ANP 200 did they evolve in the savanna or the forest
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
savanna hypothesis
long-held idea (Darwin?)
morphological change (bipedalism) as adaptation to savanna habitat
cultural change caused by expanding grasslands
climate drying and cooling, savanna expanded
→ bipedalism evolved in open habitat - 2 scenarios
ancestors of hominini were the losers who were forced by the ancestors of panini out into savanna - bias
ancestors of hominini were the opportunist; actively left forest to explore new and promising environments
forest model
rather new idea
morphological change (bipedalism) evolved before expanding grasslands
climate drying and cooling, savanna expanded
→bipedalism preadaptation; evolved in forest - 1 scenario
Hominini evolved in forest; actively left later
again, viewing human ancestors as opportunists /investors
Reconstructing paleo-environments
adaptive traits (fossils) and fossil assemblages
plant remains (plant parts or pollen)
plants - from wet or dry habitats
% wind distributed
sediments and soil
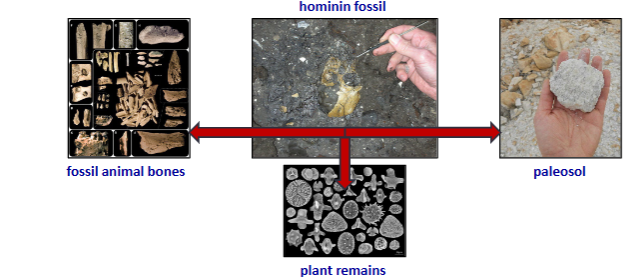
defining environments
forest - continuous tree stand, interlocked crowns
woodland - open tree stand; >40% (80%) woody cover
wooded grassland - grasses and herbs; woody cover 10-40%
grassland - grasses and herbs; woody cover <10%
Reconstructing environments vis soils
measure current habitats
amount of tree cover
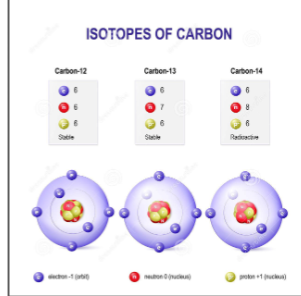
variation of carbon isotope ratios in soils
match trees cover carbon isotope ratio
compare to
carbon isotope ratio in paleosols
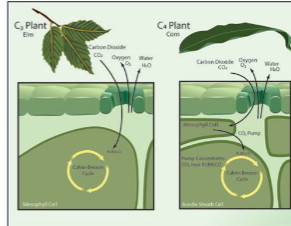
photosynthesis
different types (C3, C4/CAM)
reflected in ratio carbon 12 / carbon 13
carbon photosynthesis
more carbon - 12 in soil (negative &13C
more C3 plants (=”forest”)
more carbon - 13 in soils (close to zero &13C)
more C4 plants of C4 animals (grassland)
step 1 at ca. 8 ma BP
tectonic event separating LCA Panini - Hominini
Western part rift valley
humid, forest, ancestor panini
eastern part rift valley
dry, open savanna, ancestor hominini
early hominini through allopatric speciation
bipedalism evolved as adaptation to open habitat

step 2 at ca. 3-2.5 ma BP
cooling and drying of climate
habitat becomes more open (more grass, less trees)
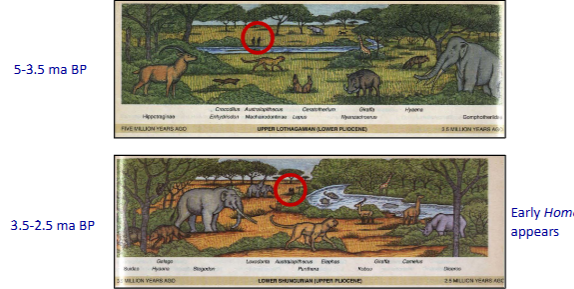
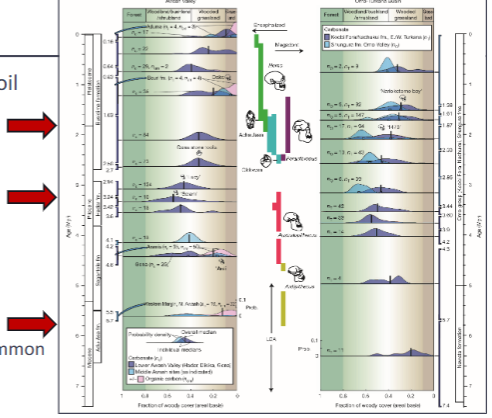
reconstruction for one particular area in East Africa(Omo river)
oldest (4 ma BP, Mursi formation)
animals w/forest adaptions
many tree pollen, few grass pollen
youngest (1 ma BP, Shungura formation
many animals w/ savanna adaptations
few tree pollen, many grass pollen
step 1 of critique
unconvincing
tectonic event only (but is this convincing?)
no climate data
habitat is unclear (4ma BP was likely woodland)
step 2 of critique
fine (though habitat is not habitat use)
Australopithecines
previous habitat reconstructions
mixed habitats
woodland, wooded grassland, savanna
validity debated
characteristic early hominini
perhaps bipedal; climbing ability
small brain
reduced canines
body size dimpophism
→status as hominins debated
example - ardipithecus spp.
“ground ape”
East Africa
ca. 4.4 ma BP
habitat of Ardipithecus
woodland
150,000
coexisted with animals which prefer woodland
→ similar reconstruction than for australopithecines (which were perhaps less arboreal than Ardi)
in which habitat did hominins evolve

hominin environment
carbon isotope ratios in soil
ca. 2 ma BP onward
more open again
3-5 ma BP
more trees / less open
7-6 ma BP
open habitat rather common
climate during human evolution
at ca. 7 ma BP no strong climate signals
at ca. 3-2.5 m BP more variable
grassland is expanding, more grassland species
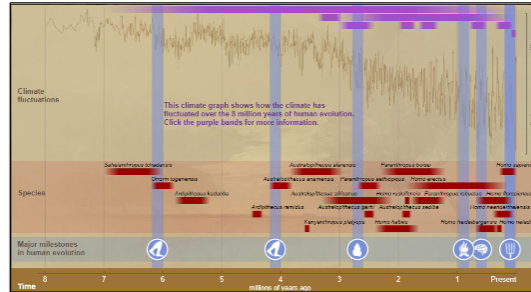
caveat
or be VERY careful
environment is NOT habitat use
if multiple habitats are available
what is used often and why
open woodland (light green) - macaques only
forest (dark green) - both leaf monkeys and macaques
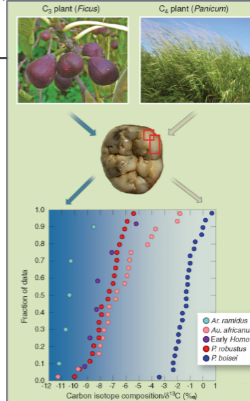
Reconstructing diet via tooth enamel
measure
carbon isotope ratios in tooth enamel
more carbon - 12 in soil (negative &13C
more C3 plants (=”forest”)
more carbon - 13 in soils (close to zero &13C)
more C4 plants of C4 animals (grassland)
problem - meat from animals - same signature as plants they ate
fish - more carbon-13 (similar to C4 plants/animals
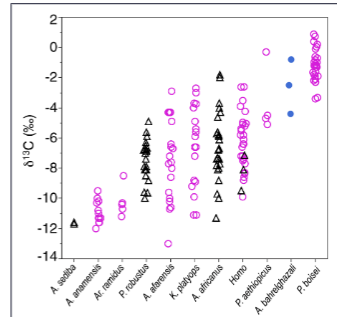
early hominini, australopith and early homo diets
carbon isotope ratios from tooth enamel
early hominini & some australopith
mostly C3 foods
some australopith and early homo
mix of C3 and C4
1 paranthropus & 1 australopith
mostly C4
overview hominin diet
7 - 4 ma BP (early hominini)
mostly C3 (fruits, leaves; meat unclear)
4-2.5 ma BP (most australopithecines)
mix of C3 (fruits, leaves) and some C4 food(grassland plants); little meat
2.5 - 1.7 ma BP (Early homo)
mix of C3 (fruits, leaves) and some more C4 food (some meat and grassland plants)
overall conclusion early hominini
habitat: mixed; little forest/ woodland, rather open
habitat use: stayed (fed) mostly in forest/ woodland
contrasts with savanna hypothesis
in which habitat did hominins evolve
perhaps forest
general categories of suggested explanations
bipedalism results from pre-adaptation*
function of a characteristic changes during evolution
→ existing behavior facilitates bipedalism
bipedalism is an adaptation
a characteristic that provides a selective advantage (increases fitness)
→ bipedalism provides a fitness benefit
fitness(survival, mate finding, reproduction) can also be indirect benefit: energy
also called exaptation
overall conclusion (australopithecines)
habitat: mixed; little forest/ woodland, rather closed
habitat use: stayed (fed) often in forest/ ventured into grassland
overall conclusion (early homo)
habitat: mixed; little forest/ woodland, rather open
habitat use: used both forest woodland and grassland
learning objective or what you should know
