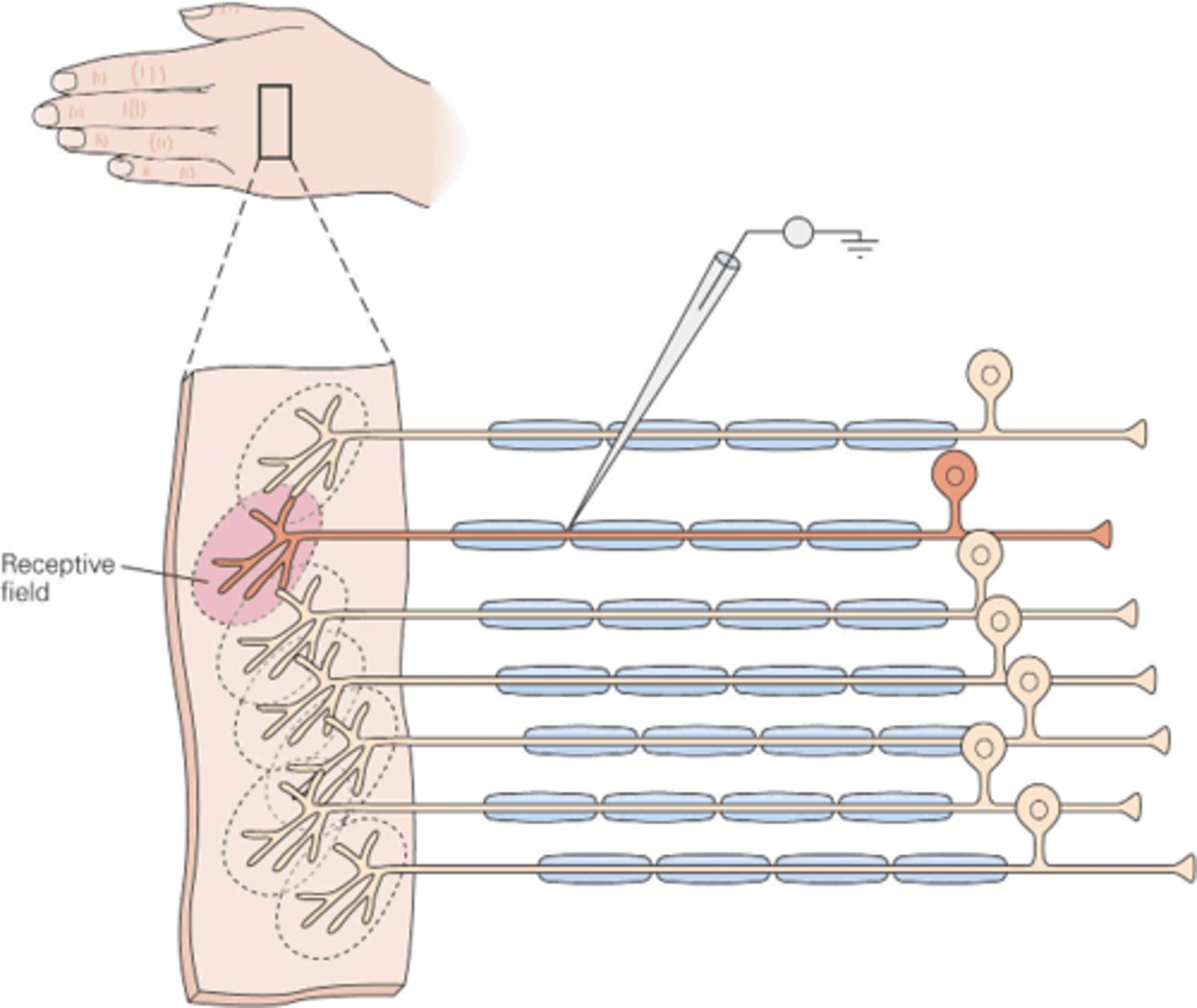
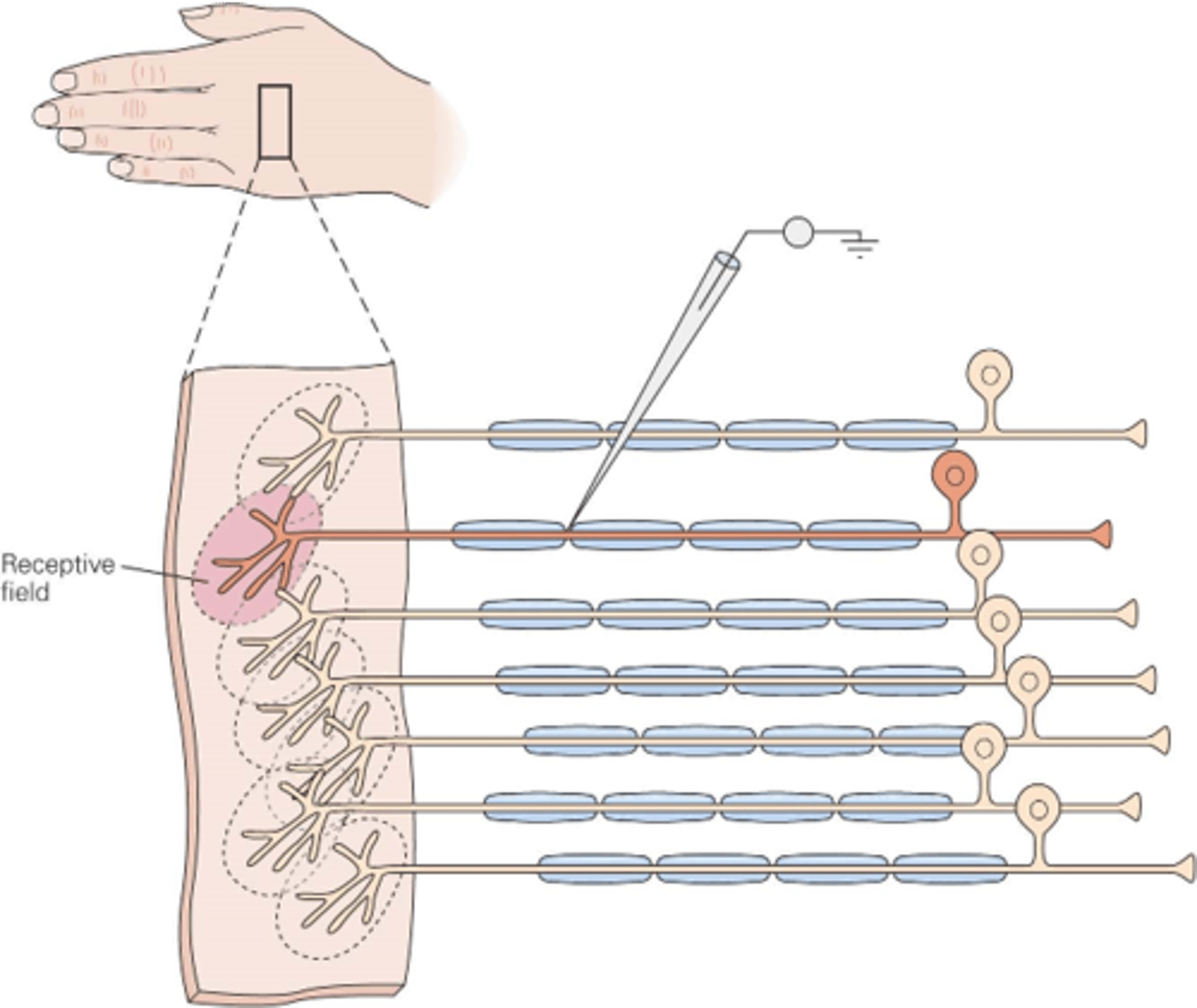
The region of skin innervated by the terminals of the receptor neuron
In the somatic system, what is a receptive field?
The region of the visual field projected onto that receptor
In the visual system, what is a receptive field of a photoreceptor?
More
Large stimuli will activate _______ neurons
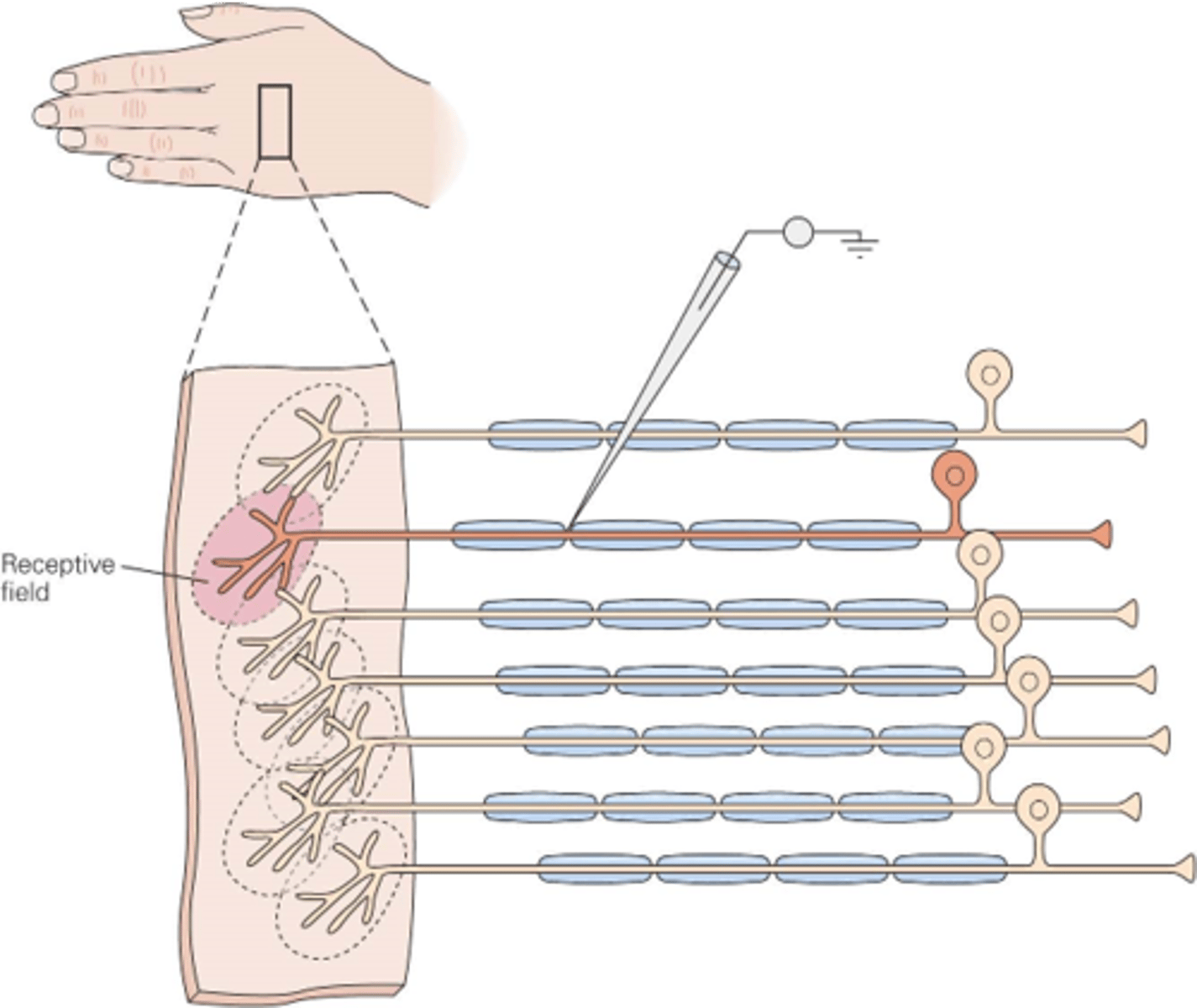
Many, few
A large object in the hand will activate receptive fields in _______ areas of the hand, whereas a small object will only activate a _____ receptive fields
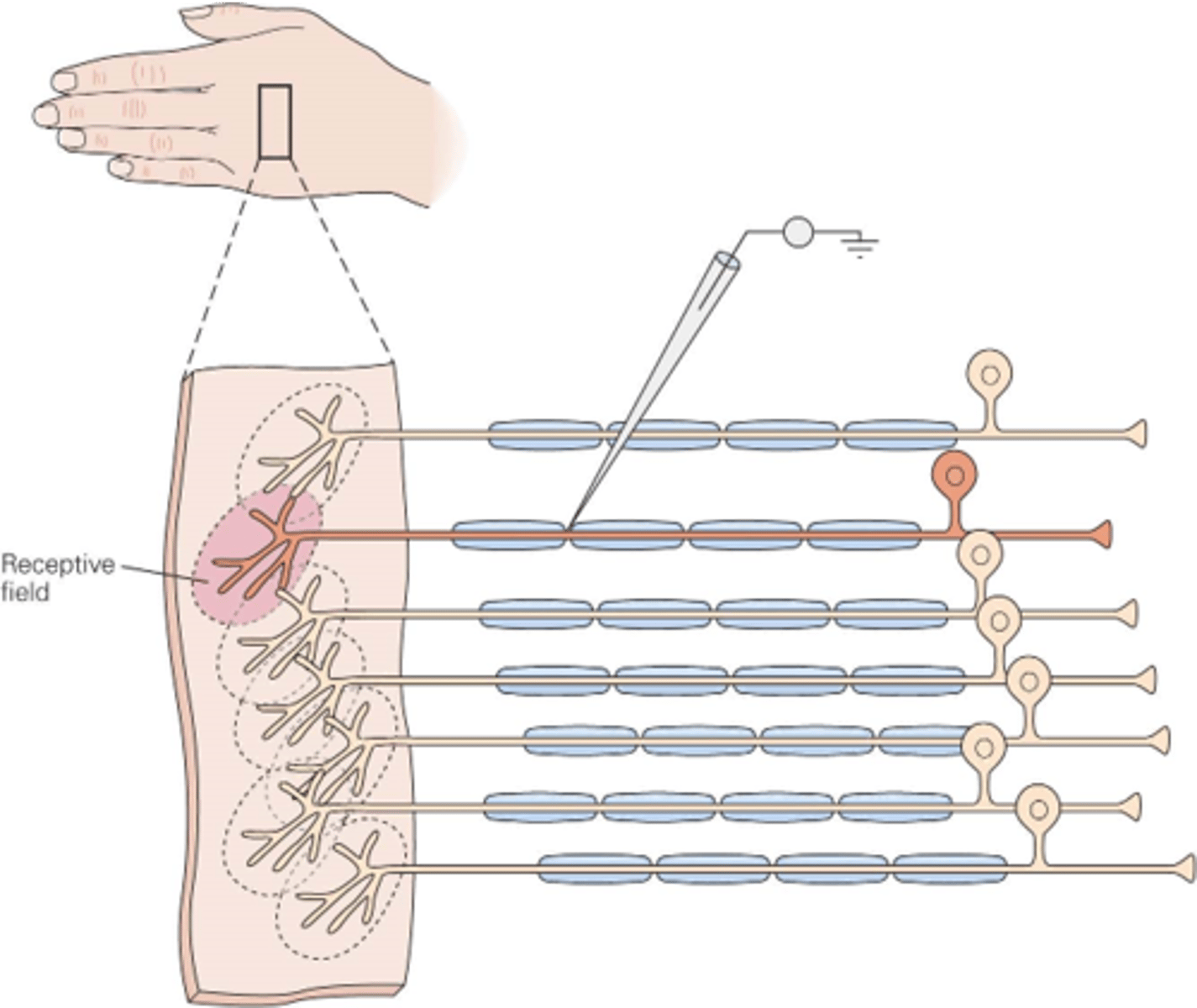
Sizes, receptive fields
Different regions of the body have different ______ of _________ __________
The total amount of stimulus energy delivered to the receptor
What is intensity?
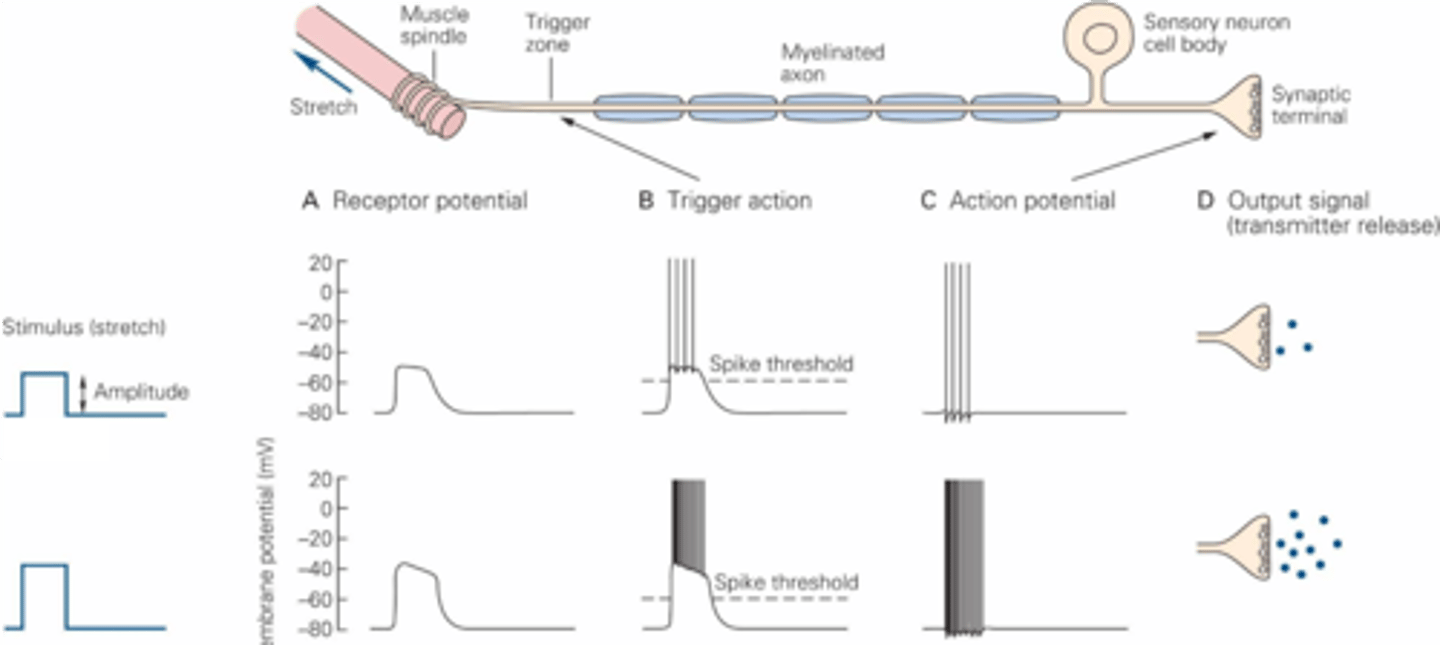
The sensory threshold
The lowest stimulus strength that can be detected is known as ...?
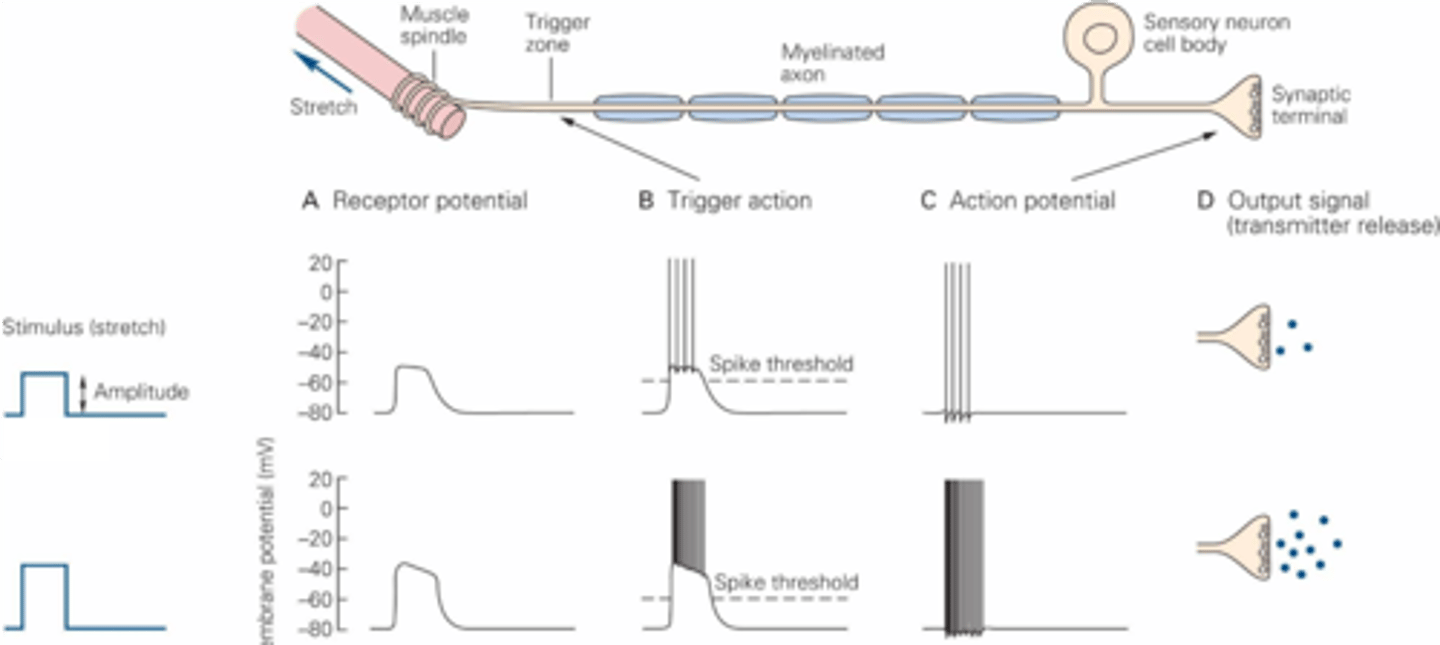
The response amplitude of the receptor and thus the firing frequency of the afferent neurons
What is intensity determined by?
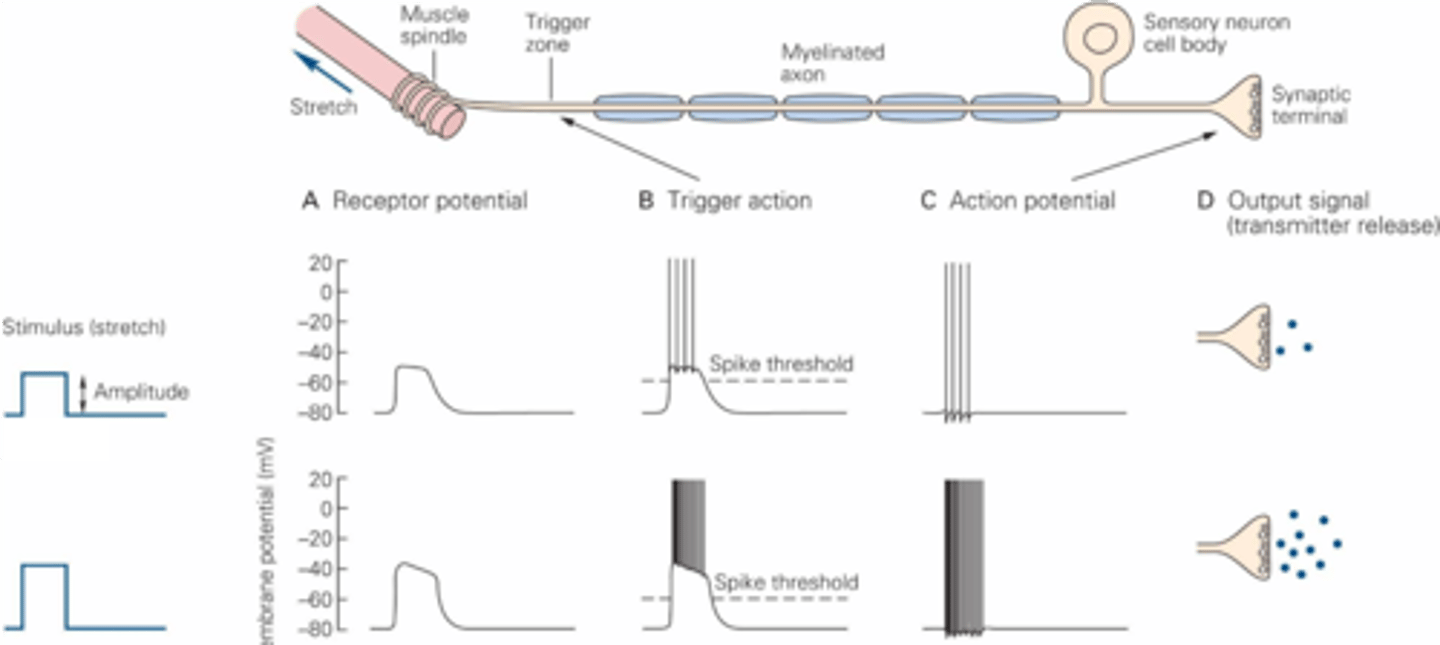
When the stimulus energy is received by the receptor and causes it to fire
What is onset timing determined by?
Adaptation rates of receptors
What is stimulus duration determined by?
In response to continuous stimuli, the firing rate of action potentials decreases
What is meant by 'adaptation'?
Tonic receptors, prolonged
Slowly adapting receptors are known as ________ _________ and respond to ___________ stimulation
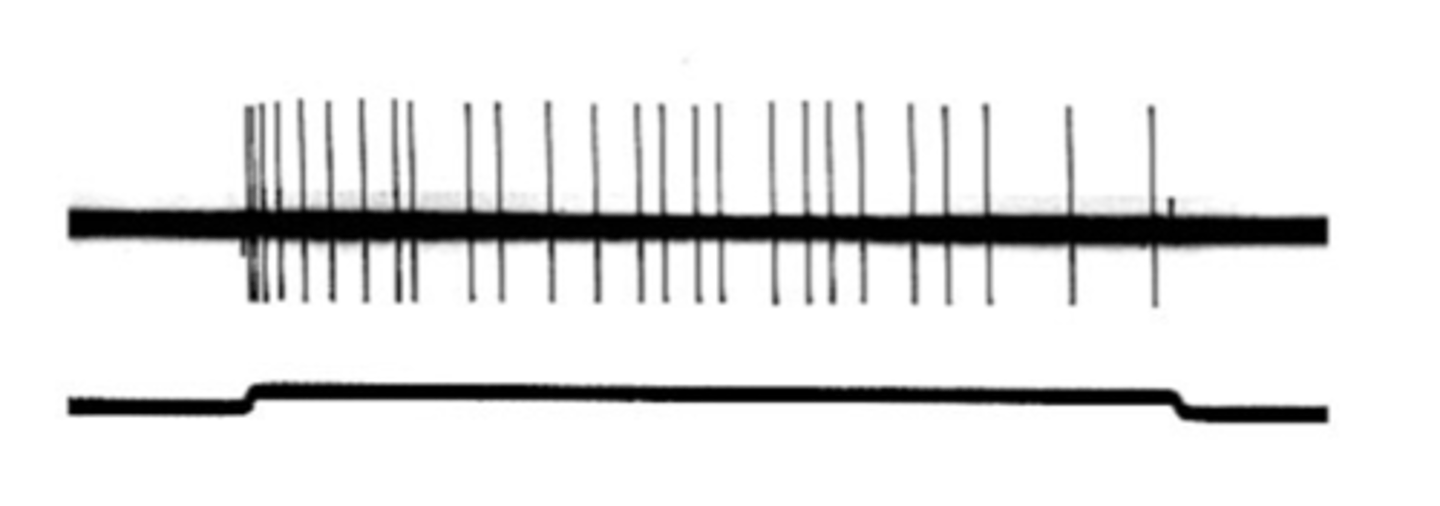
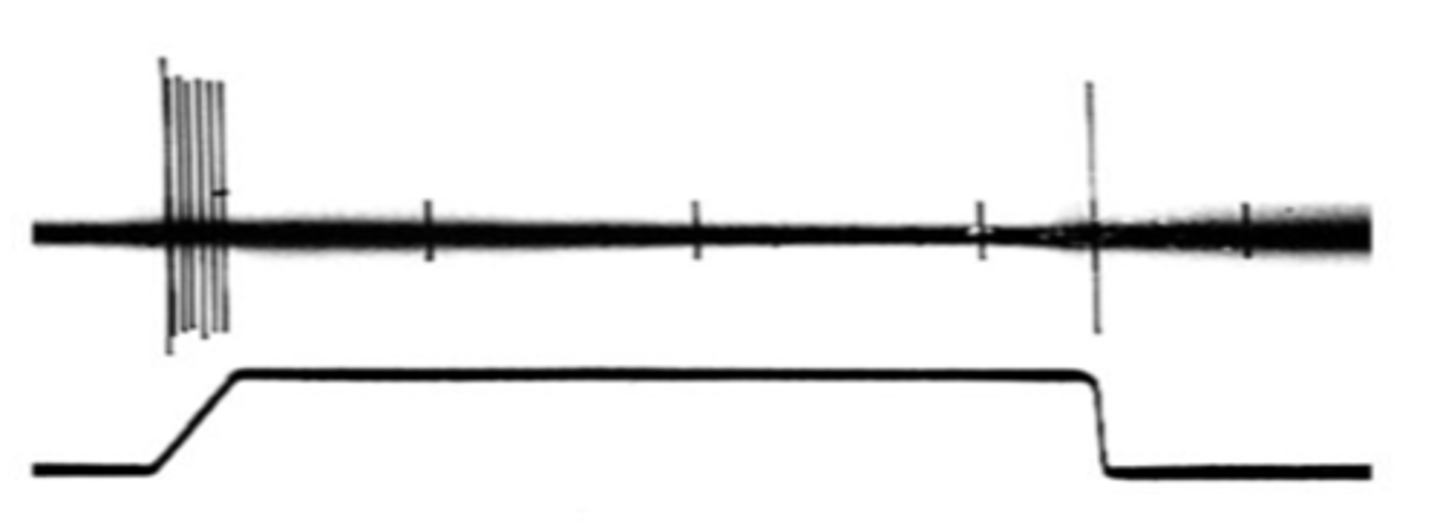
Phasic receptors, beginning, end
Rapidly activating receptors are known as _______ __________ and respond at the _____________ and ____ of a stimulus
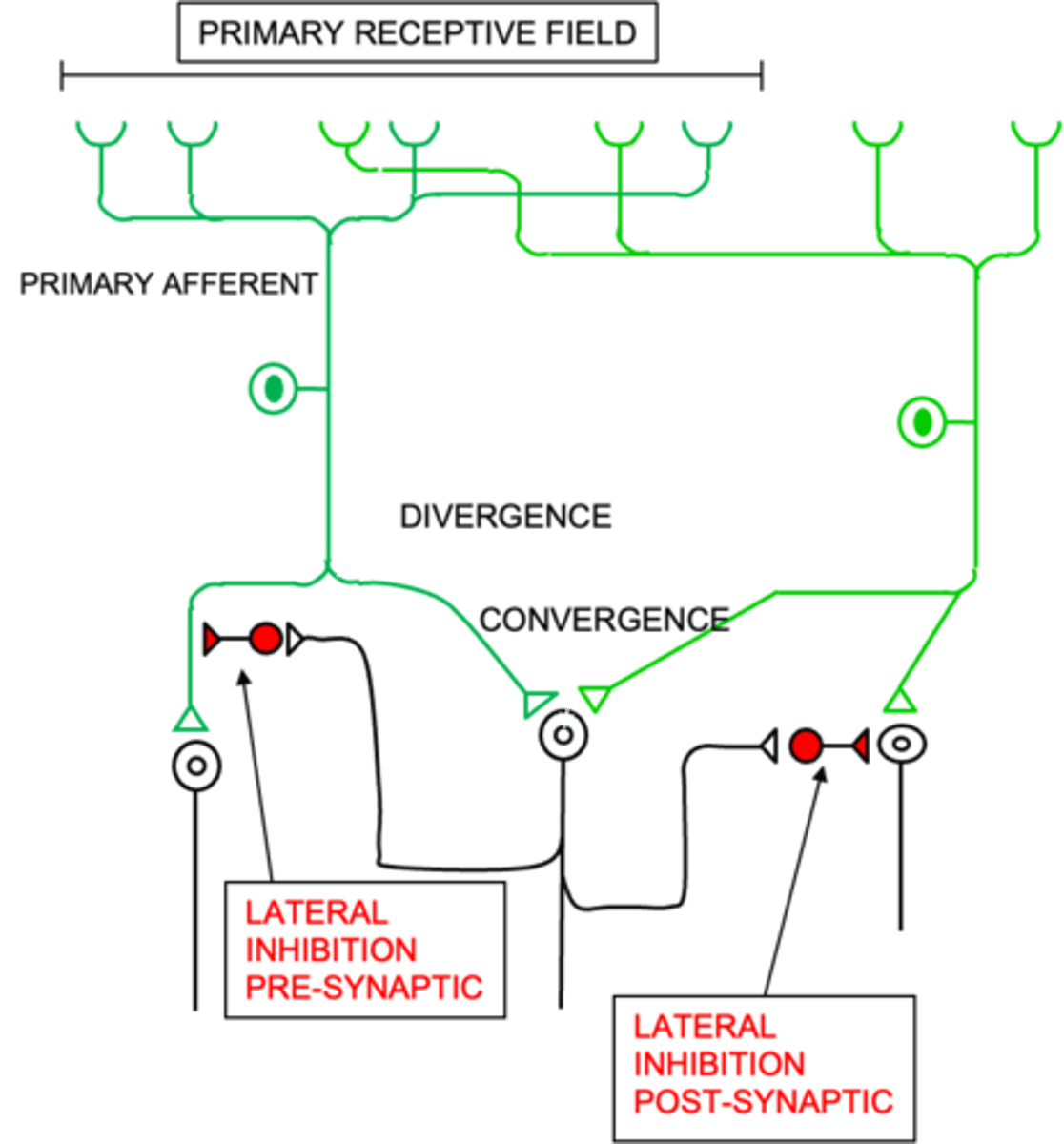
Primary afferent neurons to signal more than one relay neuron
What does divergence allow?
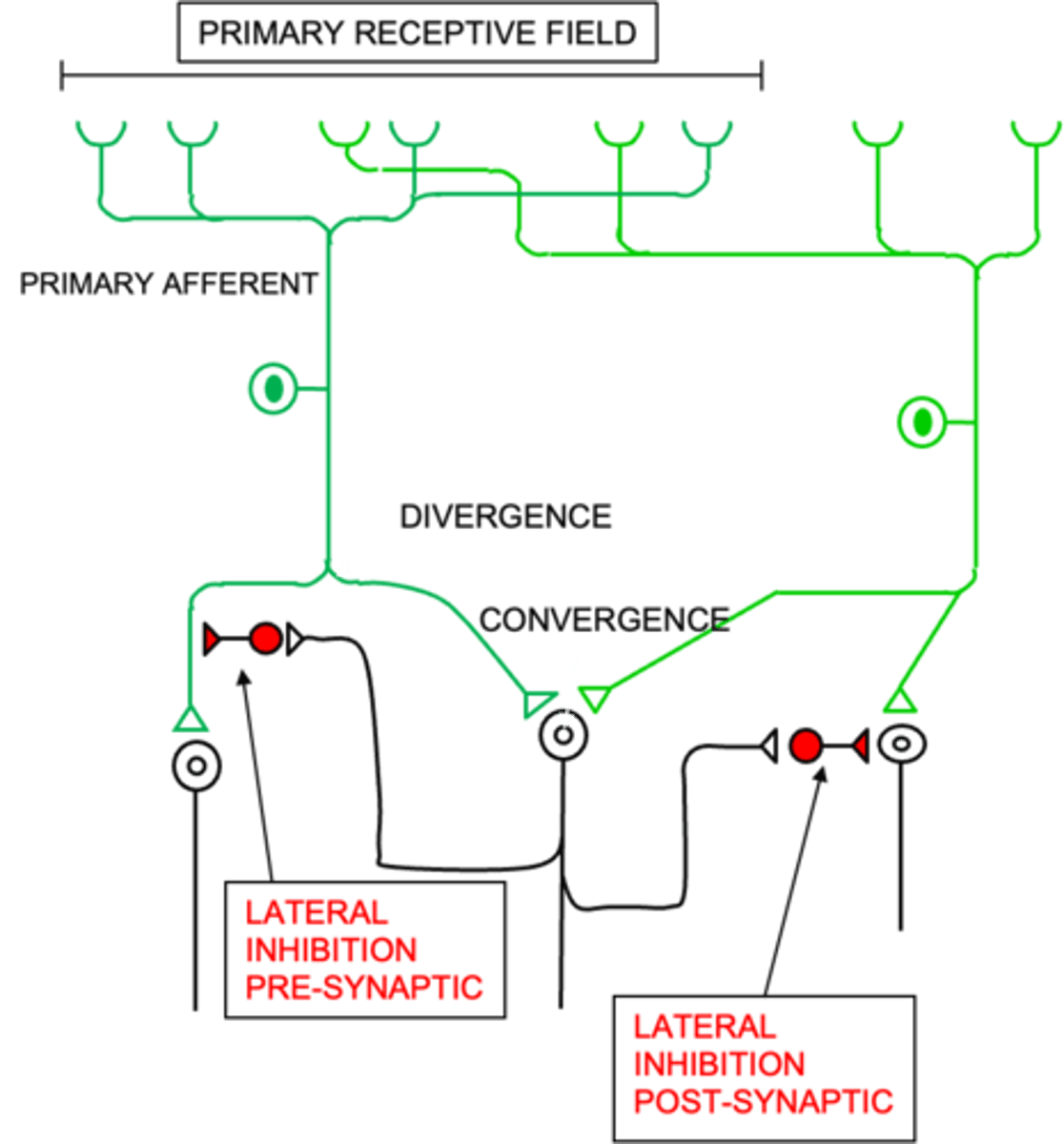
That relay neurons have larger receptive fields than primary afferent neurons
What does convergence ensure?
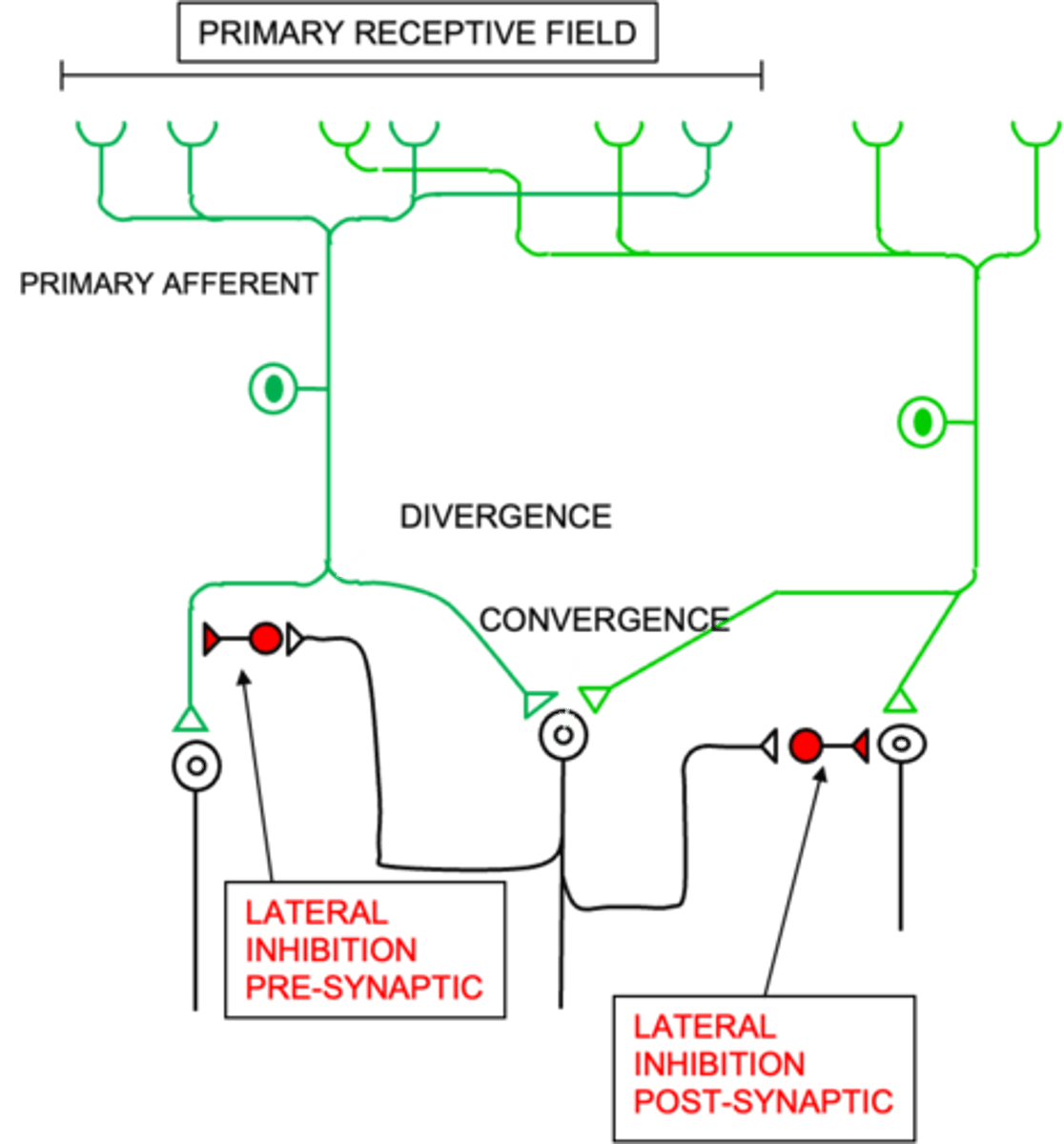
The signal is the most active neuron is propagated
What do inhibitory neurons ensure?
The stimulus energy and anatomy of the sensory organ and/or receptors
What is sensory modality determined by?
The activation of spatially distributed sensory neurons
What is stimulus location determined by?
Stimulus amplitude and neuronal firing rate
What is intensity of sensation determined by?
Adaptation rates of receptors
What is sensation duration mainly determined by?