IGCSE Computer Science
1/322
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
323 Terms
binary numbers are used in
computer systems
conversion from denary to binary and from binary to den
use place values
memory size of a computer is measured in terms of the number of
bytes
1 kilobyte is
2 to the 10 bytes
1 megabyte is
2 to 20 bytes
Or 1 kilobyte according to manufactures
1000 bytes
Increase from
kilto to mega to giga to tera
unit symbols
kilobyte-kB
megabyte, gigabyte,tera byte is- CAPITAL thenB
Each increase by
1000 so mega byte has a 1000 kilobytes so thus a 1000000 bytes and a giga byte has a 1000 mByte
binary registers
group of bits in computer memory, each bit does something different so if 1 then x does y, small piece of memory built into cpu, where values and instructions are temporarily held. Not primary or secondary, very fast read and write rate, comp systems use registers to hold values and instructions for processing to increase the speed at which they are processed
Why choose Hex
Quicker to read, easier/quicker to write in hex, less likely to make errors copying so easier to debug
Letters in Hex
A=10
B=11
C=12
D=13
E=14
F=15
Register
Temporary piece of storage, status = stores what happening for reading, control gives instructions for writing
MAC addresses
media access control address 12-bit identification number unique for each device. Unique number that identifies a device, manufacturer id and serial number of device, address is allocated by manufacturer
Defining colours in HTML
Uses hexadecimal when representing colours, combinations of hex codes are used to represent different colours
#FF 00 00 = primary red
#00 FF 00 = primary green
#00 00 FF = primary blue
Memory Dumps
If there is an error in program it is useful to carry out memory dump, this is contents of a section of computer memory, Contents of a number of memory location are outputted in Hex format, Software engineer can then look at memory dump and find where error lies. Using Hex makes it easier and faster because ^
Assembly language and machine code
Memory location can be addressed directly using assembly language or machine code, this means its easier for programmers to write the code because not using binary
sound, music, pictures, video, text and number are
stored in different formats
Musical instrument digital interface
MIDI file comprises of data stored as a list of messages telling device how to generate a sound or music. Software saves the messages as .mid file, when played on an electronic keyboard the keyboard's software follows the .mid fil instruction and produces music,
-doesn't contain actual music so file size is much smaller than MP3 or MP4 files, 1Mbyte file size to store one minute under MP3 and 10kbyte Midi
MPEG-3 files
uses audio compression technology to convert audio to MP3 format, normal music on cd is compressed by a factor of 10. Uses perceptual music shaping, which removes sounds the human ear cannot hear properly, if 2 sounds are played MP3 discards softer sound that can't be heardeg
MPEG-4 files
format which allows multimedia rather than just audio files. Work in similar way to MP3 but they store audio , video, photo and animation files. Work b compressing files without affecting the quality by making certain aspects of the file redundant
Jpeg files
image encoding system that compresses photographs and other images. Lossy format and makes use of certain properties of human vision to eliminate certain unnecessary info
Lossless file compression
breaking down into files of similar size for transmission or storage and then put back together again at receiving end so it can be used again
Lossy file compression
Lossy compression algorithm eliminates unnecessary bits of information. It becomes impossible to get back to the original file once this lossy compression algorithm has been applied and the new file stored.
Algorithm looks for redundancies in file and eliminates them to reduce file size
Lossy Compression mark scheme points
images contain less detail without noticeable degradation in quality
streams faster than lossless compression
if 2 sounds played at the same time, softer sound is removed
when decompressed some detail is lost and file is not exactly like the original
Lossless compression mark scheme points
original and decompressed file will be the same
for code, decompressed file and original file must be exactly the same otherwise file wouldn't work
after decompression original file is restored with no loss of data
Data Transmission
Transferring binary data from sender to receiver
Serial
Data transmitted one bit at a time over a single wire
Parallel
Data transmitted several bits at a time simultaneously over several wires.
Advantages of Parallel
Faster, works well over short
Advantages of Serial
Cheaper cabling, works well over long
Disadvantages of Parallel
Conductive wires close together cause interference degrade signal quality
Disadvantages of Serial
Slower, synchronisation problems, receiver can't distinguish characters as one sent after another
Asynchronous
Signals sent in previously agreed pattern. Data includes control bits which informs receiver when transmitted data start and ends. Inexpensive serial.
Uses of serial transmission in USB
asynchronous serial, 4 wires, 2 for data other for power and earth.
USB advantages
Automatically detected and configured upon first attachment, not possible for incorrect instalment and industry support.
USB disadvantages
Cable limited to 5m and transmission speed to 480Mbps.
Use of parallel transmission in Integrated Circuits
Internal circuitry of computer is made up of IC's, method of transmission is parallel, transmission channels are usually 18bit to 64bit in width, the wider the channel the faster the transmission rate. An internal clock inside the devise makes sure all transmitted bits arrives in sequence.
Synchronous
Transmission accompanied by timing signals ensure sender and receiver are in step. Receiver counts bits and reassembles the data. Faster than asynchronous because less bits sent.
Simplex
Data can only transmitted one way from sender to receiver.
Half-duplex
Data transmitted between both sender and receiver but only one way at a time.
Full-Duplex
Data transmitted between both sender and receiver simultaneously.
Paritiy Check Verification Technique
Check byte of data, performed hen data received, parity bit added, number of 1's counted to see if even, can be even or odd, if parity incorrect error is then detected,
Problems with parity check
When even number of bits have been transposed
Parity byte
Parity byte is also sent along with other binary numbers which uses a parity check for each number. Parity byte is the additional parity bits found from a vertical parity check on the binary numbers, sent to indicated end of binary block
Finding errors in parity bytes
See which rows have an incorrect parity and columns, find intersection of row and column and change to make correct parity.
Automatic repeat request verification technique
Uses acknowledgements, requests and time outs, its an error control protocol. Check is performed on receiving data. If error is detected, then resend request is repeated until data is sent correctly. Sends acknowledgment that data is received. If acknowledgment is not received in set time data is resent.
Checksum verification technique
value that is calculated from data, added to data, then recalculated after data is entered then digits compared to check for error
ARQ timeout
Stop and wait until ACK arrives. If doesn't arrive use timeouts, so keep retrying for a x amount of times before u retry
Mark scheme points for serial transmission
more accurate over longer distances and more reliable over longer distance
less chance of data being skewed out of sync because less chance of interference
cheaper connection only single wire needed
easier to collate bits together again after transmission, synchronised after transmission
Check digit
digit calculated from data, added to data, recalculated when data is entered, digits are then compared
Role of a browser
display web page
translates HTML document
Functions such as bookmarks, stores history
Identifies protocols such as SSL
Role of Internet service provider
provide user with access to the internet
customers normally pay a monthly fee for this server
Hypertext transfer protocol
set of rules for transferring files on the web, http was later developed to allow secured transactions on the web to take place. Protocol works by transmitting info using encryption.
https
indicates secure webpage
HTML
Hyper Text Mark up Language
Language that provides structure and presentation. Kept separate, easier to update features like colour then.
Creates webpages
Translated by browser to display webpage
Uses tags to display content, used to define colour, graphics and layout
Web-authoring language
HTML structure
How layout of content is displayed. Create layout of doc. Markup tags used to define structure of document.
HTML presentation
How content will be formatted. Format colour. style of document. Often stored in a file called CSS, which is linked to HTML document.
IP address
Identify a device on a network, allocated by the ISP, can be used in place of a URL. Can be IPv4 or IPv6. Can be static means it doesn't change each time it is connected to internet. Can be dynamic means it changes each time a device is connected to internet. Give example. INTERNET PROTOCOL address
Different between IP address and Mac address
MAC address rarely changes so that a device can be identified no matter where it is
url
Uniform Resource Locator, a resource path is sent to ip address found from domain
cookies
oacked of info sent by a web server to a web browser and then sent back by the web browser to the web server every time it accesses it.
cookie function
used to authenticate user "Welcome x" if you are not x log out
User tracking and maintain user preferences
although info is used to form an anonymous profile of the user they have been subject to privacy concerns
Protocol
http how data is sent and received
Domain
Names of server, same as web server name www.cie.org.uk
Resource path
same as file name
How is request to access webpage sent to server
URL contains domain name. ISP looks up IP address of company. Domain name is use to look up IP address of company. DNS - domain name server stores an index of domain names and IP addresses. Web browser then sends a request to that IP address.
How is data received from web server
Browser connects with server containing files for website, data for website stored in server. Server then sends data for website back to browser, server uses customer IP address to do this. Transferred files translated to HTML. Interpreted by browser- display page.
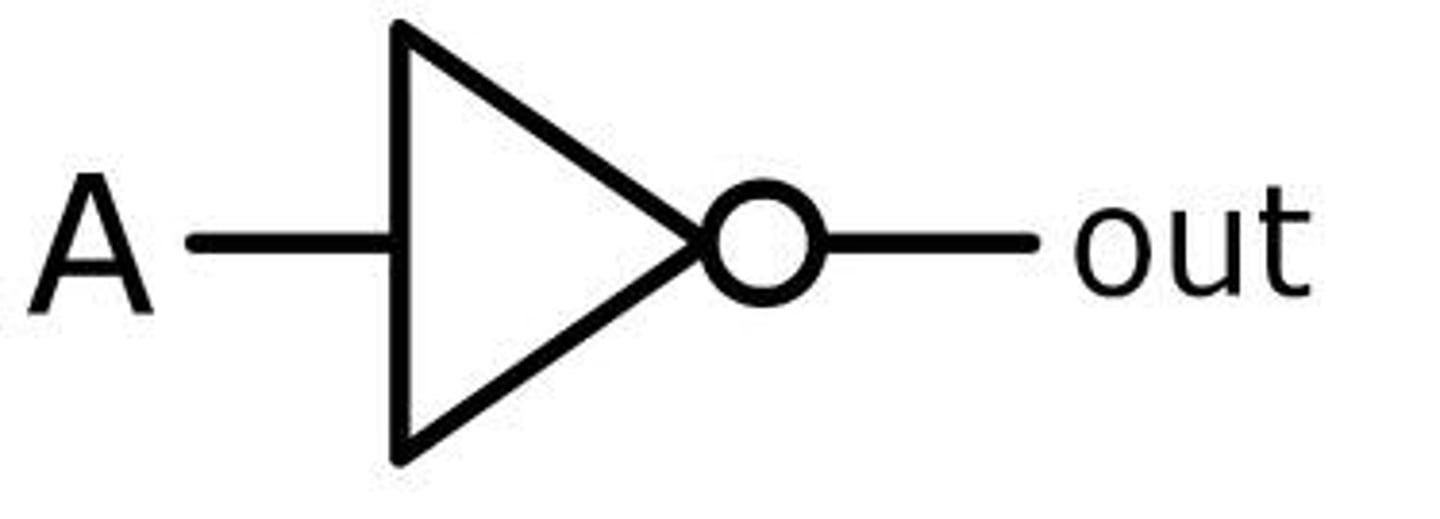
NOT logic gate
Output is equal to opposite of input
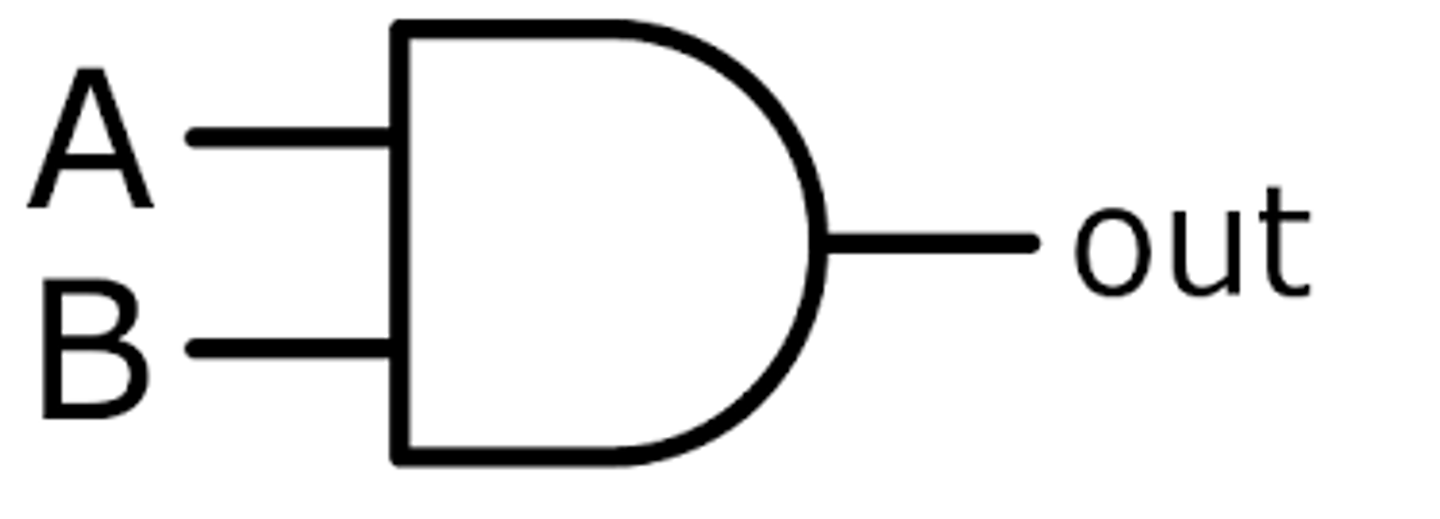
AND logic gate
Output is always 0 unless both inputs are 1
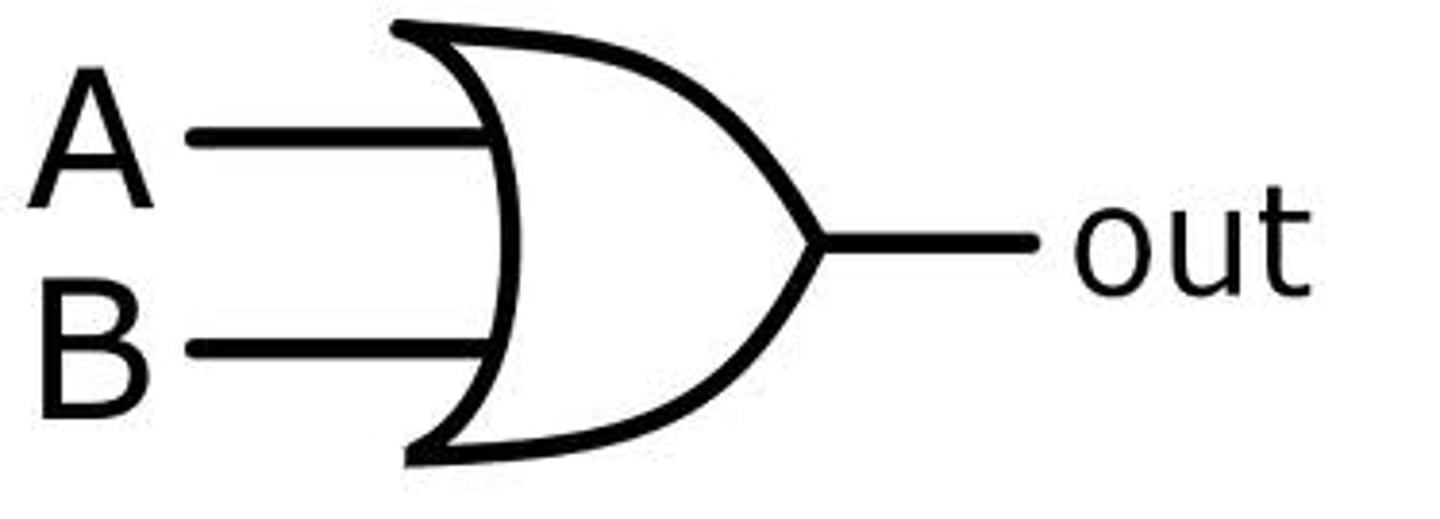
OR logic gate
Output is always 1 unless both inputs are 0
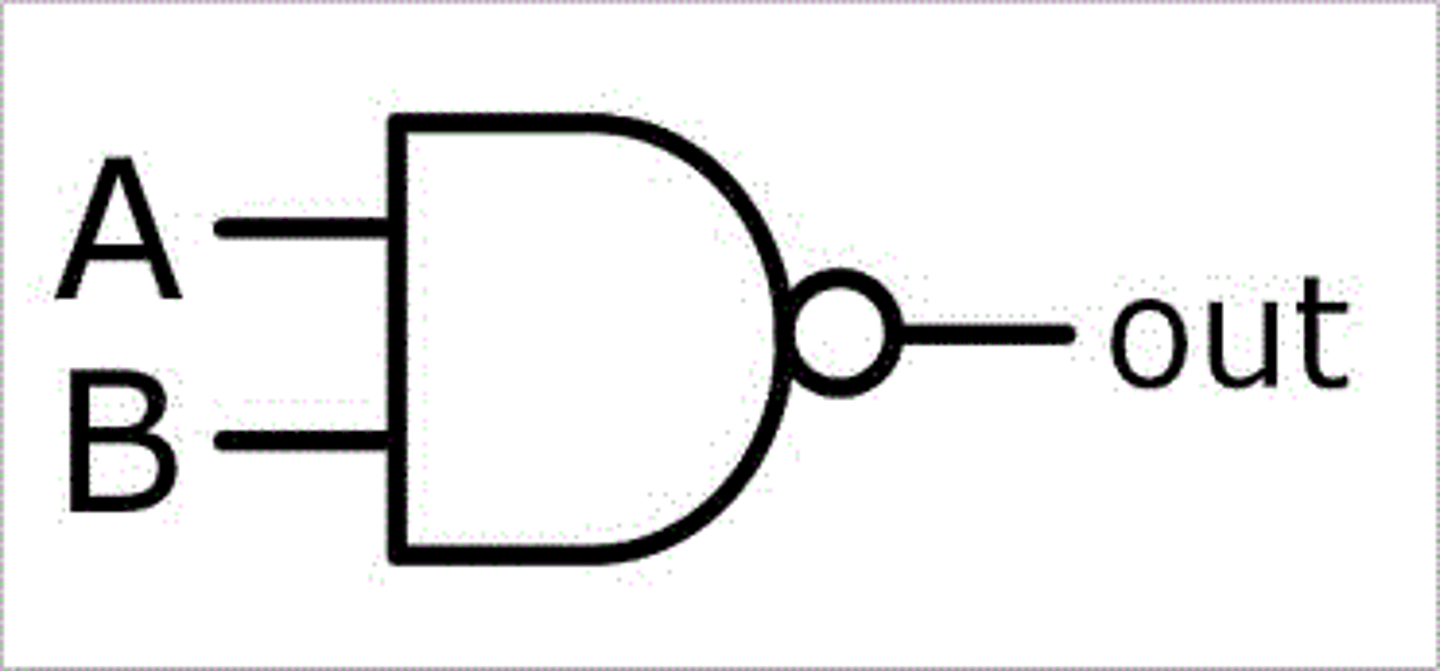
NAND logic gate
Output is always 1 unless both inputs are 1
NOR logic gate
Output is always 0 unless both inputs are 0
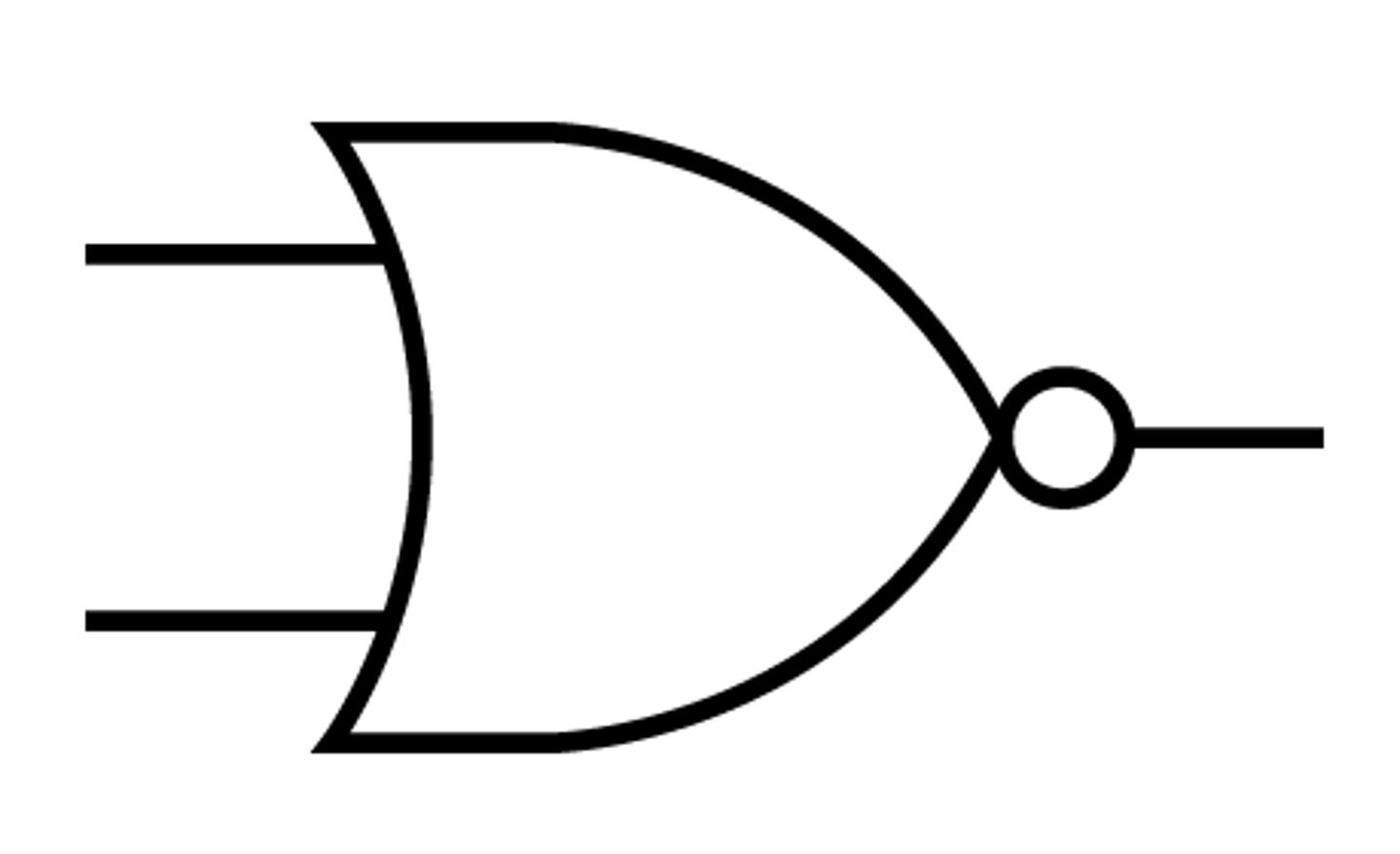
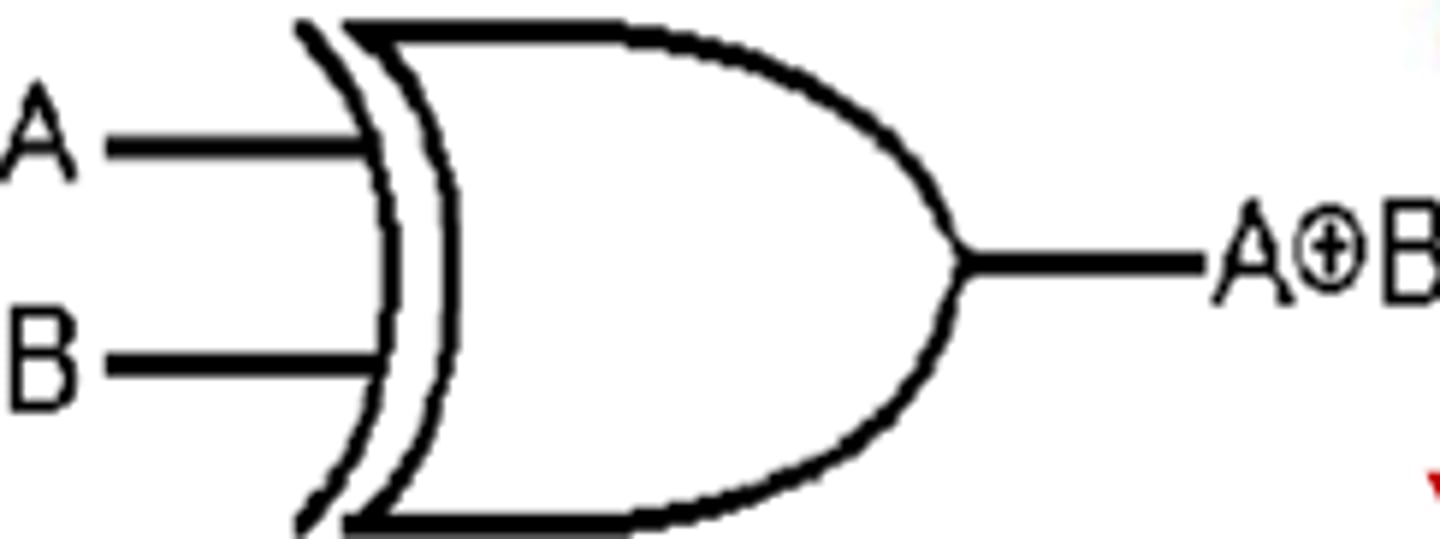
XOR or EOR logic gate
If two inputs are same then output is 0, if two inputs are different then output is 1
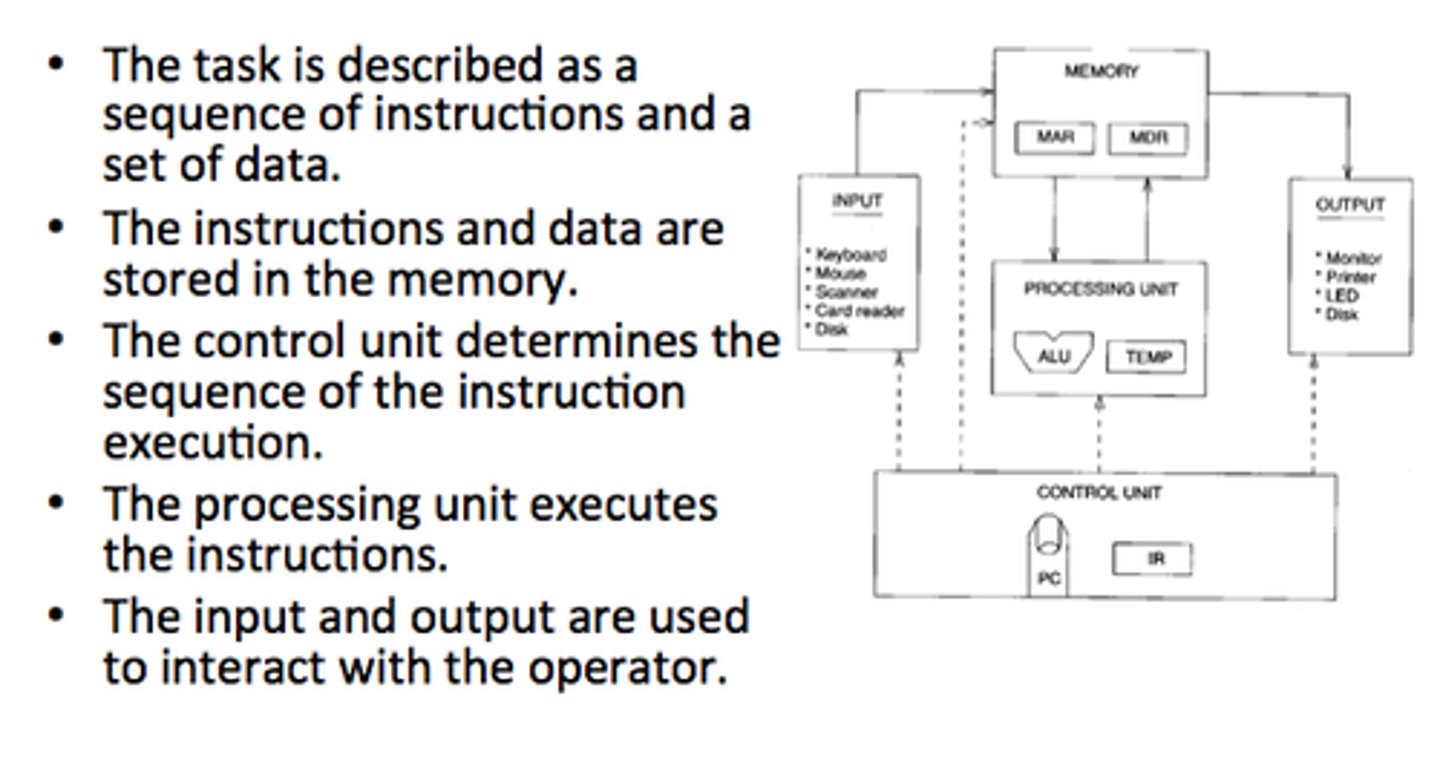
Von Neumann Model
Processor uses address bus to find out which address you need to read from in memory
RAM then uses data bus to transfer data to cpu which is then sent to peripherals which run data
Control Bus from cpu to i/o tells what peripherals should do
Address Bus
Carries location of next item to be fetched. its unidirectional
Data Bus
Transports data that is currently being processed, bidirectional
Control Bus
Carries signals that controls the actions of the CPU, either Unidirectional or bidirectional
What is the execute function in the fetch-execute cycle
Control unit passes the decoded information as a set of control signals to the appropriate components within the computer. This allows all necessary actions to be carried out.
What is the fetch function in the fetch-execute cycle
The next instruction is fetched from the memory address currently being stored in the program counter and then it is stored in the current instruction register (CIR). The PC is then incremented so that the next instruction can be acted upon
Fetch-execute cycle 1
The PC contains the address of the next instruction to be fetched
Fetch-execute cycle 2
The address contained in the PC is copied to the Memory Address Register via the address bus
Fetch-execute cycle 3
The instruction is then copied from the memory location in the MAR and is placed in the Memory Data Register
Fetch-execute cycle 4
The entire instruction is then copied from the MDR to the CIR
Fetch-execute cycle 5
The value in the PC is then incremented so that it points to the next instruction to be fetched
Fetch-execute cycle 6 (execute)
The address part of the instruction s placed in the MAR
Fetch-execute cycle 7 (execute)
The instruction is decoded then executed
Control Unit
Controls operation of memory, processor and I/O. Instructions are then interpreted, sends signal to other components telling them "what to do"
Intermediate access store
memory found inside a CPU, used to hold not only data but also instructions before they are processed.
Arithmetic Logic Unit
used to carry out calculations on data, values need to be placed in accumulator in ALU for calculations to be carried out. Carries out logic gate operations.
MDR
contents of the address are in the MDR
MAR
the actual address
Control unit
Controls operation of memory, processor and I/O. Instructions are then intepreted, sends signal to other components telling them "what to do"
Step 1- fetching the instruction
CPU fetches the necessary data and instruction and stores them in its own internal memory locations (IAS). To fetch the instruction the CPU uses the address bus, CPU puts address of the next item that needs to be fetched on the address bus. Data from this address is then moved from main memory into IAS in to CPU travelling along data bus.
Step 2 - decoding the instruction
Needs to udnerstand the instruction that has just been fetched.
Step 3 - executing the instruction
processes data, calculations carried out in ALU
2D scanner how it works
The document is illuminated by a bright light
A scan head moves across the page until all of it has been scanned
The produced image is sent to a lens
Image is focused onto CCD(charge coupled device)
CCD is made up of thousands of light sensitive elements which create an electric charge when light falls onto it thus converting it into an electric form
A digital image is created from this electric form
2D scanner how it works simple
illuminated, scan head scanning doc, scanned image sent to lens, focused on CCD, converted into digital image Reflected light is captured, through use of mirrors and lenses captured image is converted into a digital file. Producing a 2D digital image
2D scanner markscheme
uses light to illuminate document (shines light onto surface of document), scan head then scans document. Scanned image is then sent to lens, where it is focused on CCD (Charge coupled device) to be then converted into a digital image. Reflected light is captured, through use of mirrors and lenses captured image is converted into a digital file. Producing a 2D digital image.
2D scanner application
Used at airports to read passports
Scanning documents and digitizing them