AP Euro Topic 1.3 Northern Renaissance Terms and Names (Amsco Bolded)
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Northern Renaissance
Cultural and intellectual movement of northern Europe; began later than Italian Renaissance c. 1450; centered in France, Low Countries , England, and Germany; featured greater emphasis on religion than Italian Renaissance

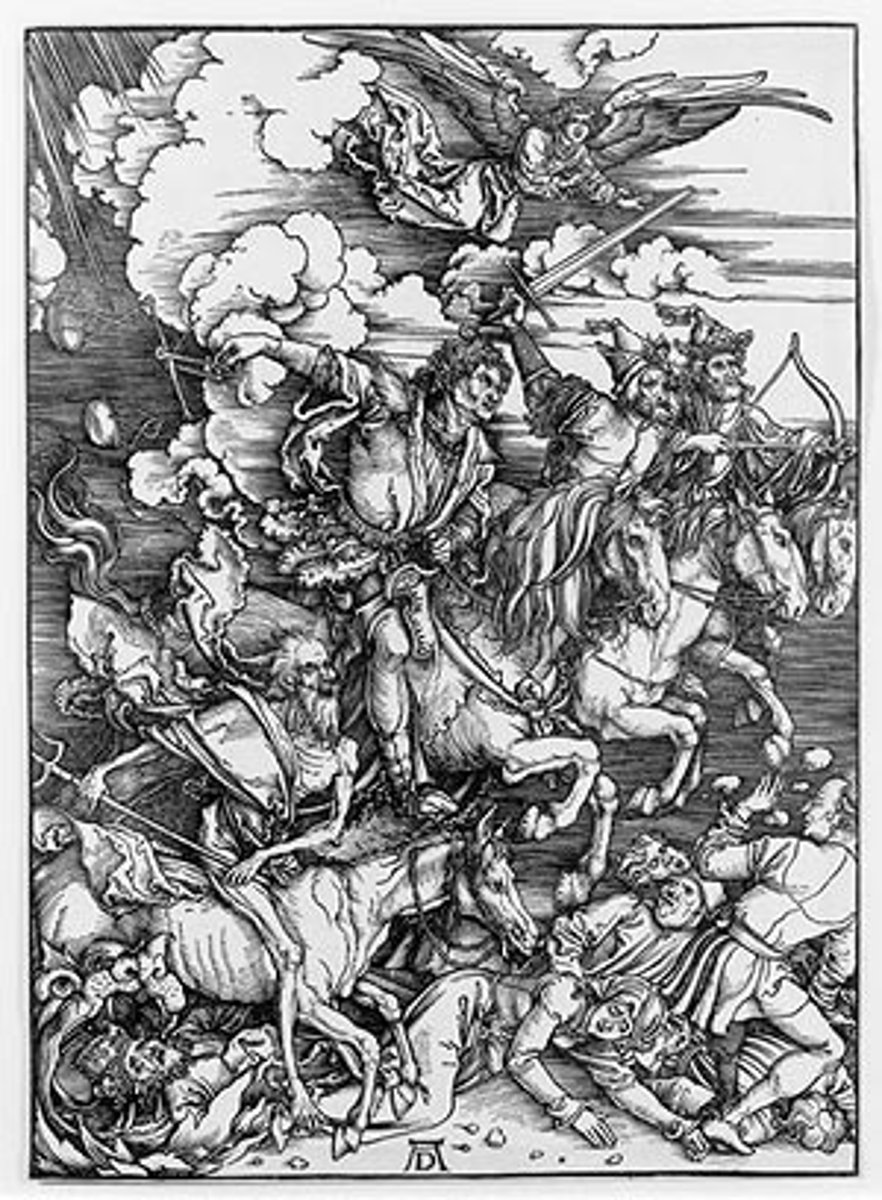
Albrecht Durer
Northern Renaissance artist, he often used woodcutting along with Italian Renaissance techniques like proportion, perspective and modeling.

Jan van Eyck
Flemish painter who was a founder of the Flemish school of painting and who pioneered modern techniques of oil painting (1390-1441)

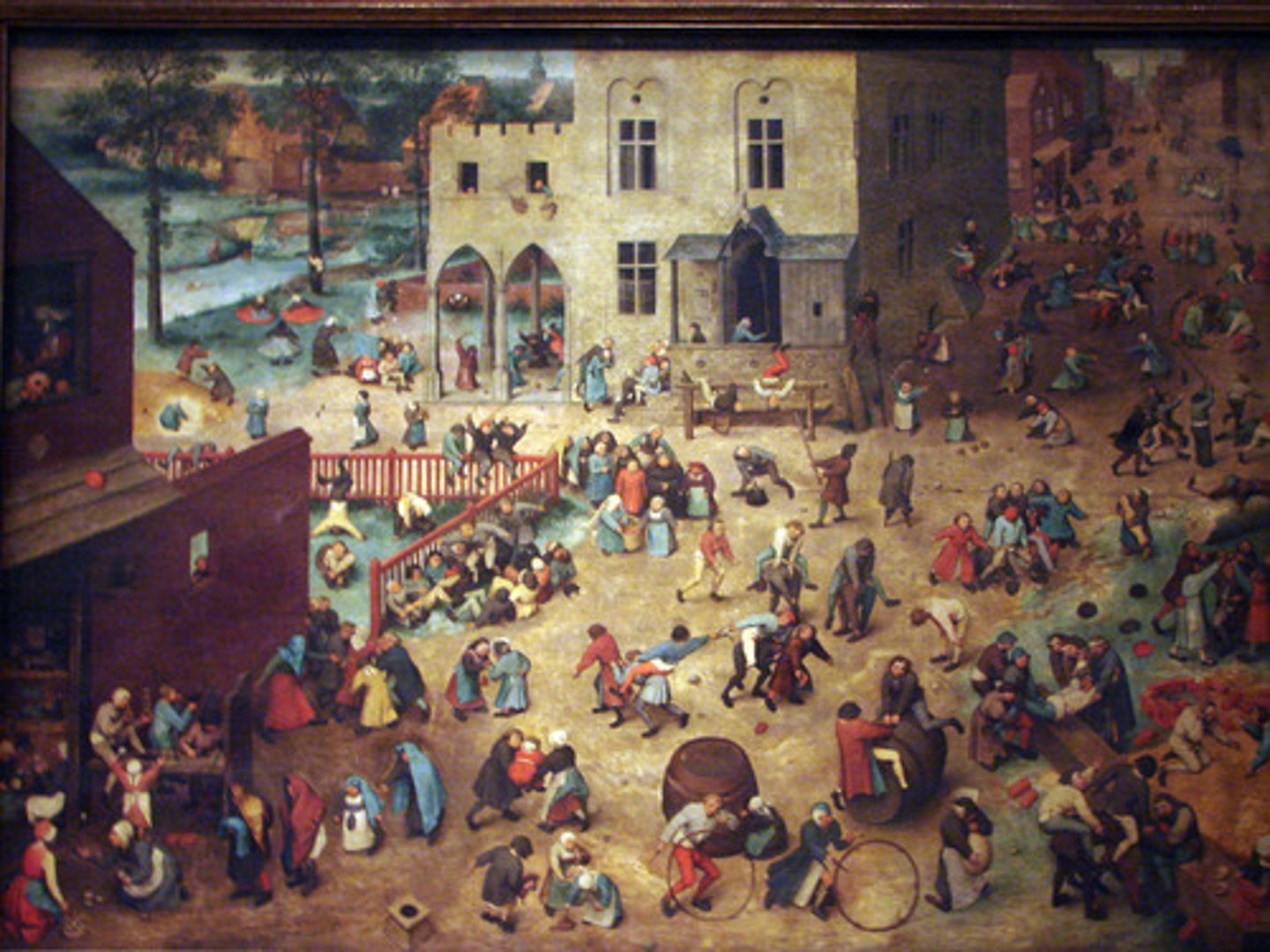
Pieter Bruegel the Elder
Flemish Renaissance painter known for landscapes and depictions of peasant life

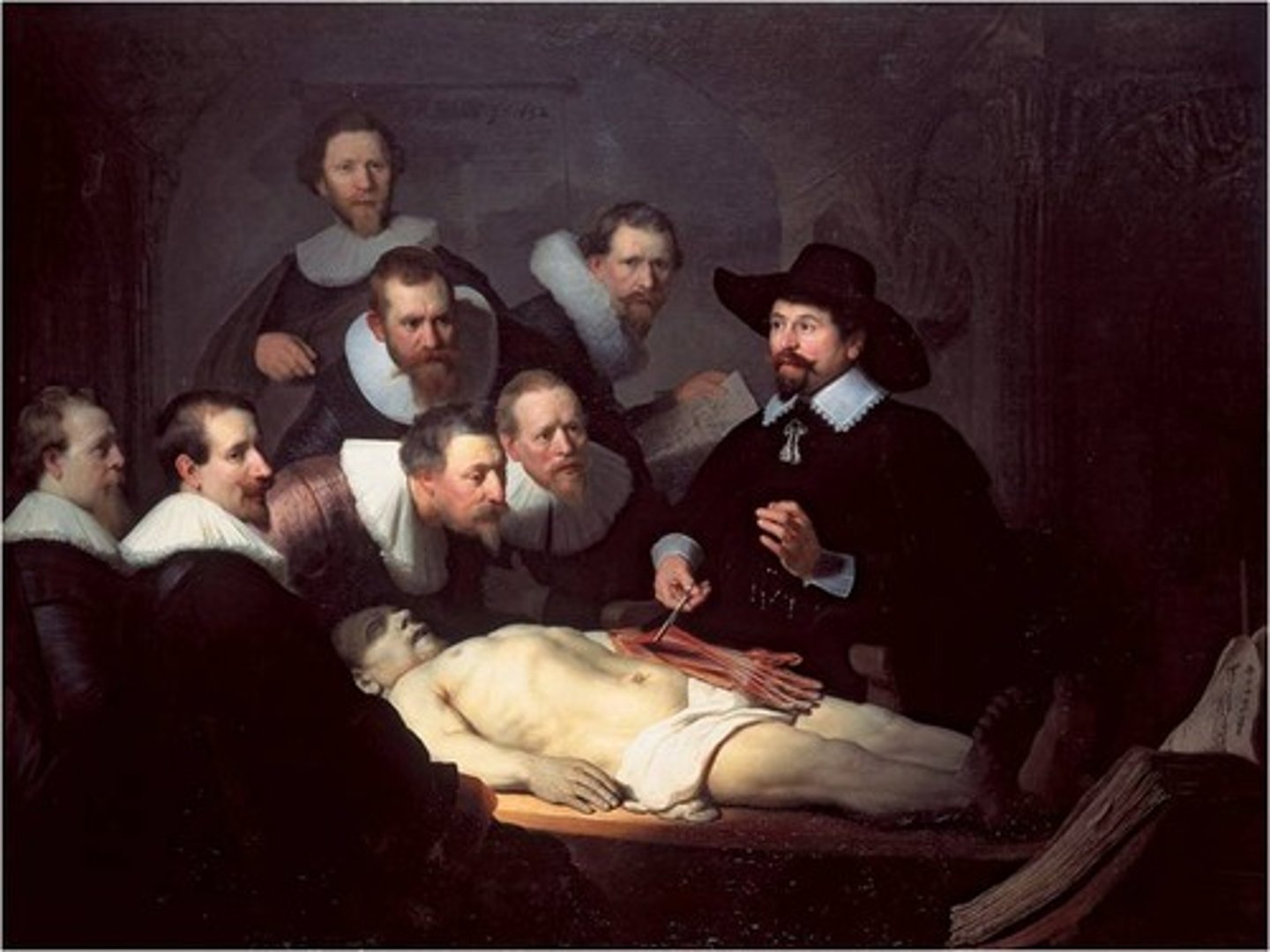
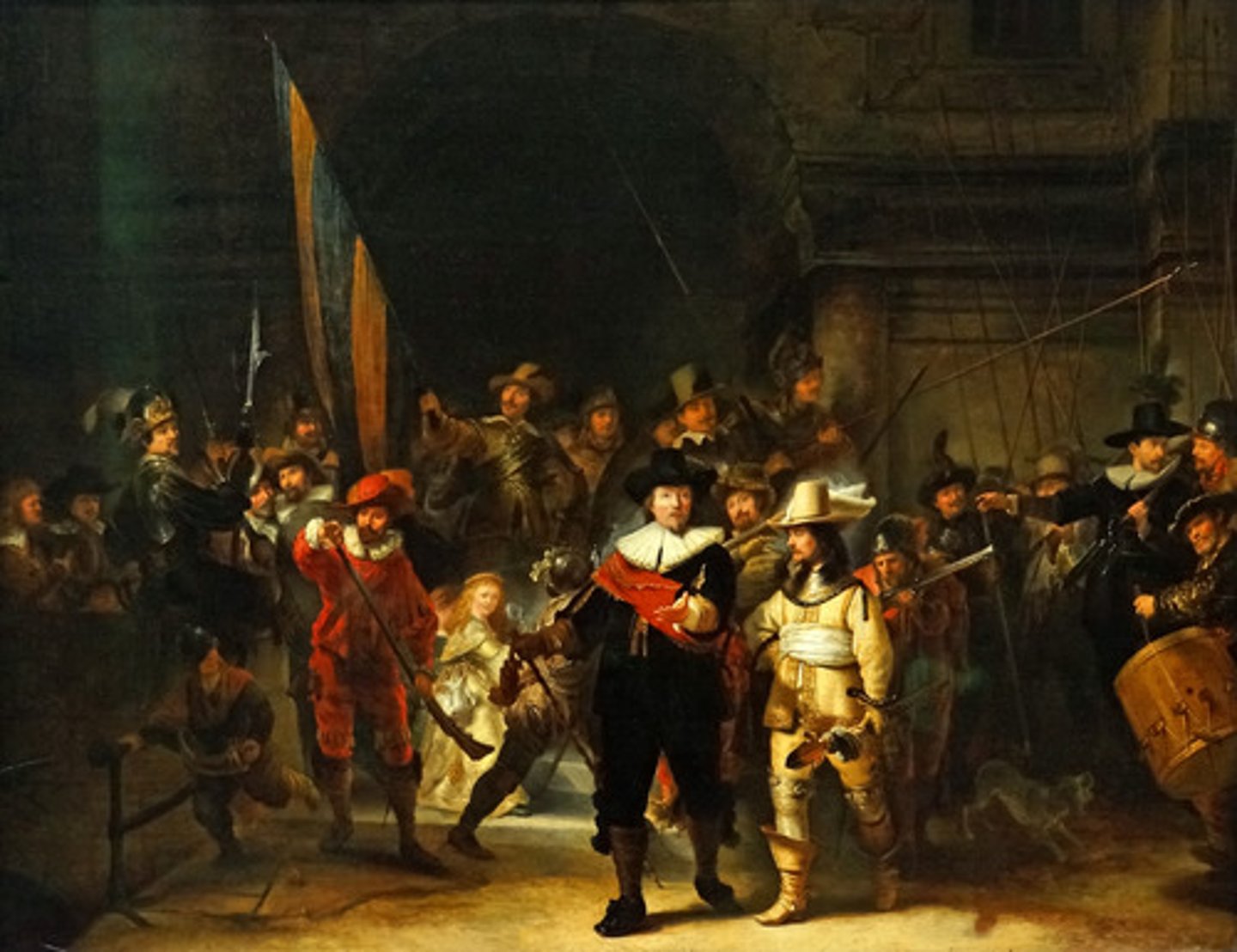
Rembrandt van Rijn
greatest Dutch artists of his time; painted portraits of wealthy middle-class merchants and biblical stories.
Christian Humanism
a movement that developed in northern Europe during the renaissance combining classical learning with the goal of reforming the Catholic Church
Desiderius Erasmus
Dutch humanist and theologian --although his criticisms of the Church led to the Reformation, he opposed violence and condemned Martin Luther. he wrote The Praise of Folly and translated the New Testament into Greek (1466-1536)
The Praise of Folly
an essay written by Erasmus that uses satire to point out corrupt practices of the Church.
Thomas More
English humanist who wrote Utopia, a book that represented a revolutionary view of society where the people lived in harmony, sharing resources.
Utopia
Book written by Thomas More that described an imagined place in which everything is perfect
The Night Watch
by artist Rembrandt, 1642

The Arnolfini Wedding
by artist Jan van Eyck, 1434

Children's Games
by artist: Pieter Bruegel the Elder

Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse
Albrecht Durer, 1498

Chiaroscuro
an effect of contrasted light and shadow created by light falling unevenly or from a particular direction on something to emphasize it.
