Lab I: Preparation of Bixin Extract and its Thin Layer Chromatography
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
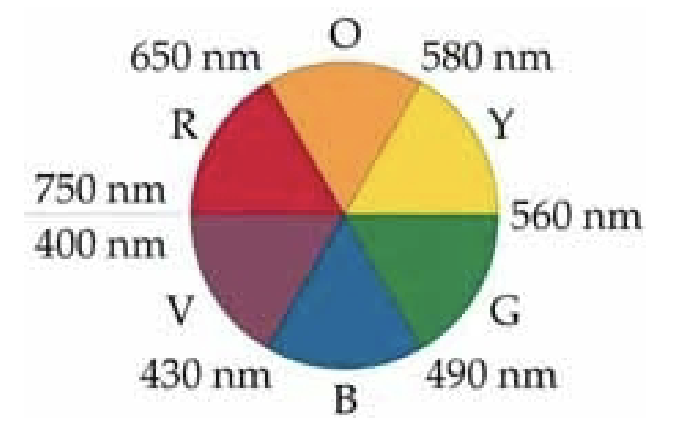
Draw the UV region of EM spectrum
Absorption at UV and visible wavelengths: promotion of e- from HOMO to LUMO
Extended conjugation reduces HOMO to LUMO gap -> lowers the frequency = absorption at longer wavelengths

What is observed color?
Observed color is complementary to the color of the wavelength absorbed.
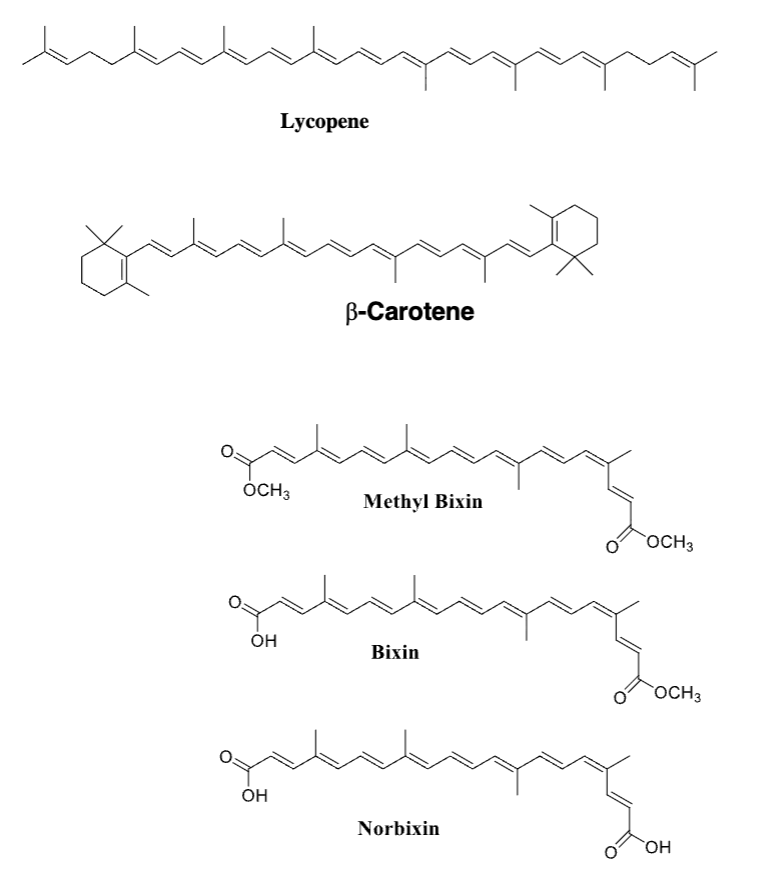
Draw the structures
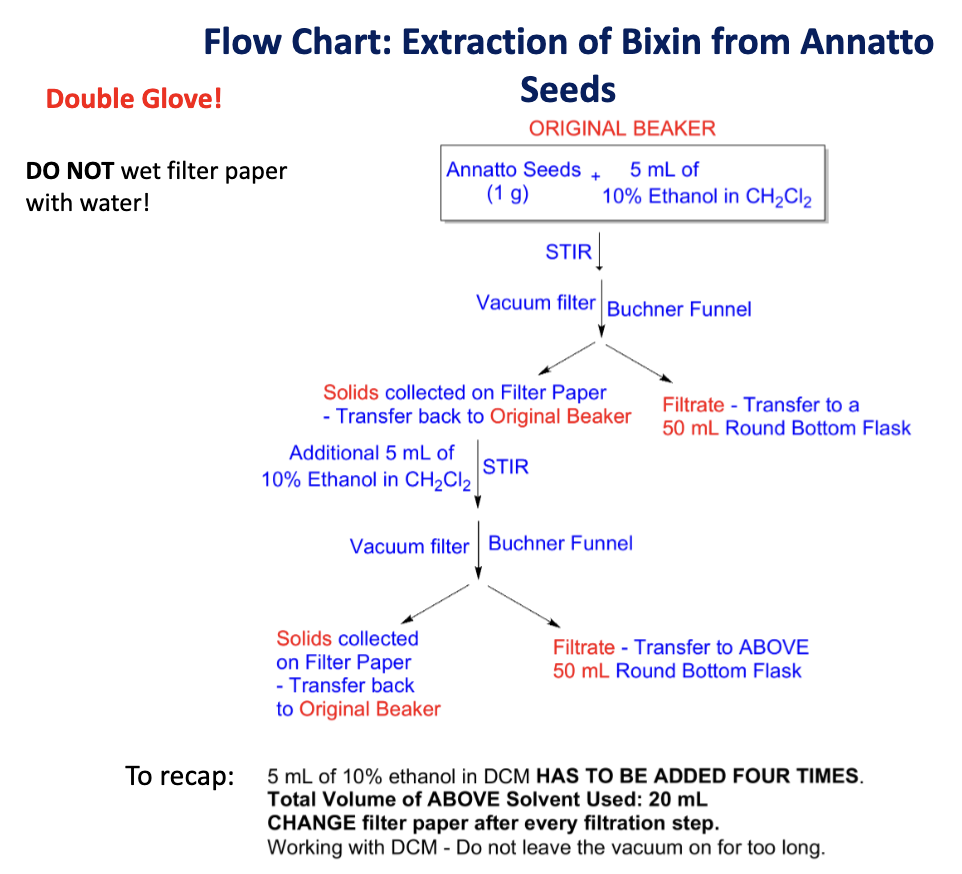
Draw the flow chart
Safety precautions?
Dichloromethane is a carcinogenic compound.
Double glove.
If gloves are damaged:
Remove gloves
Wash hands for 20 sec w/ soap + warm water
Replace w/ new pair of gloves
Waste disposal?
Annatto seeds —> biohazard waste box
Buchner funnel filter paper —> biohazard waste box
Vacuum filter flask, buchner funnel, 50mL beaker rinsed + emptied —> C,H,O Halogenated & acetone rinsings
TLC capillary tubes —> red sharps container
Properties of chromatography?
Routinely used as a qualitative analytical tool
Simple, economical method for separation of components in a mixture.
Identification of Unknowns by comparison with known reference samples.
Helps in following the progress of a chemical reaction.
Helps in determining the effectiveness of a purification.
Helps to determine the conditions for macroscopic separations (Column Chromatography).
No restriction on sample type – Organic, Inorganic, Biological or Medical.
High Sensitivity – Detection of μg amounts or less (10-6 g)
Draw the chromatography stationary phase vs. mobile phase table
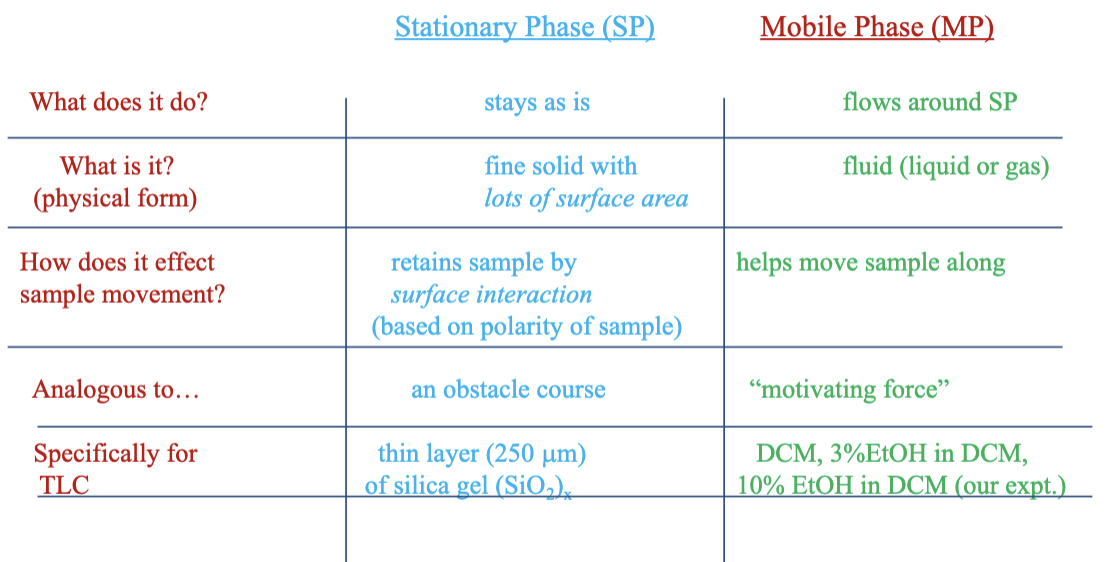
What are the 4 types of chromatographic methods?
TLC - Thin Layer Chromatography
LC – Liquid Chromatography (SP- Silica gel or Alumina; MP – a liquid)
HPLC - High Performance Liquid Chromatography (utilizes high pressure exerted by mechanical pumps to force the mobile phase through a very small diameter column packing that contains the stationary phase).
GC - Gas Chromatography (MP – a gas)
What are 2 examples of adsorbents?
Silica gel (SiO2) - most commonly used, inexpensive stationary phase.
Aluminum oxide, Alumina Al2O3
What is silica gel?
Extended covalent network of tetrahedral Si atoms bridged by “O” atoms – terminating in very polar Silanol (Si-OH) groups, thus creating a very polar surface.
The presence of these OH groups renders the surface of silica gel highly polar.
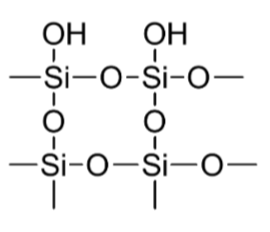
What is the composition of a TLC plate?
250 μm silica gel layer impregnated with a fluorescent indicator, on a plastic backing
What are the results of interaction w/ only stationary phase?
Highly polar molecules will interact strongly with the polar Si-OH bonds in the silica gel adsorbent – resulting in slow movement up the TLC plate.
Weakly polar molecules are held less tightly than the polar species on the silica gel adsorbent – resulting in quicker movement up the TLC plate
What does adding CaSO4 do?
CaSO4 – added to help silica gel bind to a plate compounds
What is the formula for ratio to the front (Rf) factor?
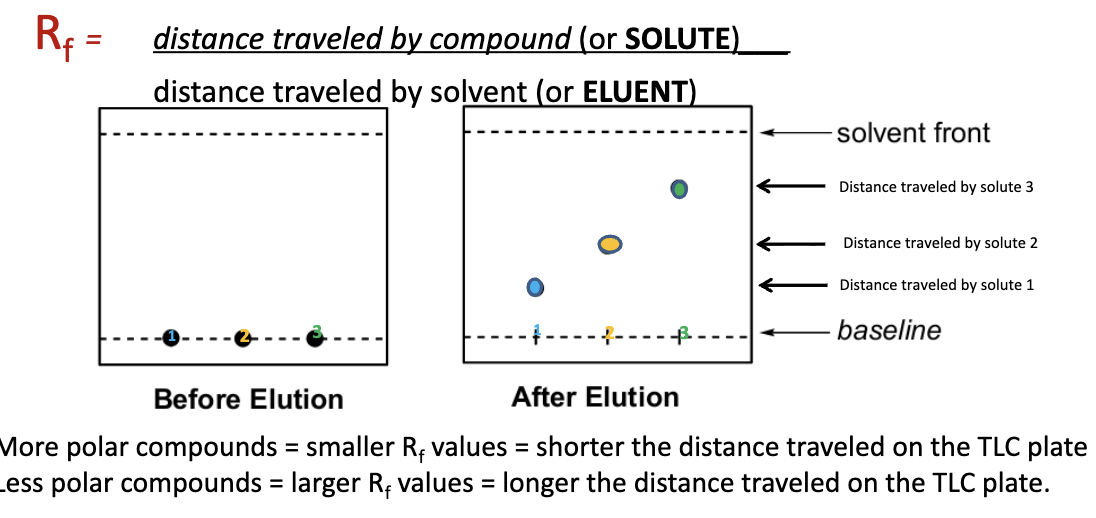
What are the 4 steps of TLC?
Application of Sample: Use a different TLC Capillary tube (open on both ends) to spot the standard solution of each solute.
Development of Sample: This is when the separation actually occurs inside the TLC Development Chamber.
Visualization of Sample: The TLC plate will be viewed under UV light.
Interpretation of Results: Comparison of Retention factors
Sample application reminders?
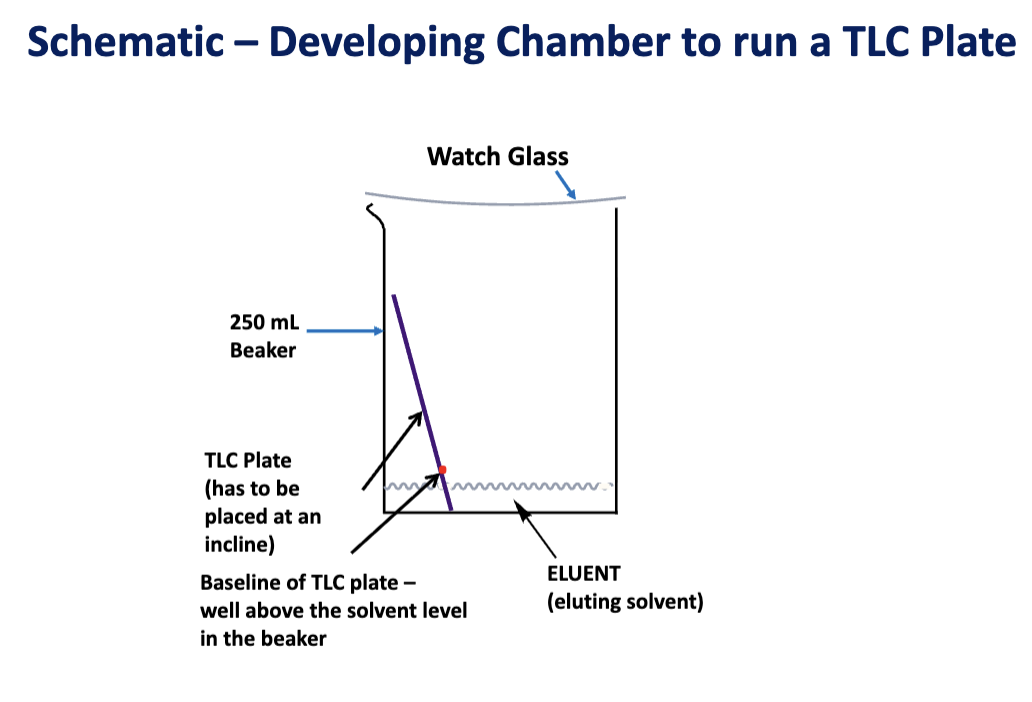
Draw baseline 1.5 cm from bottom of plate.
Spot lightly on ROUGH SIDE of TLC plate (avoid breaking silica gel).
Draw solvent front ~1 cm from top of plate.
Draw the schematic for the developing chamber to run a TLC plate