9A sexual vs asexual reproduction
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is reproduction
the biological process by which organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of the species across generations
asexual reproduction
the process where one parent produces genetically identical offspring (clones) from a single parent, without the fusion of gametes.
eg bacteria, some fungi, some plants
budding (asexual)
budding occurs when an outgrowth, or bud, on the parent body develops enough to survive on its own and then detaches as a separate organism
eg jellyfish, coral, yeast, hydra, and worms
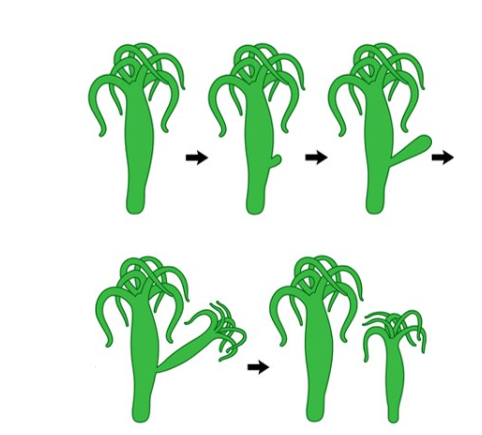
fragmentation (asexual)
occurs when a piece of the parent body breaks off and both sections regrow into two separate (identical) organisms
eg sea stars, coral, sponges and many plants
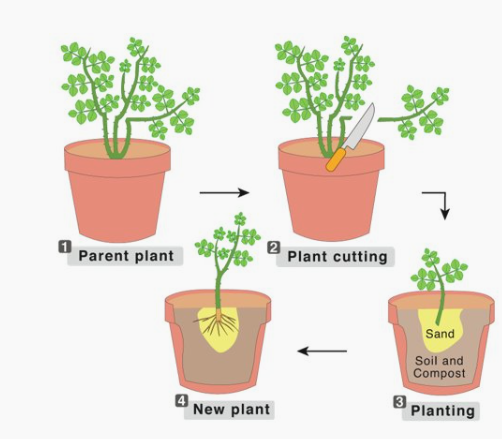
vegetative propogation (asexual)
occurs when a cutting is taken from a mature parent plant, and the cutting is planted into its own soil to grow into a new independent (identical) plant.
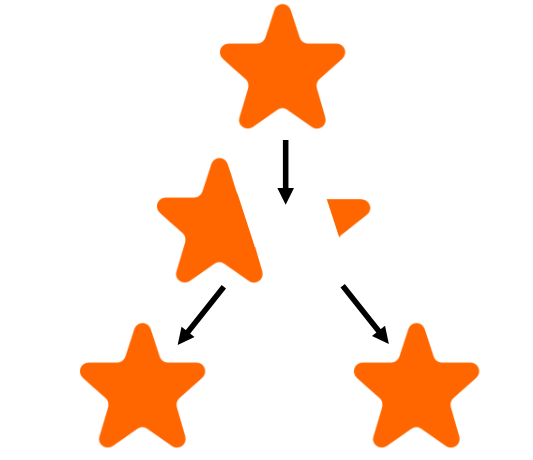
sporogenisis (asexual)
occurs when an organism makes spores that are released into the environment, like into water or air, where they can grow into a new identical organism
eg fungi, ferns, mosses some algae and bacteria
parthogenesis (asexual)
when an embryo grows from an unfertilised egg (sometimes called virgin birth). The eggs are made by mitosis (diploid) so the new organism is genetically identical to the female parent. this is very rare, only in vertebrate species.
what are advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction
adv:
fast reproduction - no mating means fast reproduction, allowing organisms to rapidly colonise environments with lots of recourses
low energy cost - no energy is spent finding a mate, producing gametes, or raising offspring.
useful traits are cloned - offspring inherit alleles that are already well suited to survive in the current environment
dis:
lack of genetic diversity - producing clones means all offspring have the same alleles. this makes the whole population vulnerable in changing or unpredictable environments.
what is sexual reproduction
the process where a male (haploid) gamete and female (haploid) gamete fuse together in fertilization to create genetically different diploid offspring
more risky and time consuming than asexual, but creates genetic diversity which helps species survive and adapt to changes in their environment
why is genetic diversity important?
helps a species survive for a long time. acts like protection against changes in the environment, such as diseases, predators, climate change, radiation, or natural disasters. bigger gene pool = more genetic diversity, which gives the species a higher chance of surviving when the environment changes.
sexual reproduction advantages and disadvantages
adv:
creates genetic diversity - offspring inherit a mix of alleles from their parents, meaning some individuals may have traits that help them survive better if the environment changes.
reduces risk of inheriting harmful genetic disorders - recombination of genes can separate ‘bad’ alleles from each other.
dis:
slow and requires more energy - finding a mate, producing gametes, raising offspring (in some species) takes a lot of time and resources
risk of STIs - due to sexual intercourse
risk of embryo damage during development
what are reproductive strategies
courtship rituals
mating behaviours
types of fertilisation
mode of embryonic development
different reproductive strategies have evolved to help species increase their chances of successful reproduction
what are the types of fertilisation
external: when sperm and egg fuse outside the body, typically in water.
internal: when the sperm and egg fuse inside the female’s body
what are the modes of embryonic development
viviparity = embryo develops inside the mother’s uterus
eg human
oviparity = embryo develops in eggs laid outside the body
eg chicken
ovoviviparity = embryo develops inside eggs inside the mother
eg shark

what are courtship rituals
actions or signals animals use to attract a mate and show they are healthy and ready to breed
eg of courtship: sounds (like bird or frog calls), movements (danceS), scents (pheromones) colour changes or body displays
what are mating behaviours
the act of sexual reproduction after successful courtship
mating behaviours have evolved to increase the chance of successful (internal or external) fertilisation