Genetic Information, Variation and Relationships Between Organisms
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
1
New cards
Describe DNA in eukaryotic cells
Nucleus contains long, linear DNA molecules with associated proteins as chromosomes, DNA is wound around histones (proteins) for strength and so it can fit, coiled very tightly to make compact chromosomes
2
New cards
Describe DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts
Have their own DNA, circular and shorter and not associated with proteins
3
New cards
Describe DNA in prokaryotic cells
Carry DNA as chromosomes, shorter, circular, not associated with proteins, condenses to fit in cell by supercoiling
4
New cards
What is a gene?
A base sequence of DNA that codes for:
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
A functional RNA
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
A functional RNA
5
New cards
How many bases make up a triplet?
3
6
New cards
How many different amino acids there are?
20
7
New cards
How many combinations of amino acids are there?
64
8
New cards
Name and describe 3 features of the genetic code
Universal - same bases for all species
Non-overlapping - read in triplets
Degenerate - different triplet codes for the same amino acid
Non-overlapping - read in triplets
Degenerate - different triplet codes for the same amino acid
9
New cards
What is functional RNA and what does it do?
RNA molecules other than mRNA (e.g. tRNA and rRNA) which perform special tasks during protein synthesis
10
New cards
What is non-coding DNA?
Introns - removed by splicing
Exons - do code for amino acids
Exons - do code for amino acids
11
New cards
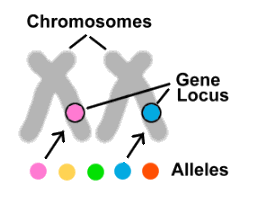
Define alleles
Different versions of the same gene
12
New cards
What are homologous chromosomes?
Pairs of matching chromosomes, same size and same genes, but could have different alleles
13
New cards
What is the locus?
The fixed position of a gene on each chromosome in a homologous pair
14
New cards
What is the genome?
Complete set of genes in a cell
15
New cards
What is the proteome?
Full range of proteins a cell is able to produce
16
New cards
Describe RNA
Single polynucleotide strand, contains uracil instead of thymine
17
New cards
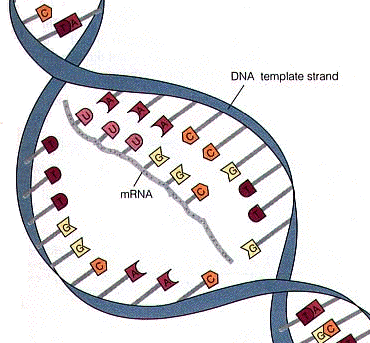
What is the role of messenger RNA (mRNA)?
Made during transcription, carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes, where it is used to make a protein during translation, single polynucleotide strand, groups of 3 adjacent bases = codons
18
New cards
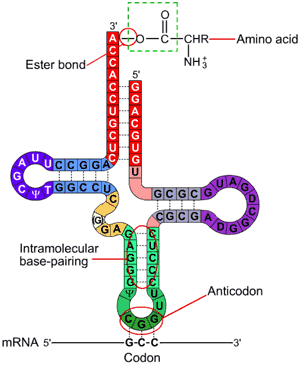
What is the role of transfer RNA (tRNA)?
Involved in translation, carries amino acids used to make proteins to ribosomes, single polynucleotide folded, H-bonds hold it in shape, have specific anticodon and amino acid binding site
19
New cards
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotes?
Nucleus
20
New cards
Where does transcription occur in prokaryotes?
Ribosomes in cytoplasm, directly produces mRNA from DNA (no splicing occurs)
21
New cards
Describe the process of transcription
1. RNA polymerase attaches to DNA at beginning of gene, breaks H-bonds, separating strands
2. RNA polymerase lines up free nucleotides, complementary mRNA formed, T is replaced with U, RNA polymerase joins together free bases, forming an mRNA strand
3. RNA polymerase moves down DNA, mRNA assembles, H-bonds reform
4. RNA polymerase reaches stop signal and detaches
5. In eukaryotes, splicing occurs, introns are removed
2. RNA polymerase lines up free nucleotides, complementary mRNA formed, T is replaced with U, RNA polymerase joins together free bases, forming an mRNA strand
3. RNA polymerase moves down DNA, mRNA assembles, H-bonds reform
4. RNA polymerase reaches stop signal and detaches
5. In eukaryotes, splicing occurs, introns are removed
22
New cards
Where does translation take place in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Ribosomes in cytoplasm
23
New cards
Describe the process of translation
1. mRNA attaches to ribosome and tRNA molecules carry amino acids to it, ATP provides energy for bond between amino acid and tRNA to form
2. tRNA (carrying amino acid) with complementary anticodon attaches to mRNA, a second tRNA does the same
3. The 2 amino acids join by a peptide bond
4. Process continues as ribosome moves along mRNA, produces polypeptide chain, until it reaches a stop signal
5. Polypeptide chain is complete
2. tRNA (carrying amino acid) with complementary anticodon attaches to mRNA, a second tRNA does the same
3. The 2 amino acids join by a peptide bond
4. Process continues as ribosome moves along mRNA, produces polypeptide chain, until it reaches a stop signal
5. Polypeptide chain is complete
24
New cards
Normal body cells have a ________ number
Diploid (2n)
25
New cards
Gametes have a _________ number
Haploid (n)
26
New cards
What is the human haploid and diploid number?
Diploid = 46
Haploid = 23
Haploid = 23
27
New cards
What happens during sexual reproduction?
2 gametes joining together at fertilisation to form a zygote, which divides and develops into a new organism
28
New cards
What happens during fertilisation?
Haploid egg fuses with haploid sperm, to make a cell with normal diploid number of chromosomes (1/2 from father, 1/2 from mother)
29
New cards
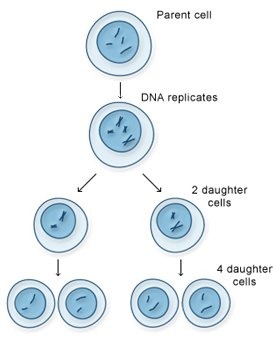
Describe the process of meiosis
1. Before meiosis starts, DNA unravels and replicates, so there are 2 copies chromosome = sister chromatids
2. DNA condenses to form double-armed chromosomes, each made from 2 sister chromatids joined by centromeres
3. First division - chromosomes arrange themselves in homologous pairs then homologous pairs separated, halving the chromosome number
4. Second division - Pair of sister chromatids are separated (centromere divides)
5. 4 haploid cells that are genetically different from each other are produced
2. DNA condenses to form double-armed chromosomes, each made from 2 sister chromatids joined by centromeres
3. First division - chromosomes arrange themselves in homologous pairs then homologous pairs separated, halving the chromosome number
4. Second division - Pair of sister chromatids are separated (centromere divides)
5. 4 haploid cells that are genetically different from each other are produced
30
New cards
Where does meiosis occur?
In reproductive organs of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms
31
New cards
What is a mutation?
Change in DNA base sequence of chromosomes
32
New cards
What is base addition?
One or more bases added, changes whole code
33
New cards
What is base deletion?
One or more bases deleted, changes whole code
34
New cards
What is base substitution?
One base is substituted for another, only 1 triplet will be changed, sometimes changes degenerate code
35
New cards
What do mutagenic agents do?
Increase probability of a mutation occurring
36
New cards
Name 4 examples of mutagenic agents
UV radiation, ionising radiation, some chemicals, some viruses
37
New cards
What do chromosome mutations lead to?
When meiosis goes wrong, cells produced contain variations in numbers of whole or parts of chromosomes, leads to inherited conditions
38
New cards
What happens during non-disjuction in meiosis 1?
Homologous pairs fail to separate
39
New cards
What happens during non-disjunction in meiosis 2?
Zygote haas 3 copies of a chromosome
40
New cards
Describe crossing over of chromatids
1. During meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes pair up
2. Chromatids twist and entangle (form chiasma) and swap over same length of genes
3. New combinations of alleles formed
2. Chromatids twist and entangle (form chiasma) and swap over same length of genes
3. New combinations of alleles formed
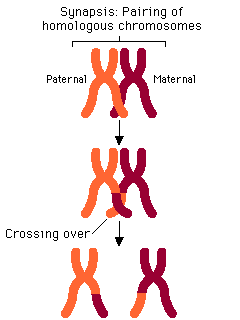
41
New cards
Describe independent segregation of chromosomes
When homologous pairs are separated in meiosis 1, it is completely random which chromosome from each pair ends up in which daughter cell, so the 4 daughter cells have different combinations of alleles, leads to genetic variation
42
New cards
What is variation?
Difference between same species organisms
43
New cards
Define genetic diversity
Total number of different alleles of genes in a population
44
New cards
Define population
Total number of organisms in a habitat
45
New cards
Define allele frequency
Frequency of specific alleles in a population
46
New cards
Why is genetic diversity important?
If a population has low genetic diversity, it might not be able to adapt to a change in the environment and the whole population could be wiped out by a single event
47
New cards
How is genetic diversity within a population increased?
Mutations in DNA forming new alleles, gene flow (different alleles being introduced into a population when individuals from another population migrate into it and reproduce)
48
New cards
What are genetic bottlenecks?
An event that causes a big reduction in a population, reduces number of different alleles in a gene pool which reduces genetic diversity, the survivors reproduce and a larger population is created from a few individuals
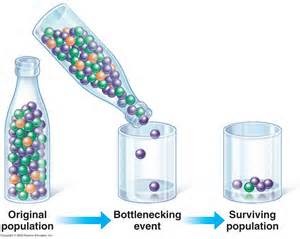
49
New cards
What is the founder effect?
When a few organisms from a population start a new colony and there are only a small number of different alleles in the initial gene pool, genetic diversity is reduced
50
New cards
Why is natural selection good?
It increases proportions of advantageous alleles within a population
51
New cards
Describe the process of natural selection
1. Presence of advantageous alleles
2. Survival of the fittest
3. More likely to survive, reproduce and pass on genes to offspring
4. Frequency of allele increases
5. Leads to evolution
2. Survival of the fittest
3. More likely to survive, reproduce and pass on genes to offspring
4. Frequency of allele increases
5. Leads to evolution
52
New cards
What is evolution?
The gradual change in species over time, leads to diversity of living organisms on earth
53
New cards
What is directional selection?
Where individuals with alleles for characteristics of an extreme type are more likely to survive and reproduce, this could be in response to an environmental change
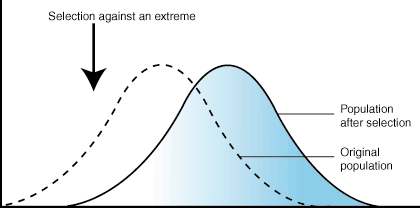
54
New cards
What is stabilising selection?
Where individuals with alleles for characteristics towards the middle of the range are more likely to survive and reproduce, occurs when environment isn't changing and it reduces the range of possible characteristics
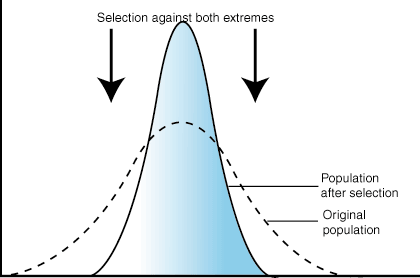
55
New cards
What is phylogeny?
The study of evolutionary history of groups of organisms
56
New cards
What do phylogenic trees show? Draw an example
Closely related species diverged away from each other more recently
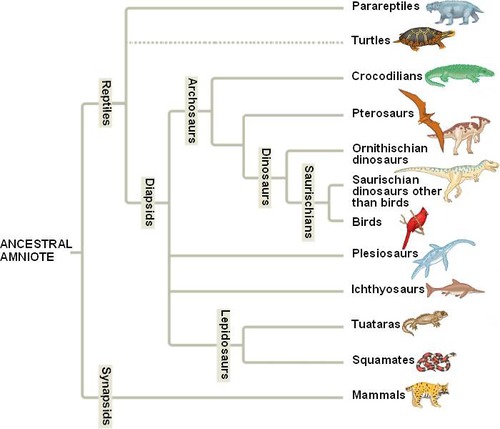
57
New cards
What is taxonomy?
The science of classification, naming organisms and putting them into groups
58
New cards
What is speciation?
The production of a new species
59
New cards
What does phylogenetic classification show?
Organises species on how closely they are related
60
New cards
Name the groups of classification
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
61
New cards
As you go down the groups of classification, what happens?
More groups, but fewer organisms in each group, organisms in each group become more closely related
62
New cards
Why are classification systems constantly being updated?
Discoveries of new species and new evidence about known organisms (e.g. DNA sequencing data)
63
New cards
What taxons does the binomial naming system use? And why is this system used?
Genus and species, universal
64
New cards
How do you write out a binomial name properly?
First - genus, second - species, in italics or underlined, 1st letter - uppercase, 1st letter of second word - lowercase
65
New cards
What is courtship behaviour?
Behaviour carried out by organisms to attract a mate of the same species
66
New cards
Name 2 simple courtship behaviours
Releasing a chemical using sound, visual displays
67
New cards
Name 2 complex courtship behaviours
Dancing, building
68
New cards
Who carries out courtship behaviours?
Male or female, may sometimes involve both sexes
69
New cards
How can courtship behaviour be used to classify species?
Courtship behaviour is species specific, the more closely related a species is, the more similar their courtship behaviour
70
New cards
Define biodiversity
Number of different ecosystems and communities of organisms, number of different species and degree of genetic diversity within those species
71
New cards
Define habitat
Place where an organism lives
72
New cards
Define community
All the different species that live together in a habitat
73
New cards
What is species richness?
A measure of the number of different species in a community
74
New cards
What is the index of diversity? And how is it calculated?
Relationship between number of species in a community and number of individuals in a species
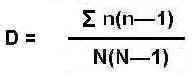
75
New cards
How is agriculture threatening biodiversity?
Woodland clearance, hedgerow removal, pesticides, herbicides, monoculture
76
New cards
How can diversity be investigated?
1. Frequency of measurable or observable characteristics
2. Base sequence of DNA / immunology
3. Base sequence of mRNA
4. Amino acid sequence of proteins encoded by DNA and mRNA
2. Base sequence of DNA / immunology
3. Base sequence of mRNA
4. Amino acid sequence of proteins encoded by DNA and mRNA