AP Bio Unit 1
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mr. Austin's AP Bio class including pictures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space (has volume). Exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into any simpler substances; composed of only one type of atom.
CHNOPS
An acronym for the six main elements found in all living organisms: Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur.
Trace Elements
Elements required by an organism, but only in minute quantities. Ex: Iron (Fe) in humans.
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element.
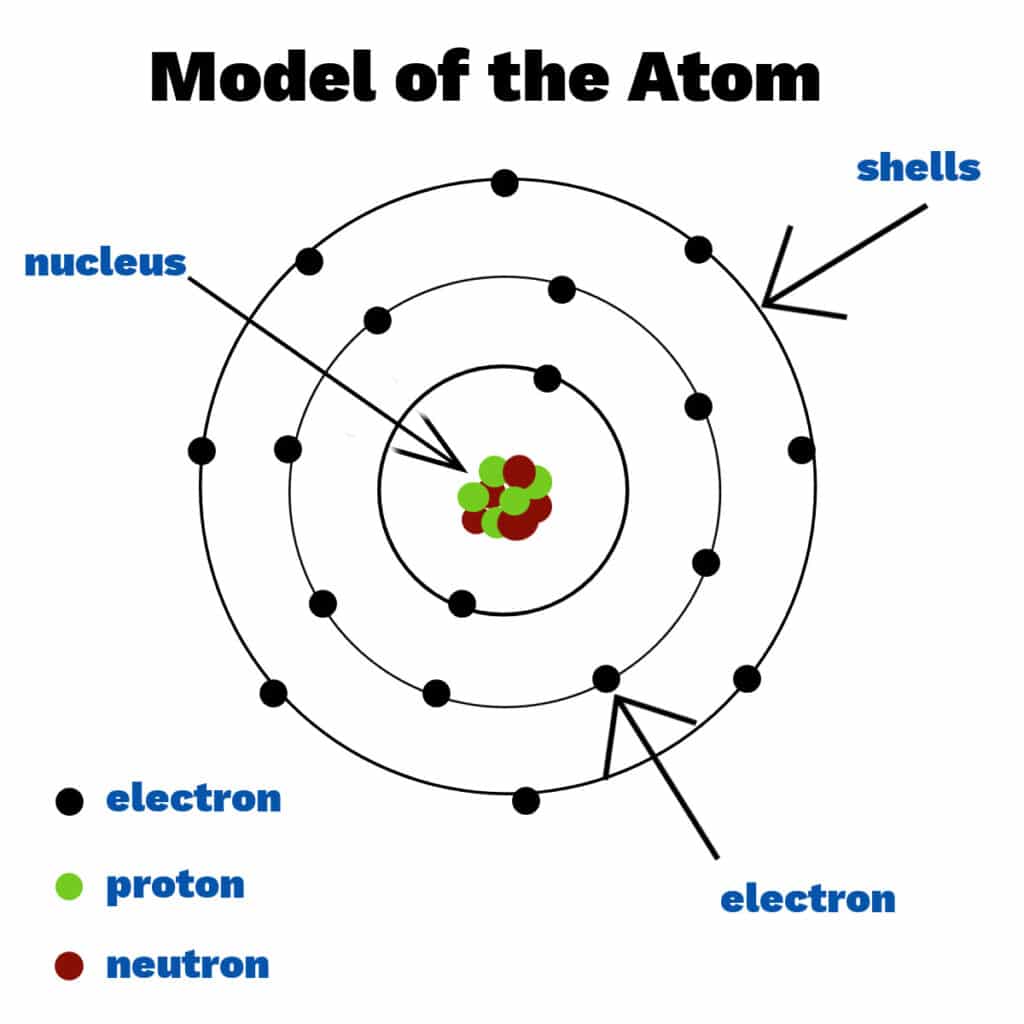
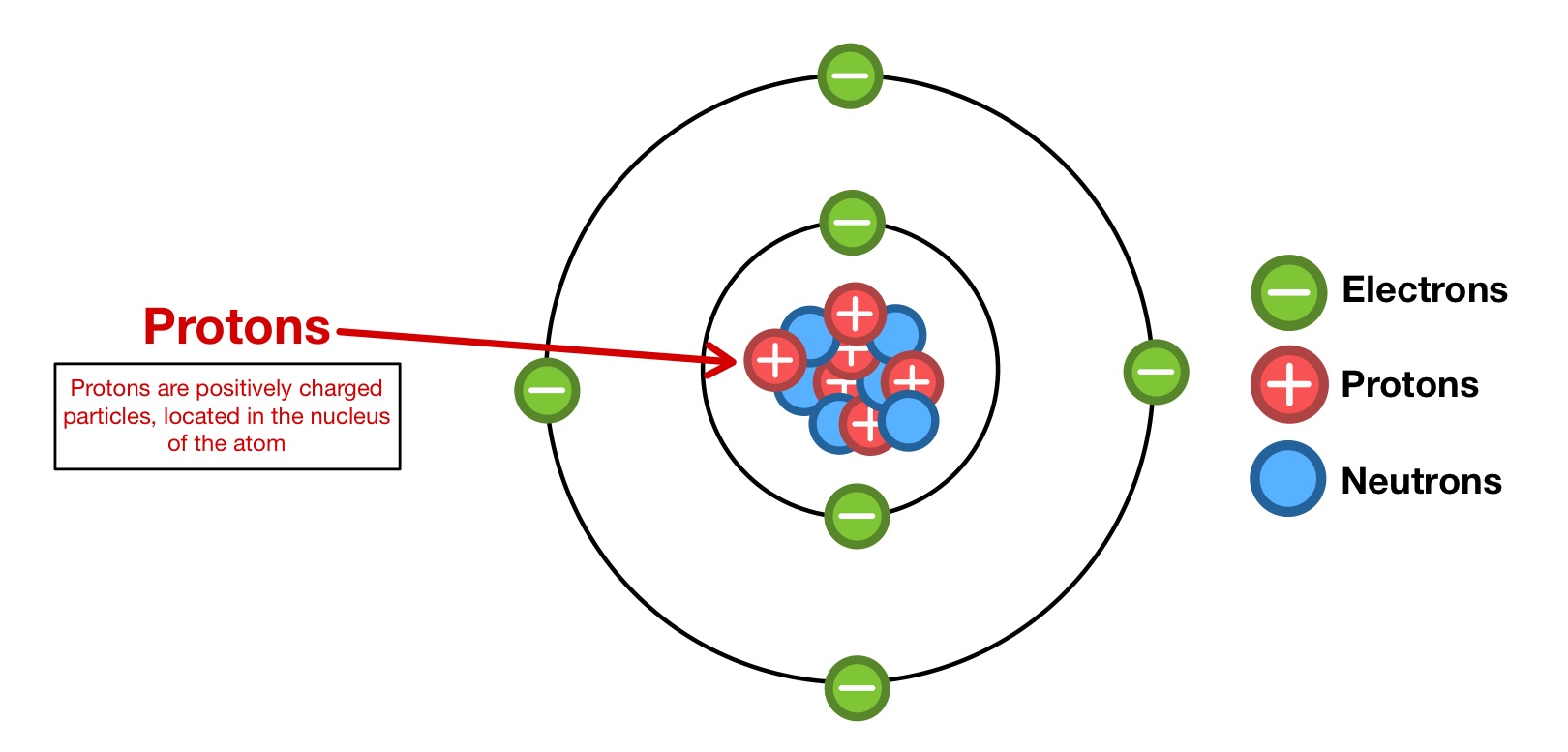
Proton
A positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
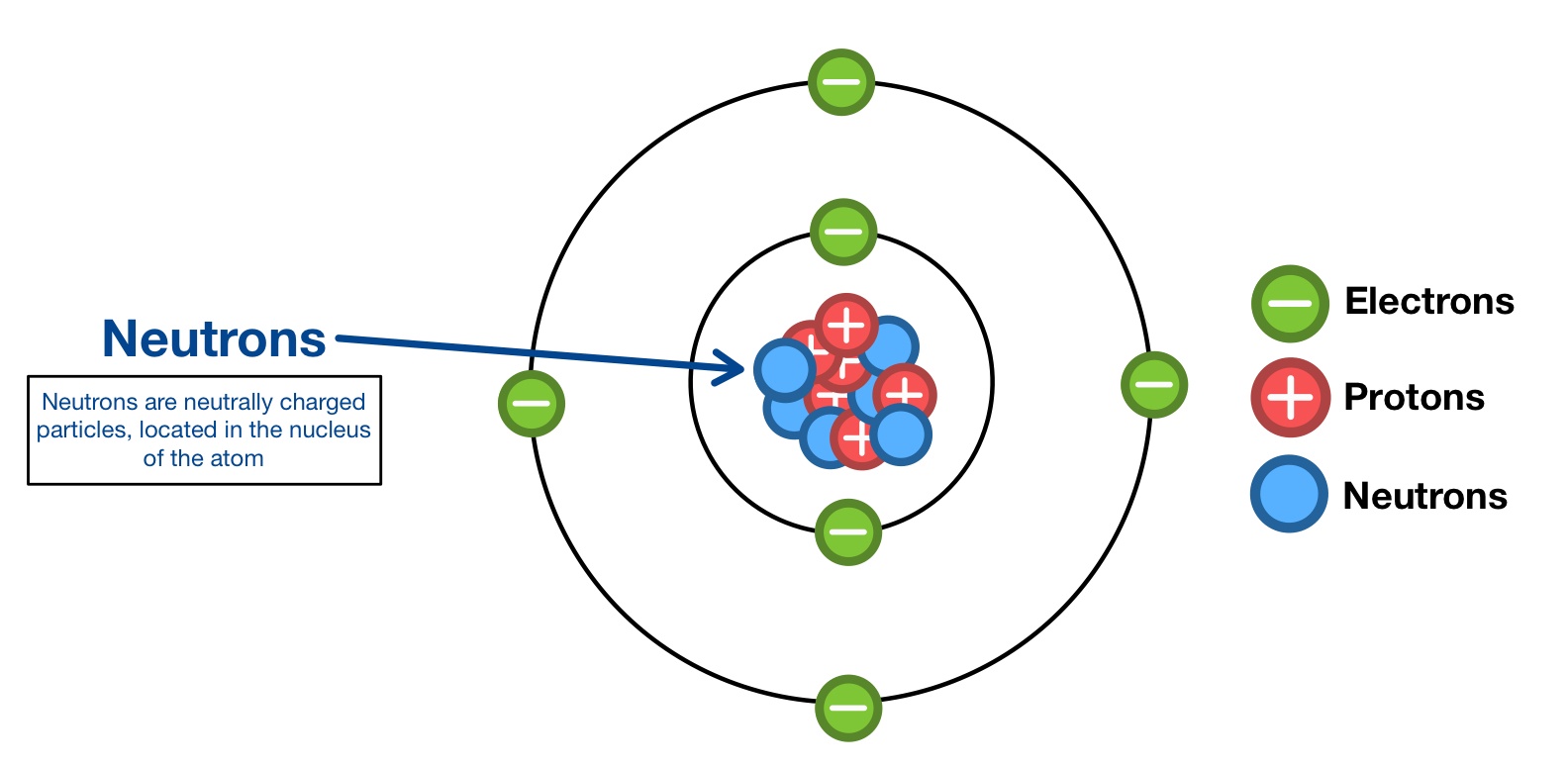
Neutron
A subatomic particle with no charge found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle that orbits the nucleus in electron shells.
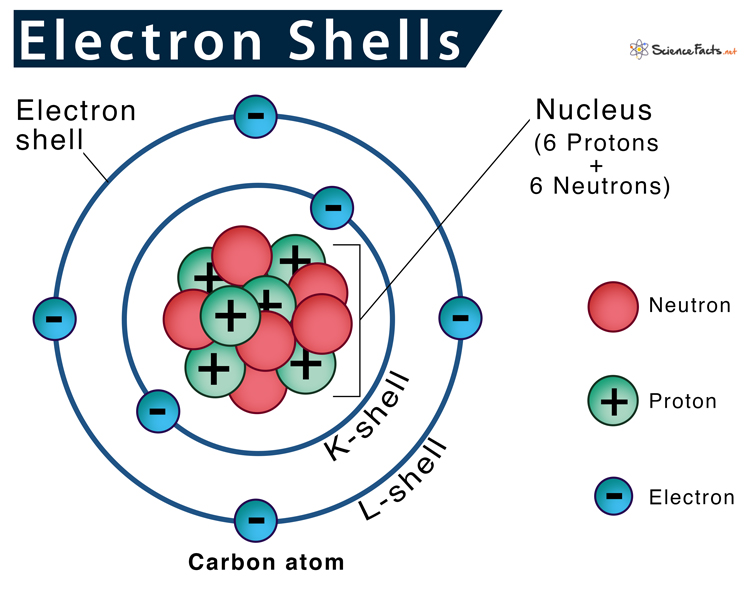
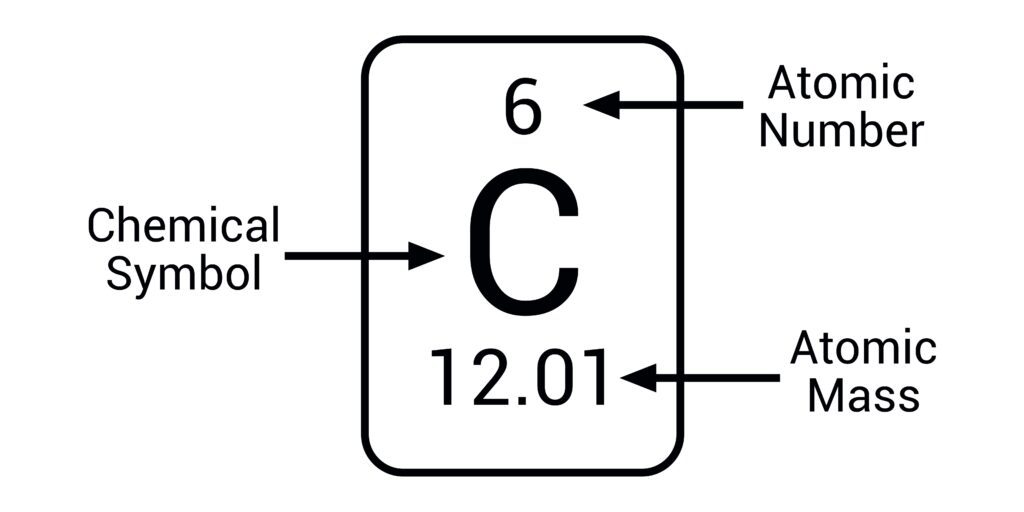
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom; determines the element.
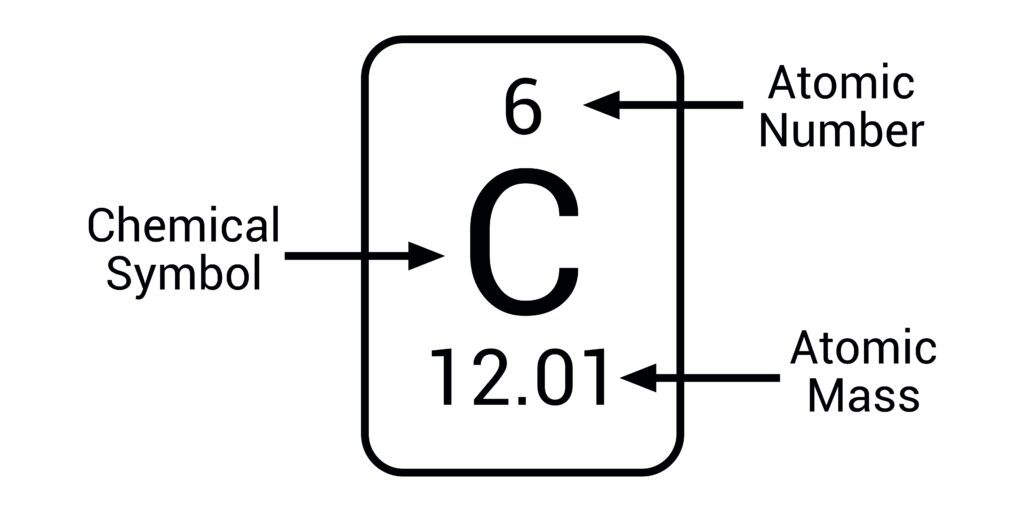
Atomic Mass Number
The average number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Isotope
Atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that have a different number of neutrons.
Radioactive Isotope
An unstable isotope whose nucleus decays (breaks down) into a more stable atom.
Half-life
The amount of time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay.
Radioactive Dating
The process of using the half-life of isotopes to determine the age of fossils, rocks, and other relics.
Tracer
A molecule synthesized ("labeled") using a radioactive isotope, allowing scientists to track its movement in biological processes.
Compound
A substance formed by the chemical bonding of two or more elements. Ex: H₂O, CO₂, NaCl.
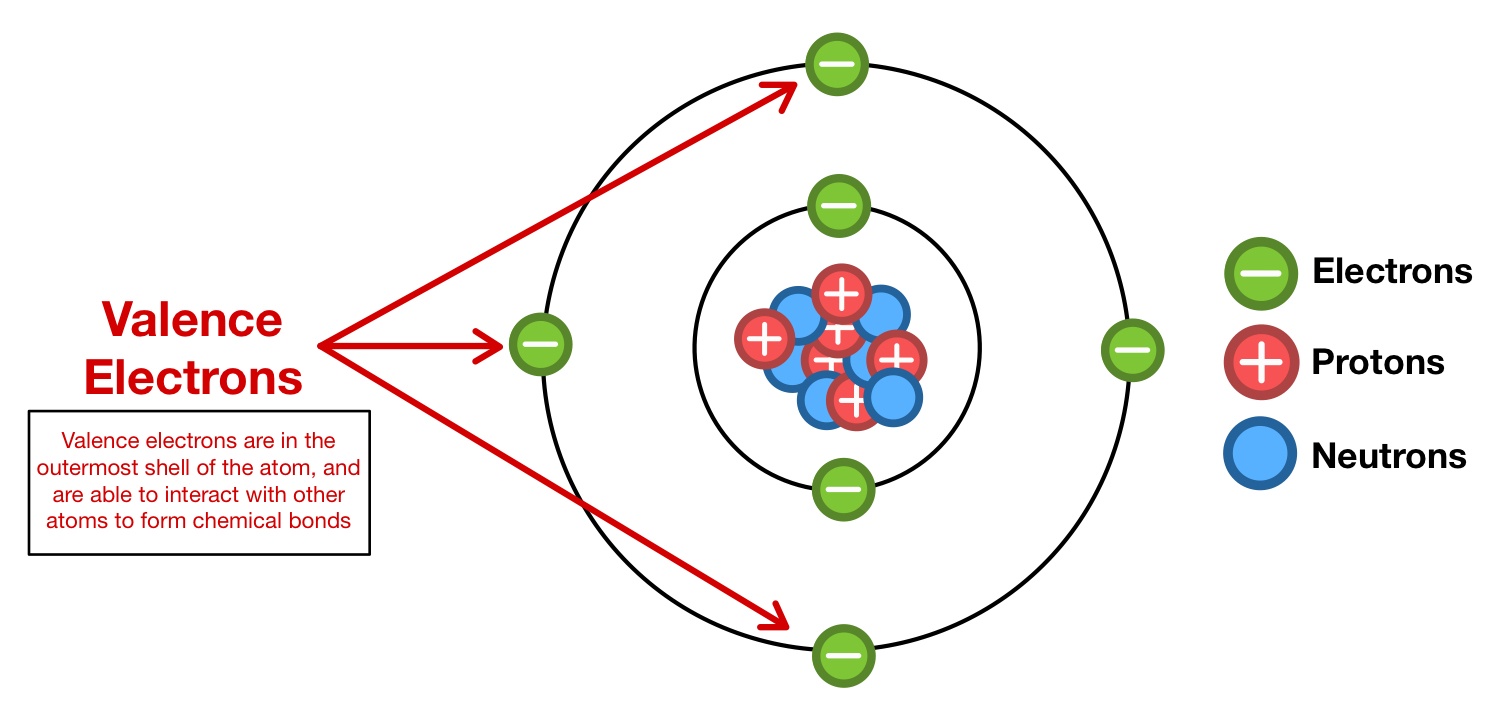
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost electron shell of an atom.
Ionic Bond
A chemical bond formed when atoms transfer electrons to one another, creating positively and negatively charged ions.
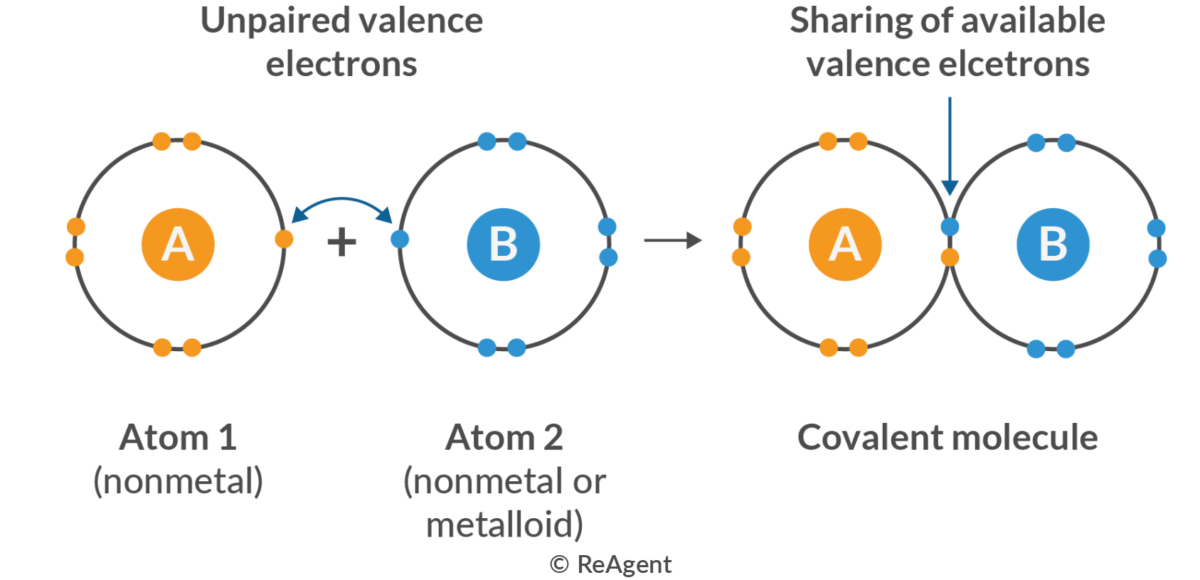
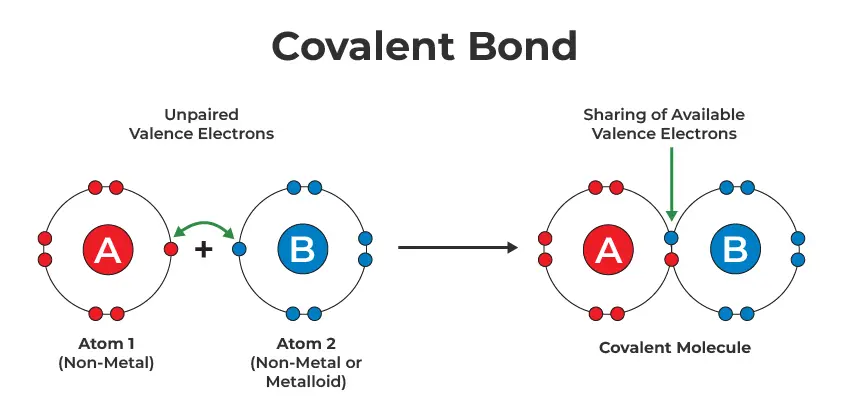
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond formed when atoms share electrons.
Ionic Compound
A compound formed by ionic bonds, generally known as a "salt." Typically consists of a metal and a nonmetal. Bonds can break (dissociate) in water.
Covalent Compound (Molecule)
A compound formed by covalent bonds. Bonds do NOT break in water; a chemical reaction is required to break them.
Chemical Reaction
A process that changes one set of chemicals into another; required to break and form covalent bonds. Ex: Photosynthesis.
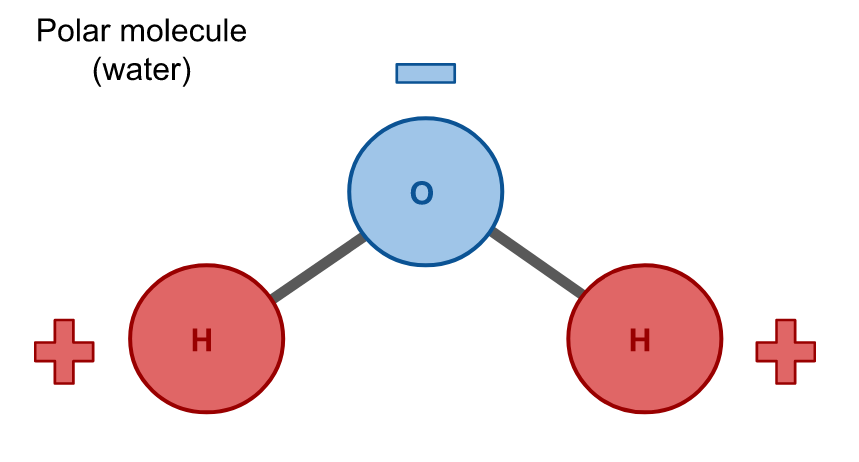
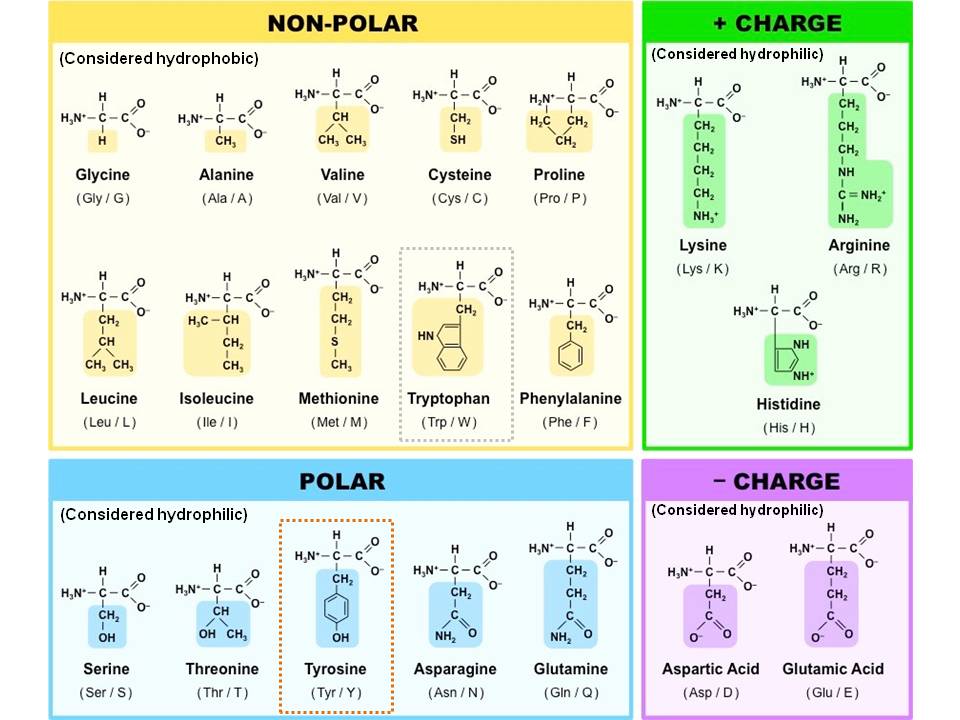
Polar Molecule
A molecule in which atoms do not share electrons equally, creating partial positive and partial negative regions. Ex: Water. Hydrophilic.
Nonpolar Molecule
A molecule in which atoms share electrons equally, with no partial charges. Ex: Fats and oils. Hydrophobic.
Hydrophilic
"Water-loving"; describes polar molecules and ions that mix or dissolve in water.
Hydrophobic
"Water-fearing"; describes nonpolar molecules that repel or do not mix with water.
Molecular Shape
The unique 3-dimensional shape of a molecule determined by its covalent bonds; key to its function and how it interacts with other molecules.
Hydrogen Bond
A weak attraction between a partially positive hydrogen atom of one molecule and a partially negative atom (N, O, or F) of another molecule. Collectively, they are strong.
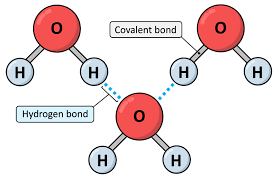
Cohesion
The ability of water molecules to cling to each other due to hydrogen bonding. Ex: Water droplets.
Adhesion
The ability of water molecules to cling to other polar surfaces due to hydrogen bonding. Ex: Water on glass.
Capillary Action
The ability of water to "climb" narrow spaces against gravity, caused by the combined effects of cohesion and adhesion. Ex: Water moving up a plant.
Surface Tension
A force at the surface of water caused by cohesion, making the surface resistant to breaking. Ex: Insects walking on water.
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of heat a substance must absorb to raise its temperature. It absorbs a lot of heat without a large temperature change.
Heat of Vaporization
The amount of thermal energy required for a liquid to evaporate.
Evaporative Cooling
The process where a surface cools down as liquid water on it evaporates, because the body's heat is used to break hydrogen bonds and vaporize the water. Ex: Sweating.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture made up of a solute dissolved in a solvent.
Solute
The substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
The substance that does the dissolving in a solution. Water is the "universal solvent."
Acidic Solution
A solution in which the concentration of H⁺ ions is greater than the concentration of OH⁻ ions. pH is less than 7.
Basic (Alkaline) Solution
A solution in which the concentration of H⁺ ions is less than the concentration of OH⁻ ions. pH is greater than 7.
Neutral Solution
A solution in which the concentration of H⁺ ions equals the concentration of OH⁻ ions. pH equals 7. Ex: Pure water.
pH Scale
A scale from 0 to 14 that measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution.
Organic Chemistry
The study of carbon-containing compounds.
Organic Molecule
A carbon-containing molecule, typically associated with living things.
Hydrocarbon
A molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen atoms; nonpolar (hydrophobic).
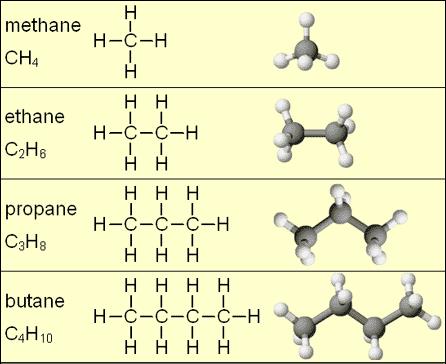
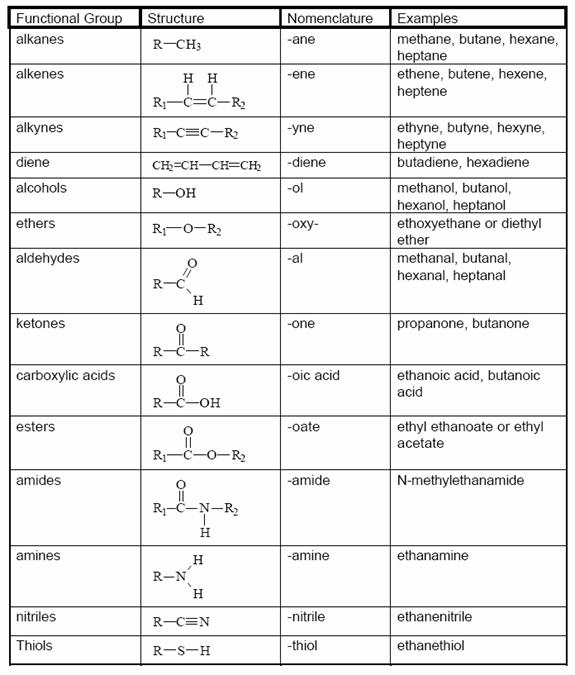
Functional Group
A specific cluster of atoms attached to a carbon skeleton that gives organic molecules their particular chemical properties and reactivity. Ex: -OH (hydroxyl).
Monomer
A small molecular subunit that serves as a building block for a polymer. Ex: A single glucose molecule.
Polymer
A large molecule composed of many repeating monomers bonded together. Ex: Starch (a polymer of glucose).
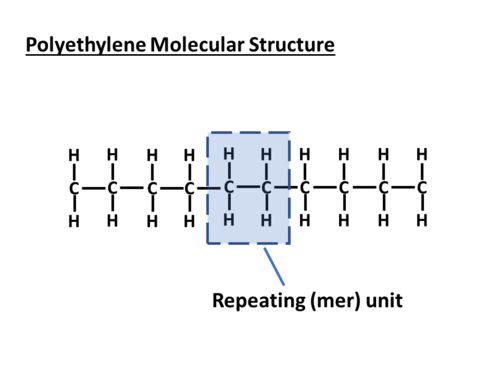
Macromolecule
A giant molecule formed by the bonding of smaller molecules; refers to large polymers. Ex: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
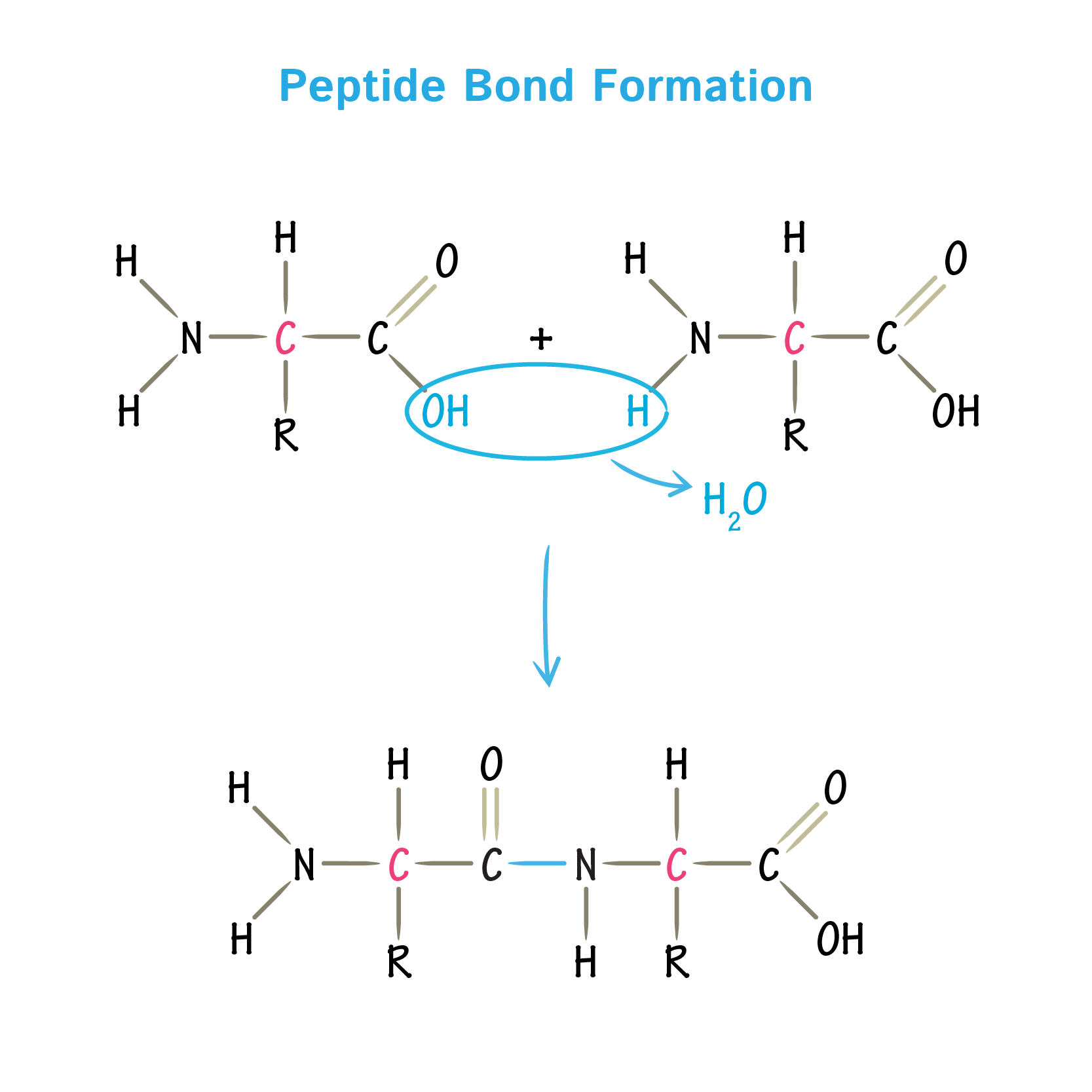
Dehydration Reaction (Synthesis)
A chemical reaction that links monomers together to form a polymer by removing a water molecule to form a new covalent bond.
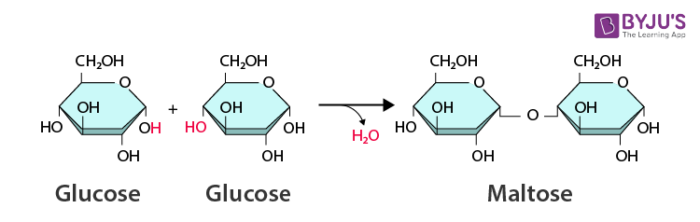
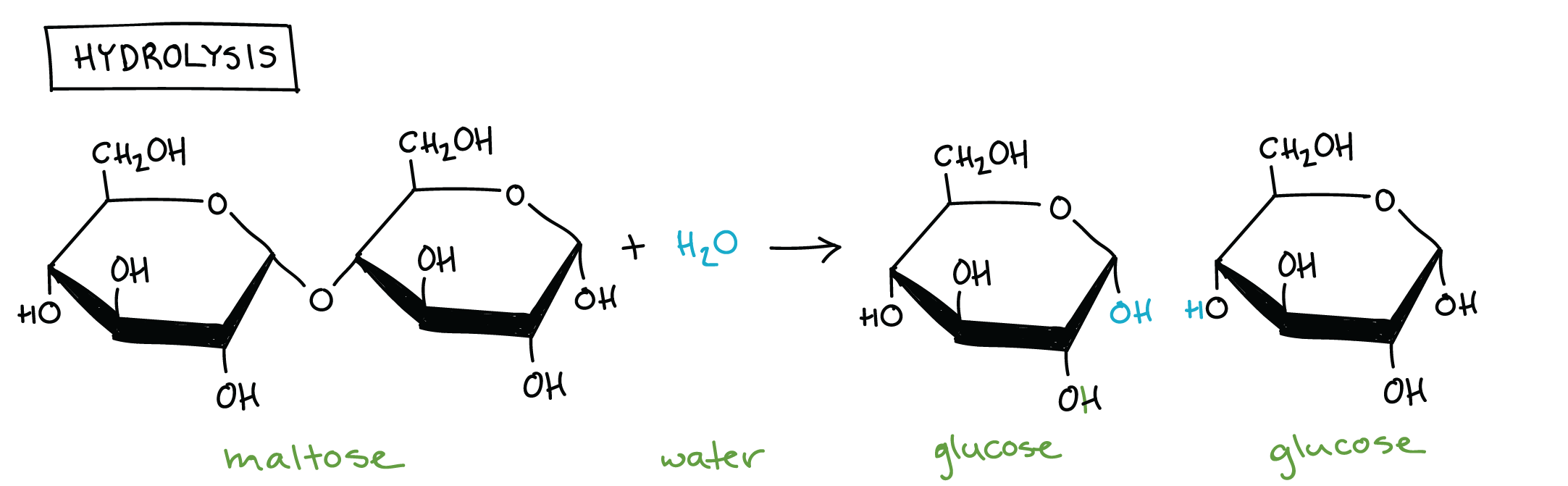
Hydrolysis Reaction
A chemical reaction that breaks the covalent bonds between monomers in a polymer by adding a water molecule.
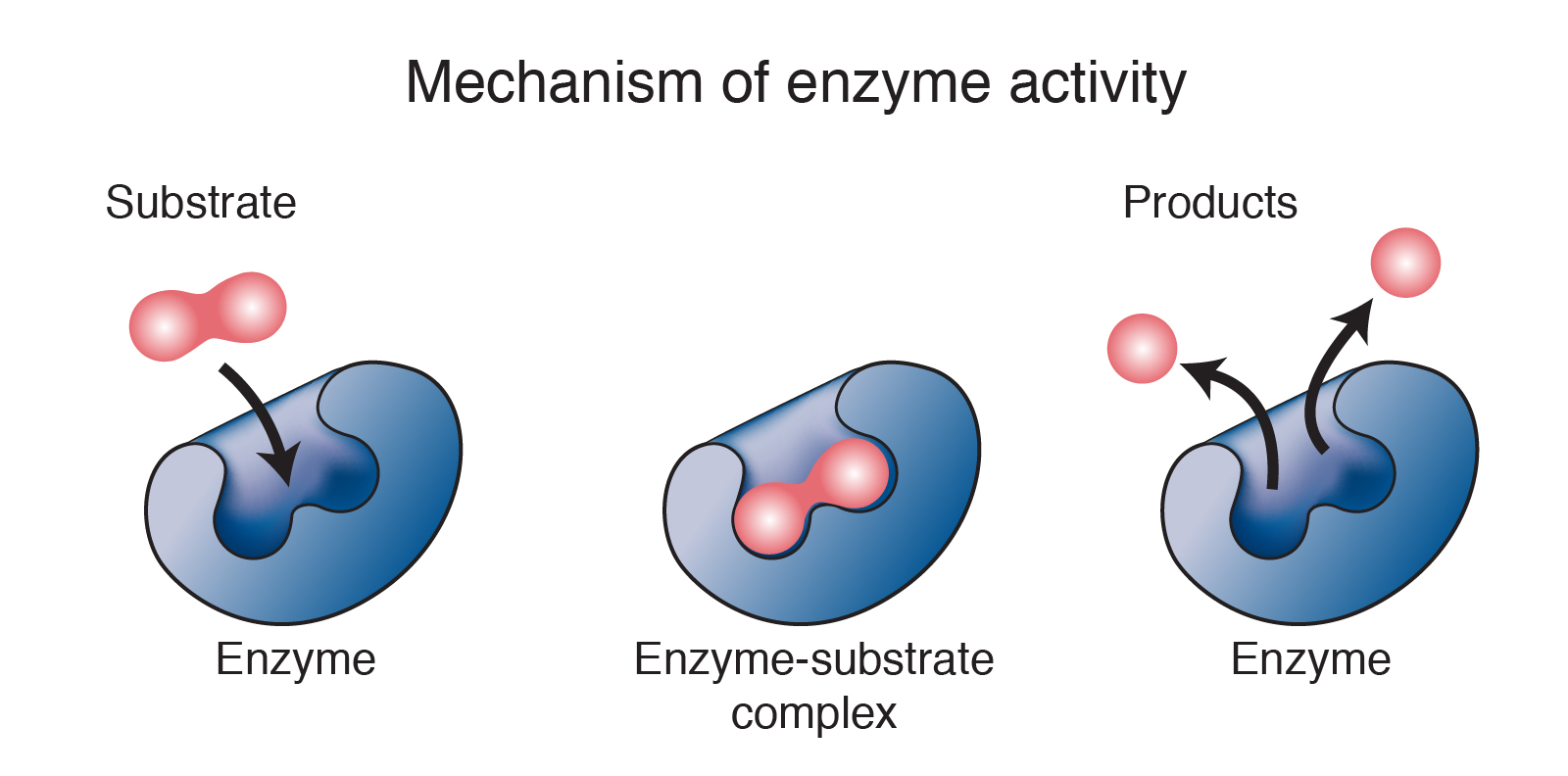
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst, speeding up metabolic reactions by lowering the activation energy.
Carbohydrate
A class of macromolecules whose functions include short-term energy storage and providing building material. Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
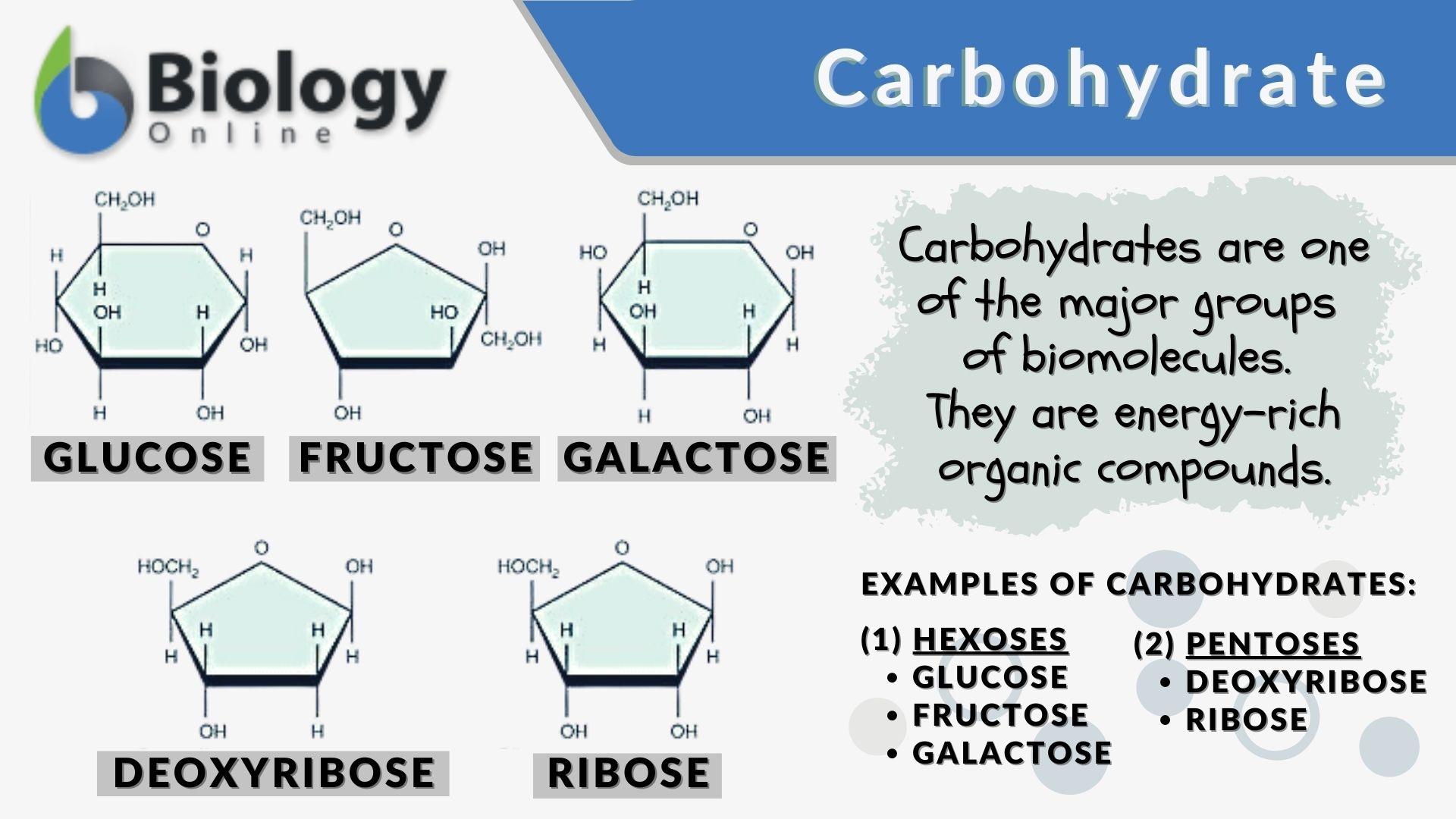
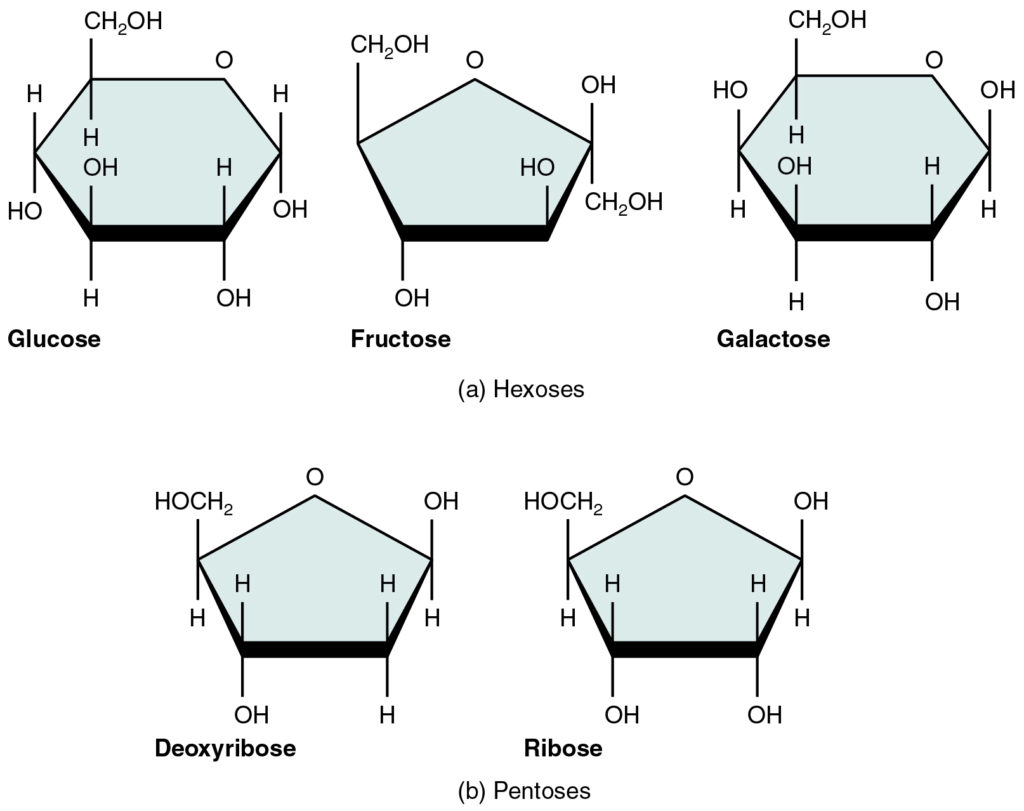
Monosaccharide
The monomer of a carbohydrate; a simple sugar. Ex: Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and Deoxyribose (C₅H₁₀O₅).
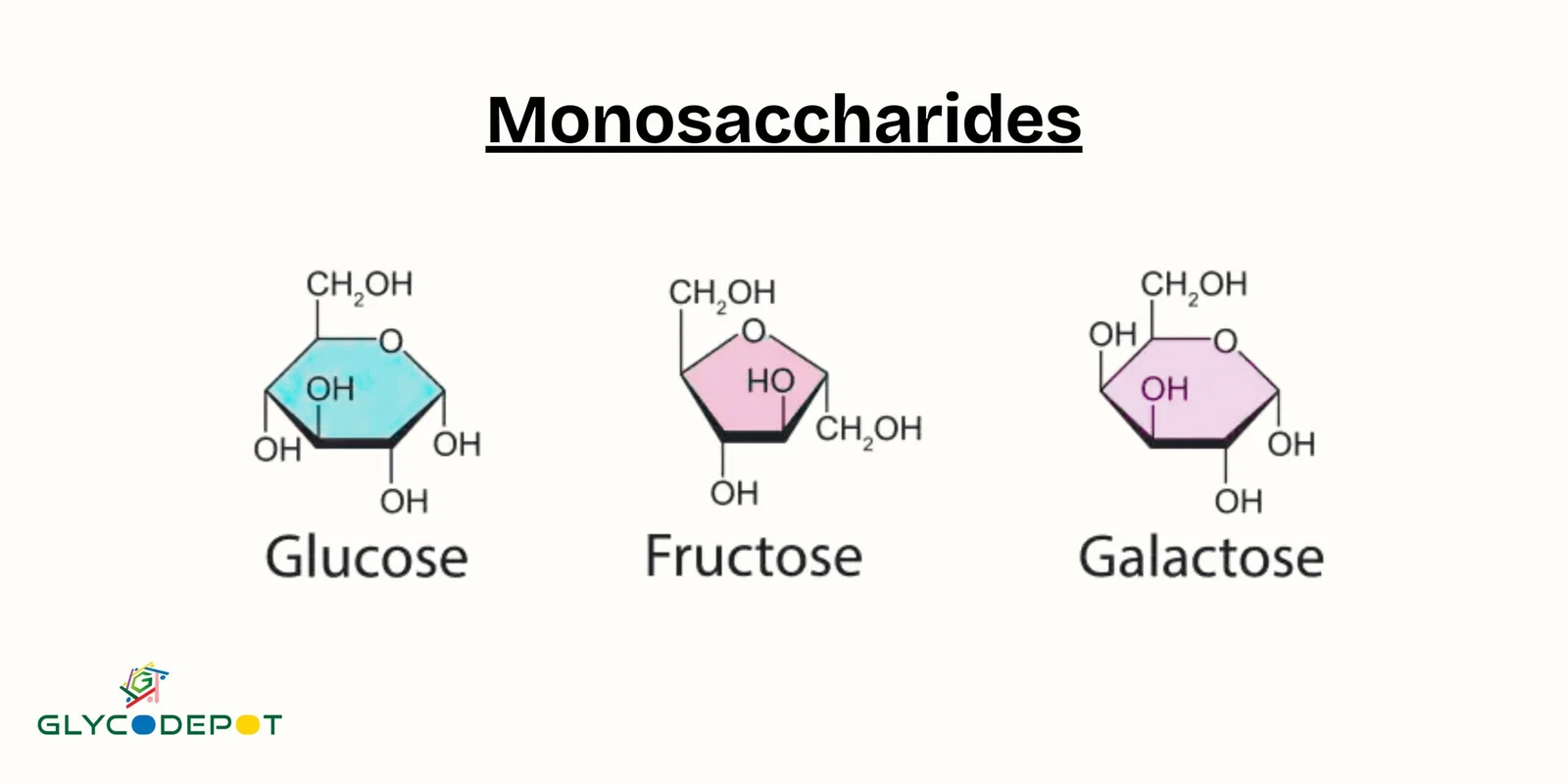
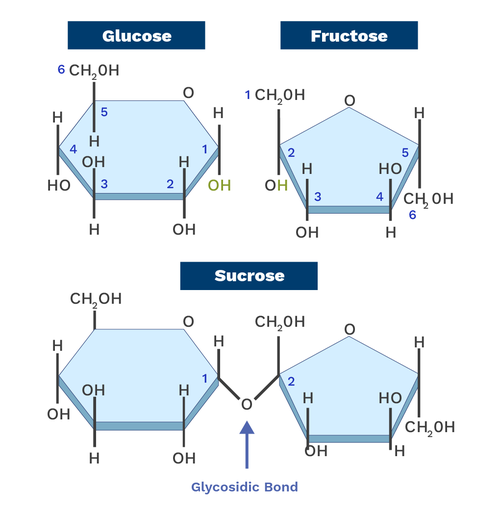
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharides bonded together by a glycosidic linkage formed via dehydration synthesis. Ex: Sucrose, Lactose.
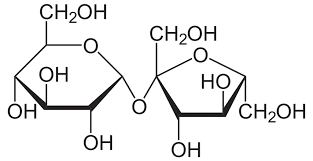
Glycosidic Linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides.
Polysaccharide
A polymer of many monosaccharides.
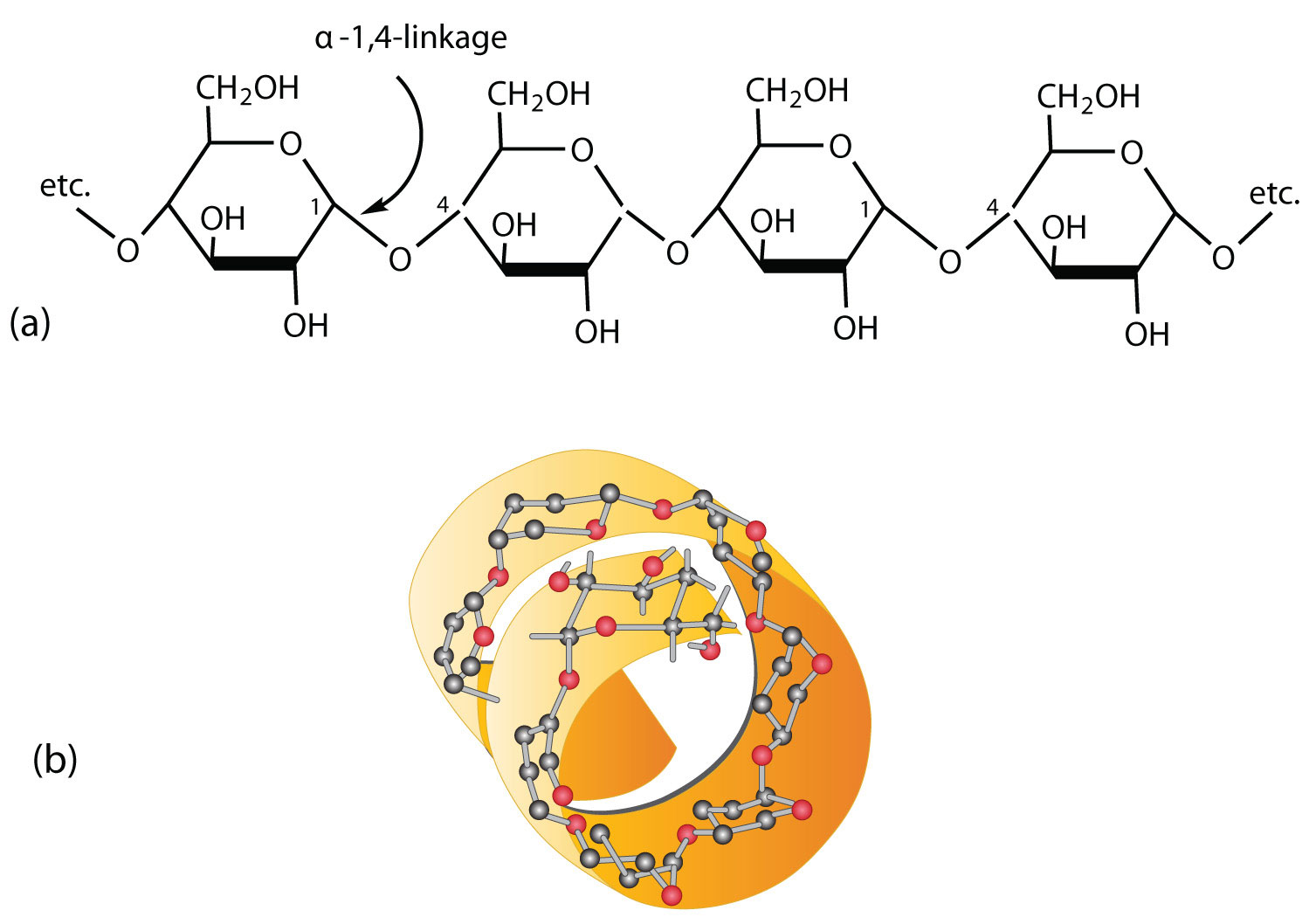
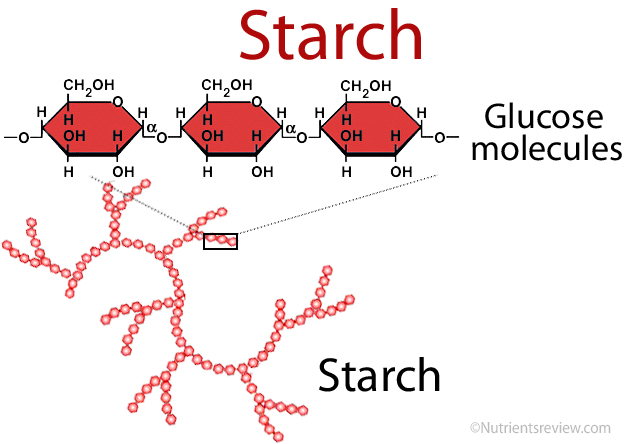
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants, made of glucose monomers in an alpha (α) configuration. Helical and branched.
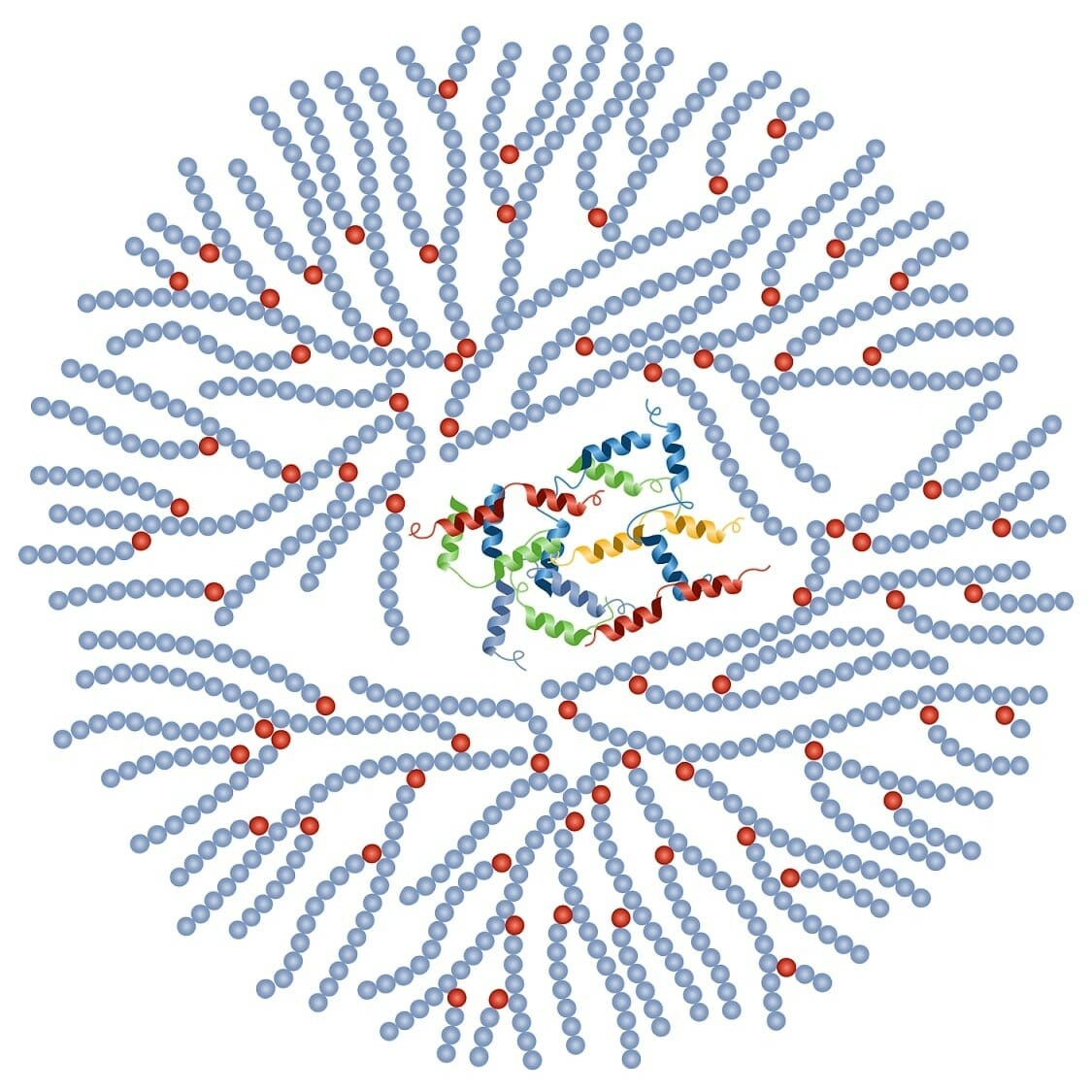
Glycogen
A storage polysaccharide in animals, made of glucose monomers. Stored in liver and muscle cells.
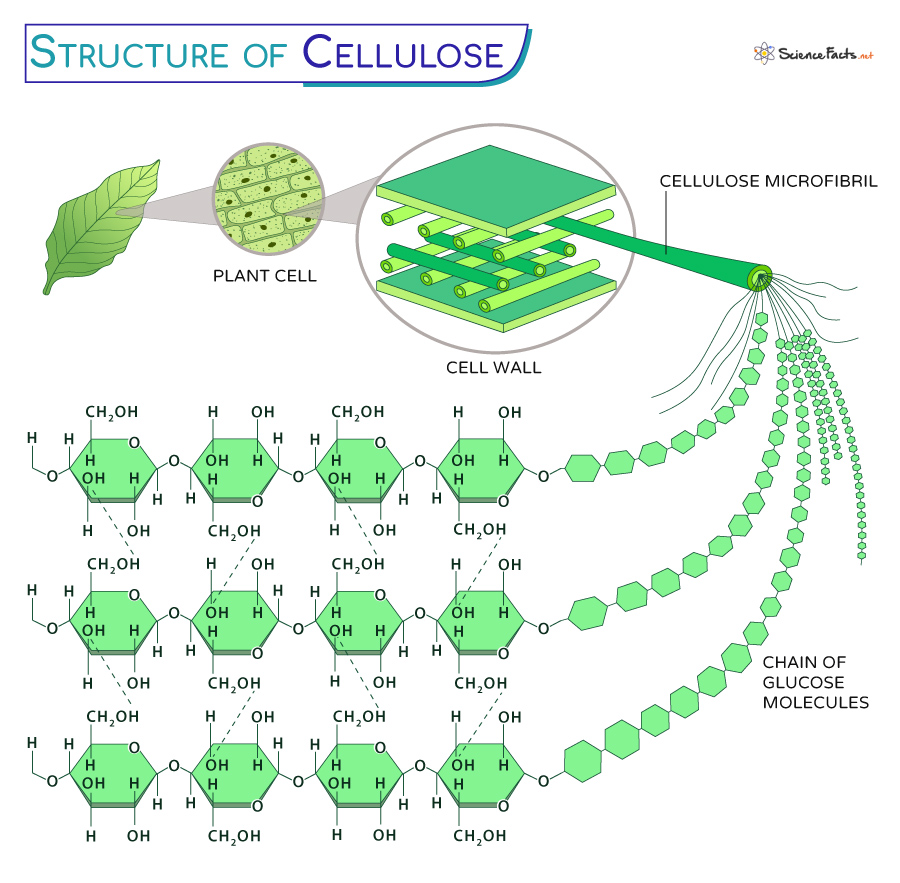
Cellulose
A structural polysaccharide that is a major component of the tough walls that enclose plant cells. Made of glucose monomers in a beta (β) configuration, forming straight, strong microfibrils.
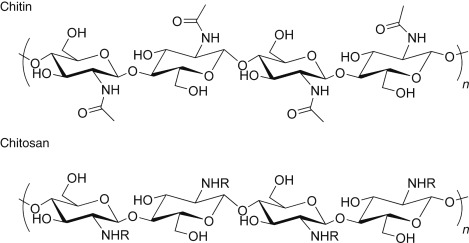
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide used by insects and crustaceans to build their exoskeletons and by fungi to build their cell walls.
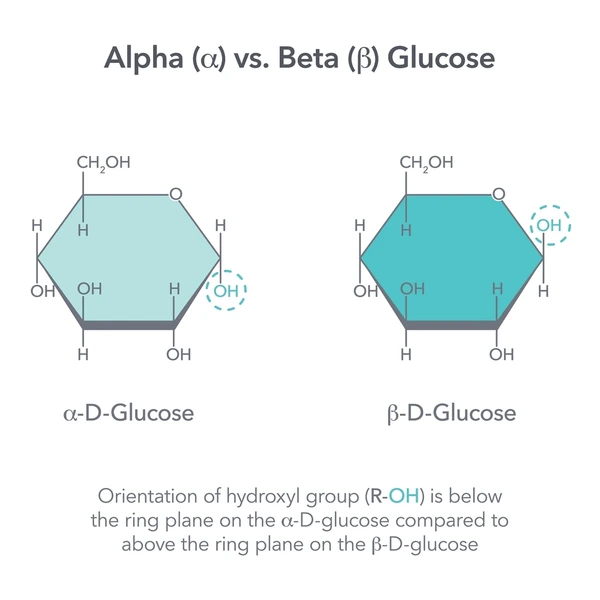
Alpha (α) Glucose
The ring form of glucose where the hydroxyl group on carbon 1 is below the ring plane; used to build starch and glycogen.
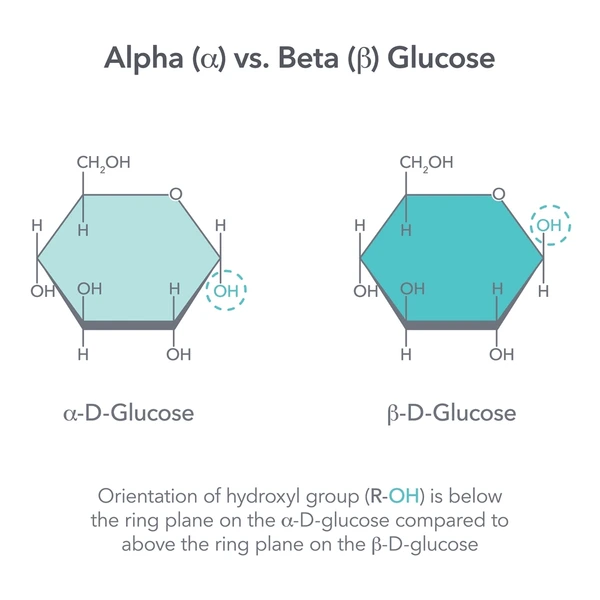
Beta (β) Glucose
The ring form of glucose where the hydroxyl group on carbon 1 is above the ring plane; used to build cellulose.
Protein
A class of macromolecules with a huge diversity of structures and functions, including defense, transport, communication, movement, and structural support. Composed of C, H, O, N, and S.
Amino Acid
The monomer of a protein. There are 20 different kinds, each with an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a unique R group, all bonded to a central carbon.
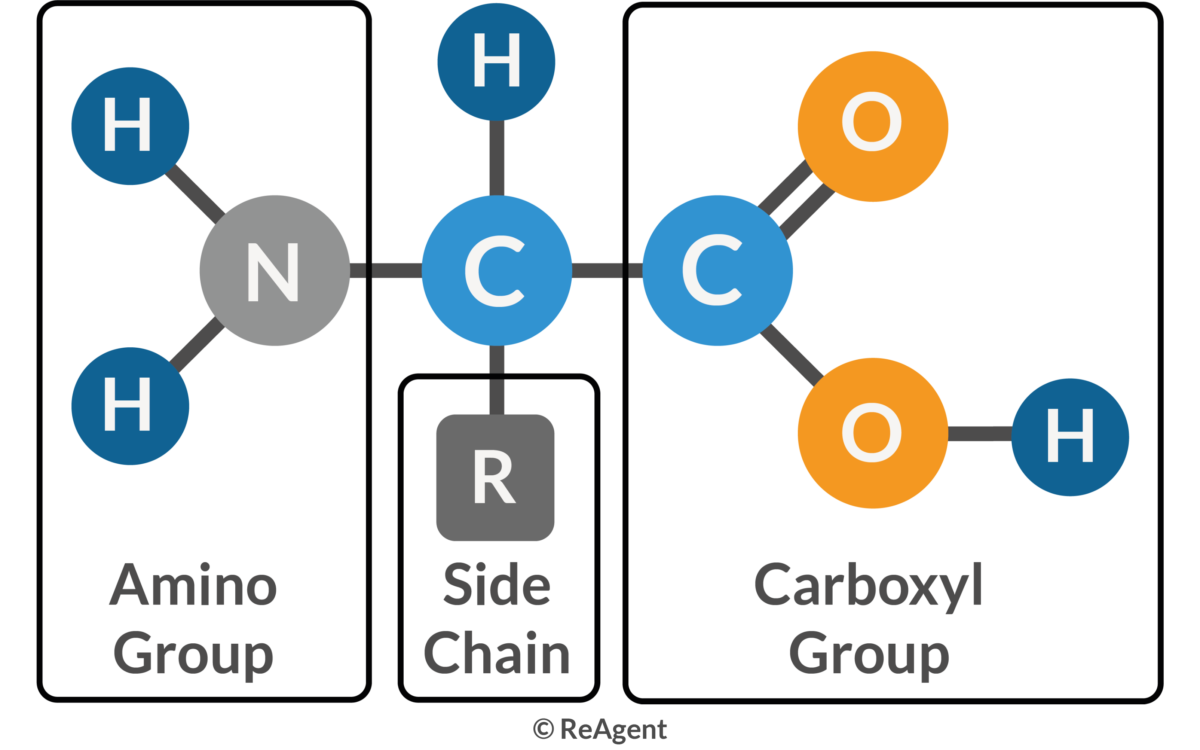
Amino Group
A functional group (-NH₂) found in amino acids.
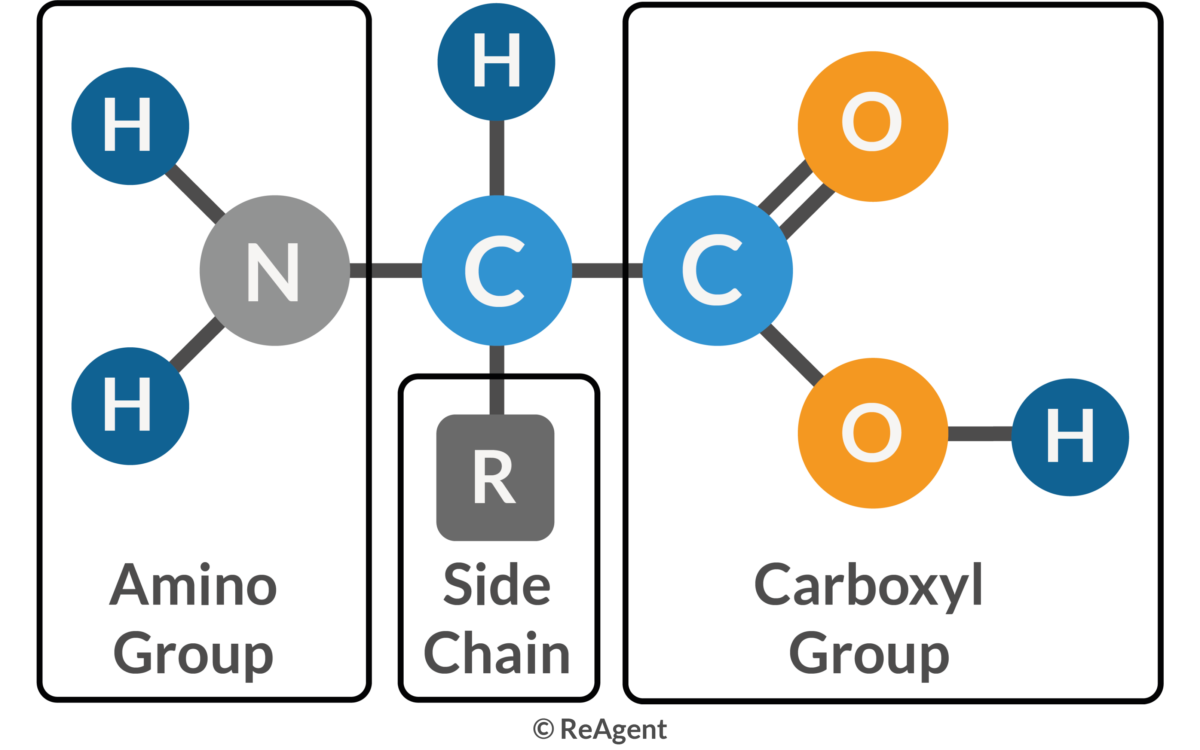
Carboxyl Group
A functional group (-COOH) found in amino acids.
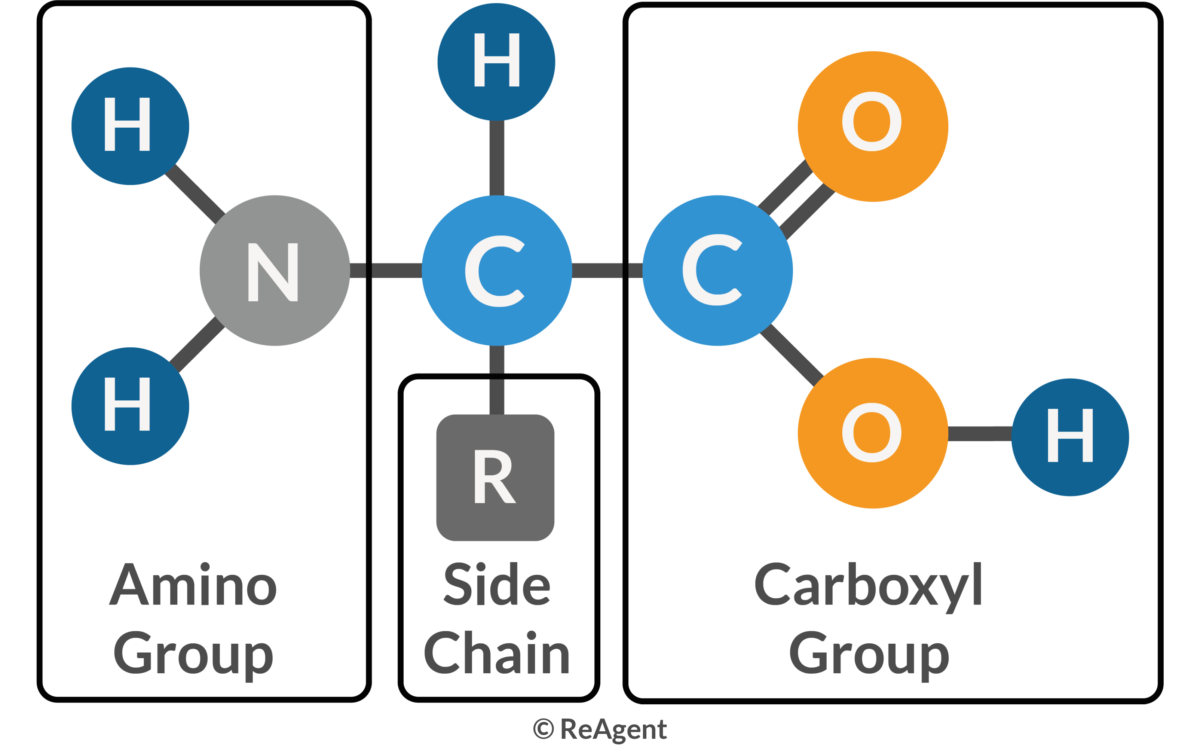
R Group (Side Chain)
The variable side chain of an amino acid that determines its chemical properties (hydrophobic, hydrophilic, ionic).
Peptide Bond
The covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, formed by a dehydration reaction.
Polypeptide
A polymer of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Has an amino (N) terminus and a carboxyl (C) terminus.
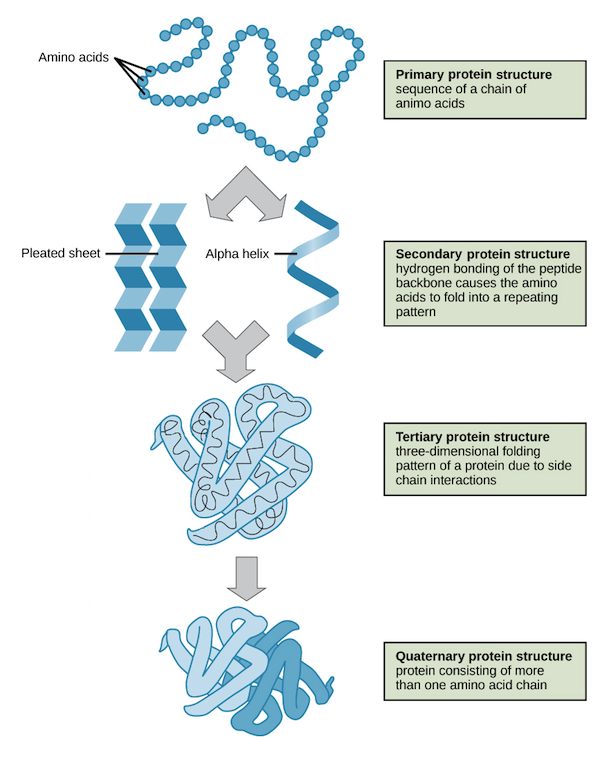
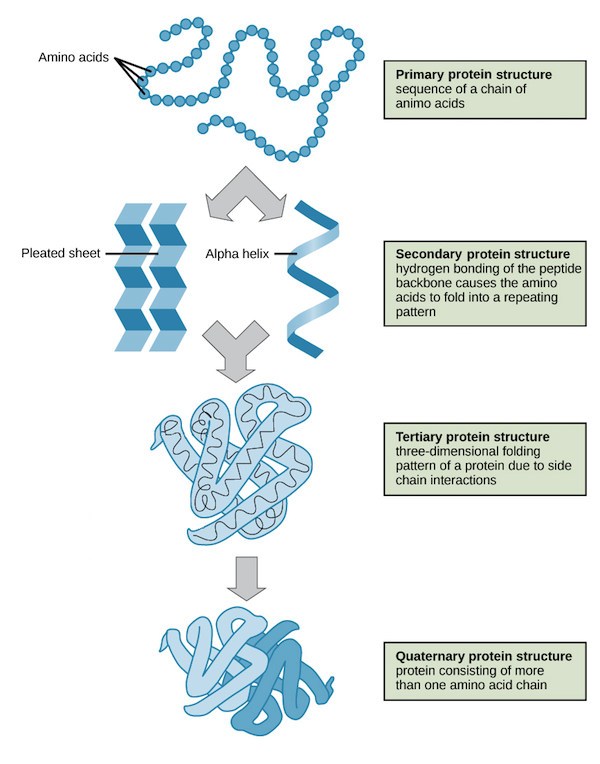
Primary Structure
The first level of protein structure; the linear, specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
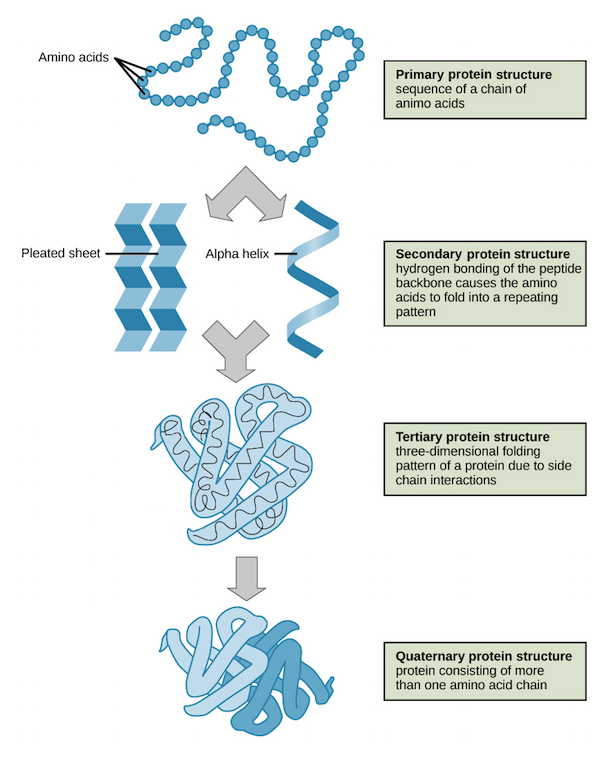
Secondary Structure
The second level of protein structure; local patterns of coiling (alpha helices) or folding (beta pleated sheets) stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
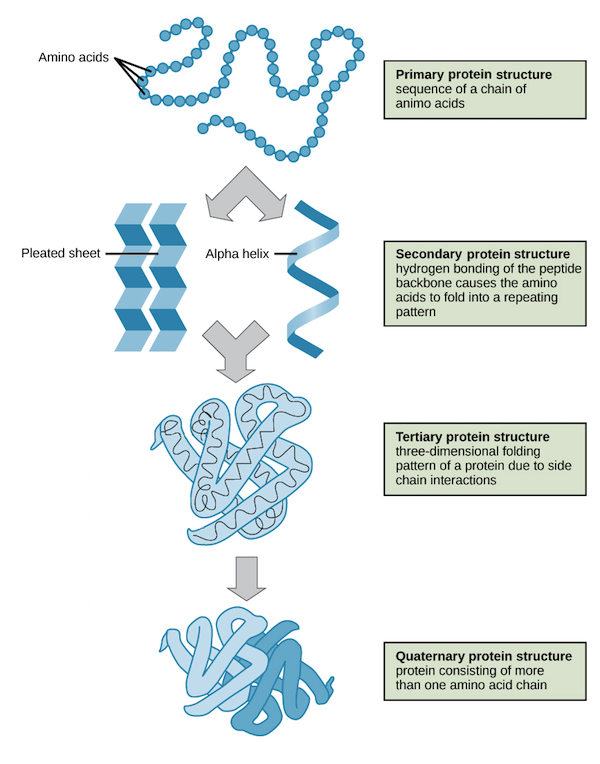
Tertiary Structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide, stabilized by interactions between R groups (hydrophobic, H-bonding, ionic, disulfide bridges).
Disulfide Bridge
A strong covalent bond between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids that stabilizes a protein's tertiary structure.
Quaternary Structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the association of two or more folded polypeptide subunits to form a single functional protein. Ex: Hemoglobin.
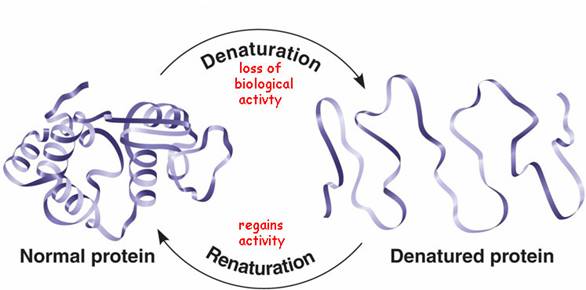
Denaturation
The loss of a protein's native, functional structure (secondary, tertiary, quaternary) due to the disruption of bonds by changes in pH, salt, temperature, etc. The protein becomes biologically inactive.
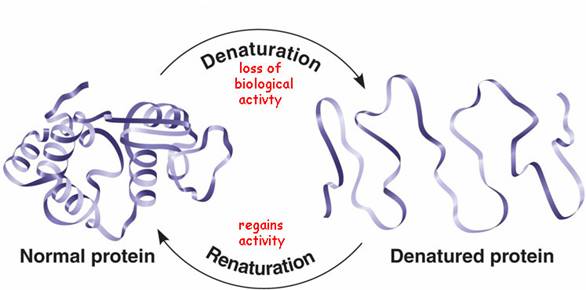
Renaturation
The process by which a denatured protein returns to its functional shape when environmental conditions return to normal.
Enzymatic Protein
A protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions within cells.
Transport Protein
A protein embedded in the cell membrane that controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell.
Contractile/Motor Protein
Proteins responsible for movement. Motor proteins move materials inside cells; contractile proteins (like in muscles) are responsible for muscle contraction.
Receptor Protein
A protein that binds to a specific chemical signal (like a hormone) and initiates a response in the cell.
Hormonal/Signaling Protein
Proteins that are released as hormones to regulate the activity of an organism by binding to receptors on cells.
Defense Protein
Proteins that protect an organism from infection, such as antibodies in the immune system.
Structural Protein
Long, fibrous proteins that provide physical support. Ex: Keratin (hair, nails), Collagen (connective tissue), Cytoskeleton proteins.
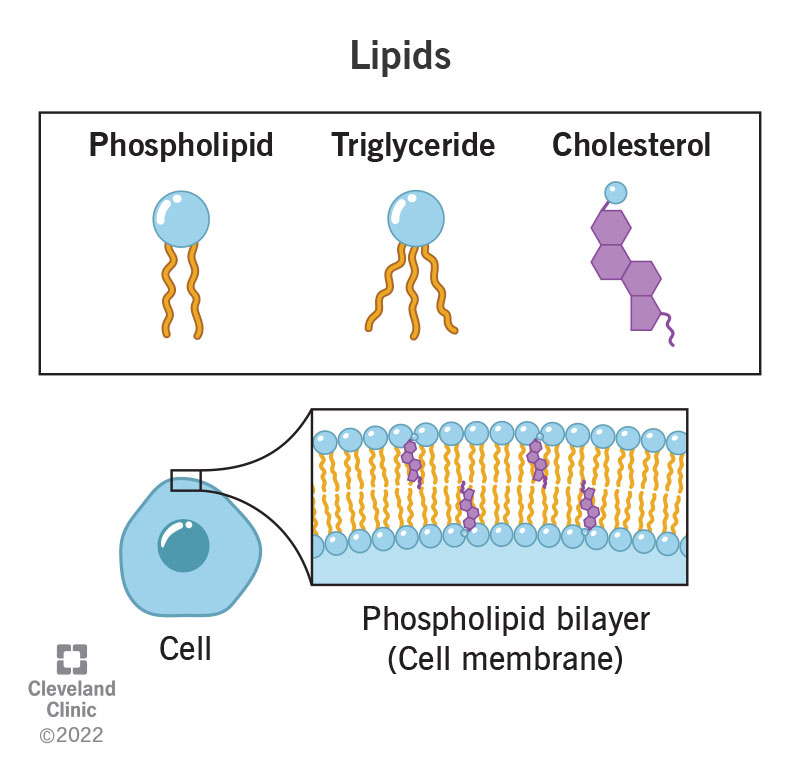
Lipid
A diverse group of hydrophobic macromolecules, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Composed mainly of C and H, with some O.
Triglyceride
A type of lipid; a fat composed of one glycerol molecule bonded to three fatty acid molecules via ester linkages.
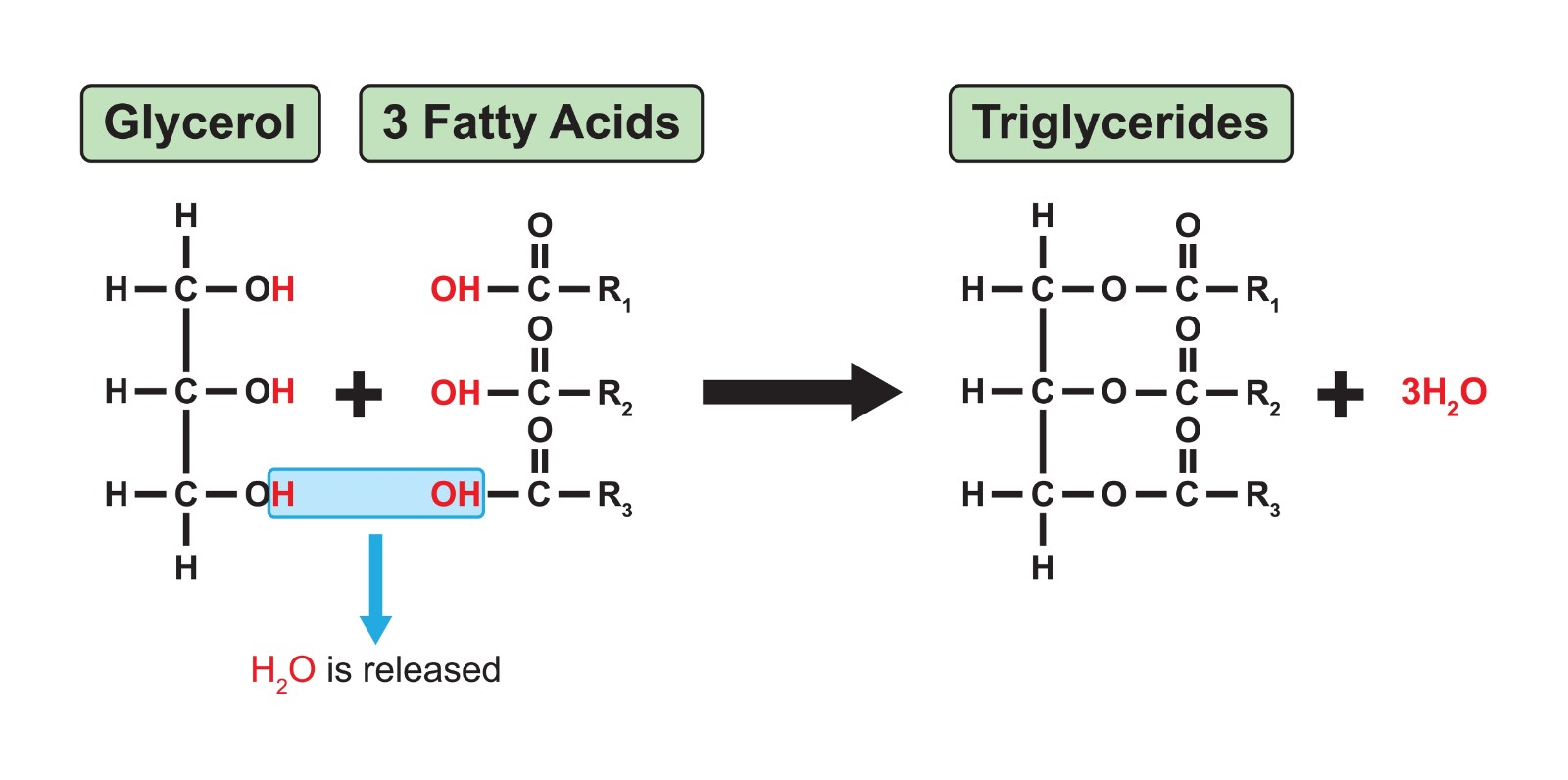
Glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol that is a component of fats and phospholipids.
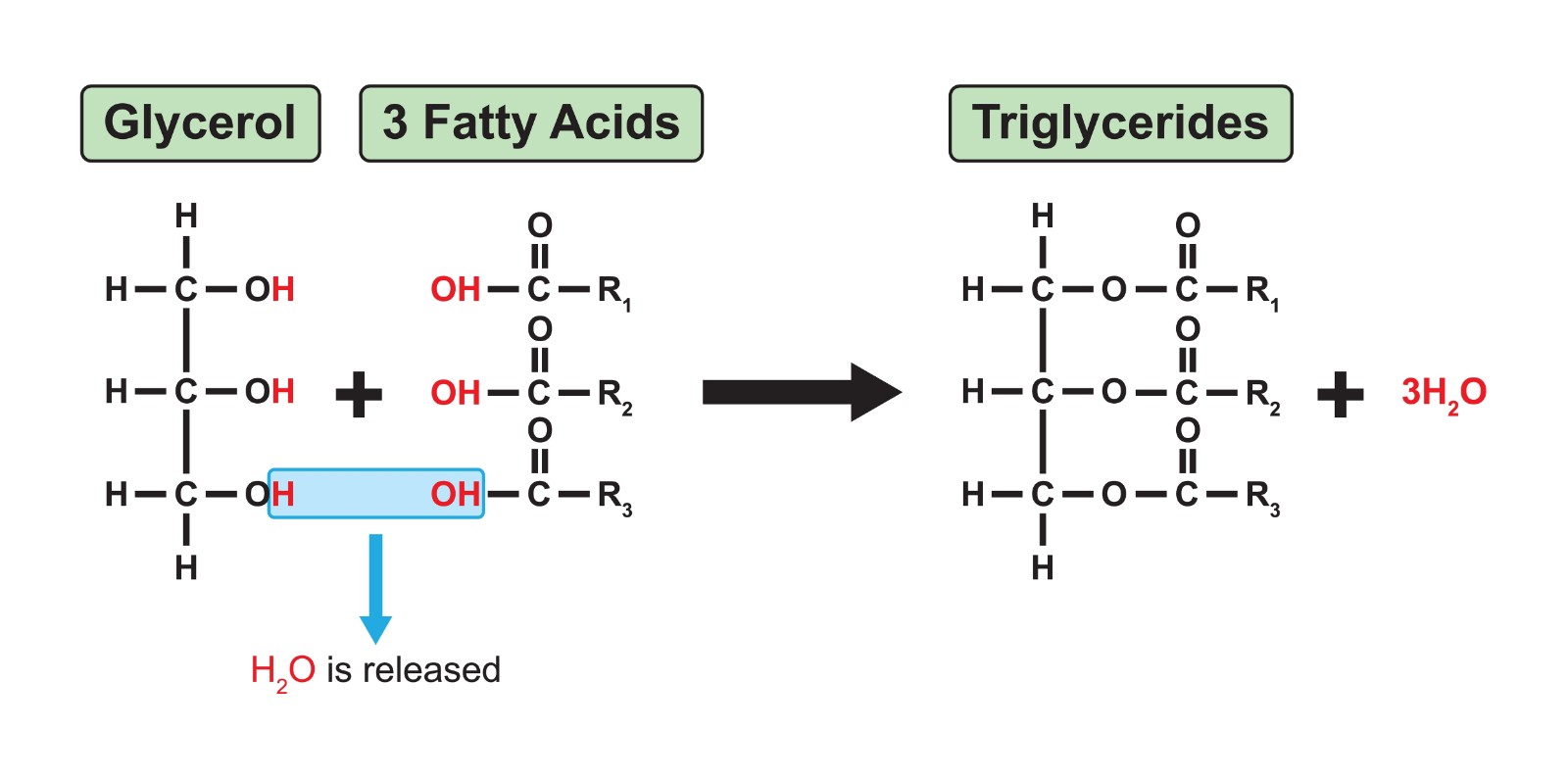
Fatty Acid
A long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end; a component of fats and phospholipids.
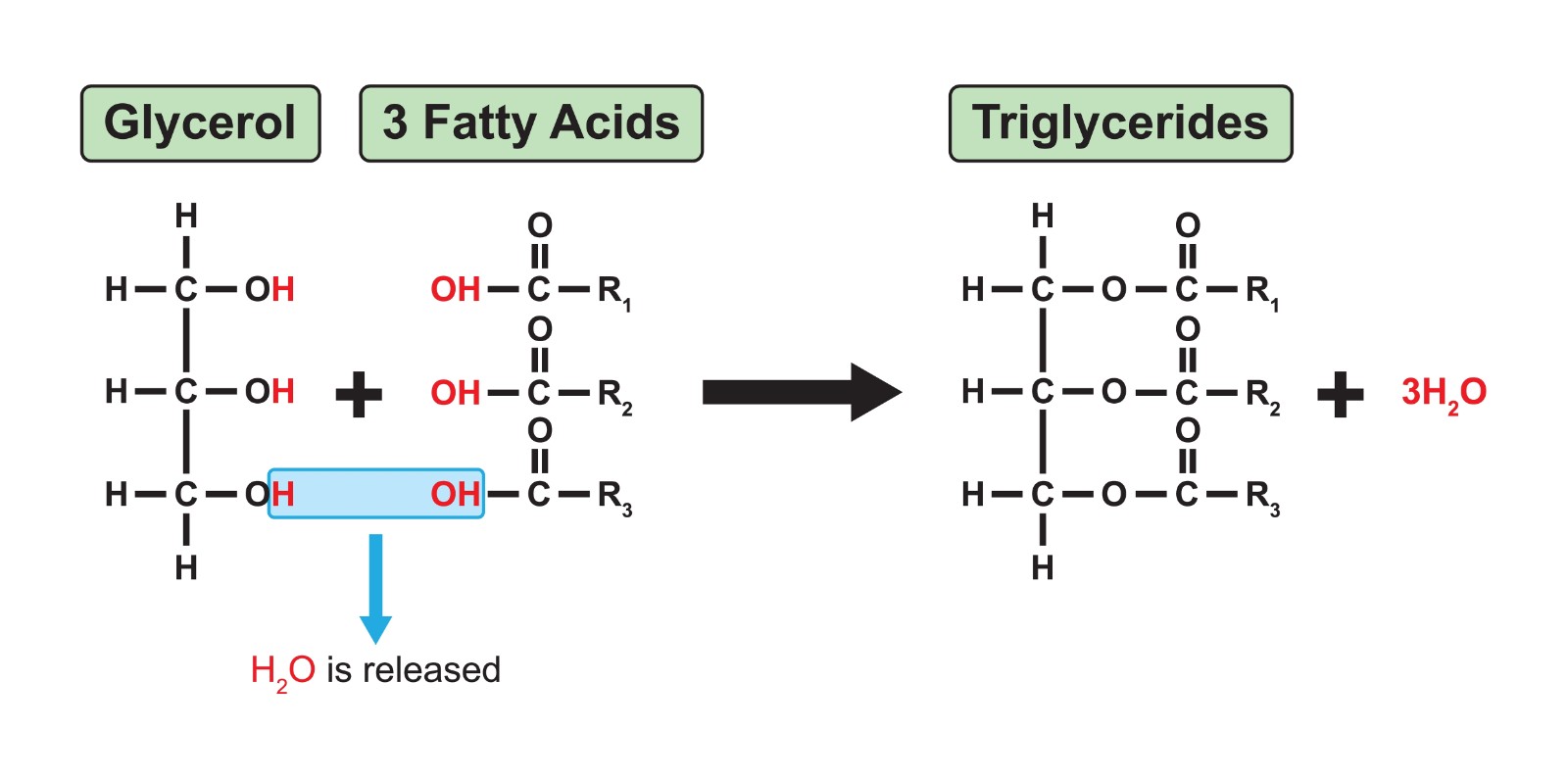
Ester Linkage
A covalent bond formed between a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group, such as the bond between glycerol and a fatty acid in a fat.
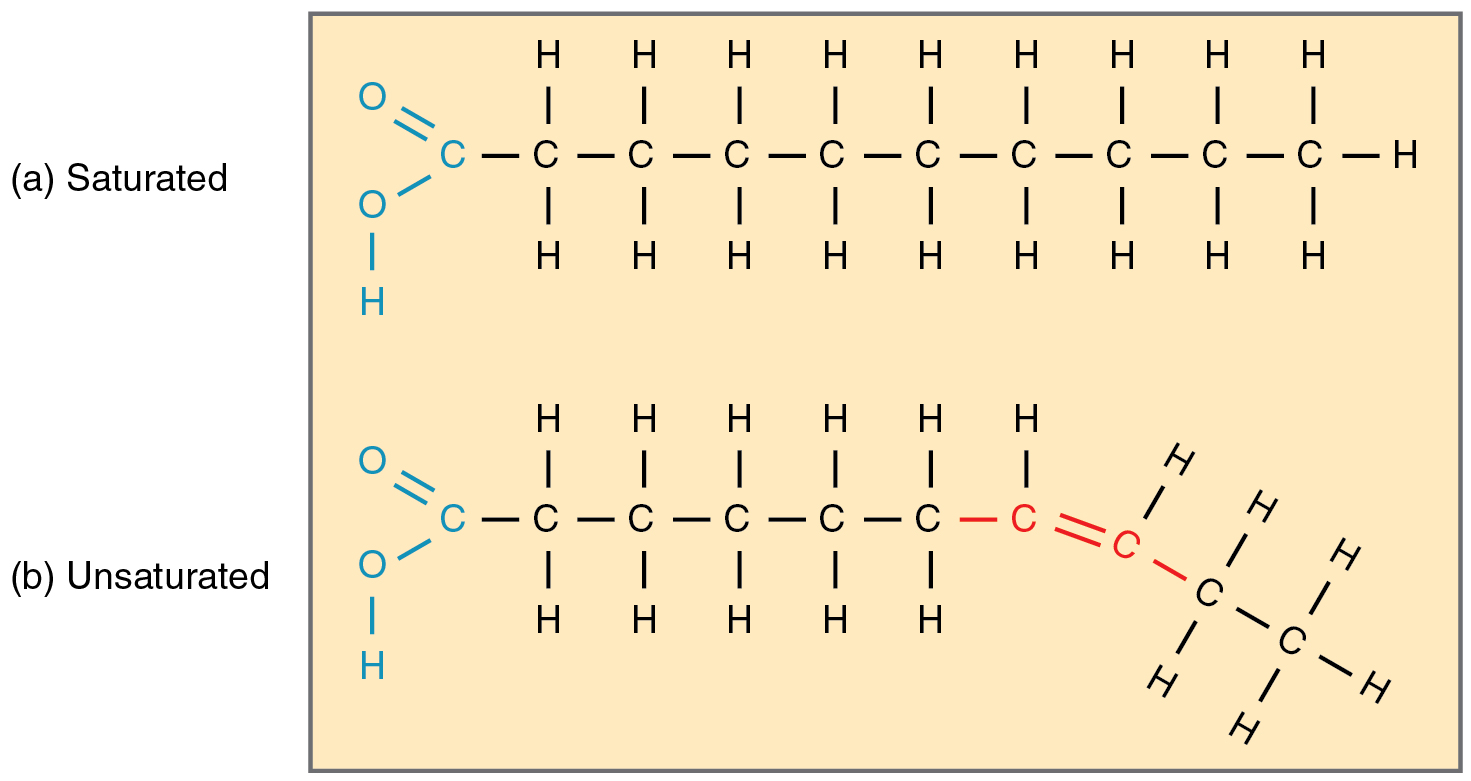
Saturated Fat
A fat in which the fatty acid chains have no double bonds between carbon atoms, making them straight and allowing them to pack tightly. Solid at room temperature. Ex: Animal fat.
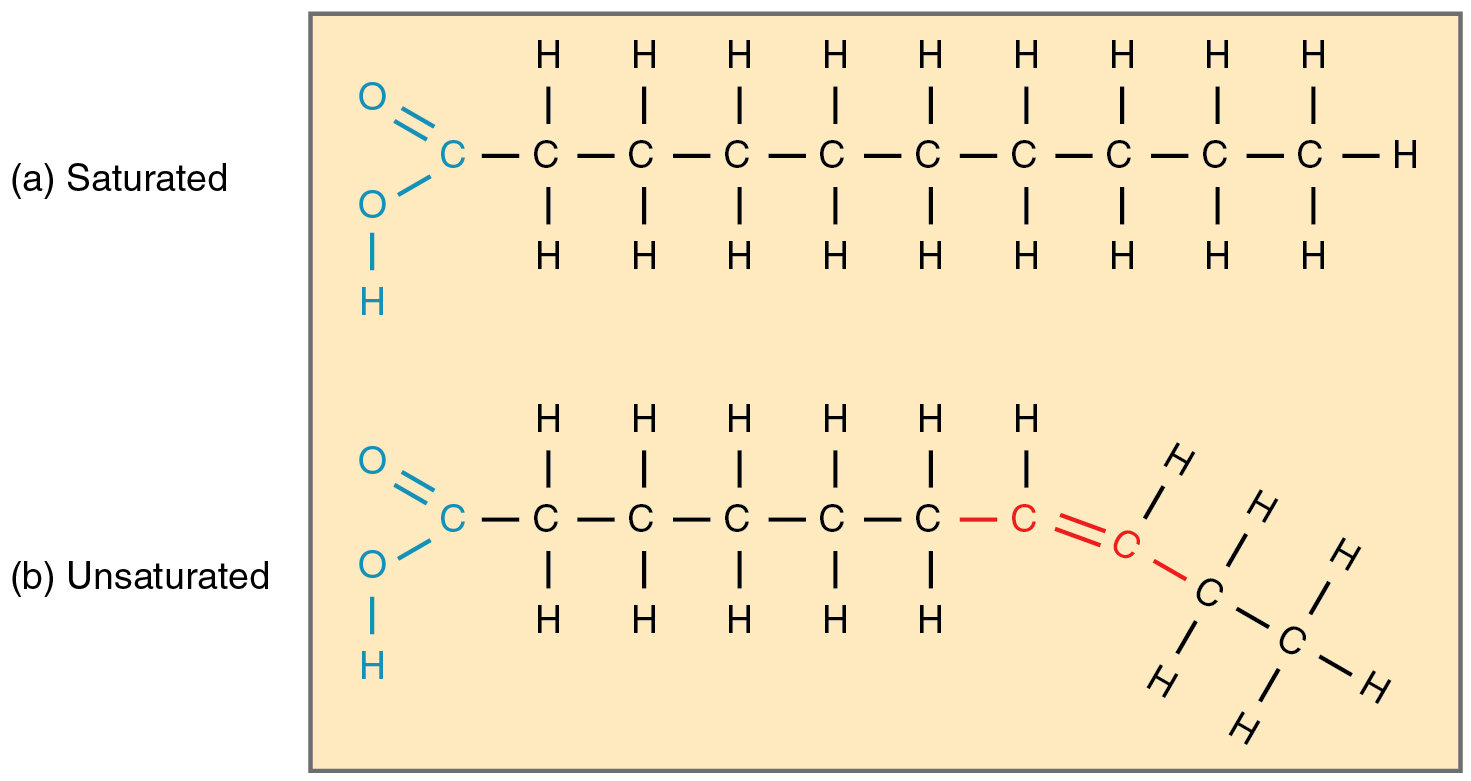
Unsaturated Fat
A fat in which the fatty acid chains have one or more double bonds, putting "kinks" in the chain and preventing tight packing. Liquid (oil) at room temperature. Ex: Vegetable oil.
Phospholipid
A lipid made of a glycerol linked to two fatty acids and a modified phosphate group. The main component of all cell membranes.
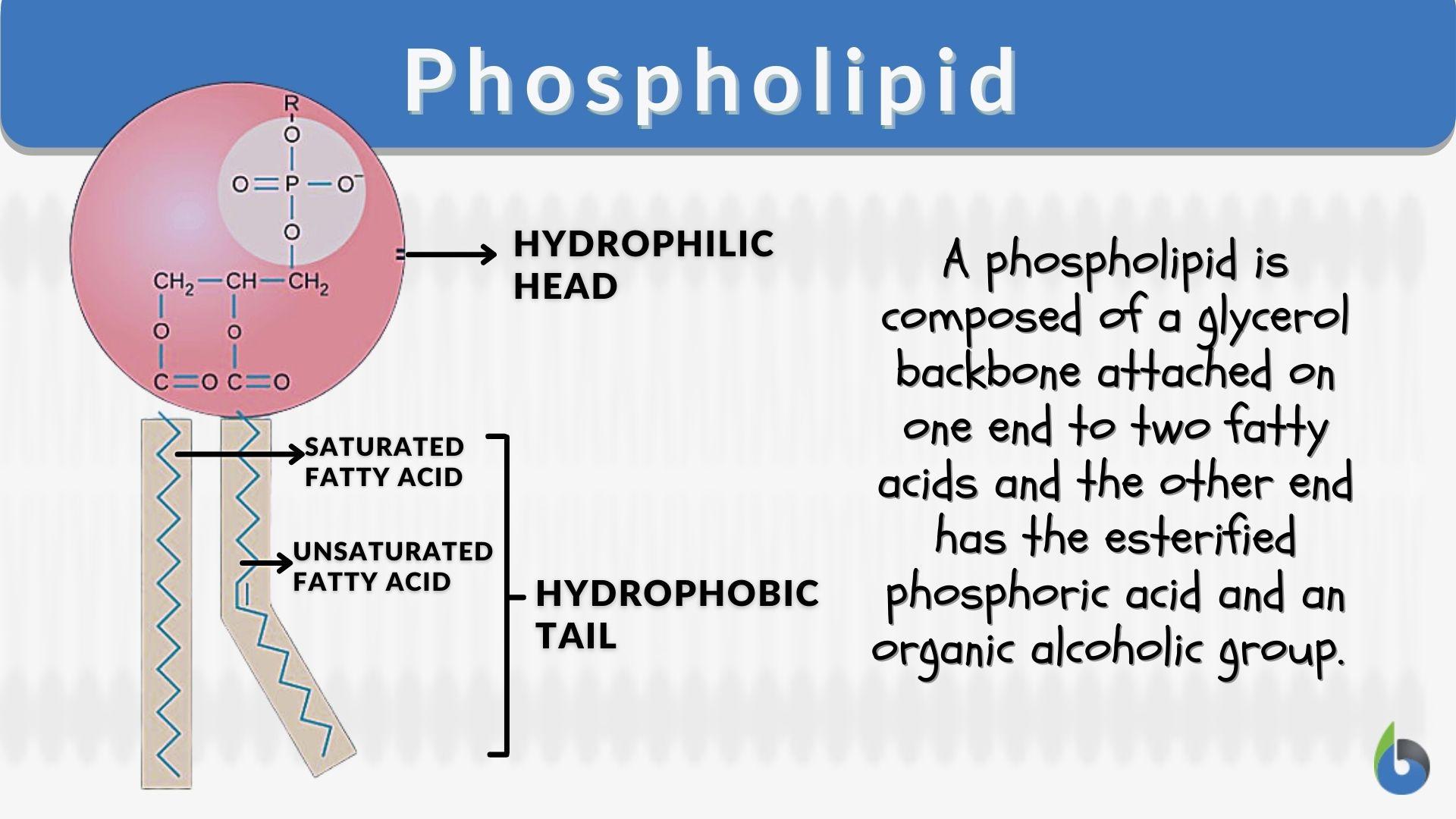
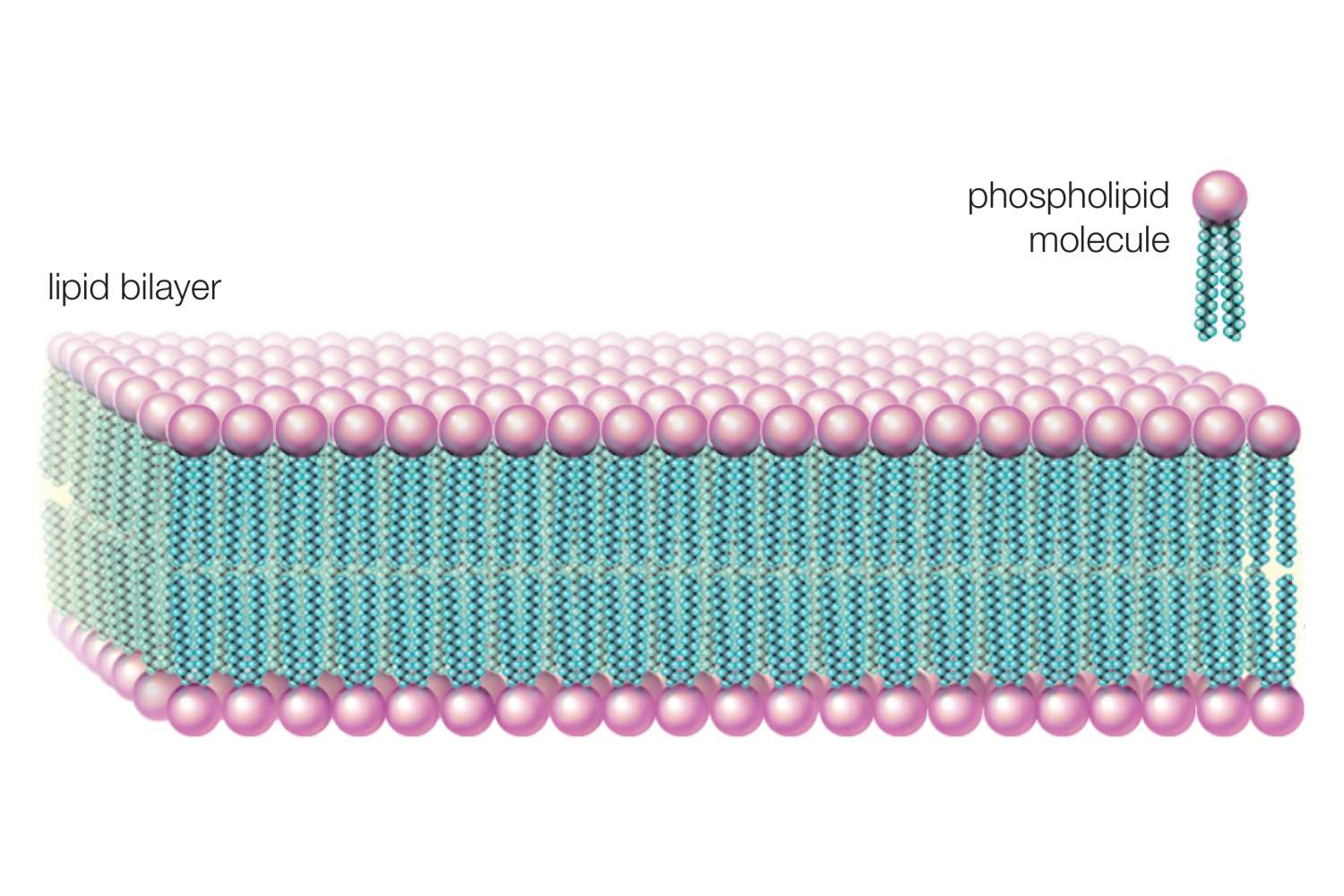
Lipid Bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that forms the foundation of all cellular membranes. Hydrophilic heads face outward, hydrophobic tails face inward.
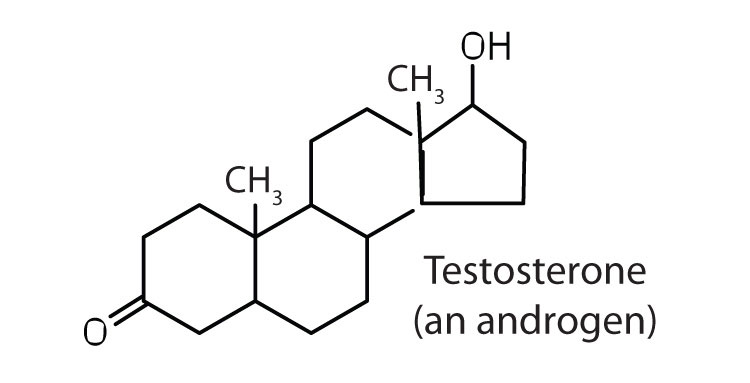
Steroid
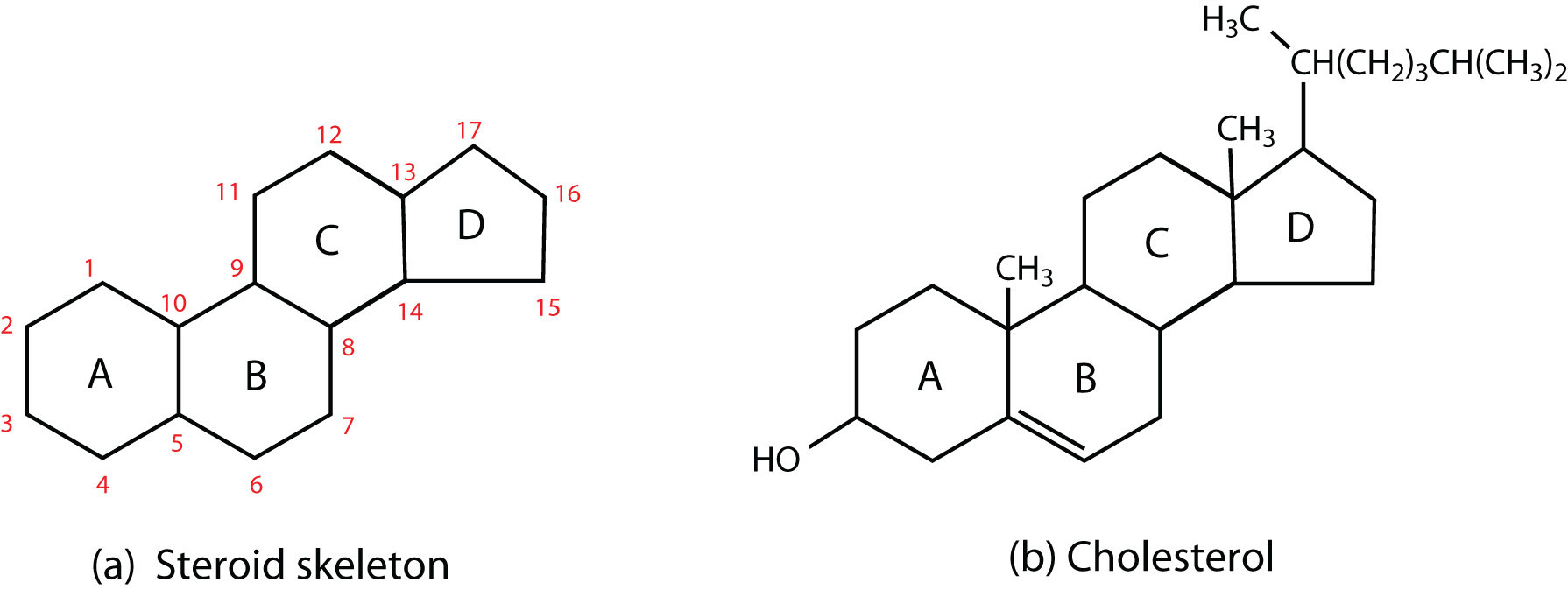
A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings. Ex: Cholesterol (in cell membranes) and sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen).
Cholesterol
A steroid that is an important component of animal cell membranes.
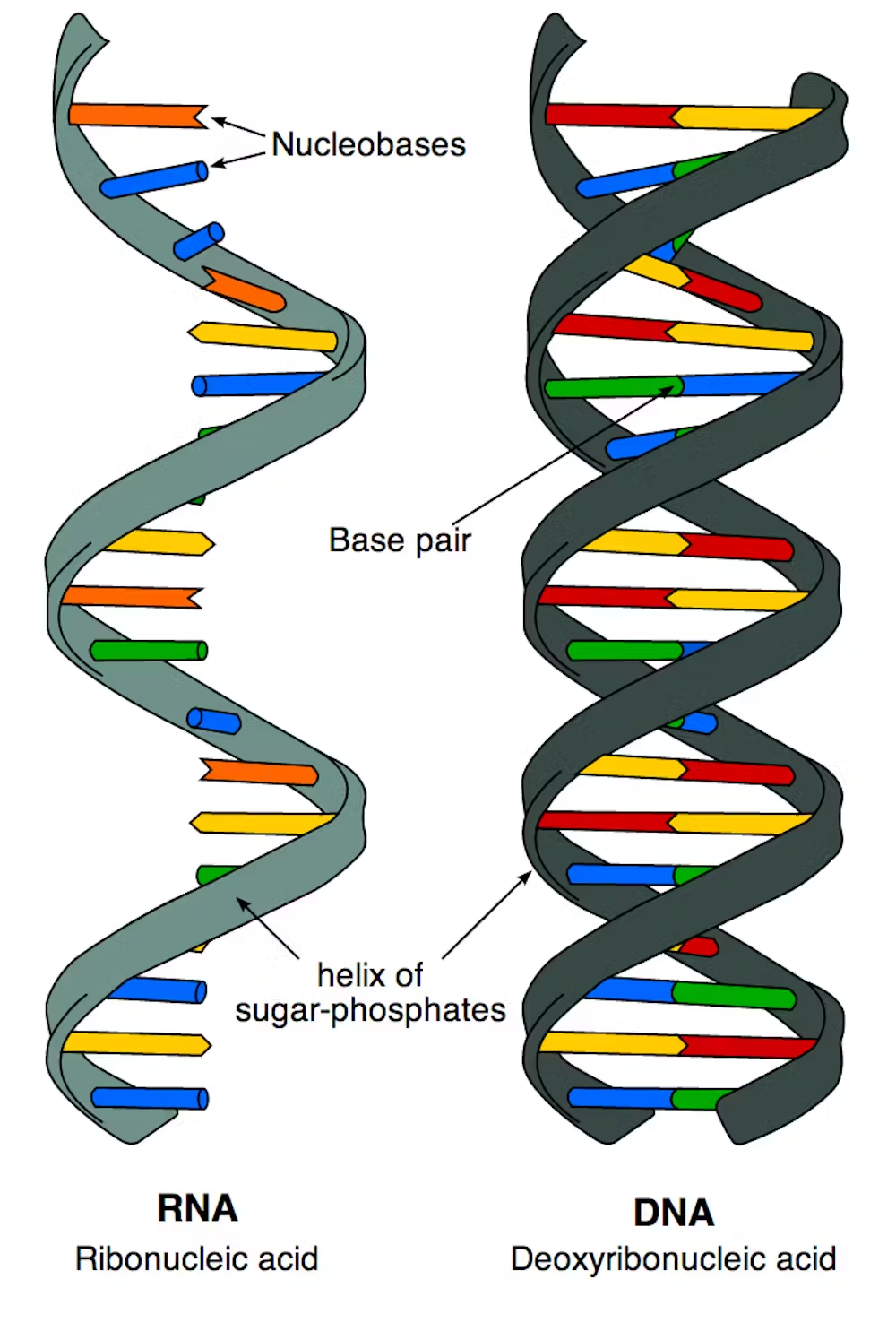
Nucleic Acid
A polymer of nucleotides; functions include storing and transmitting hereditary information. The two types are DNA and RNA.
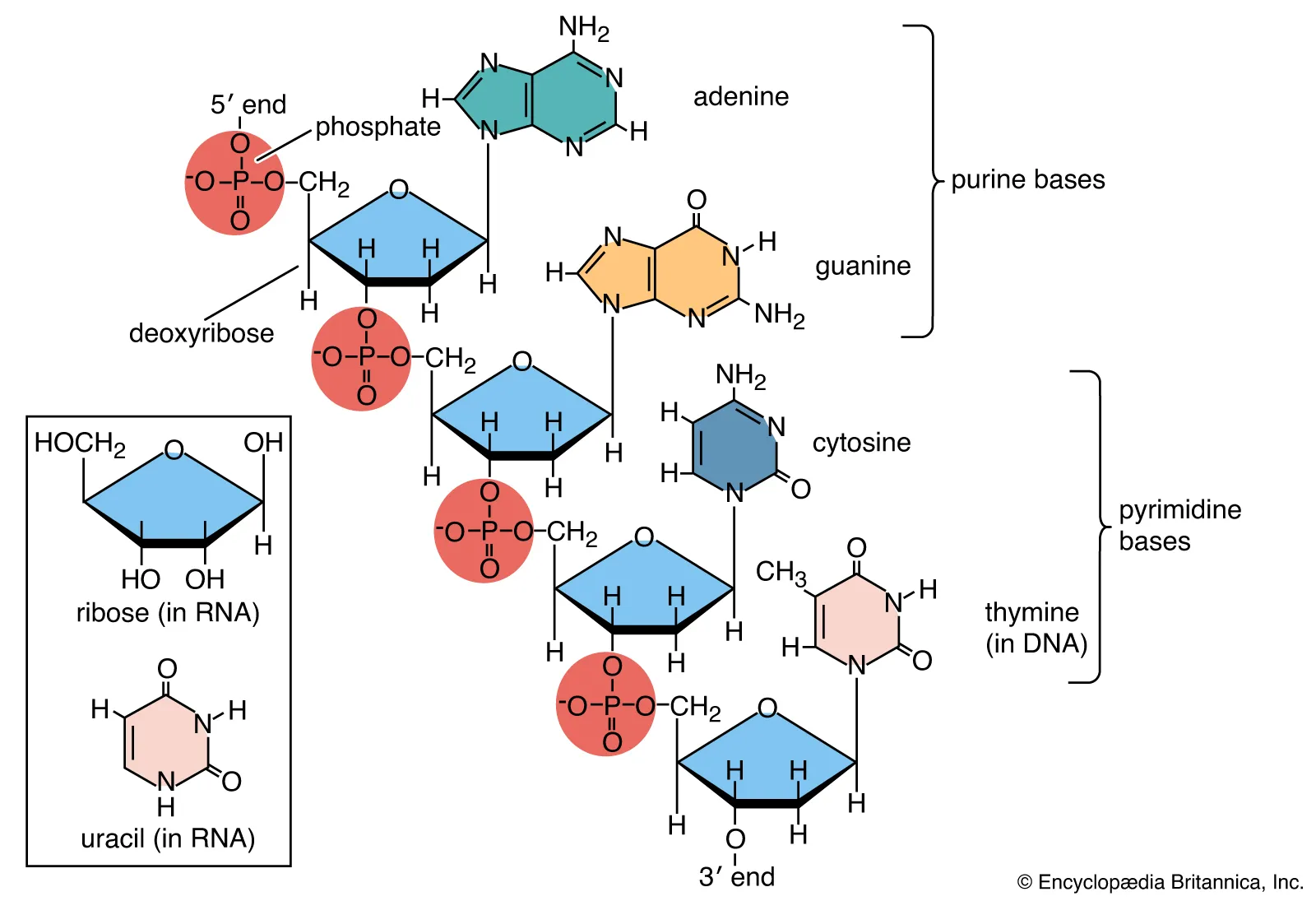
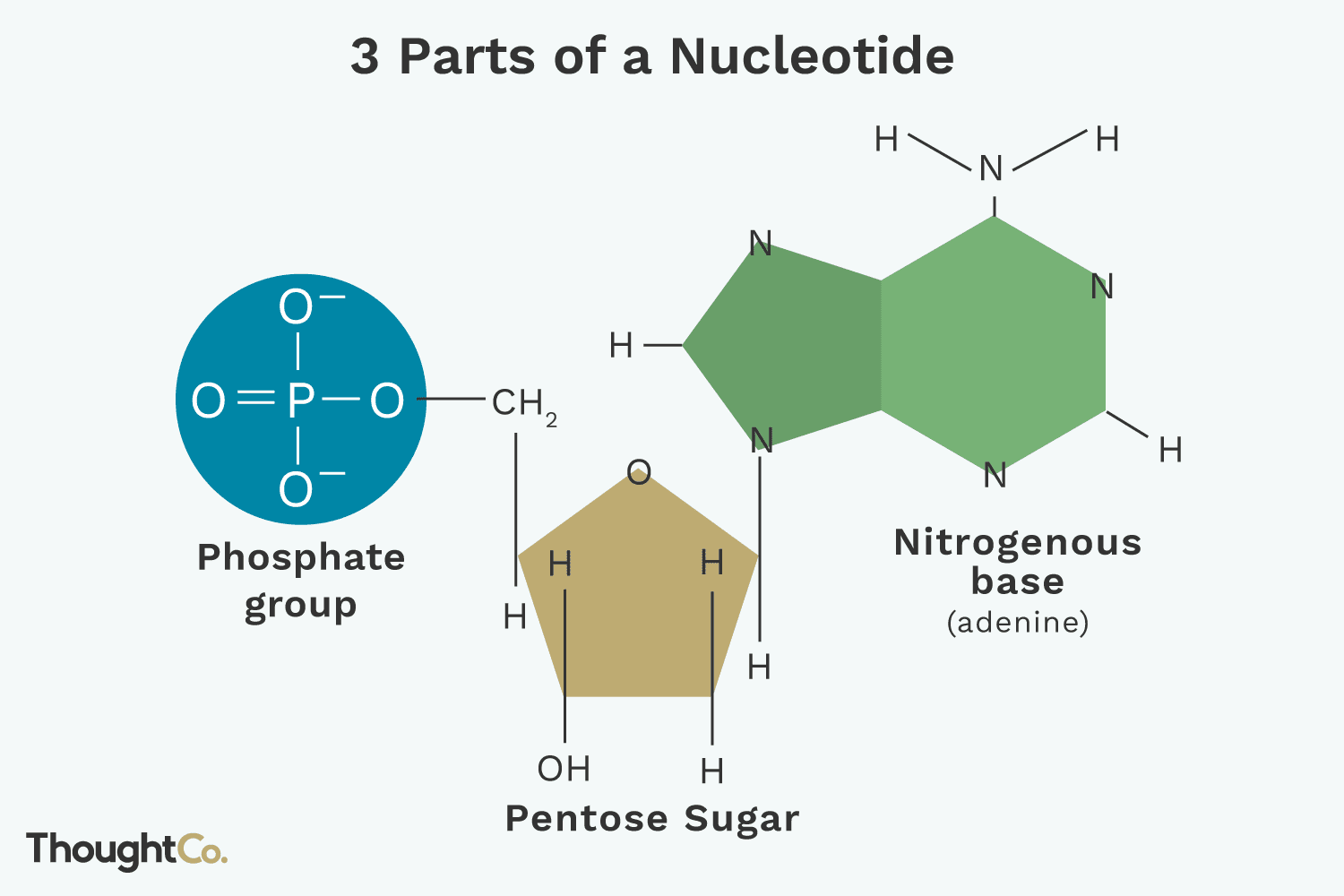
Nucleotide
The monomer of a nucleic acid; composed of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base.
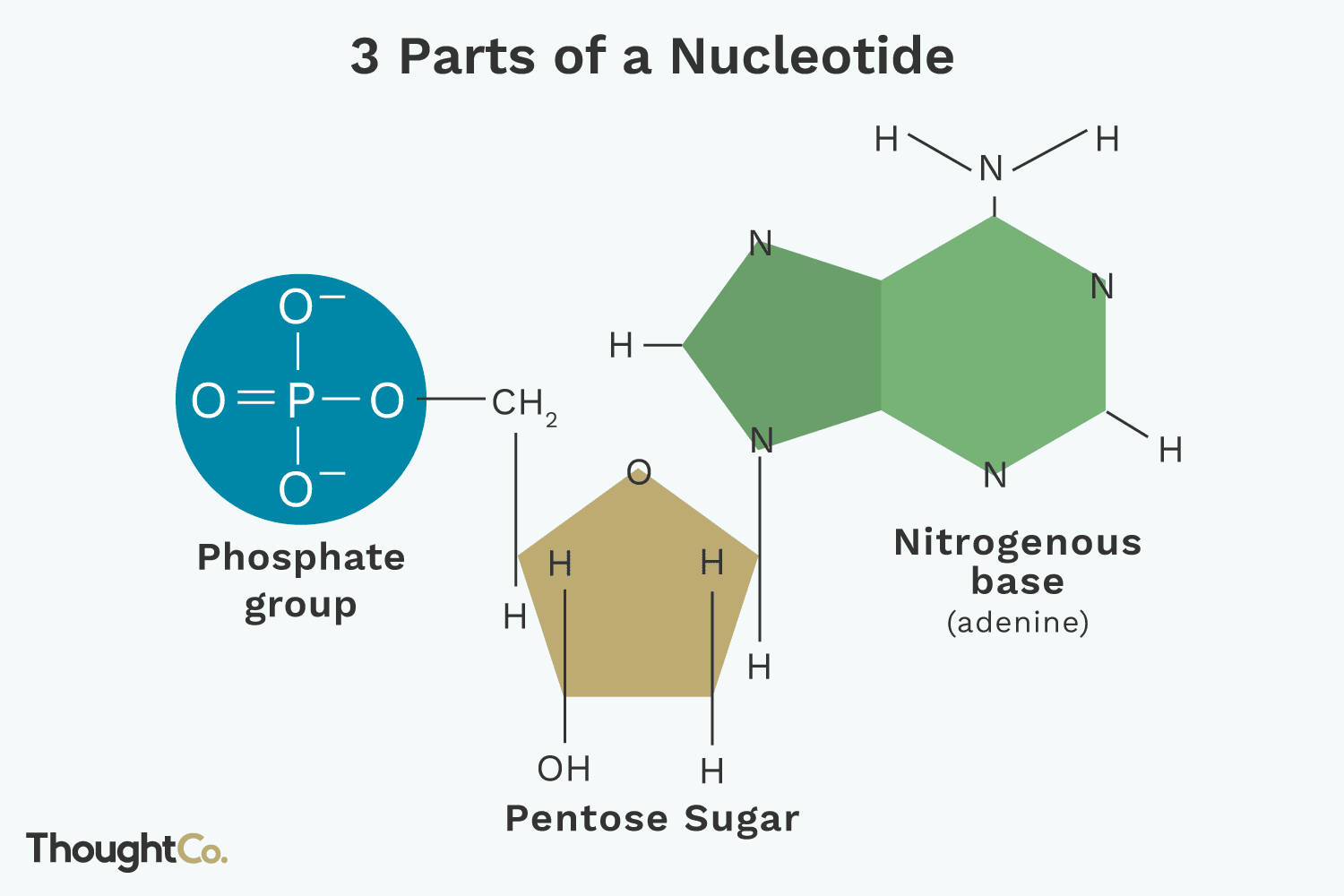
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
A nucleic acid that is the genetic material; stores information for its own replication and for the sequence of amino acids in proteins.
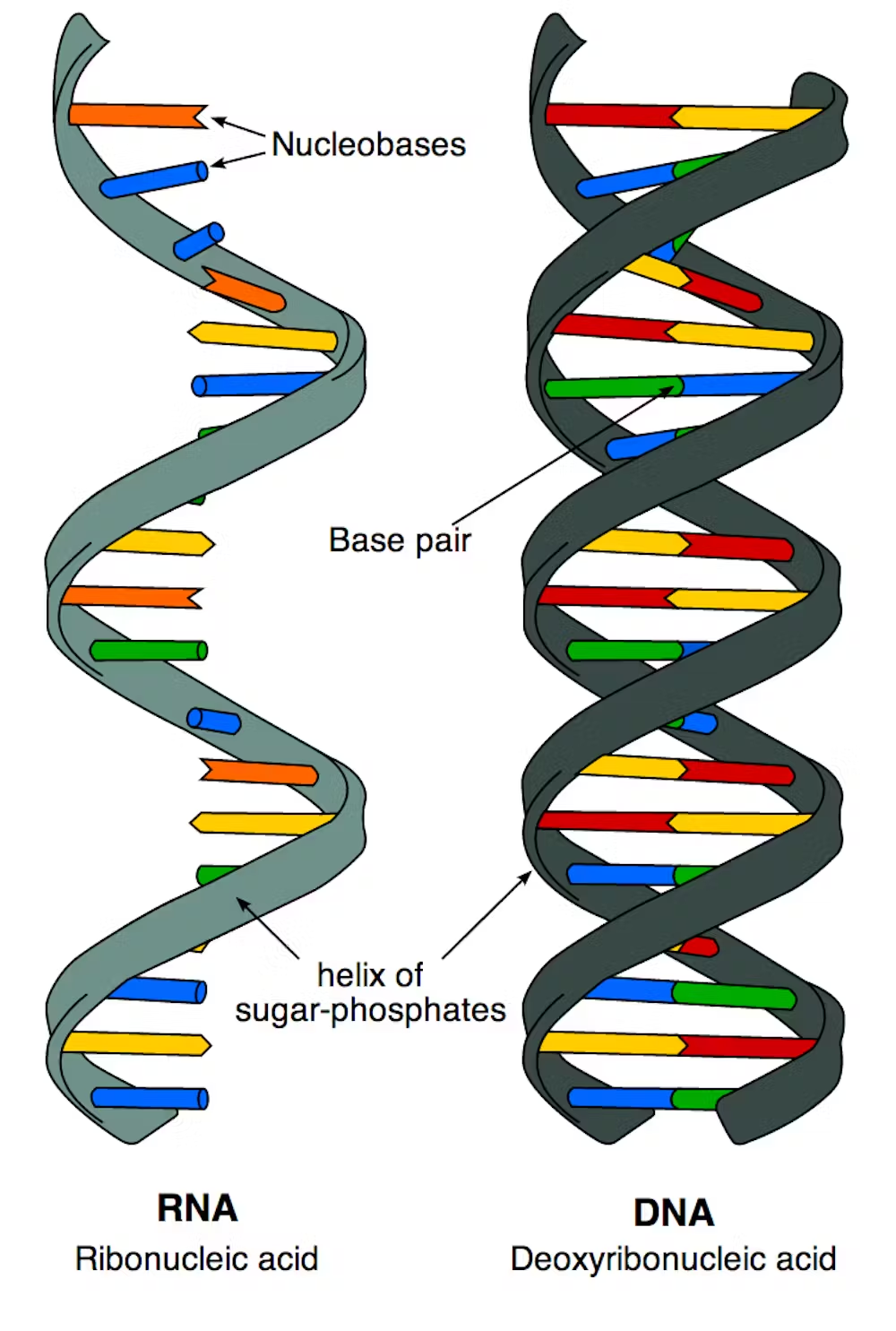
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
A nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis and gene regulation; has a wide range of functions.
Pentose Sugar
The 5-carbon sugar in a nucleotide; ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA.