Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Strategies in Marketing
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Segmentation Methods
Different methods used to divide a market into distinct groups.
Geographic Segmentation
Grouping the market by country, region, or specific areas like state, city, or neighborhoods.
Demographic Segmentation
The most common segmentation strategy based on easily identifiable and measurable characteristics like age, gender, income, and education.
Psychographic Segmentation
Segmentation based on how consumers describe themselves in terms of self-values, lifestyle, and self-concept.
Benefit Segmentation
Dividing the market into segments based on the benefits that the product provides to satisfy needs and wants.
Behavioral Segmentation
Segmenting the market based on consumer behavior, including occasion and loyalty segmentation.
Occasion Segmentation
Segmentation based on when a product or service is purchased or consumed.
Loyalty Segmentation
Identifying loyal customers who are the most profitable in the long term.
Tapestry Segmentation System
A system that uses a combination of geographic, demographic, and lifestyle characteristics to classify consumers.
Segment Attractiveness
Criteria used to evaluate whether a market segment is worth pursuing.
Identifiable
Determining who is in the market and whether segments are distinct from one another.
Substantial
Assessing the size and buying power of a market segment to ensure it can generate sufficient profits.
Reachable
The ability to effectively communicate with and distribute products to the market segment.
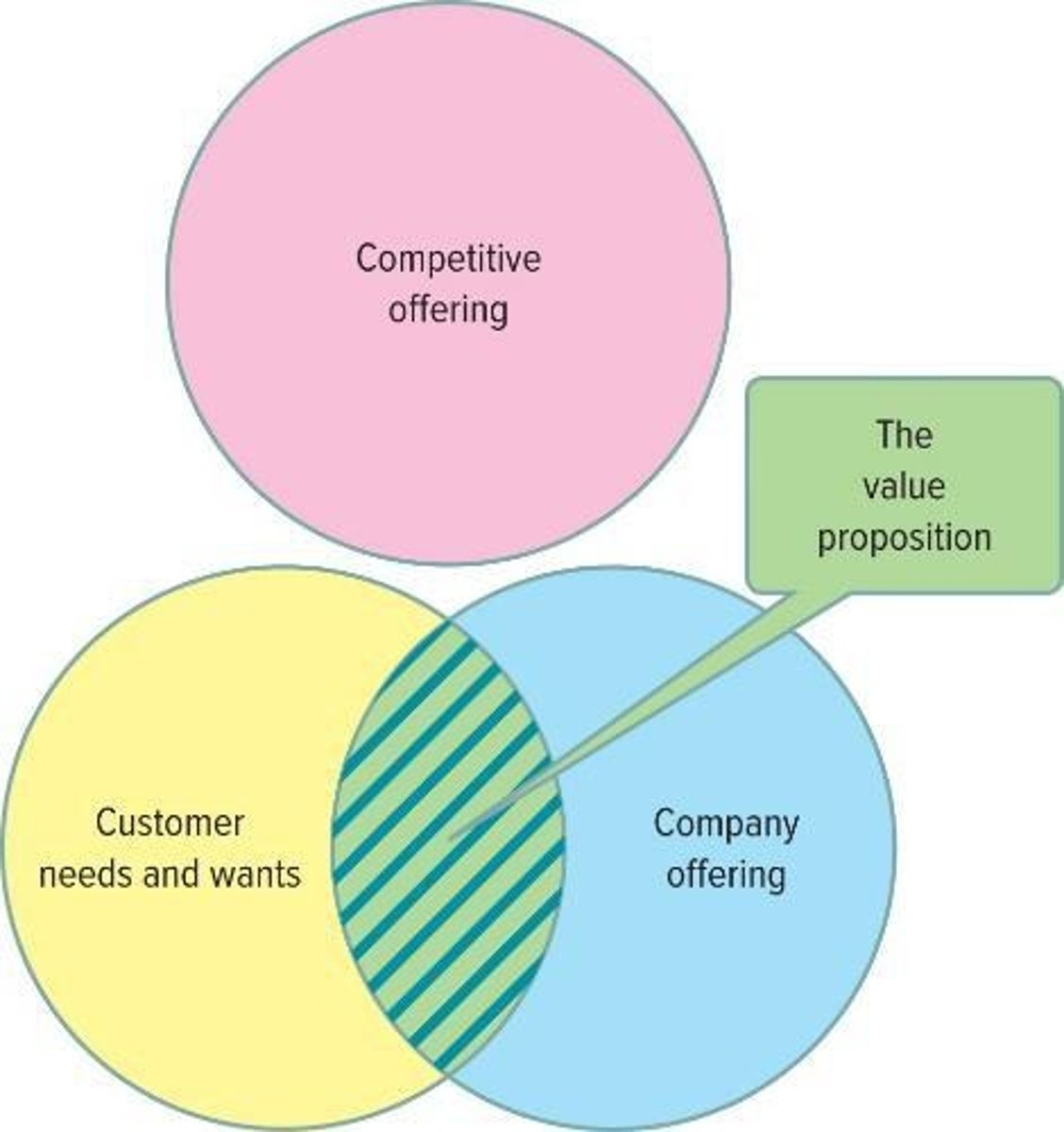
Value Proposition
The unique value a product or service offers to meet the needs of a target market.
Positioning
The process of establishing a brand or product in the minds of consumers relative to competitors.
SWOT Analysis
A strategic planning tool that identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Market Segment
A subgroup of a larger market that shares similar characteristics or needs.
Marketing Mix
The combination of product, price, place, and promotion strategies used to market a product.
Food Marketers
Professionals who segment food products based on consumer preferences, such as meat inclusion in pasta sauces.
Consumer Recognition
The awareness and understanding consumers have about a product and its benefits.
Buying Power
The financial ability of a market segment to purchase products or services.
Responsive
Customers must react similarly and positively to the firm's offering.
Profitable
Assess potential profitability of each segment, both current and future.
Key factors for profitability assessment
Current market growth rate, future growth rate, market competitiveness, market access costs.
Segment
Children under 15.
Segment size
60 million (<15 yrs.).
Segmentation Adoption Percentage
35%.
Purchase Behavior
$500× 1 time purchase.
Profit margin %
10%.
Fixed Cost
$50M.
Target Market Selection
The key factor is the marketer's ability to pursue the market.
Targeting Strategies
Four different targeting strategies can be used.
Market positioning
Defining marketing mix variables so target customers have a clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does.
Positioning Methods
Value Proposition, Salient Attributes, Symbols, Competition.
Perceptual Map
A perceptual map displays, in two or more dimensions, the position of products or brands in the consumer's mind.
Ideal Points
Where a particular market segment's ideal product would lie on the map.
Geodemographic segmentation
Uses a combination of geographic, demographic, and lifestyle characteristics to classify consumers.
Segmentation process
Involves step 1: establish strategy or objectives and step 2: use segmentation methods.
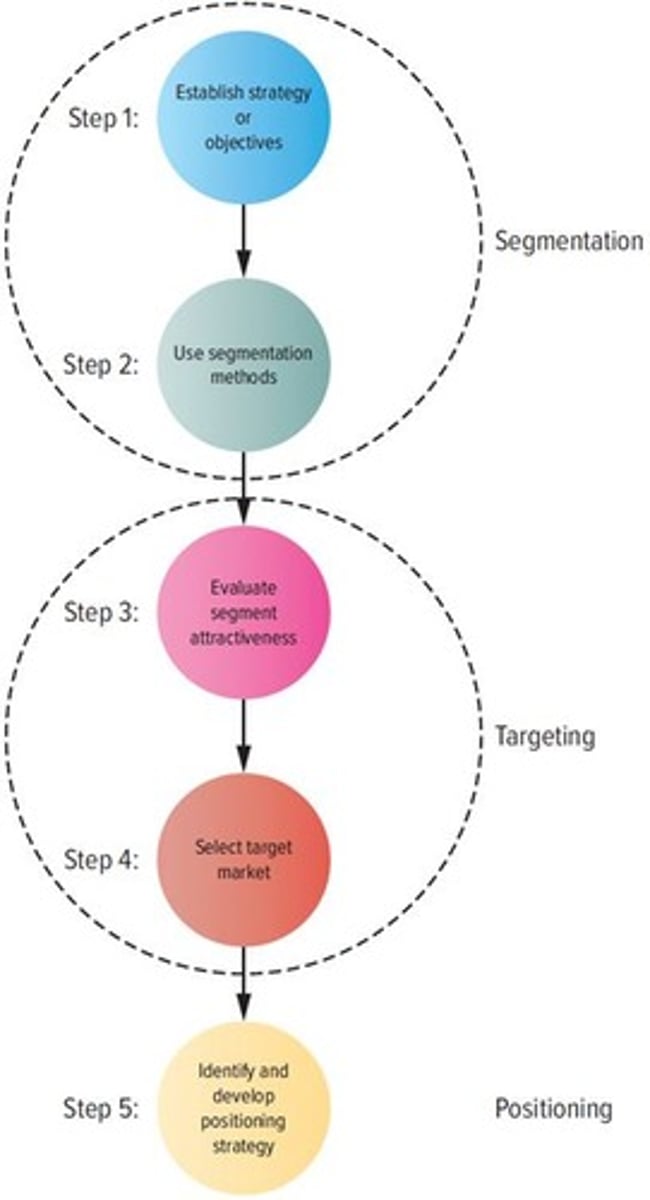
Targeting process
Involves step 3: evaluate segment attractiveness and step 4: select target market.
Positioning process
Involves step 5: identify and develop positioning strategy.
Firm's value proposition
The unique value a firm promises to deliver to its customers.
Customer's unmet needs
Identifies marketing opportunities based on what customers require but are not currently receiving.
Firm's benefits that are not required
Benefits that may educate customers or redesign products but are not essential.
Key benefits
Benefits that both the firm and competitor provide that customers require, necessitating careful performance monitoring.
Competitor's value proposition
The unique value a competitor promises to deliver to its customers, which should be monitored and imitated if needed.
Benefits both firms provide that customers do not appear to need
Benefits that are offered by both the firm and competitor but are not essential to customers.
Competitor benefits that are not required
Benefits provided by competitors that customers do not require.
Perceptual Maps
Charts that plot products based on consumer preferences across different dimensions.
Sweet taste vs. light taste
Dimensions used in perceptual maps to categorize soft drinks.
Healthy vs. less natural
Dimensions used in perceptual maps to categorize soft drinks.
Market size indicators
Indicated by icon size on perceptual maps, representing the largest and smallest target markets.
Gatorade repositioning
Gatorade's strategy to introduce a new product and reposition itself within the sweet taste and healthy market.
