Ch. 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:25 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
heart circulates entire blood supply every ___
minute
2
New cards
three functions of the blood
transport, defense, regulation
3
New cards
___ in the blood carry things in the blood
lipoproteins
4
New cards
blood transports ___ from broken proteins to kidneys for elimination
nitrogen
5
New cards
some blood cells destroy pathogens by ___; engulfing the foreign particles
phagocytosis
6
New cards
some white blood cells produce and secrete ___
antibodies
7
New cards
blood clotting defense against blood loss are done by (2)
platelets; proteins
8
New cards
blood maintains its own water-salt balance through plasma’s salts and proteins which create ___
osmotic pressure
9
New cards
blood is a form of ___ tissue
liquid connective
10
New cards
two main elements of blood
formed elements, plasma
11
New cards
three main formed elements of blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
12
New cards
red blood cells are ___ micrometers, biconcave disks
6-8
13
New cards
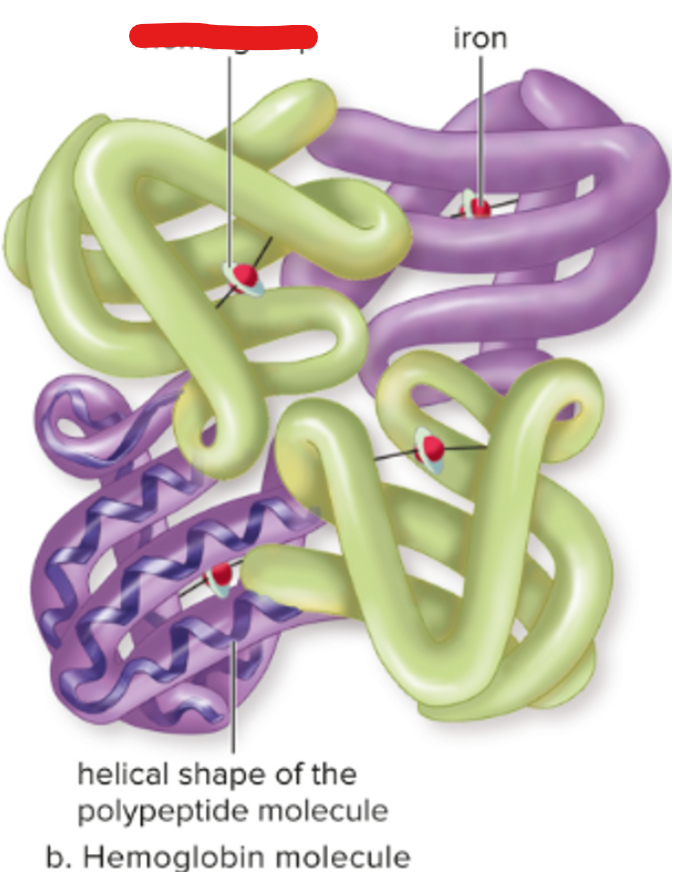
heme group
14
New cards
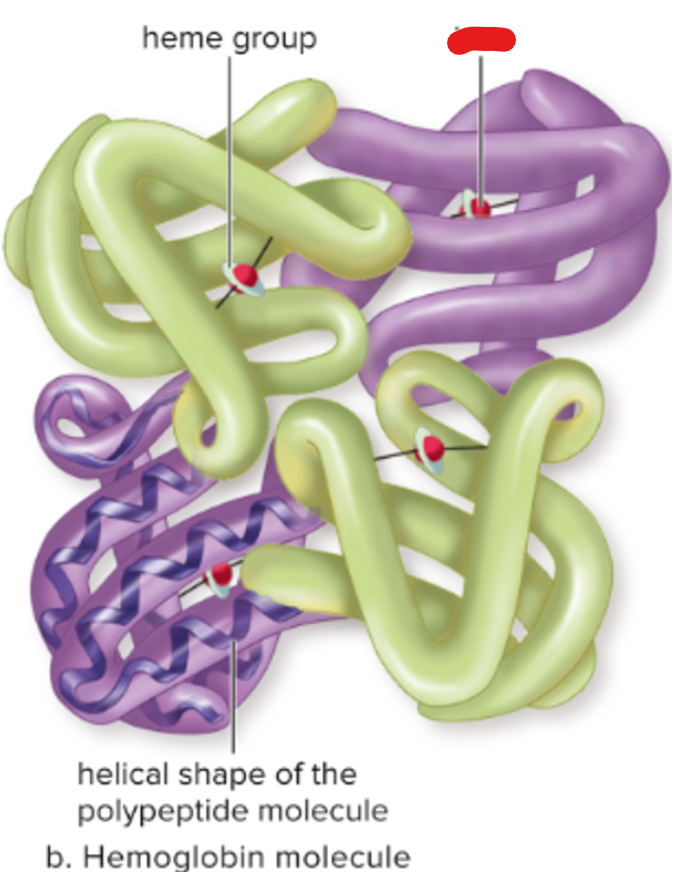
iron
15
New cards
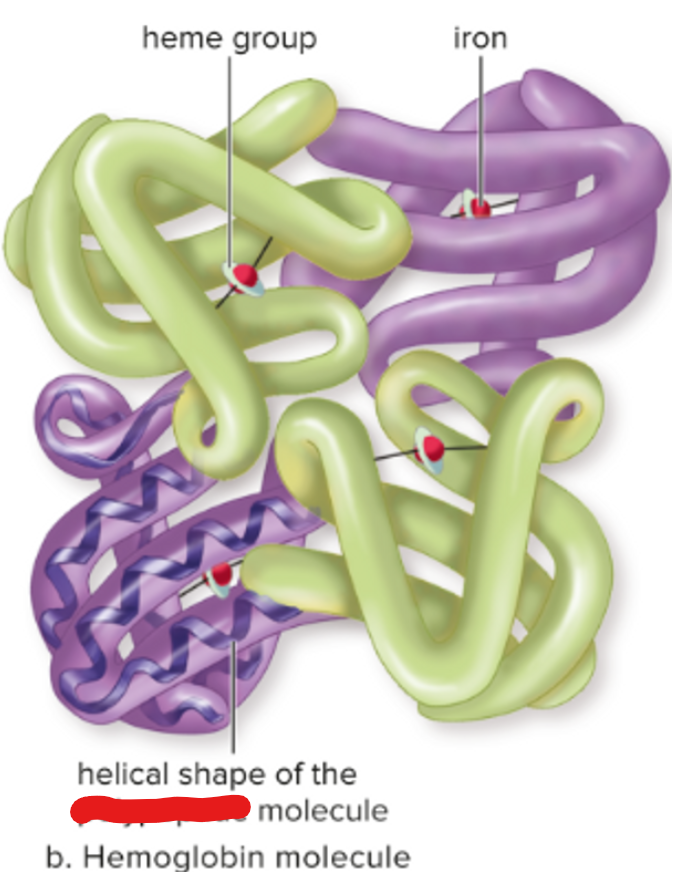
polypeptide
16
New cards
protein with four polypeptides in hemoglobin
globin
17
New cards
iron-containing group at the center of each chain; combines with oxygen
heme
18
New cards
heme does not easily let go of ___; why it is dangerous
CO
19
New cards
how many molecules of oxygen can each hemoglobin molecule transport
4
20
New cards
hemoglobin with oxygen
oxyhemoglobin
21
New cards
hemoglobin without oxygen
deoxyhemoglobin
22
New cards
can also carry carbon dioxide to keep the plasma CO2 levels at bay - hemoglobin is called
carbaminohemoglobin
23
New cards
plasma carries most CO2 as
bicarbonate
24
New cards
enzyme in plasma that speeds up reaction between carbon dioxide and carbonic acid
carbonic anhydrase
25
New cards
most RBCs live for ___ days
120
26
New cards
not enough RBCs = kidneys release ___ for more RBCs
erythropoietin
27
New cards
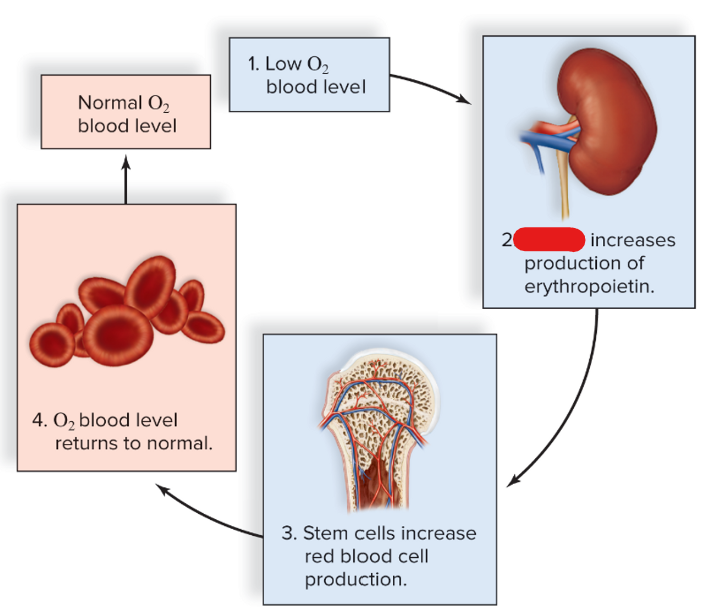
kidney
28
New cards
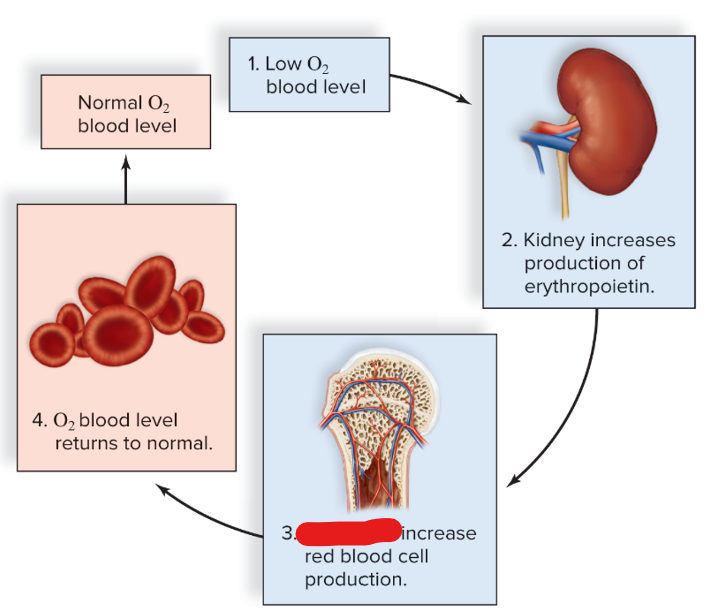
stem cells
29
New cards
breakdown of hemoglobin → waste product:
bilirubin
30
New cards
too much bilirubin leads to this disorder
jaundice
31
New cards
insufficient RBCs or insufficient hemoglobin (disorder)
anemia
32
New cards
rupturing of RBCs
hemolysis
33
New cards
sickle cell red blood cells which rupture as they pass through capillaries
sickle-cell disease
34
New cards
life expectancy of a sickled RBC (in days)
90
35
New cards
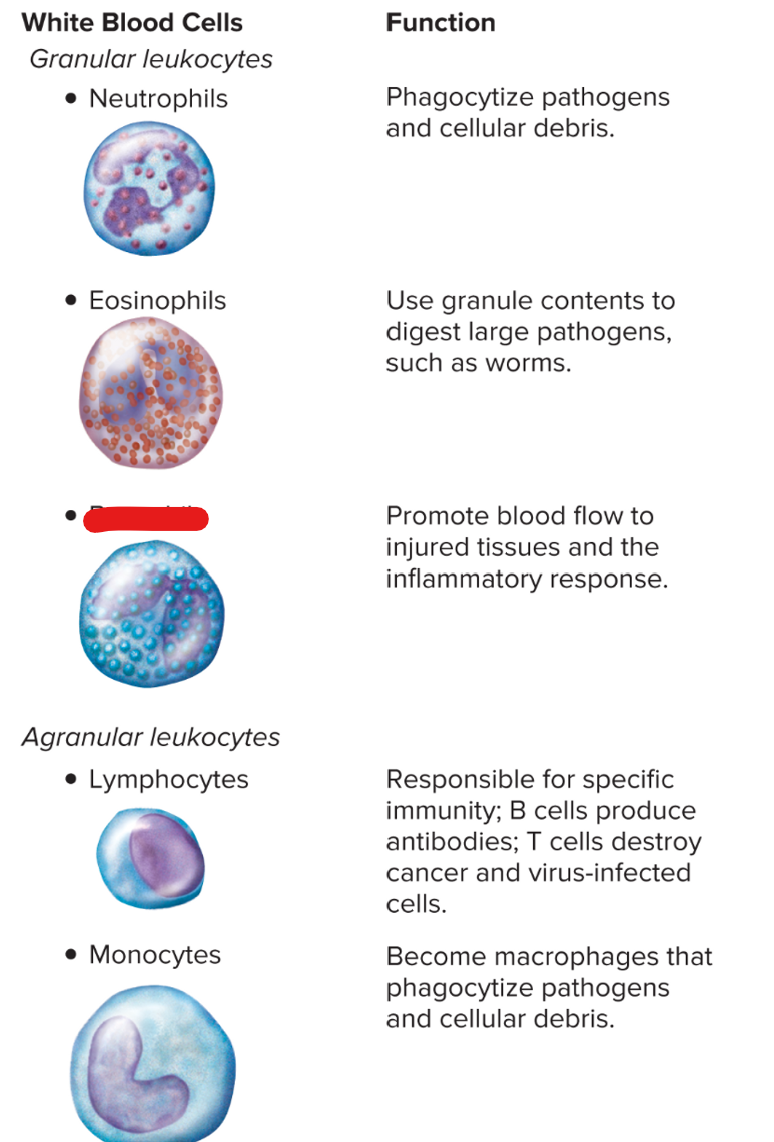
basophils
36
New cards
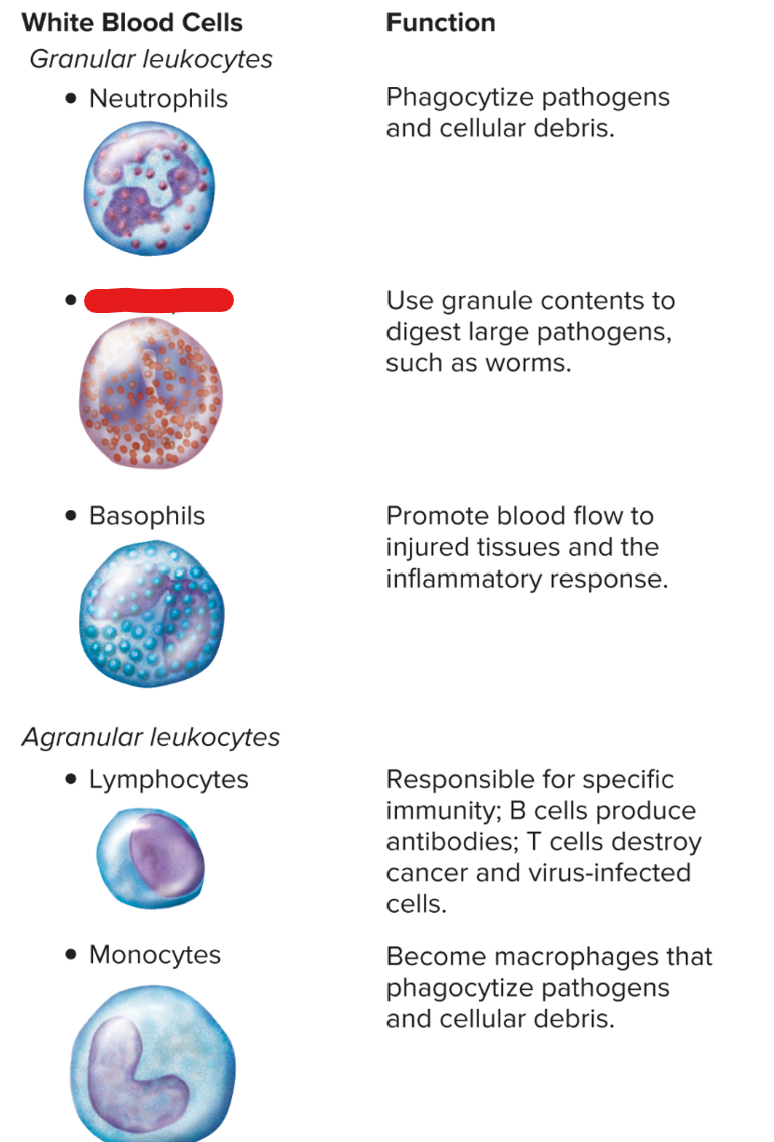
eosinophils
37
New cards
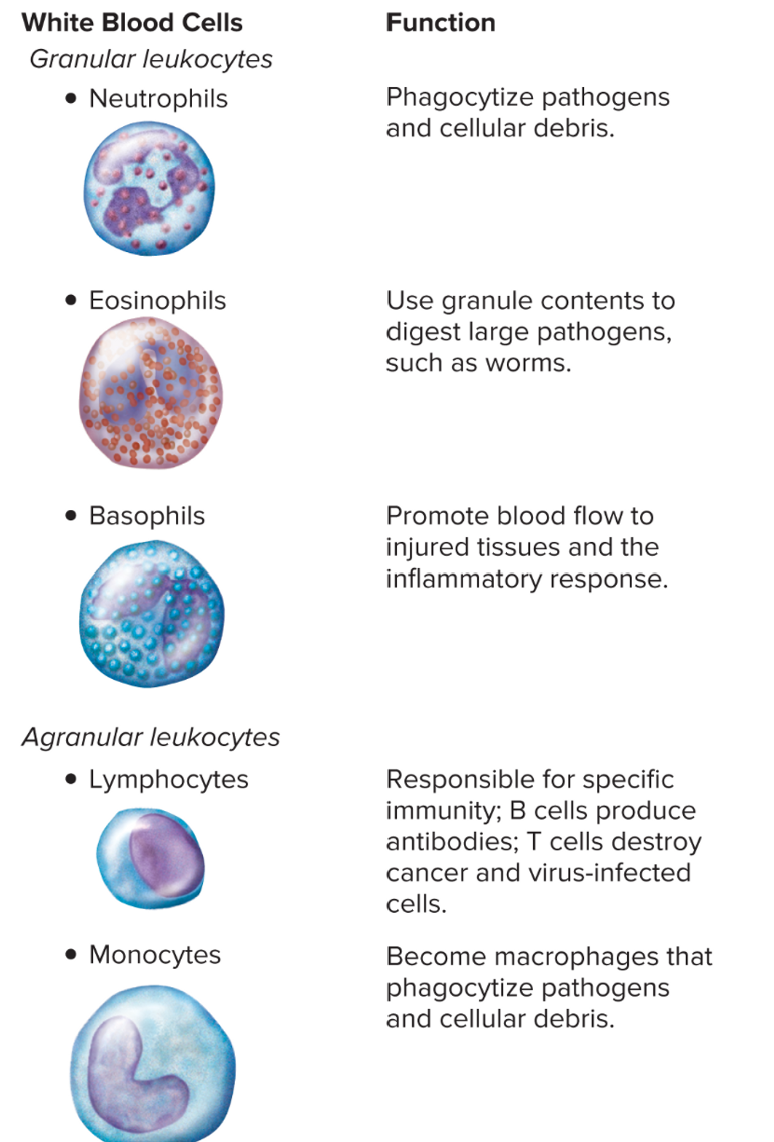
lymphocytes
38
New cards
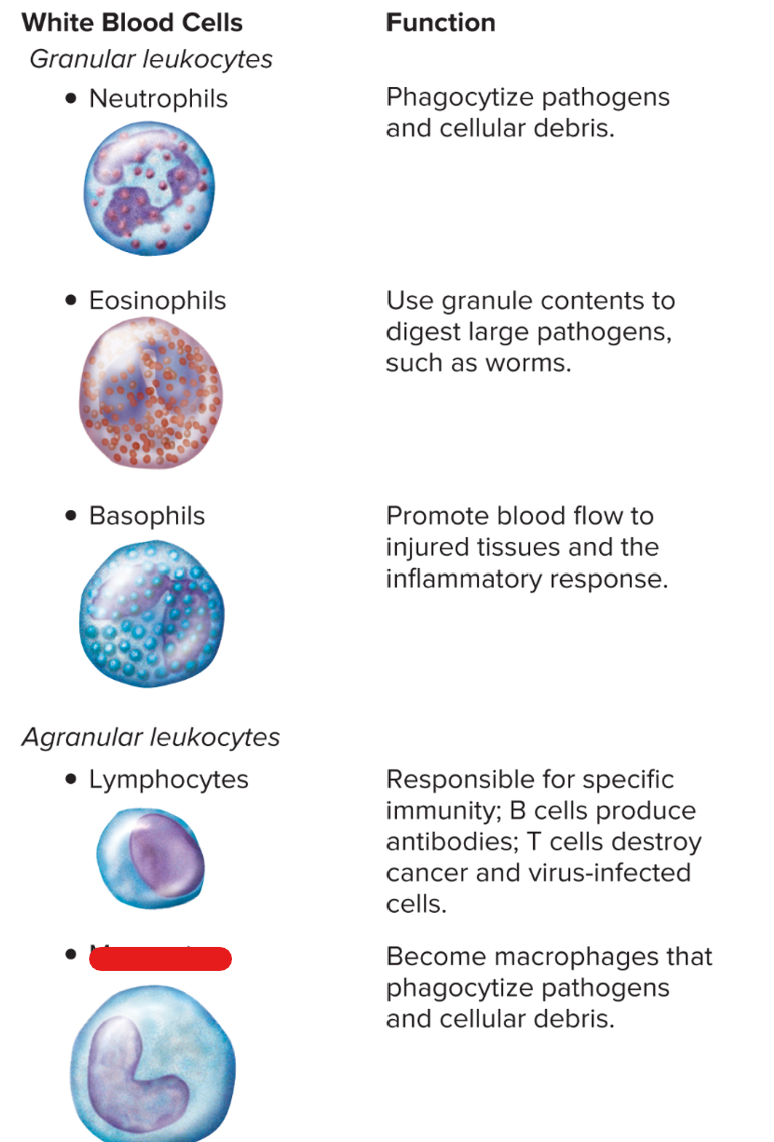
monocytes
39
New cards
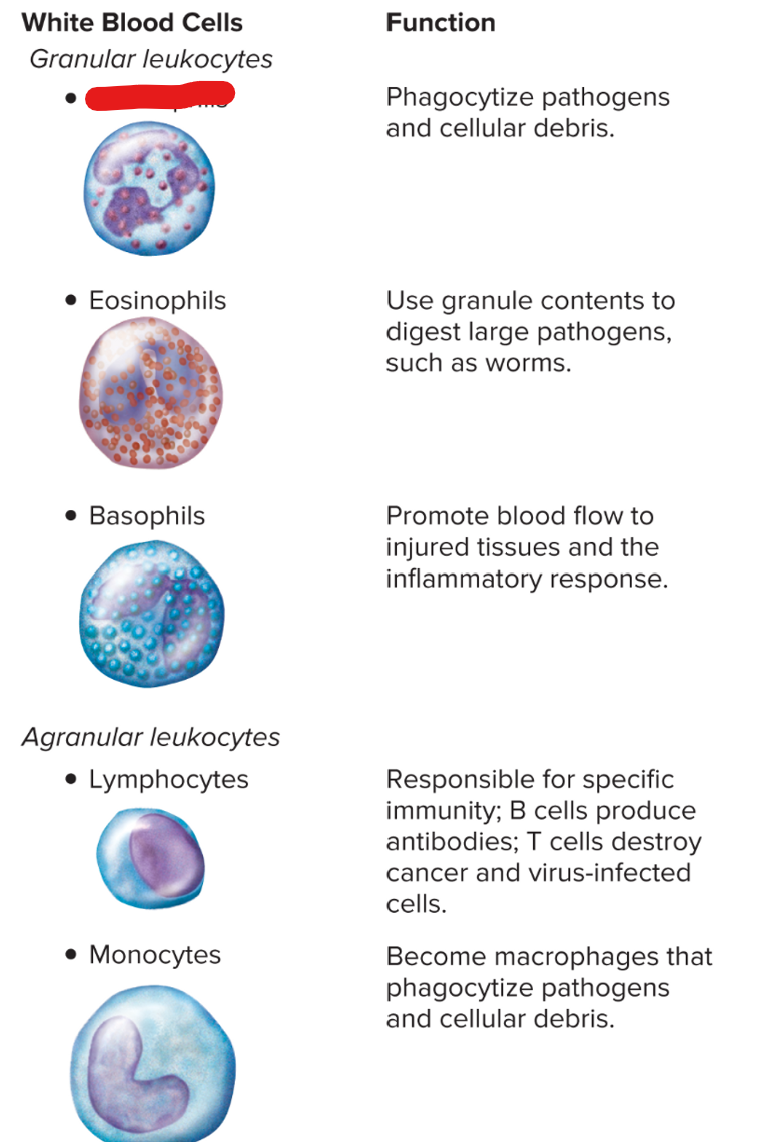
neutrophils
40
New cards
phagocytosis: surrounds pathogen → ___ with pathogen formed → lysosomes attach and empty enzymes into vesicle
vesicle
41
New cards
phagocytosis: vesicle with pathogen formed → ___ attach and empty enzymes into vesicle → enzymes break down pathogens
lysosomes
42
New cards
phagocytosis: lysosomes attach and empty enzymes into vesicle → ___ break down pathogens
enzymes
43
New cards
___: surrounds pathogen → vesicle with pathogen formed → lysosomes attach and empty enzymes into vesicle → enzymes break down pathogens
phagocytosis
44
New cards
foreign particles that combine with antibodies
antigens
45
New cards
type of WBC that has neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
granular leukocytes
46
New cards
type of WBC that has lymphocytes, monocytes
agranular leukocytes
47
New cards
50-70% of all WBCs
neutrophils
48
New cards
WBC: first responder; phagocytosis; multilobed
neutrophil
49
New cards
WBC: bilobed, large, for large parasites
eosinophil
50
New cards
WBC: U-shaped, produces histamine
basophil
51
New cards
produced by basophils for allergic reactions; can dilate vessels and constrict air passages
histamine
52
New cards
WBC for specific immunity, produces B cells and T cells
lymphocytes
53
New cards
lymphocytes produce these for antibodies
B cells
54
New cards
lymphocytes produce these to destroy pathogens; attacked by AIDs
T cells
55
New cards
WBC: largest, can stimulate other WBCs
monocytes
56
New cards
disorder: stem cells lack adenosine deaminase → lack B and T lymphocytes → can’t fight infections
severed combined immunodeficiency
57
New cards
enzyme that produces B and T lymphocytes in the bone marrow
adenosine deaminase
58
New cards
disorder: too many white blood cells
leukemia
59
New cards
disorder: infects lymphocytes
Epstein-Barr virus
60
New cards
platelets: fragmentation of ___ in the bone marrow
megakaryocytes
61
New cards
platelets + prothrombin + fibrinogen
coagulation
62
New cards
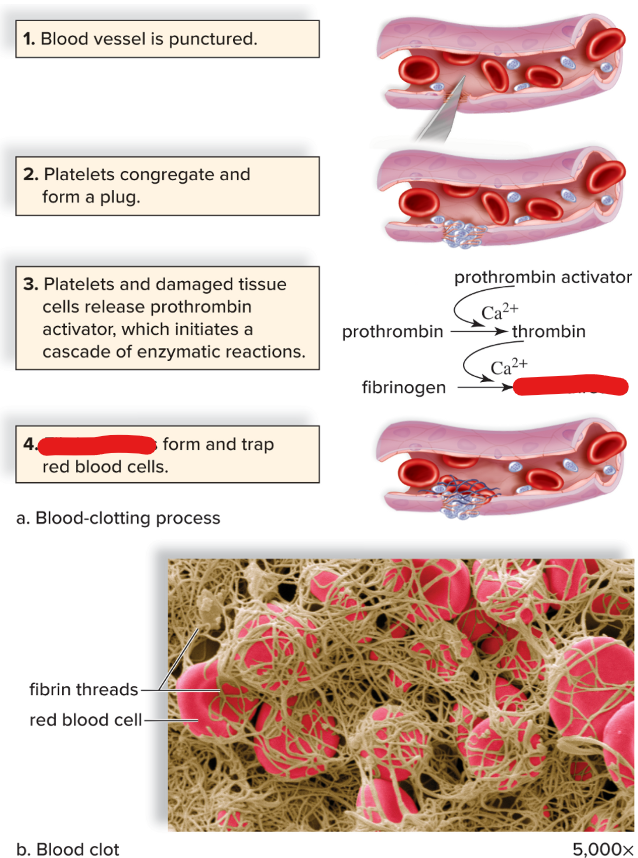
fibrin threads
63
New cards
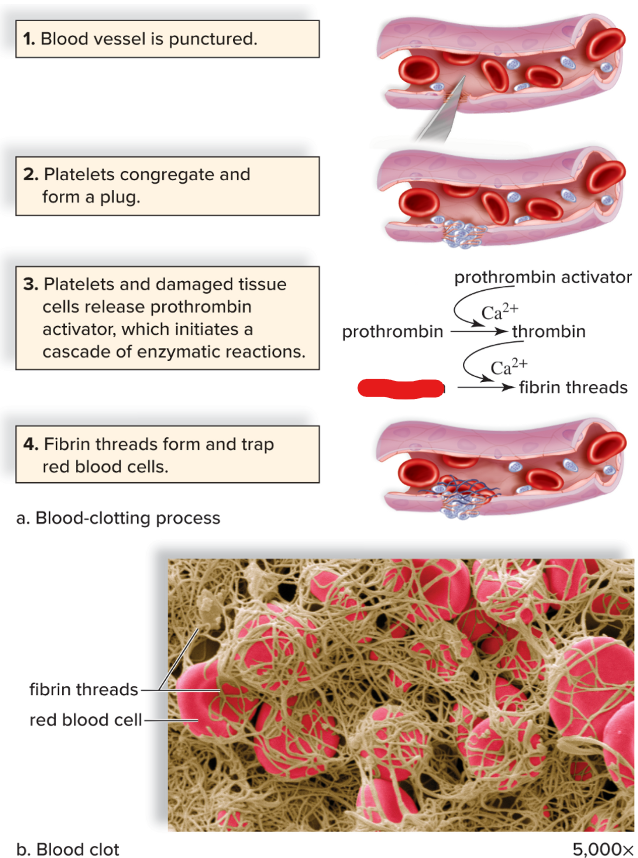
fibrinogen
64
New cards
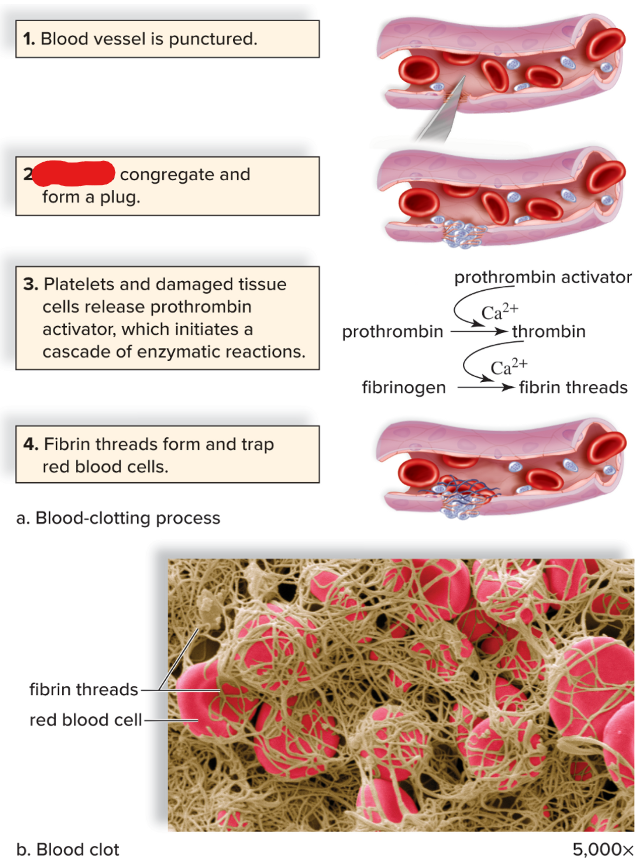
platelets
65
New cards
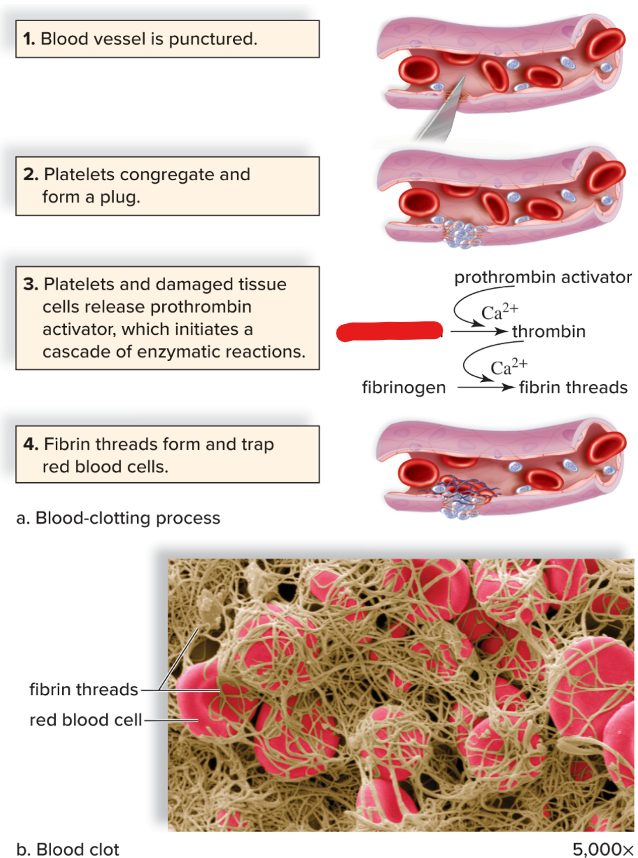
prothrombin
66
New cards
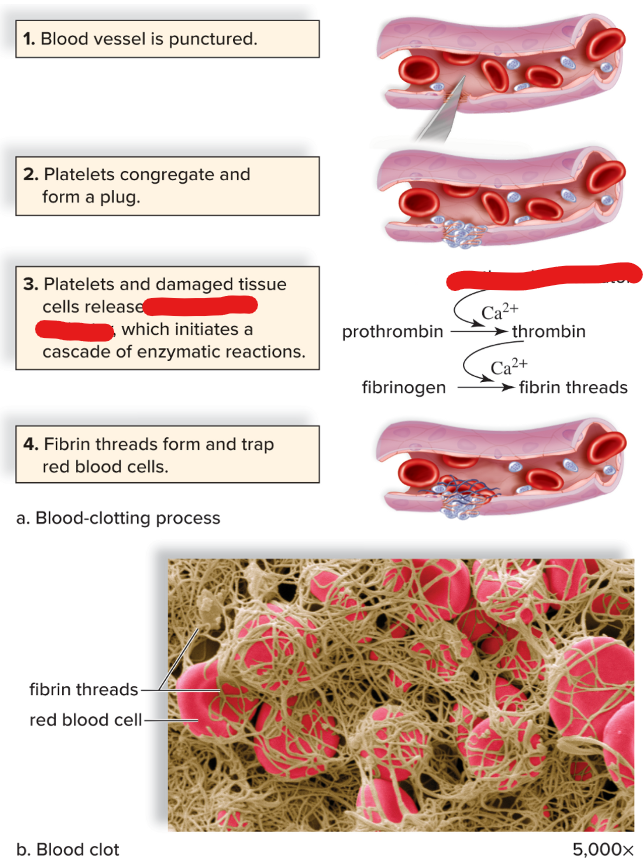
prothrombin activator
67
New cards
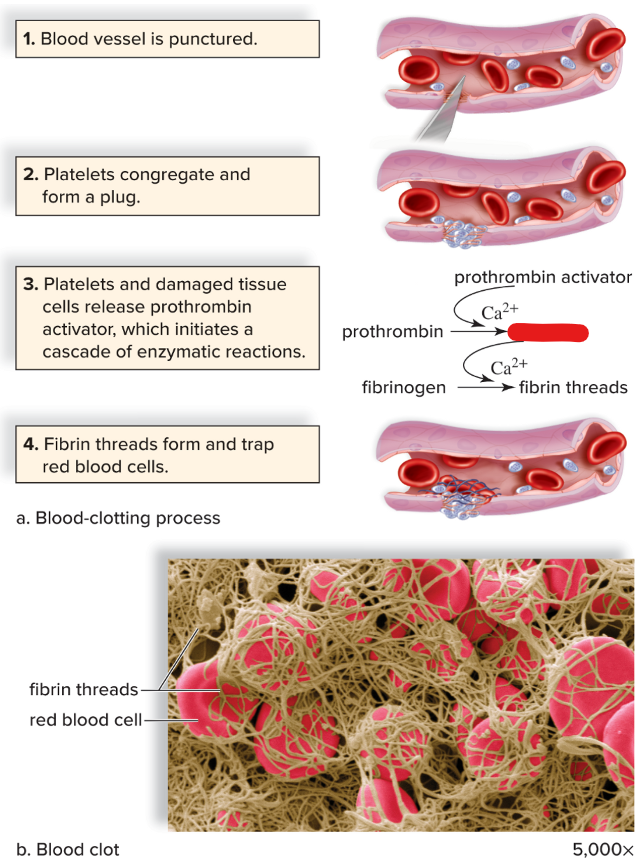
thrombin
68
New cards
clump at the side of vessel punctures to partially seal the leak
platelets
69
New cards
thrombin severs amino acids from fibrinogen; which form long threads of
fibrin
70
New cards
destroys fibrin once vessel repair starts
plasmin
71
New cards
escapes from a mature clot
serum
72
New cards
disorder: insufficient platelets
thrombocytopenia
73
New cards
disorder: spontaneous clots
thrombi
74
New cards
if a thrombus dislodges and travels in the vessel
embolus
75
New cards
if an embolus blocks a blood vessel it’s called
thromboembolism
76
New cards
disorder: caused by a deficiency in a clotting factor
hemophilia
77
New cards
cells that are able to easily differentiate that are produced in the red bone marrow
stem cells
78
New cards
91% of blood plasma is this
water
79
New cards
what do most of the salts in the plasma do
buffer
80
New cards
2 main examples of organic molecules found in blood plasma
amino acids, glucose
81
New cards
organic molecules produced by liver and act as a buffer
plasma proteins
82
New cards
three types of plasma proteins
albumins, globulins, fibrinogen
83
New cards
plasma protein that is the most abundant and establishes osmotic pressure and helps with transportation
albumins
84
New cards
three types of globulins
alpha, beta, gamma
85
New cards
globulins that help with transportation
alpha, beta
86
New cards
globulins that are produced by lymphocytes
gamma
87
New cards
the plasma protein that helps with blood clotting
fibrinogen
88
New cards
clumping of red blood cells
agglutination
89
New cards
blood types carry antigens, which is this type of protein
glycoprotein
90
New cards
blood types
A, B, AB, O
91
New cards
blood type with the A antigen and B antibody
A
92
New cards
blood type with the A antibody and B antigen
B
93
New cards
blood type with both antigens
AB
94
New cards
blood type with no antigens
O
95
New cards
blood type with both antibodies
O
96
New cards
blood type with no antibodies
AB
97
New cards
when blood from one person is transferred to another
transfusion
98
New cards
how does cardiac muscle tissue play a role in the cardiovascular system’s contribution to homeostasis
circulate blood
99
New cards
how does smooth muscle tissue play a role in the cardiovascular system’s contribution to homeostasis
blood pressure
100
New cards
how does skeletal muscle tissue play a role in the cardiovascular system’s contribution to homeostasis
compress vessels