biochem hmwk 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the approximate strength of an ionic interaction?
Approximately 19 kcal/mol
For a set of species, how do you determine the predominant intermolecular force?
All molecules → London dispersion forces
Polar molecules → Dipole–dipole interactions
Molecules with N–H, O–H, or F–H → Hydrogen bonding
Which intermolecular forces do acetaldehyde molecules exhibit with each other?
Dipole–dipole forces and London dispersion forces
Match molecules to intermolecular forces: what rules apply?
Nonpolar molecules → Only London dispersion
Polar molecules → Dipole–dipole
Polar molecules with N–H, O–H, or F–H → Hydrogen bonding
When a nonpolar solute partitions from water (polar) into benzene (nonpolar), what is the sign of the entropy change (ΔS) at 25 °C?
Positive
What is the primary reason oil separates from water?
The entropic effect of freeing bulk water molecules from unfavorable clathrate structures around nonpolar molecules
What is the “normal” freezing point of water (at 1 atm)?
0 °C or 32 °F
What is the “normal” boiling point of water (at 1 atm)?
100 °C or 212 °F
Water has a much lower boiling point than expected given its size. True or False?
False — water has a much higher boiling point due to hydrogen bonding
What is the pH of a 0.15 M solution of a weak acid (HA) with a pKa of 5.02?
2.92
A 0.2 M solution of a weak acid HA dissociates such that 99.4% remains intact. What is the pKa?
5.1
Propylaminium ion (CH3CH2CH2NH3+) has a pKa of 10.71. Would a 0.1 M propylaminium/propylamine solution at pH 9.71 be an effective buffer against 0.1 M NaOH?
True — pH 9.71 is within the buffering region, though near the lower end
You have 100 mL of 0.10 M H3AsO4 (pKas = 2.24, 6.96, 11.49). After adding 150 mL of 0.10 M KOH, what is the pH?
6.96 — the second proton is half-titrated, so pH ≈ pKa2
In a titration of phosphoric acid (H3PO4), what species are present when 0.5 equivalents of OH− have been added?
50:50 H3PO4 and H2PO4−
In a titration of phosphoric acid (H3PO4), what species predominate after 1 equivalent of OH− has been added?
Essentially all H2PO4−
In a titration of phosphoric acid (H3PO4), what species are present when 1.5 equivalents of OH− have been added?
50:50 H2PO4− and HPO42−
In a titration of phosphate ion (PO43−), what species are present when 1.0 equivalent of H+ has been added?
Essentially all HPO42−
In a titration of phosphate ion (PO43−), what species are present when 1.5 equivalents of H+ have been added?
50:50 H2PO4− and HPO42−
If the equilibrium constant for H2O + CO2 ⇌ H2CO3 is 3 × 10−3, and for H2CO3 ⇌ H+ + HCO3− is 1.7 × 10−4, what is the pKa of the overall reaction H2O + CO2 ⇌ H+ + HCO3−?
6.3
At 37 °C, if [HCO3−] = 24 mM and [CO2] = 1.2 mM, what is the pH of the system (overall reaction H2O + CO2 ⇌ H+ + HCO3−)?
7.4 (physiological pH)
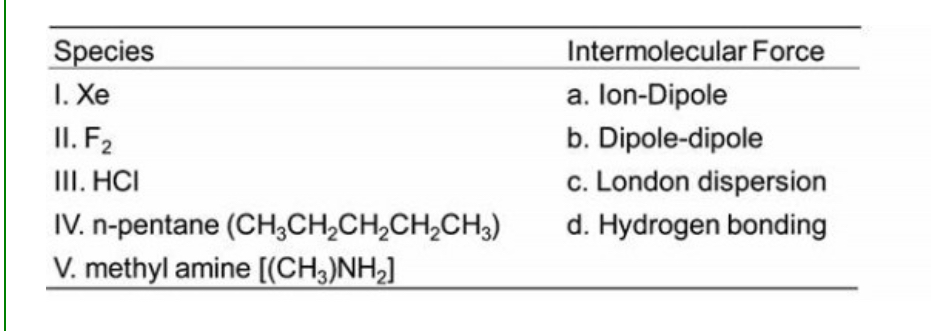
For the species indicated below indicate which of the intermolecular forces would be the predominant intermolecular force.
I. c II. c III. b IV. c V. d
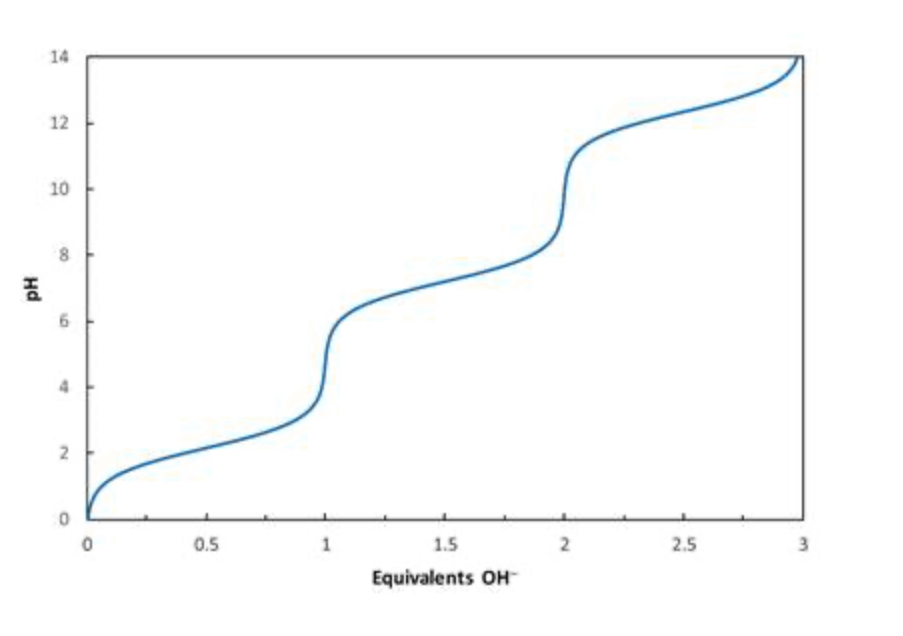
Consider the titration curve of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) shown below. What species will be present when 1.5 equivalents of OH−has been added?
50:50 H2PO4− and HPO42−
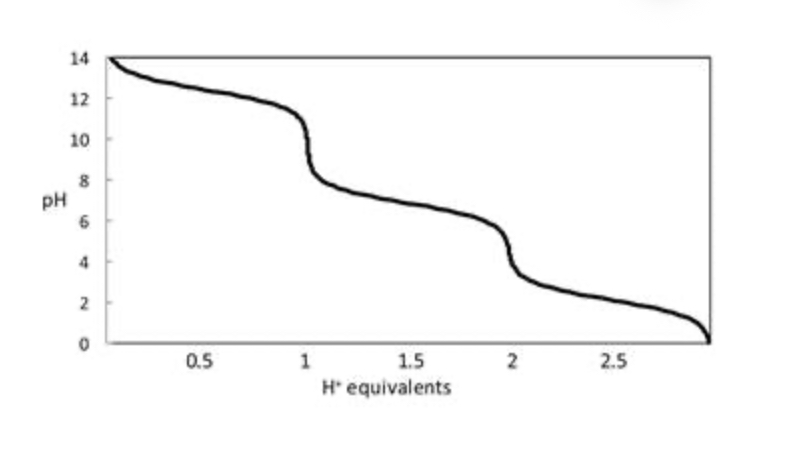
Consider the titration curve of phosphate (PO43−) ion shown below. When 1.5 equivalents of H+ has been added to a solution of phosphate ion, what species predominates?
50:50 H2PO4− and HPO42−
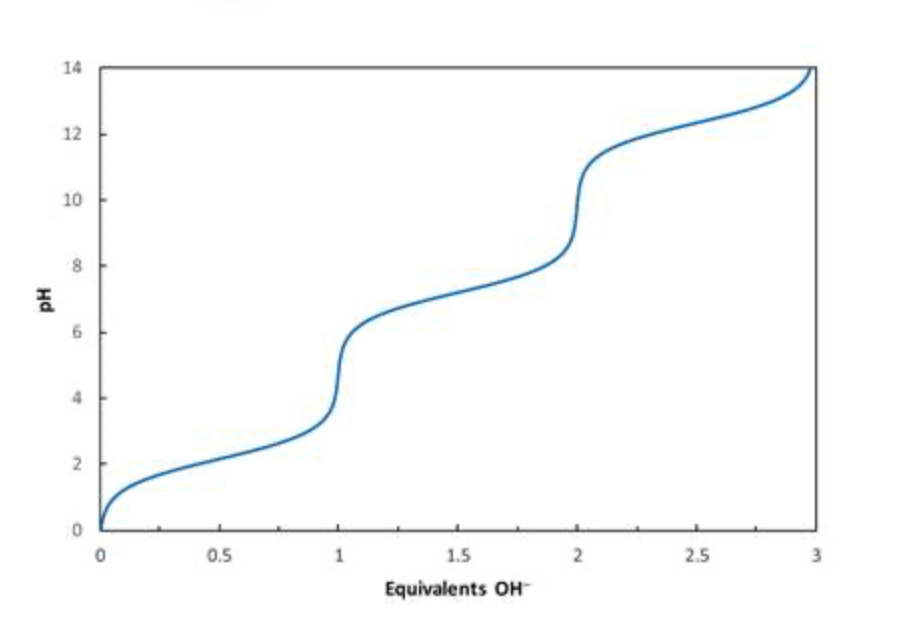
Consider the titration curve of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) shown below. What species will be present when 0.5 equivalents of OH−has been added?
50:50 H3PO4
and H2PO4−
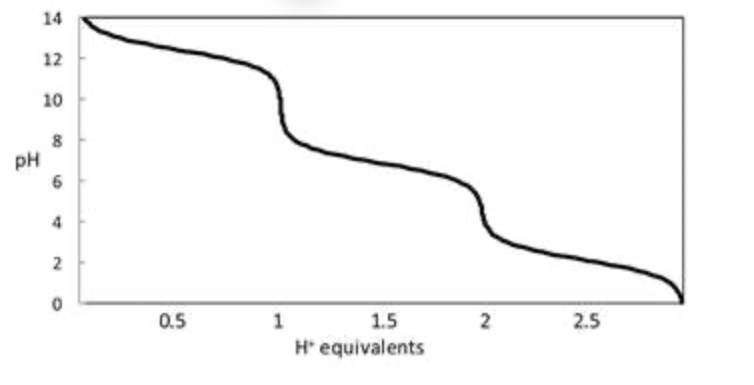
Consider the titration curve of phosphate (PO43−) ion shown below. When 1.0 equivalent of H+ has been added to a solution of phosphate ion, what species predominates?
essentially all HPO42-
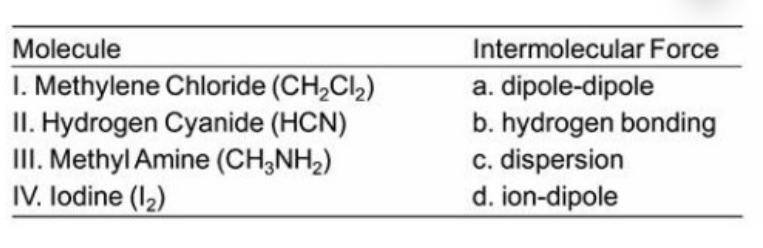
Match each molecule below with the type(s) of intermolecular force(s) applicable to it from the choices on the right. Some of the choices many be used more than once or not at all.
I. a, c II. a, c III. a, b, c IV. c
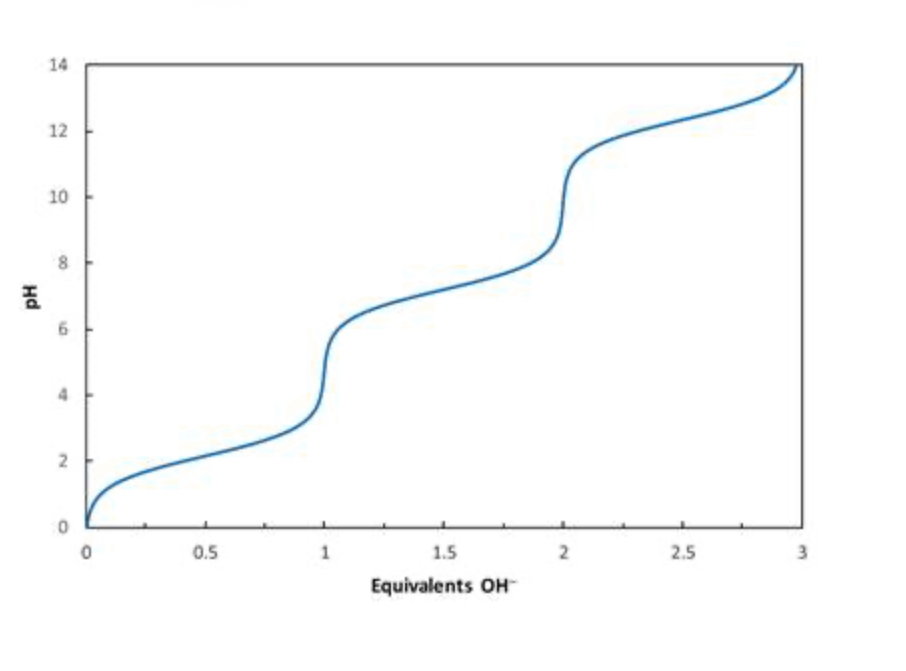
Consider the titration curve of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) shown below. What species will be present when 1 equivalent of OH−has been added?
essentially all H2PO4−