Scapula
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are the articulations of the scapula?
clavicle: acromioclavicular joint
humerus: glenohumeral joint
Describe the scapula’s Angles, borders, surfaces, fossa and processes
3 angles:
lateral: Bears the glenoid cavity
superior: Near C7/T1 spinous process
inferior: near T7 spinous process (important palpation landmark)
3 borders:
superior: contains the suprascapular notch (for= suprascapular nerve)
lateral: Thick, extends from glenoid cavity to inferior angle
medial: Parallel to the spine
2 surfaces: costal and posterior
3 processes: Acromion, Spine and
coracoid process3 Fossa:
Supraspinous fossa: superior to spine (posterior)
Infraspinous fossa: inferior to spine, larger (posterior)
Subscapular fossa - in the costal surface of the scapula
What are the key landmarks of the scapula?
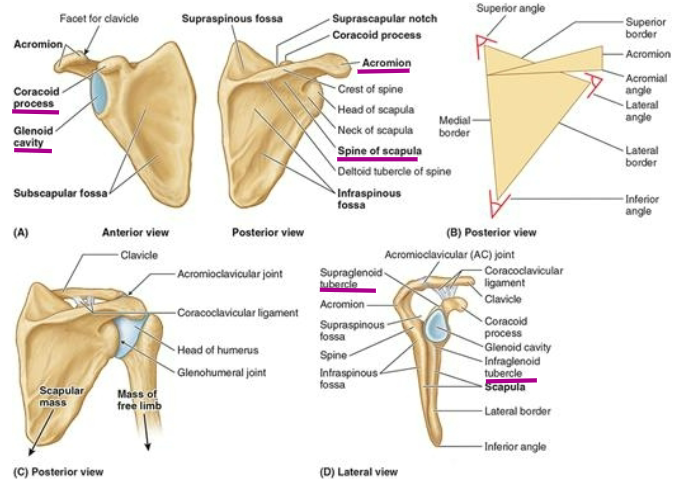
What does the acromion provide attachements for?
Provides attachment for deltoid and trapezius
What does the Supraglenoid tubercle provide an origin for?
origin of the long head of biceps brachii
What does the Infraglenoid tubercle provide an origin for?
origin of long head of triceps brachii
What does the Coracoid Process provides attachment for?
attachment for pec minor, coracobrachialis and short of the biceps
Describe the Scapulothoracic Joint. Why it is important. and purpose
NOT a true synovial joint
functional articulation between the scapula and the posterior thoracic wall.
Provides stability and mobility of entire shoulder
Purpose:
Allows ROM of upper extremity,
provides a stable base for GH joint
dissipates forces
List out the motions of the scapula
Elevation/Depression
Protraction/Retraction
Upward/Downward Rotation
Anterior/Posterior Tilt, Internal/External Rotation (subtle but important)
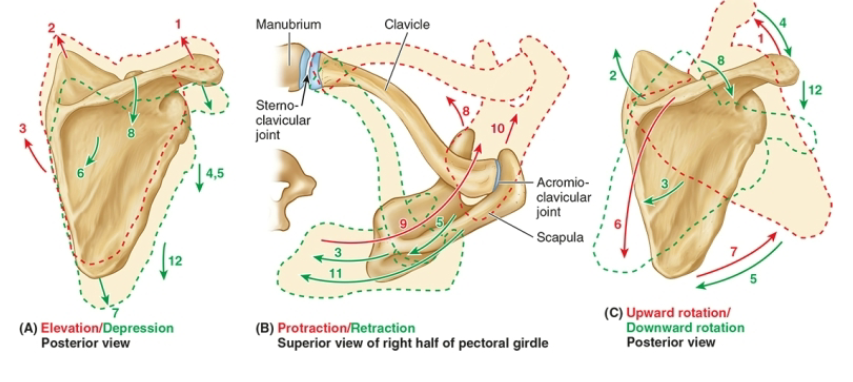
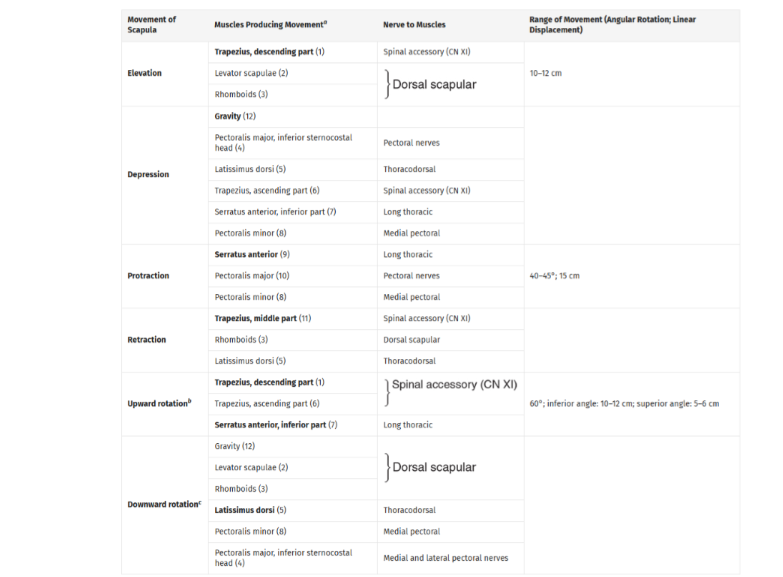
Describe the muscles used for each type of motion that the scapula can do (elevation, depression, protraction, retraction, upward/downward rotation)
Describe the extrinstic and intrinsic muscles acting on the scapula
Extrinsic Muscles Acting on the Scapula (Movers and Stabilizers):
Trapezius
Latissimus dorsi
Rhomboid Major and Minor
Levator Scapulae
Serratus Anterior
Pectoralis Minor
Intrinsic Muscles originating from the scapula (Scapulohumeral/Rotator cuff)
Deltoid
Teres Major
Rotator Cuff muscles (SITS)
List out the origin, insertion, innervation and action of Serratus Anterior
Origin: outer surface of the ribs 1-8/9
Insertion: Entire medial border of scapula
(anterior surface)Innervation: Long thoracic nerve (C5,C6,C7)
Actions:
Protraction of the scapula:
Upward rotation of scapula (upper fibers)
holds scapula against thoracic wall
What is scapula winging?
Defect in the Serratus Anterior;
leads to weak protraction and inability to hold scapula to rib cage causing the medial border to protrude
Describe impingement syndrome (of serratus anterior)
weakness/ dysfunction of Serratus anterior
reduces upward rotation of scapula → superior displacement of humerus and impingement of rotator cuff tendons under acromion
List out the origin, insertion, innervation and action of Pectoralis Minor
Origin: Ribs 3-5 (anterior surface)
Insertion: Coracoid process of scapula
Innervation: Medial pectoral nerve (C8,T1)
Actions: Depresses scapula, protracts scapula, downward rotation of scapula, accessory muscle of inspiration
What are intrinsic muscles crucial for?
glenohumeral joint stability and movement
What is the origin, insertion, innervation and action of deltoid
Origin: Spine of scapula, acromion, lateral clavicle
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Innervation: Axillary nerve (C5,C6)
Actions: Major abductor of the humerus (all fibers)
Anterior fibers(Clavicular): flexion, medial rotation of arm
Middle fibers (Acromial): abducts arm
Posterior fibers (Spinal): extension, lateral rotation of arm
Describe the biomechanics of abduction of arms? Describe the biomechanics of swinging limbs during walking? How does the deltoid help stabilization during movement of upper limb? How do we clinically test the deltoid’s function?
Abduction: Supraspinatus initiate first 15 degrees of abduction →followed by abduction of deltoid
Swinging:
anterior part of deltoid: assists the pectoralis major in flexing the arm
Posterior part of deltoid: assists the latissimus dorsi in extending the arm
Deltoid’s role in stabilization:
helps stabilize glenohumeral joint → hold head of humerus in glenoid cavity during movements of the upper limb
Clinical:
the arm is abducted, starting from approximately 15°, against resistance
List out the origin, insertion, innervation and actions of Teres Major
Origin: Dorsal surface of inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: Medial lip of intertubercular groove of humerus
Innervation: Lower subscapular nerve (C5,C6)
Actions: Extends, Adducts, Medially rotates humerus
What is the SITS muscle crucial for? How are they arranged? Combined function of the SITS?
Critical for dynamic stability of the glenohumeral joint
Arrangement:
SITS muscles pass laterally to engulf the head of the humerus
Tendons attach to greater and lesser tubercles
Function:
“grasp” and pulls large head of humerus medially, holding it against the smaller glenoid cavity of scapula
SITS’ Tendons + fibrous layer of capsule → musculotendinous rotator cuff → reinforces the capsule on three sides (anteriorly, superiorly, and posteriorly) → providing active support for the joint
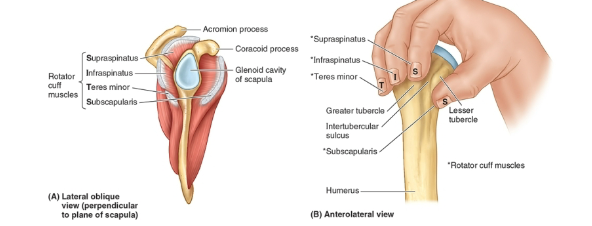
What is the origin, insertion, innervation, and action of the Supraspinatus
Origin: Supraspinous fossa
Insertion: Greater tubercle of humerus
Innervation: Suprascapular nerve (C5,C6)
Action: Initiates abduction (first 15 degrees) of the arm
What is the origin, insertion, innervation, and action of the Infraspinatus
Origin: Infraspinous fossa
Insertion: Greater tubercle of humerus
Innervation: Suprascapular nerve (C5,C6)
Action: Primary lateral rotator of humerus
What is the origin, insertion, innervation, and action of the Teres Minor
Origin: posterior surface of scapula adjacent to lateral
border of scapulaInsertion: Greater tubercle of the humerus
Innervation: Axillary nerve (C5,C6)
Action: Lateral rotator of the humerus
What is the origin, insertion, innervation, and action of the Subscapularis
Origin: Subscapular fossa (anterior surface)
Insertion: Lesser tubercle of humerus
Innervation: Upper and Lower subscapular nerves (C5,C6,C7)
Action: Primary medial rotator of humerus
What forms the Suprascapular Forament? What passes through here?
Formation:
suprascapular notch of scapula + superior transverse scapular ( suprascapular) ligament) → converts notch into a foramen)
Suprascapular nerve pass through the foramen
Suprascapular artery and vein pass superior to suprascapular ligament
ARMY over NAVY
What are the boundaries of the Quadrangular space? What passes through it?
Boundaries
Inferior margin of teres minor
Surgical neck of humerus
Superior margin of teres major
Lateral margin of long head of triceps brachii
Vessels passing through:
Axillary nerve
Posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein
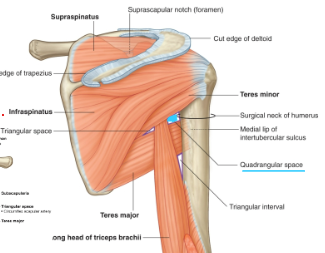
Causes and symptoms of Quadrangular space syndrome
impingement of axillary nerve (hypertrophy of muscles or fibrosis of muscle edges) → weakness of deltoid muscle; atrophy of teres minor (affects control that the rotator cuff muscles exert on shoulder movement)
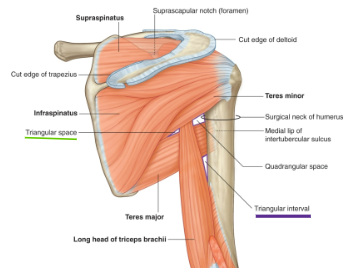
What are the boundaries of the Triangular space? What passes through it?
Boundaries
Medial margin of the long head of the triceps brachii
Superior margin of the teres major
Inferior margin of the teres minor
Structures passing through
Circumflex scapular artery and vein
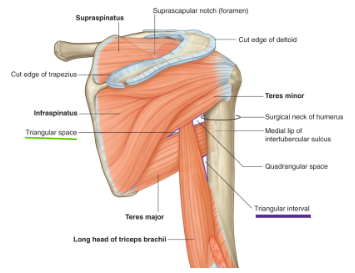
What are the boundaries of the Triangular interval? What passes through it?
Boundary:
Inferior portion of Teres Major
Medial Side of humerus
Lateral side of Triceps Brachii
Structures passing through
Radial nerve
Profunda brachii artery (deep artery of the arm) and veins
Describe the route and innervation of Suprascapular nerve
Superior Trunk of Brachial Plexus → Passes posteriolaterally through suprascapular foramen → Posterior Sapular region → Innervates supraspinatus → Pass through spinoglenoid notch (between root of spine and glenoid cavity) → Innervates Infraspinatus
Describe the route and innervation of Axillary Nerve
(cutaneous branch?)
Posterior cord of Brachial Plexus → exits Axilla via passing through Quadrangular Space → Post. Scapular region → Innervates Deltoid/Teres Minor
Related to surgical neck of humerus with the posterior circumflex humeral artery
Cutaneous branches (superior lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm) – carries general sensation from skin over inferior part of deltoid muscle
Causes and symptoms of Axillary Nerve Damage?
Axillary nerve damage → atrophy of Deltoid and Teres minor
Causes:
Surgical neck fracture of humerus
Anterior shoulder dislocation
Improper use of crutches
Symptoms:
Flattened appearance of shoulder
Loss of sensation over lateral side of proximal arm supplied by superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (cutaneous branch of axillary nerve)
Describe the route and supply of Suprascapular artery
from base of neck as branch of thyrocervical trunk (branch of subclavian artery)
Enters posterior scapular region superior to
suprascapular foramenSupply the supraspinatus and infraspinatu
Describe the route and supply of Posterior circumflex humeral artery
from the third part pf the axillary artery in the axilla.
Leave axilla through quadrangular space with axillary nerve and enter posterior scapular region
Describe the route and supply of Circumflex scapular artery
branch of subscapular artery from third part of axillary artery
Leaves axilla through triangular space and enter posterior scapular region, pass through the origin of the teres minor muscle and form anastomosis with other arteries
What is Scapular dyskinesis? Describe the affected muscles of : inferior angle prominence, medial border prominence, early/excessive elevation/ Limited upward rotation;
Any alteration in the position or motion of the scapula during static posture or dynamic shoulder movements
Common patterns:
Inferior angle prominence
tight pectoralis minor, weak lower trapezius/serratus anterior
Medial border prominence:
Classic scapular winging (weak serratus anterior/long thoracic nerve)
Early/Excessive Elevation:
Overactive upper trapezius, levator scapulae
Limited Upward Rotation:
tight downward rotators (rhomboids, levator scapulae, pectoralis minor)
or weak upward rotators (serratus anterior, upper/lower trapezius)
Describe Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Scapular dysfunction → scapula fails to rotate upwards and tilt posteriorly → acromion does not move out of the way → leads to compression of the rotator cuff tendons (especially supraspinatus) and bursa under the acromion during overhead movements
In a rotator cuff tear, what muscle is the most commonly ruptured?
Supraspinatus
Who is most commonly affected with degenerative tendonitis?
Elderly people
Describe the consequences of a Nerve Entrapment of the Long Thoracic Nerve?
leads to Serratus anterior palsy and classic scapular winging
Describe the consequences of a Nerve Entrapment of the Dorsal Scapular nerve; how can it be entrapped?
Affects rhomboids and Levator scapulae. Can be entrapped by Scalenes
Describe the consequences of a Nerve Entrapment of the Suprascapular nerve
Nerve compression via ligament or muscle as it passes through the suprascapular foramen → affecting
supraspinatus/infraspinatus → difficulty initiating abduction and
weak lateral rotation of the arm
Describe how the brachial plexus could be entrapped?
can be compressed by tight pectoralis minor in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome