Westward Expansion, Gilded Age, and Industrialization: Key Causes, Effects, and Movements
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What were the causes of Westward Expansion from 1877 to 1898?
Causes included improvements in mechanization, government subsidies for transportation and communication, and the pursuit of self-sufficiency and independence by migrants.
What were the effects of Westward Expansion from 1877 to 1898?
Effects included a decline in food prices, the creation of cooperative organizations among farmers, and the establishment of new communities due to economic growth.
What is the purpose of the Farmers' Alliance and the Grange?
Both organizations aimed to support farmers through cooperative efforts, improve their economic conditions, and advocate for their interests.
How did government policies promote economic growth during Westward Expansion?
Government policies included subsidies for railroads and communication systems, which facilitated access to new markets and resources.
What were the causes of social and cultural changes during Westward Expansion?
Migrants sought opportunities in rural and boomtown areas for jobs in railroads, mining, farming, and ranching, leading to increased competition for land.
Describe the conflict between white settlers and American Indians.
Conflicts arose due to competition for land and resources, leading to violent confrontations and the U.S. government's military response to resistance.
What was the Dawes Severalty Act?
The Dawes Severalty Act aimed to assimilate American Indians by allotting them individual plots of land and promoting farming, undermining tribal sovereignty.
What characterized the 'New South' from 1877 to 1898?
The 'New South' saw industrialization in some sectors, but agriculture based on sharecropping and tenant farming remained dominant.
What was the significance of Plessy v. Ferguson?
The Supreme Court decision upheld racial segregation laws, marking a setback for African American political gains made during Reconstruction.
What were the goals of African American reformers during the 'New South'?
They sought political and social equality despite facing violence and discrimination.
What were some significant technological innovations during the Gilded Age?
Innovations included advancements in manufacturing processes, transportation (like railroads), and communication technologies.
How did industrial capitalism grow from 1865 to 1898?
Growth was driven by large-scale industrial production, technological changes, and pro-growth government policies that facilitated business consolidation.
What practices did businesses use to consolidate during the Gilded Age?
Businesses formed trusts and holding companies to concentrate wealth and control over markets.
What was the impact of labor unions during the Gilded Age?
Labor unions organized workers to advocate for better wages and working conditions, often facing resistance from businesses.
What were some examples of labor unions during the Gilded Age?
Examples include the American Federation of Labor (AFL) and the Knights of Labor.
What were the motivations for migration during the Gilded Age?
Economic opportunities, cultural factors, and the search for better living conditions drove both internal and external migrations.
What were the responses to immigration during the Gilded Age?
Responses included public debates over assimilation, Americanization efforts, and cultural compromises by immigrants.
What were settlement houses?
Settlement houses were community centers that provided services and education to immigrants and the poor, helping them adapt to American society.
What is the Gospel of Wealth?
The Gospel of Wealth is the idea that the wealthy have a moral obligation to help the less fortunate through philanthropy.
What was the Social Gospel movement?
The Social Gospel movement sought to apply Christian ethics to social problems, advocating for social justice and reform.
What were the arguments for and against government intervention in the economy during the Gilded Age?
Proponents of laissez-faire argued that government intervention hindered economic growth, while others believed intervention was necessary to protect workers and consumers.
What was the role of political machines during the Gilded Age?
Political machines provided social services to immigrants and the poor in exchange for political support, often leading to corruption.
What were the main issues surrounding patronage during the Gilded Age?
Patronage involved the distribution of government jobs and contracts based on political loyalty rather than merit, leading to corruption and inefficiency.
What was the platform of the Populist Party?
The Populist Party called for government regulation of railroads, a graduated income tax, and the direct election of Senators.
Who supported the Populist Party?
The Populist Party was supported by farmers, laborers, and those disillusioned with the major political parties.
What were some examples of strikes that ended in violence during the Gilded Age?
Examples include the Haymarket Affair, the Pullman Strike, and the Homestead Strike.
what helped open markets in north america
government subsidies for transportation and communication
what promoted economic growth and created new communities and centers of commercial activity
the building of continental railroads, the discovery of mineral resources, and government policies
Lasseiz-faire means:
"Hands off" philosophy. Government should not interfere with the economy.
what caused the substantial increase in agricultural production
improvements in mechanization (ex:reaper, steel plow, barbed wire)
how did farmers respond to the increasing consolidation in agricultural markets and their dependence on the evolving railroad system?
by creating local and regional cooperative organizations
Bonanza Farms
Large scale farms often over 50,000 acres, often owned by railroad companies or investors rather than private farmers
3 causes of economic hardship for farmers in the late 19th century
low prices, heavy local taxes, high freight rates, price dependent on local markets
Granger Laws
A set of laws designed to address railroad discrimination against small farmers, covering issues like freight rates, storage prices, and railroad rebates.
Homestead Act of 1862
this allowed a settler to acquire 160 acres by living on it for five years, improving it and paying about $30
Morrill Act
(1862) Federal law that gave land to western states to build agricultural and engineering colleges.
impact of mechanization on agricultural prices
made prices substantially lower because it resulted in a higher crop yield
Dawes Severalty Act
The act passed with the intent to assimilate Native Americans into mainstream of American life by dissolving tribes as legal entities and eliminating tribal ownership of land. Land taken from american indians was then sold to the railroads
Second Treaty of Fort Laramie
moved the remaining Sioux to the Black Hills in the Dakota Territory beginning the reservation system
conflict between white settlers and american indians
conflict between settlers form east and military and indians intensifies as more people move west, land disputes, "indian hunting"
who settled in western territory
immigrants from northern europe looking for cheap land, immigrants from china for mining/railroad jobs, African Americans to get away from south
where did immigrants move and why
rural and boomtown areas in the west fro economic opportunities in railroads, mining, farming, and ranching
marketing strategy for standard oil
provide uniform quality of kerosene to calm peoples fears
who made standard oil
rockefeller
Who was Carnegie?
owner of steel industry
how doas carnegie adjust his business plan after railroads decline
switches to structural steel fro skyscrapers
What strategy did Rockefeller use to convince workers?
He convinced workers to buy stock in Standard Oil.
What did Rockefeller do with smaller refineries?
He bought all smaller refineries and shut them down.
How did Rockefeller avoid paying railroad companies?
He used miles of pipeline.
how did kerosene change americans lives
provided clean safe light, opened new market and job opportunities, high demand, used to build and power things
why did the deal between rockerfeller and vanderbilt upset farmers
took away land from farmers in order to expand railroads to transport oil
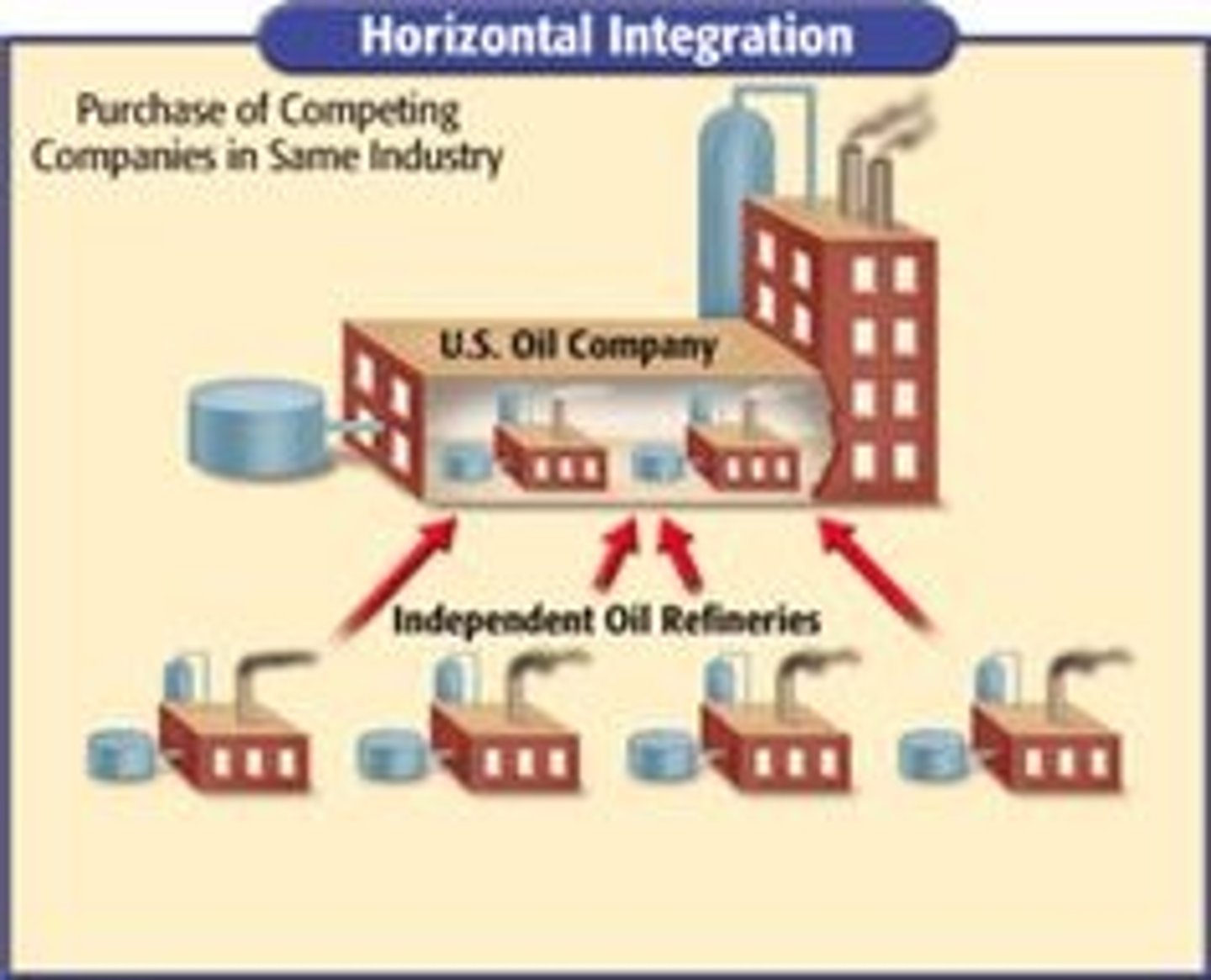
Horizontal Integration
Type of monopoly where a company buys out all of its competition. Ex. Rockefeller
Vertical Integration
Practice where a single entity controls the entire process of a product, from the raw materials to distribution

Bessemer process (steel)
Method of making steel. Improved on iron because it did not rust and was lighter. was also much cheaper to make. Enabled the construction of skyscrapers and railroads.
how did business leaders seek to increase profits
by consolidating corporations into large trusts and holding companies
two principles of capitalism
free competition in all markets, little government intervention
3 problems confronting labor in the late 19th century
child labor laws, boom and bust cycle of economy, labor strikes fro higher wages
why would immigrants negatively impact those in labor unions
becuase if the laborers were on strike fro higher wages, they would just hire immigrants fro less money to do their job
3 factors that weakened labor during the period 1865-1898
ironclad contracts that prevented unions, black lists, lockouts
why did homestead strike fail
the national gaurd was sent in there were not enough people to fight them
why did the pullman strike fail
sent labor union leaders to jail
how did northern cities change in the period 1865-1898
population growth, sanitation problems, crime problems
how did immigration change in the period 1865-1898
immigration from southern and eastern europe increased, seeking industrial jobs, pushed out of home countries
how did migration change in the period 1865-1898
formed cultural enlcaves, migration made easier by steam ships
Growth of middle class
need for clerical workers, need for managers, greater access to public education
leisure activities
bicycling, tennis, spectator sports, vaudeville theater amusement parks, dance halls,
Gospel of Wealth
The belief that, as the guardians of society's wealth, the rich have a duty to serve society; promoted by Andrew Carnegie; Carnegie donated more than $350 million to libraries, school, peace initiatives, and the arts
Social Gospel Movement
preached salvation through service to the poor, mainly aimed at religious figures
Suffrage Movement
The drive for voting rights for women that took place in the United States from 1890 to 1920.
Jim Crow Laws
Laws designed to enforce segregation of blacks from whites, literacy tests
examples of encouraging the assimilation of immigrants
teaching english in public schools, most employers requiring english, establishment of hull house
Hull House
Settlement home designed as a welfare agency for needy families. It provided social and educational opportunities for working class people in the neighborhood as well as improving some of the conditions caused by poverty.
examples of nativism
congress passing laws to restrict groups of inpouring immigrants, formation of APA, prohibiting the importation of foreign workers under contract
What is the APA?
American Protective Association
What was the New South?
A vision for the post-Civil War South based on economic diversity, industrial growth, and laissez-faire capitalism. This led to industrial growth in Southern cities, Southern states surpassing New England textile manufacturing, and population growth. Still, the South relied on agricultural production through sharecropping.
provide two examples of attempts to create a new south
improving railroads, increased jobs
how does book t washington think african americans should go about achieving equality
accomadate and adapt to their situation and learn trades to gain economic stability
how deos WEB dubois think african americans should go about achieving equality
full access to education, formation of the NAACP
What is the NAACP?
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
who wanted to annex hawaii
US businessmen fro resources
who did not want the government to reduce unemployment/get involved in the economy
business leaders
Social Darwinism
The application of ideas about evolution and "survival of the fittest" to human societies - particularly as a justification for their imperialist expansion.
changes in the west
increased agricultural production, declining food prices, formation of cultural enclaves, tensions with american indians, formation of reserves, opening of new markets
changes in the north
concentration of wealth, increased economic development, creation of labor unions, immigration/diversity in the workforce, americanization, technological advancements
changes in the south
industrialization, limitation of AA societal growth
where were political machines most impactful
cities
What were political machines?
Organizations that provided social services and jobs in exchange for votes.
how did immigrants benefit from political machines
they were given better housing, aid and jobs
why were political machines considered corrupt
dumped votes into rivers, had people vote more than once under an alias, took votes from dead people
how is patronage an example of corruption
"buying votes" by taking advantage of the lower class in order to gain votes rather than getting elected because the american people want you
What is patronage?
providing a government job to someone in exchange for their political support
What was the Pendleton Act?
Act in 1883 that changed from the spoils system to make jobs in public institutions based on merit
what was the unintended effect of the pendleton act
made candidates forms relationships with large corporations in order to gain funding
what happened to the populist party
The populist party fell because people do not like the idea of a third party to be present in an election, ideas got absorbed by the other parties
what did the populists want
they wanted a larger government role in regulating the american economic system
who did major political parties appeal to
lingering division from the civil war, people who contended over tarrifs and currency issues
what did reformers argue about the economy
that economic greed and self interest had corrupted all levels of the government
Bimetallism
the use of both gold and silver as a basis for a national monetary system
who did bimetallism benefit
farmers
Omaha Platform/Populist Party
direct election of US senators, voters propose issues and vote on them, nationalize railroad, telephone and telegraph, income tax, free silver