MIS 301 exam 1 review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:21 AM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
IOT
internet of things. interconnected network through low-cost processors embedded into a wide array of products
2
New cards
IPO
Initial public stock offering. The first time a firm makes a share public through public stock exchange. "going public"
3
New cards
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Sarbox or SOX. U.S. legislation enacted during accounting scandals of the early 2000s. Raises executive and board responsibility and ties criminal penalties to certain accounting and financial violations .Requires the CEO and CFO to certify that their firm's financial statements are accurate.
4
New cards
\#In the previous decade, tech firms have created profound shifts in the way firms\__________ and individuals and organizations \_____________
a) adapt;thrive
b)communicate;listen
c)advertise;communicate
a) adapt;thrive
b)communicate;listen
c)advertise;communicate
advertise;communicate
5
New cards
strategic positioning
performing tasks differently than rivals, or performing the same tasks in a different way
6
New cards
straddling
When you attempt to occupy multiple positions, failing to efficiently match the benefits of a focused rival
7
New cards
fast follower problem
when a savy rival learn from a pioneers success and missteps and enter the market quickly with a comparable/superior product at a lower cost before the pioneer can dominate
8
New cards
commodity
a basic good that is interchanged thats nearly identical to other offerings. competition is based on price
9
New cards
sustainable competitive advantage
Financial performance that consistently outperforms industry averages.
10
New cards
inventory turns
the number of times inventory is sold or used during a given period, calculates how quickly products are selling. the higher the figure the better. inventory turnover, stock turns, or stock turnover.
11
New cards
resource-based view of competitive advantage
approach that if a firm is to maintain sustainable competitive advantage, it must control an exploitable resource, or resources. These resources must be
(1) valuable
(2) rare
(3) imperfectly imitable
(4) non substitutable.
(1) valuable
(2) rare
(3) imperfectly imitable
(4) non substitutable.
12
New cards
augmented-reality
A technology that superimposes content, such as images and animation, on top of real-world images.
13
New cards
operational effectiveness
Performing the same tasks better than rivals perform them.
14
New cards
DWDM
dense wave division multiplexing. technology that increases the transmission capacity (and hence speed) of fiber-optic cable. Transmissions using fiber are accomplished by transmitting light inside "glass" cables. In DWDM, the light inside fiber is split into different wavelengths in a way similar to how a prism splits light into different colors
15
New cards
scale advantages
Advantages related to size.
16
New cards
value chain
The set of activities through which a product or service is created and delivered to customers.
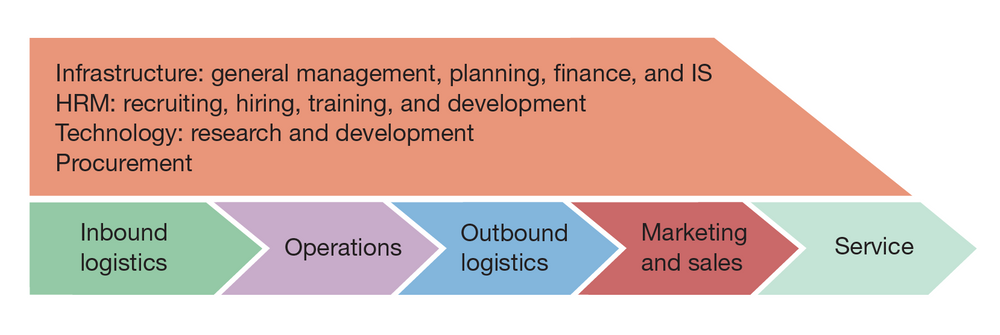
17
New cards
**economies of scale**
**when costs can be spread across increasing units of production or in serving multiple customers. Businesses that have favorable economies of scale (like many Internet firms) are sometimes referred to as being highly scalable.**
18
New cards
**Brand**
**The symbolic embodiment of all the information connected with a product or service.**
19
New cards
**distribution channels**
**path through which products or services get to customers.**
20
New cards
**Non-Practicing Entities**
**firms make money by acquiring and asserting patents, rather than bringing products and services to market. patent trolls**
21
New cards
**APIs**
**Application programing interface. Programming hooks, or guidelines, published by firms that tell other programs how to get a service to perform a task such as send or receive data.**
22
New cards
**viral marketing**
**Leveraging consumers to promote a product or service**
23
New cards
**Affiliates**
**Third parties that promote a product or service, typically in exchange for a cut of any sales.**
24
New cards
**network effects**
**When the value of a product or service increases as its number of users expands. Metcalfe’s Law, or network externalities.**
25
New cards
**switching cost**
**cost a consumer incurs when moving from one product to another. It can involve actual money spent (e.g., buying a new product) as well as investments in time, any data loss, and so forth.**
26
New cards
**imitation-resistant value chain**
**way of doing business that competitors struggle to replicate and that frequently involves technology in a key enabling role**
27
New cards
**Private**
**Buying up a publicly traded firm’s shares. Usually done when a firm has suffered financially and when a turnaround strategy will first yield losses that would further erode share price. Firms (often called private equity, buyout, LBO, or leveraged buyout firms) that take another company private hope to improve results so that the company can be sold to another firm or they can reissue shares on public markets.**
28
New cards
**information asymmetry**
**decision situation where one party has more or better information than its counterpart**
29
New cards
**price transparency**
**degree to which complete information is available**
30
New cards
**Porter’s five forces** \n
**Competitive Analysis. A framework considering the interplay between**
**(1) the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors**
**(2) the threat of new entrants**
**(3) the threat of substitute goods or services**
**(4) the bargaining power of buyers**
**(5) the bargaining power of suppliers.**
\
**(1) the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors**
**(2) the threat of new entrants**
**(3) the threat of substitute goods or services**
**(4) the bargaining power of buyers**
**(5) the bargaining power of suppliers.**
\
31
New cards
**contract manufacturing**
**outsourcing production to third-party firms. Firms that use contract manufacturers don’t own the plants or directly employ the workers who produce the requested goods.**
32
New cards
**PDAs**
**Personal digital assistants, an early name for handheld mobile computing devices.**
33
New cards
**Logistics**
**Coordinating and enabling the flow of goods, people, information, and other resources among locations.**
34
New cards
1) inbound operations
2) operations
3) outbound logistics
4) marketing and sales
5) service
2) operations
3) outbound logistics
4) marketing and sales
5) service
value chain
35
New cards
**(1) the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors**
**(2) the threat of new entrants**
**(3) the threat of substitute goods or services**
**(4) the bargaining power of buyers**
**(5) the bargaining power of suppliers.**
**(2) the threat of new entrants**
**(3) the threat of substitute goods or services**
**(4) the bargaining power of buyers**
**(5) the bargaining power of suppliers.**
**Porter’s five forces**
36
New cards
**the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors**
**Porter’s five forces**
37
New cards
**the threat of new entrants**
**Porter’s five forces**
38
New cards
**the threat of substitute goods or services**
\
\
**Porter’s five forces**
39
New cards
**the bargaining power of buyers**
\
\
**Porter’s five forces**
40
New cards
**the bargaining power of suppliers.**
**Porter’s five forces**
41
New cards
inbound operations
\
\
value chain
42
New cards
operations
\
\
value chain
43
New cards
outbound logistics
\
\
value chain
44
New cards
marketing and sales
\
\
value chain
45
New cards
service
value chain
46
New cards
**POS**
**point-of-sale. Transaction processing systems that capture customer purchases. Cash registers and store checkout systems are examples of point-of-sale systems. These systems are critical for capturing sales data and are usually linked to inventory systems to subtract out any sold items.**
47
New cards
**ROI**
**return on investment. The amount earned from an expenditure.**
48
New cards
**Greige**
**Goods to be further customized based on designer/manager collaboration**
49
New cards
**RFID**
**Radio frequency identification. Small chip-based tags that wirelessly emit a unique identifying code for the item that they are attached to. Think of RFID systems as a next-generation bar code.**
50
New cards
**vertical integration**
**When a single firm owns several layers in its value chain.**
51
New cards
**IS**
**information system. integrated solution that combines five components:**
**hardware**
**software**
**data**
**procedures**
**people who interact with and are impacted by the system.**
**hardware**
**software**
**data**
**procedures**
**people who interact with and are impacted by the system.**
52
New cards
**Omnichannel**
**approach to retail that offers consumers an integrated and complementary set of shop, sales, and return experiences (e.g., retail store, online, and sometimes even phone and catalog).**
53
New cards
**Operations**
**organizational activities that are required to produce goods or services. Operations activities can involve the development, execution, control, maintenance, and improvement of an organization’s service and manufacturing procedures.**
54
New cards
**Showrooming**
**the concept where customers browse at physical retailers, but purchase products from lower-cost online rivals**
55
New cards
**Moore’s Law**
**Chip performance per dollar doubles every eighteen months.**
56
New cards
**volatile memory**
**Storage (such as RAM chips) that is wiped clean when power is cut off from a device.**
57
New cards
**price elasticity**
**The rate at which the demand for a product or service fluctuates with price change. Goods and services that are highly price elastic (e.g., most consumer electronics) see demand spike as prices drop, whereas goods and services that are less price elastic are less responsive to price change (think heart surgery)**
58
New cards
__**Outsourcing**__
using any other firms who employ workers to produce goods
59
New cards
__**Offshoring**__
going outside the US for in-house job
60
New cards
__**Cloud computing**__
using internet server to store data (Google Drive)
61
New cards
__**SaaS**__
__**Software as a service.**__ access application/software via the Internet through third party
62
New cards
__**Slotting fees**__
\
\
payments by suppliers for prime shelf space, which is common in traditional retail.
63
New cards
__**DWDM**__
__**Dense wave division multiplexing.**__ technology that increases the transmission capacity (and hence speed) of fiber-optic cable
64
New cards
__**Channel conflict**__
when retailers sense its suppliers are competing with it through a direct-sales effort (Chooses another supplier that sells a nearly identical product)
65
New cards
__**Information asymmetry**__
decision situation where one party has more or better information than its counterparty.
66
New cards
__**Fair Factories Clearinghouse**__
provides systems where apparel and other industries can share audit information on contract manufacturers
67
New cards
__**Churn rate**__
rate at which customers leave a product or service.
68
New cards
__**Long tail**__
an extremely large selection of content or products. Phenomenon where firms can make money by offering a near-limitless selection. Selection attracts customers, and offline firms can’t match the Internet
\
\
69
New cards
__**Collaborative filtering**__
software that monitors trends among customers and uses this data to personalize an individual customer’s experience
70
New cards
__**Decision fatigue**__
where consumers avoid selection decisions with an overwhelming number of choices
71
New cards
__**First Sale Doctrine**__
US Supreme Court ruling stating that an individual who knowingly purchases a copy of a copyrighted work from the copyright holder receives the right to sell, display or otherwise dispose of that particular copy, notwithstanding the interests of the copyright owner. Applies only to the atoms of the physical disc, not to the bits needed in streaming
72
New cards
__**Transfer pricing**__
price paid when divisions of the same company transact with each other.
73
New cards
__**Windowing**__
anything that gives you a window of time to do something
74
New cards
__**Coopetition**__
situation where firms may both cooperate and compete with one another. Netflix on Amazon’s servers
75
New cards
__**Disintermediation**__
\
\
removing an organization from a firm’s distribution channel.
Collapses the path between supplier and customer.
Collapses the path between supplier and customer.
76
New cards
__**Bandwidth caps**__
\
\
a limit, imposed by the ISP (e.g., a cable or telephone company) on the total amount of traffic that a given subscriber can consume
77
New cards
__**Crowdsourcing**__
\
\
taking a job traditionally performed by a designated agent and contracting it out to an undefined generally large group of people in the form of an open call
78
New cards
__**Colocation facilities**__
\
\
place where the gear from multiple firms can come together and where the peering of Internet traffic can take place.
79
New cards
__**Cord shavers**__
cable subscribers who drop premium cable channels
80
New cards
__**Flash (nonvolatile) memory**__
chip-based storage, often used in mobile phones, cameras, and MP3 players… called flash RAM, holds charge when power goes out. Flash memory, __**hard disk**__, or DVD storage… **slower** than RAM. *Solid state electronic*
81
New cards
__**Semiconductor**__
substance like silicon dioxide used inside most computer chips that is capable of enabling as well as inhibiting the flow of electricity (or just computer chips)
82
New cards
__**Solid state electronics**__
Semiconductor-based devices (chips). Fewer failures and require less energy since they have no moving parts.
__**RAM**__, __**flash memory**__, and __**microprocessors**__… **NOT hard drives**
__**RAM**__, __**flash memory**__, and __**microprocessors**__… **NOT hard drives**
83
New cards
__**Fabs**__
semiconductor fabrication facilities; chip manufacturing factories
84
New cards
__**Silicon wafer**__
thin, circular slice of material to create semiconductor devices
85
New cards
__**Optical fiber line**__
high-speed glass or plastic-lined networking cable used in telecommunications
86
New cards
__**Microcontrollers**__
Special-purpose computing devices that don't have an operating system and can't do as much as general purpose computers or smartphones
87
New cards
__**Microprocessor**__
part of computer that executes the instructions of a computer program (the brain of the computer). *Solid state electronic*
88
New cards
__**Multicore microprocessors**__
with two or more (typically lower power) calculating processor cores on the same piece of silicon. Can run older software written for single-brain chips. Software executing on a multi-core system does **NOTrun faster by amultiple of the number of cores**
89
New cards
__**Latency**__
delay, especially when discussing networking and data transfer speeds. Low-latency systems are faster systems.
90
New cards
__**Massively parallel**__
\
\
Computers designed with many microprocessors that work together, simultaneously, to solve problems.
\
\
91
New cards
__**HPC or supercomputer**__
\
\
massively-parallel computers specifically designed to deliver significantly more calculating power than conventional off-the-shelf computing technologies.
92
New cards
__**Grid computing**__
\
\
uses special software to enable several computers to work together on a common problem, as if a massively parallel supercomputer
93
New cards
__**Cluster computing**__
Connecting server computers via software and networking so that their resources can be used to collectively solve computing tasks as one
94
New cards
__**Server farm**__
\
\
massive network of computer servers running software to coordinate their collective use. Provide infrastructure backbone to SaaS and many large-scale Internet services
95
New cards
__**E-waste**__
Discarded, often obsolete technology; also known as electronic waste. There’s **more gold** in one pound of e-waste than in one pound of mined ore. Sending e-waste **abroad** can be ten times **cheaper** than dealing with it at home
96
New cards
__**VoIP**__
\
\
the technology used in internet telephony (example of disruptive innovations)
\
\
97
New cards
__**Innovator’s Dilemma**__
\
\
name sometimes is ascribed to disruptive innovation theory. Disruptive tech gains smallest market of sustainable company, company stops competing in that market, then disruptive comes for next market and so on…
\
\
98
New cards
__**“Creosote bush effect”**__
\
\
Threatened managers act just like the bush-they'll pull high-quality engineers off emerging projects if a firm's top offerings need staff to grow
\
\
99
New cards
__**ARM chips**__
Advanced RISC Machine. Once computational weaklings, are now fast enough to invade the established market for server chips. Far more power efficient (require less power to operate) than the chips Intel sells for PCs, laptops, and servers. (never designed for power efficiency; they evolved from markets where computers were always plugged in) **ARM** is the firm whose processor designs **power the majority of smartphones.** Unlike Intel-compatible rival AMD, ARM chips **can't run Intel software**, so all of a firm's old code would need to be rewritten to work on any ARM-powered servers, laptops, or desktops.
100
New cards
__**Liquid**__
\
\
assets that can be easily turned into cash.