NPTE Neuro DD - SCI, CVA, TBI, MS, PD, MG, etc
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
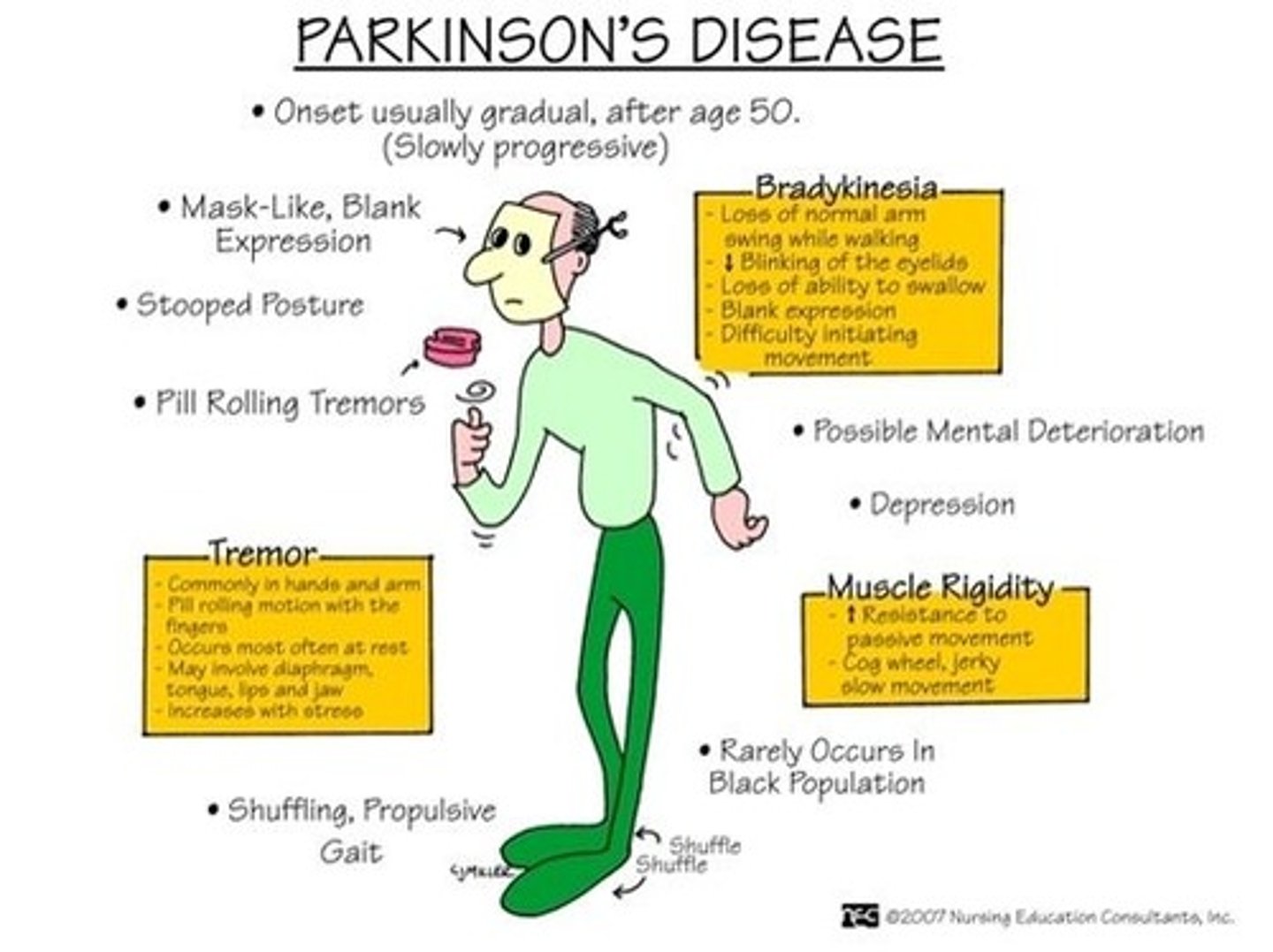
TRAP for Parkinson's
T- tremors (oscillatory movements)
R- rigidity, stiffness in limbs, neck or trunk
A- akinesia, loss or impairment in power of voluntary mvmnt
P- posture and balance
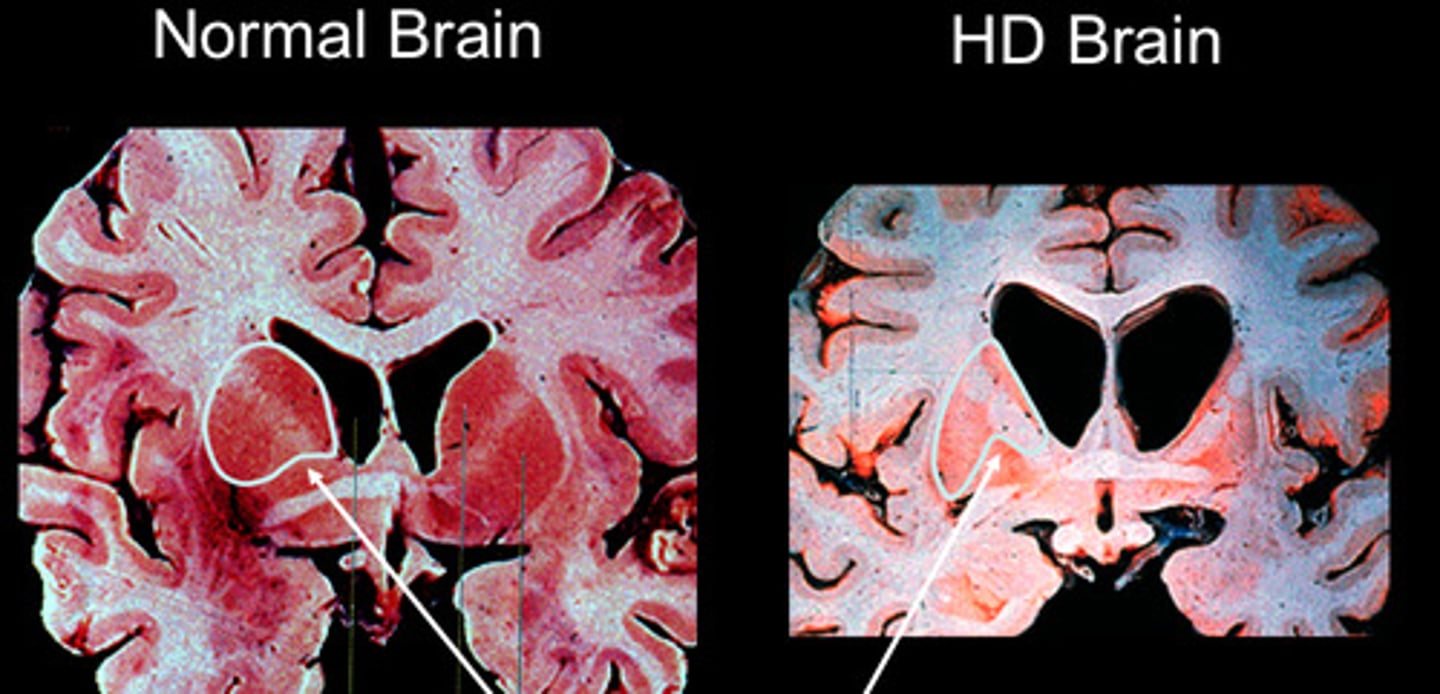
HuntinGton's disease
is Genetic!
-hereditary disease that is neurodegenerative
-autosomal-dominate illness
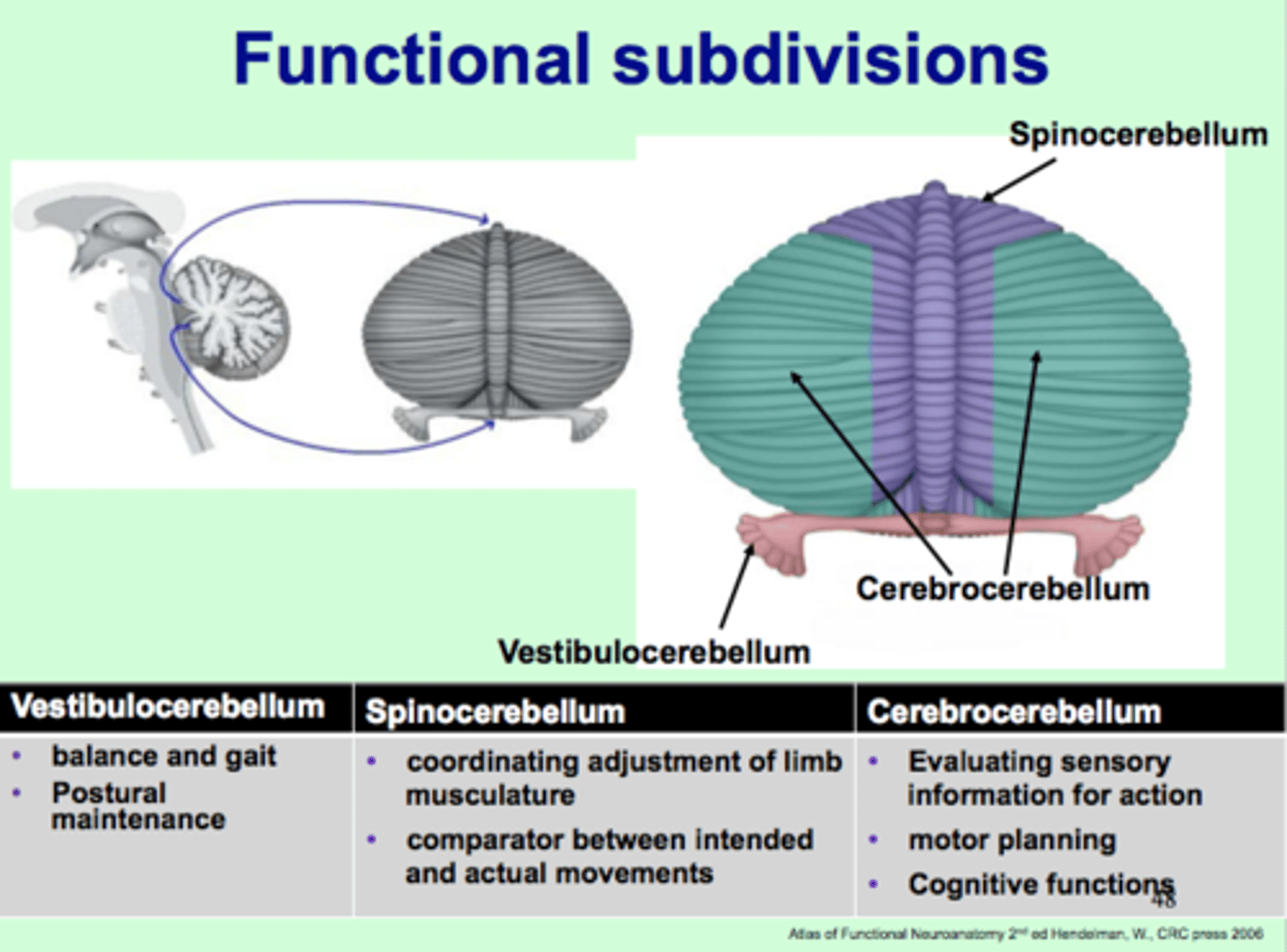
Cerebellar Disorders: three cerebellar regions are:
Vestibulocerebellum:
-eye movements = nystagmus
-balance and equilibrium = truncal ataxia
Spinocerebellum:
-gait ataxia
-limb ataxia
Cerebrocerebllum:
- decreased coordination of finger movement
Coordination testing for cerebellar disorders
-Finger to nose
-Heel to shine
(overshoot or undershoot = dysmetria)

Signs of cerebellar damage = VANISHED
V- vertigo
A- ataxia
N- nystagmus
I- intentional tremor
S- slurred speech
H- hypotonia
E- exaggerated broad based gait (ataxia)
D- dysdiadochokinesia (unable to do rapid alternating movements
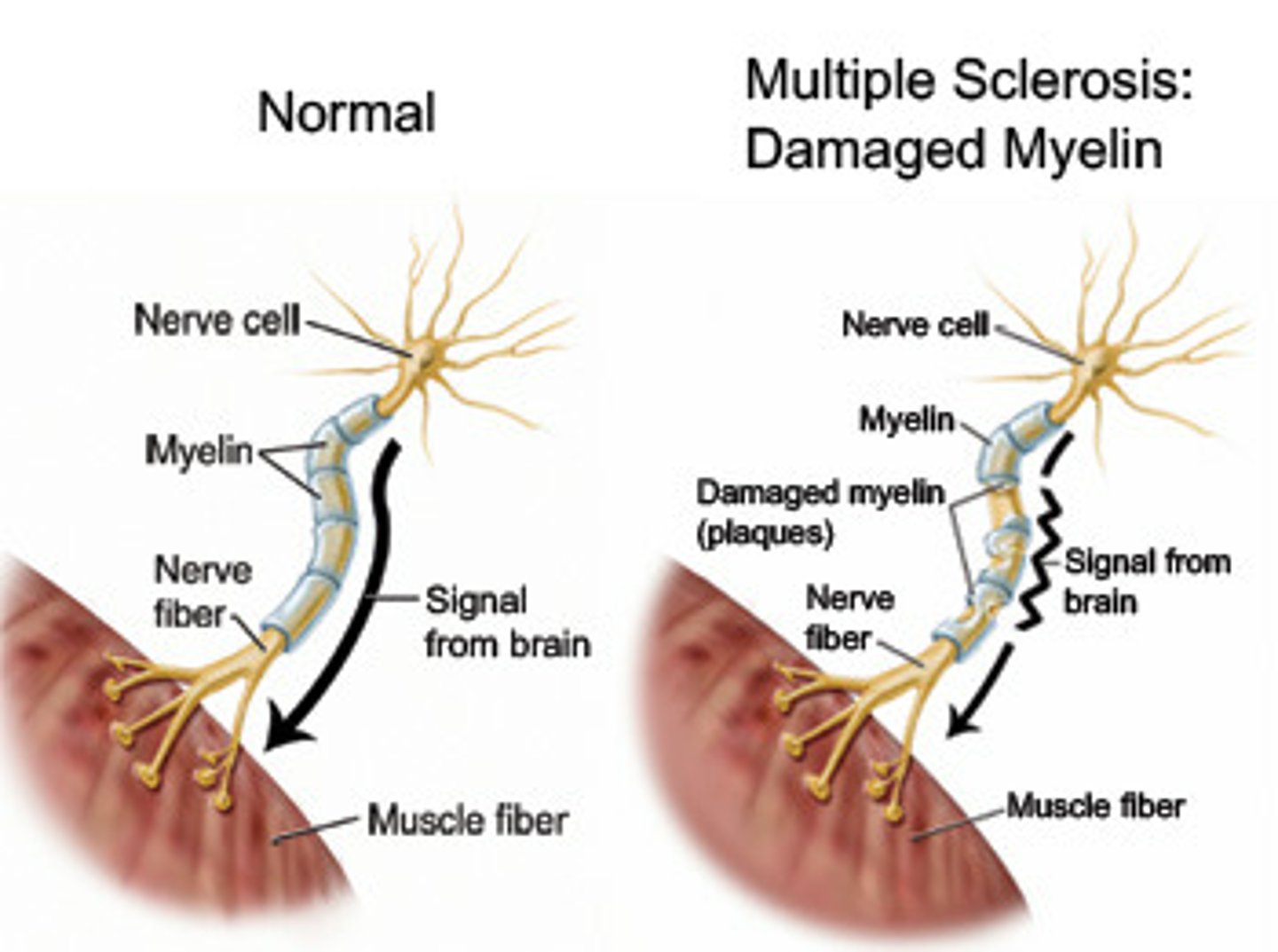
Multiple Sclerosis
What: autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation, selective demyelination and gliosis; chronic demyelination of central nervous system
Where: mainly in CNS but can affect cortical, subcortical, cerebellum, spinal cord, CN
Who: females 2:1, onset 20-40 yo, case presentation is usually very active pt with declining function, more common in caucasians
Clinical Presentation:
-visual impairments
-sensory and motor impairments
-intention tremor
-neuropathic pain
-fatigue that lasts for DAYS-WEEKS
-emotional disturbance and psychosocial problems due to unpredictable status
-Lhermittes' Sign: flexion of neck= electric shock in extremities
-Uthoff's Phenomenon: heat exposure=exaggerated symps
Dx:
-MRI with 2 lesions separated by TIME and SPACE
-CSF: elevated immunoglobins and presence of oligoclonal IgG bands and protein elevation
-Decreased nerve conduction velocity
PT Tx
-Don't let them overheat
-AM sessions due to increased fatigue with day
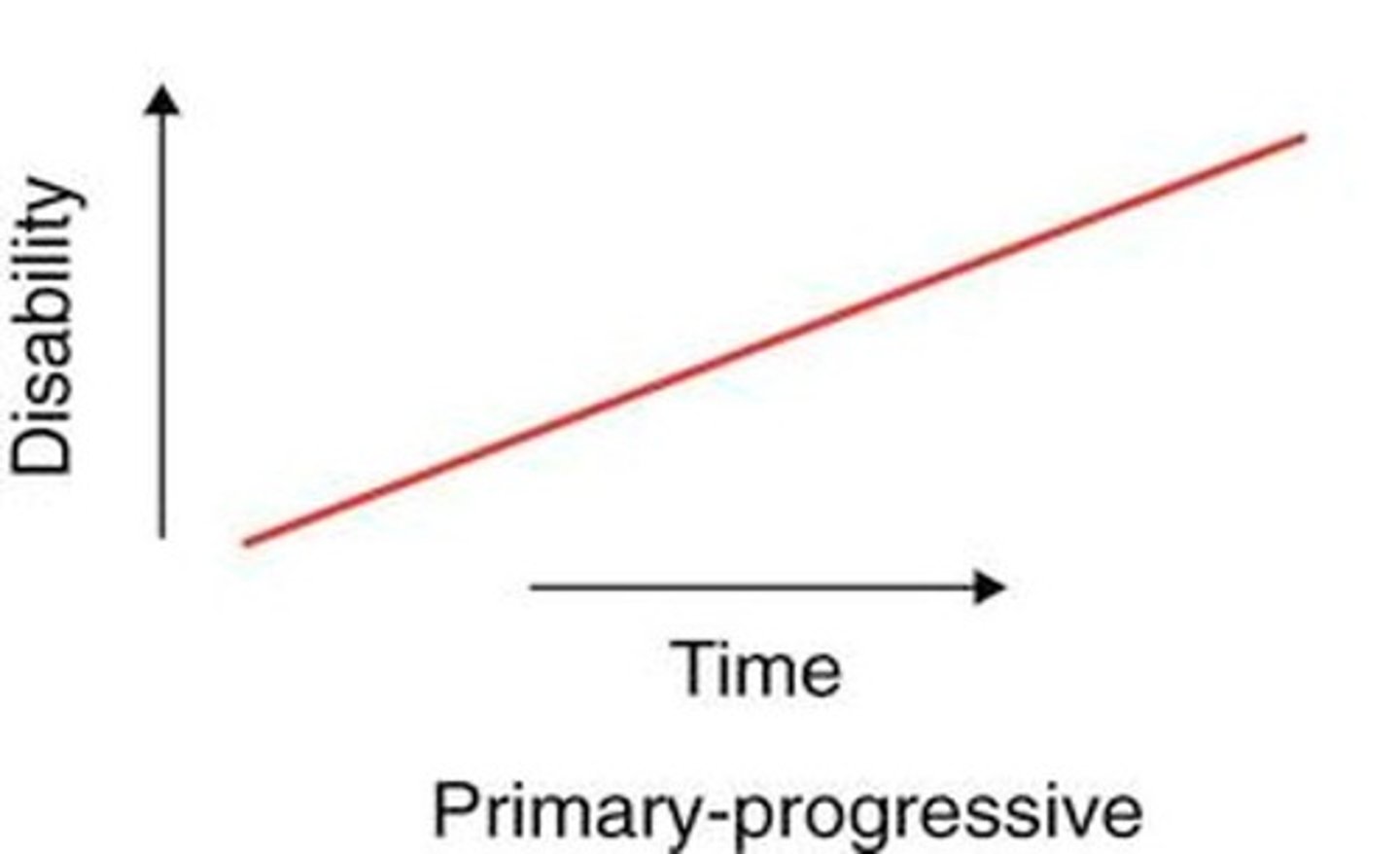
MS: Primary Progressive
PPMS
-Steady worsening from the start
-Steady decline W/O attacks
-No remissions (so no relapses)
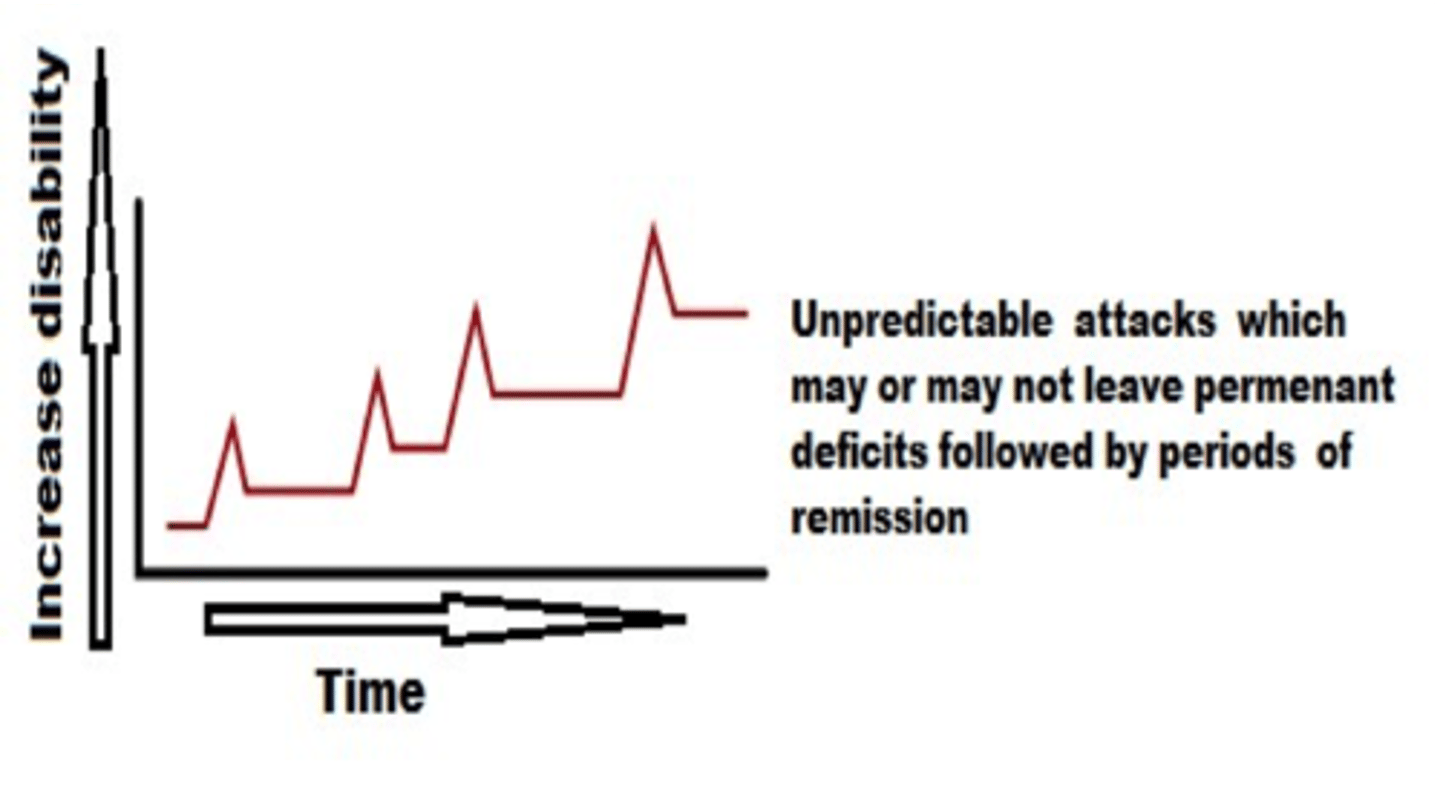
MS: Relapsing-Remitting
RRMS
-Unpredictable attacks which may or may not leave permanent deficits followed by periods of remission
-May be symptom free for months or years
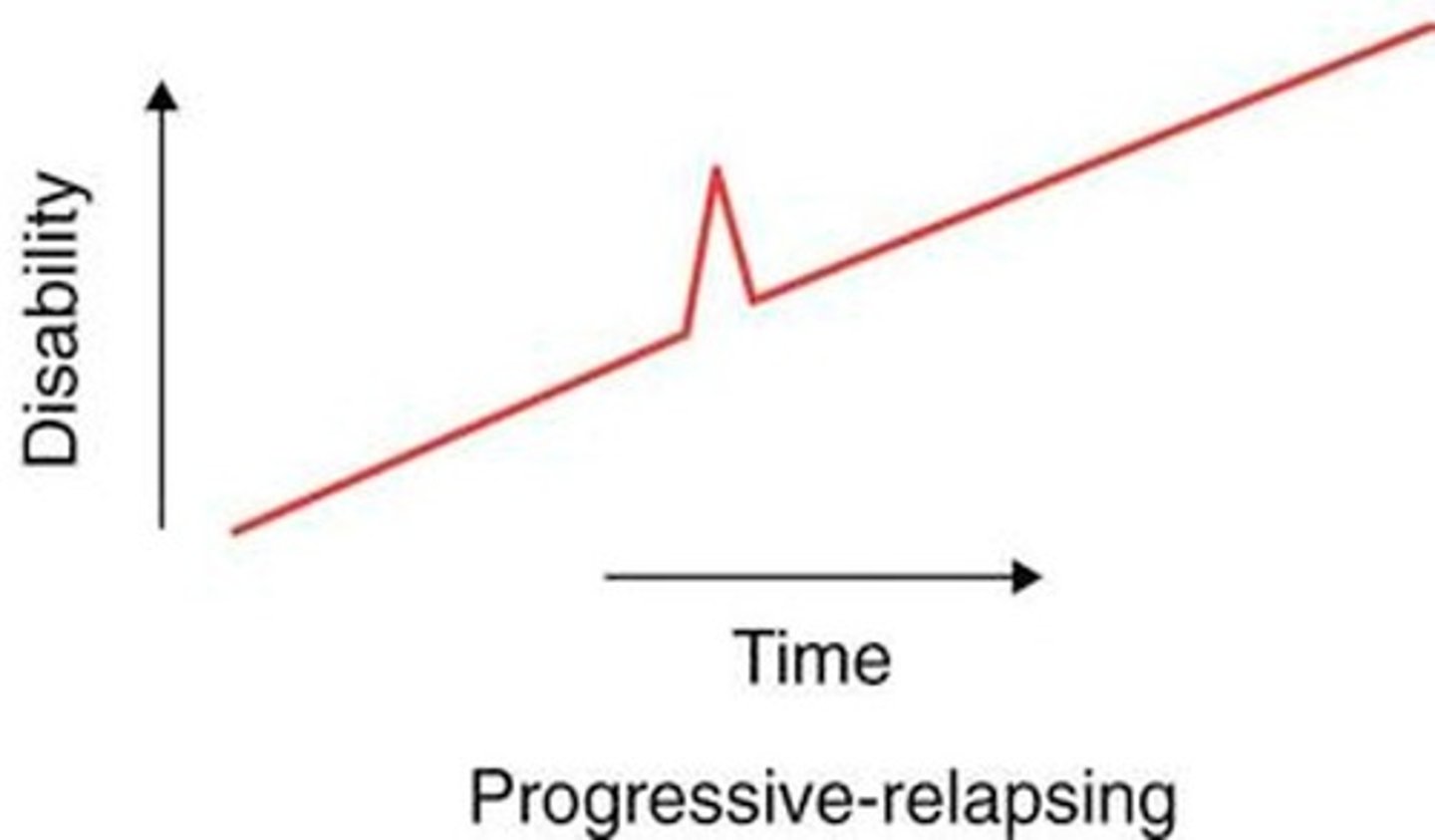
MS: Progressive-Relapsing
PRMS
-Steady decline since onset with superimposed attacks
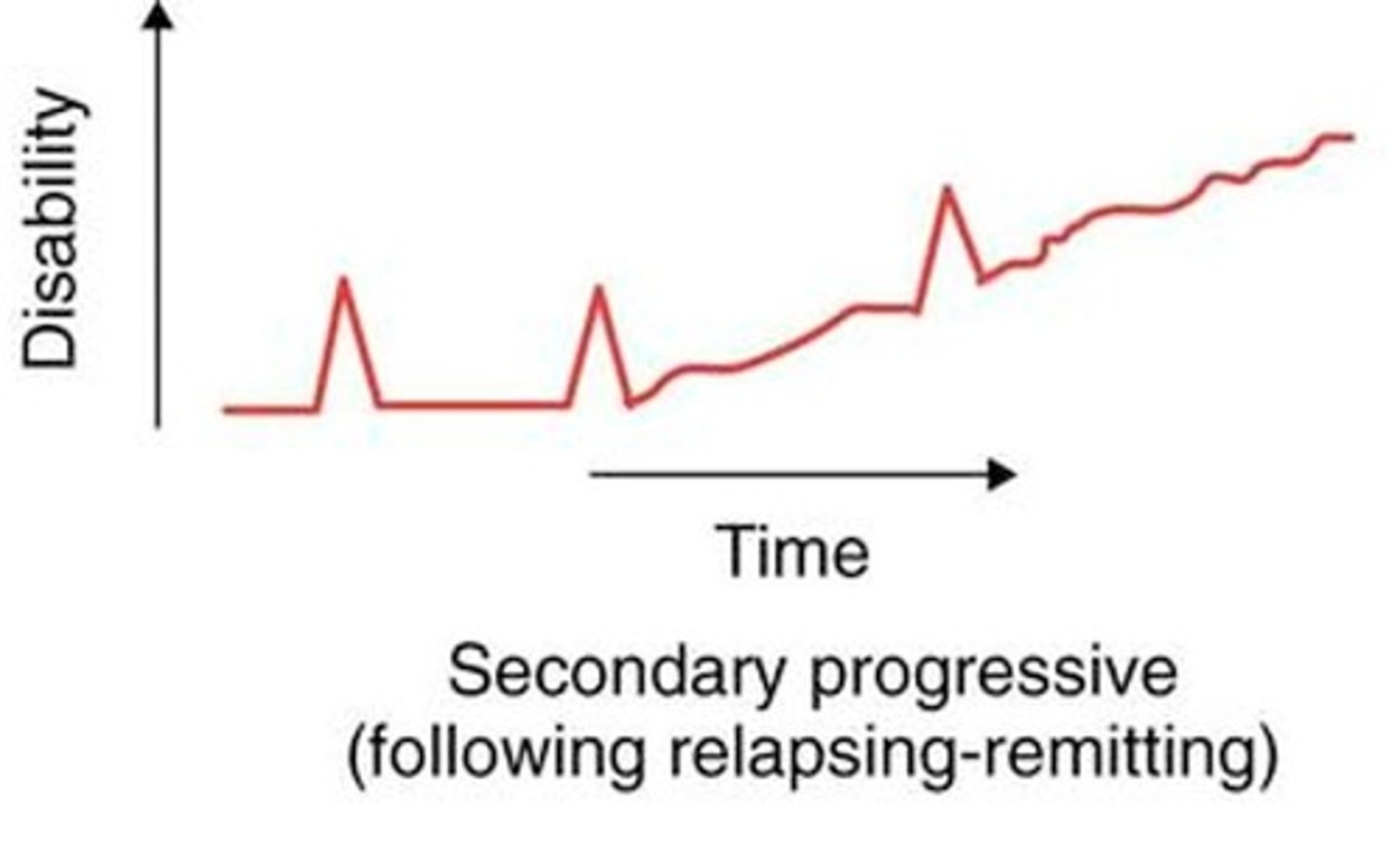
MS: Secondary Progressive
SPMS
-Initially RRMS that suddenly begins to have decline without periods of remission
MS and gait
-Weakness: can cause toe drag and lead to vaulting
-Spasticity
-Balance issues: "drunken gait"
-Sensory deficits
-fatigue
Visual symptoms are the first symptom of _______________________
MS
-Optic neuritis
-Marcus Gunn- reduced pupillary constriction
-Nystagmus
-Diplopia: double vision
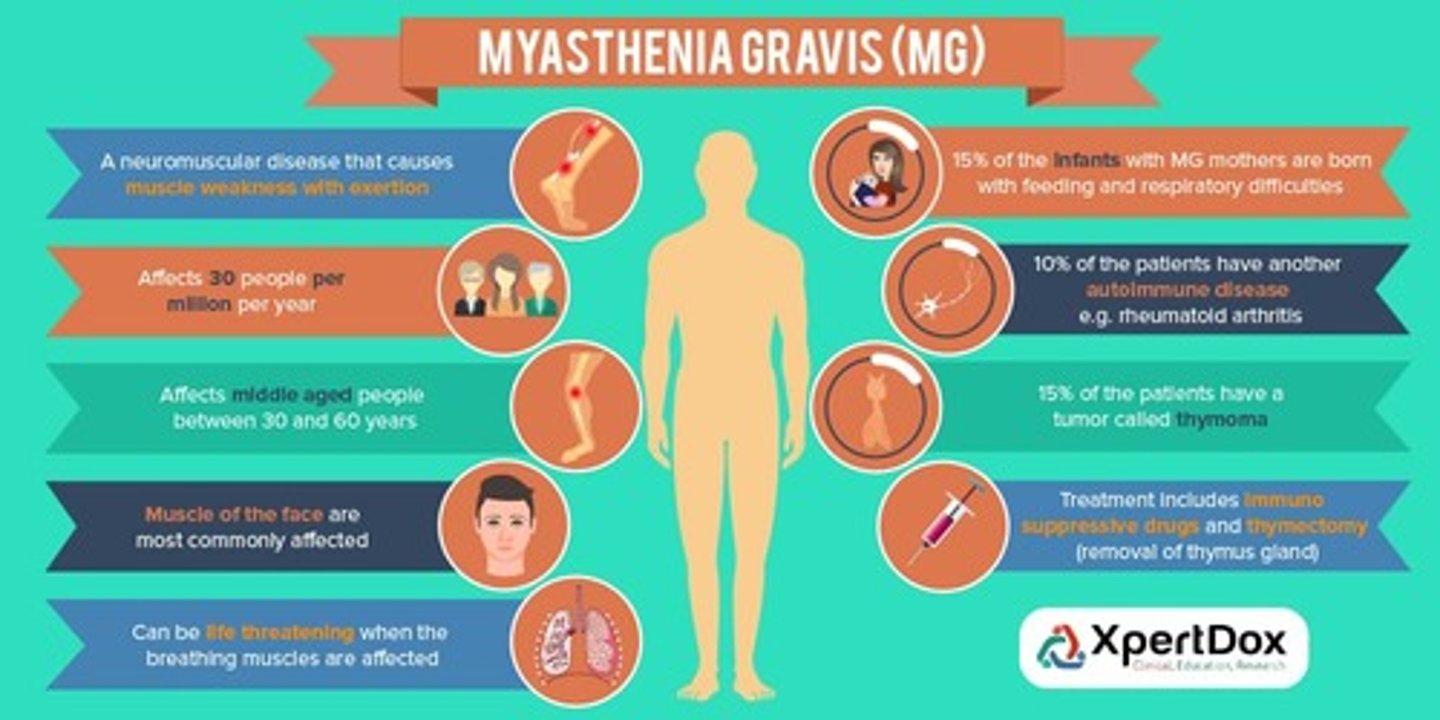
Myasthenia Gravis
What: Neuromuscular junction disorder caused by autoimmune medicated acetylcholine receptor damage resulting in NM transmission deficits
Who: all genders, races, ages, average age onset 20-50's
Clinical Presentation:
-asymmetrical ptosis
-diplopia
-unstable/waddle gait
-limb/cervical weakness
-facial expression changes
-dysarthria
-dysphagia
-respiratory weakness
-Weakness will improve after resting
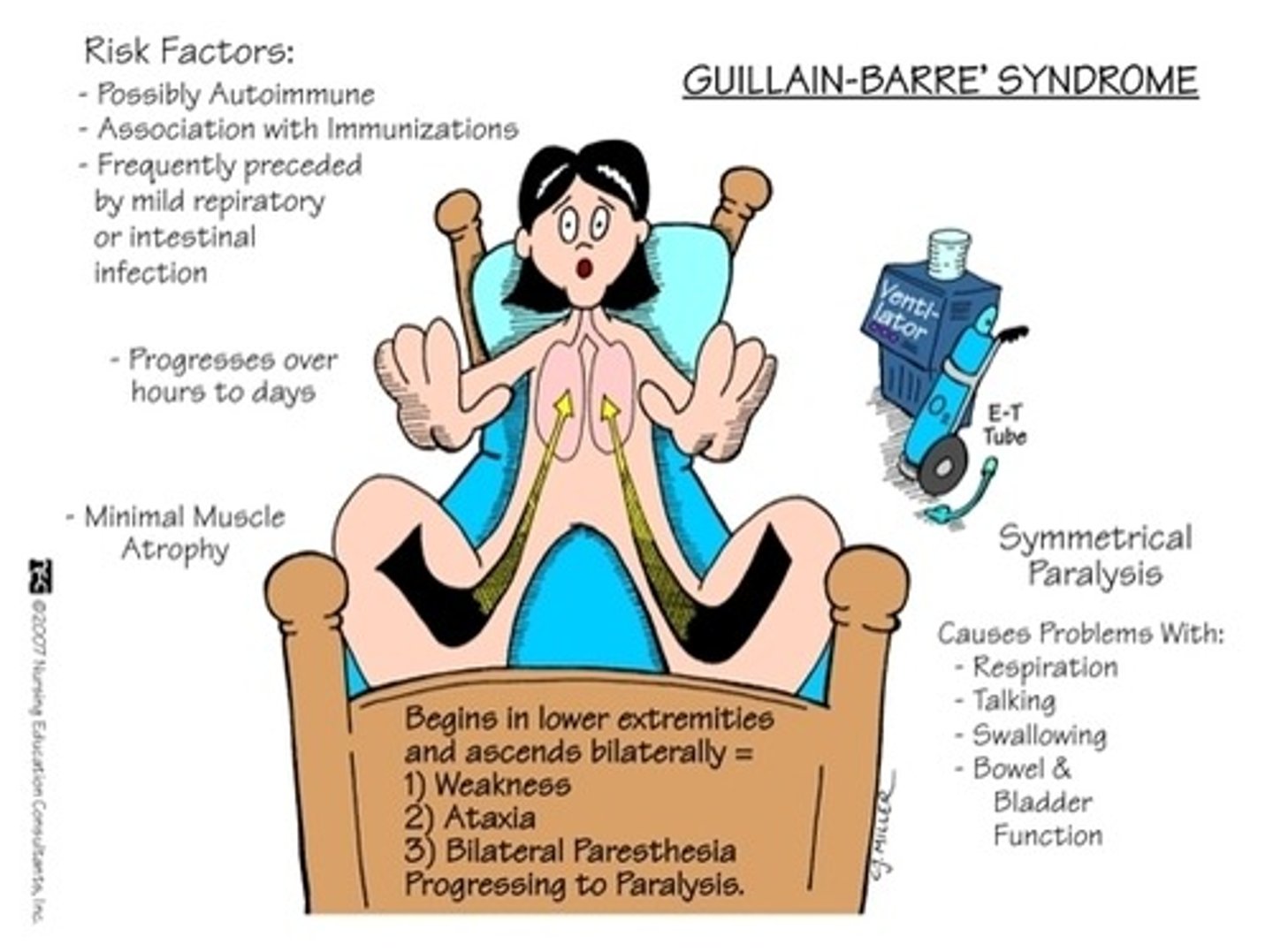
Gullain-Barre syndrome (GBS)
B for bilaterally
AKA: Acute demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy
What: autoimmune disease that attacks own peripheral nerves distal to proximal affecting bilaterally and ascends
LMN disorder
Who: Male>Female, any age group, usually someone that has had recent Respiratory or GI infection/virus
Clinical presentation
-Stocking glove distribution of ascending and bilateral weakness that rapidly occurs for 2-3 weeks but progressing no greater than 4 weeks (nadir)
- can progress to lung function and put pt on vents
-Diminished DTRs
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
What: LMN and UMN disorder that causes ultimately respiratory failure and death within 3-5 years
Clinical Presentation
-Hyporeflexia and hyperreflexia
-Fasciculations
-Pseudo-bulbar affect
-respiratory weakness
-frontotemporal dementia
-cognitive impairments
-behavioral impairments
-Clinical sign- cervical extensor weakness
Level of SCI and Degree of Respiratory Function: C1 or C2
-VC 5-10% of norm
-No cough
-On ventilator
Level of SCI and Degree of Respiratory Function: Injuries below T11
- essentially normal VC and strong cough
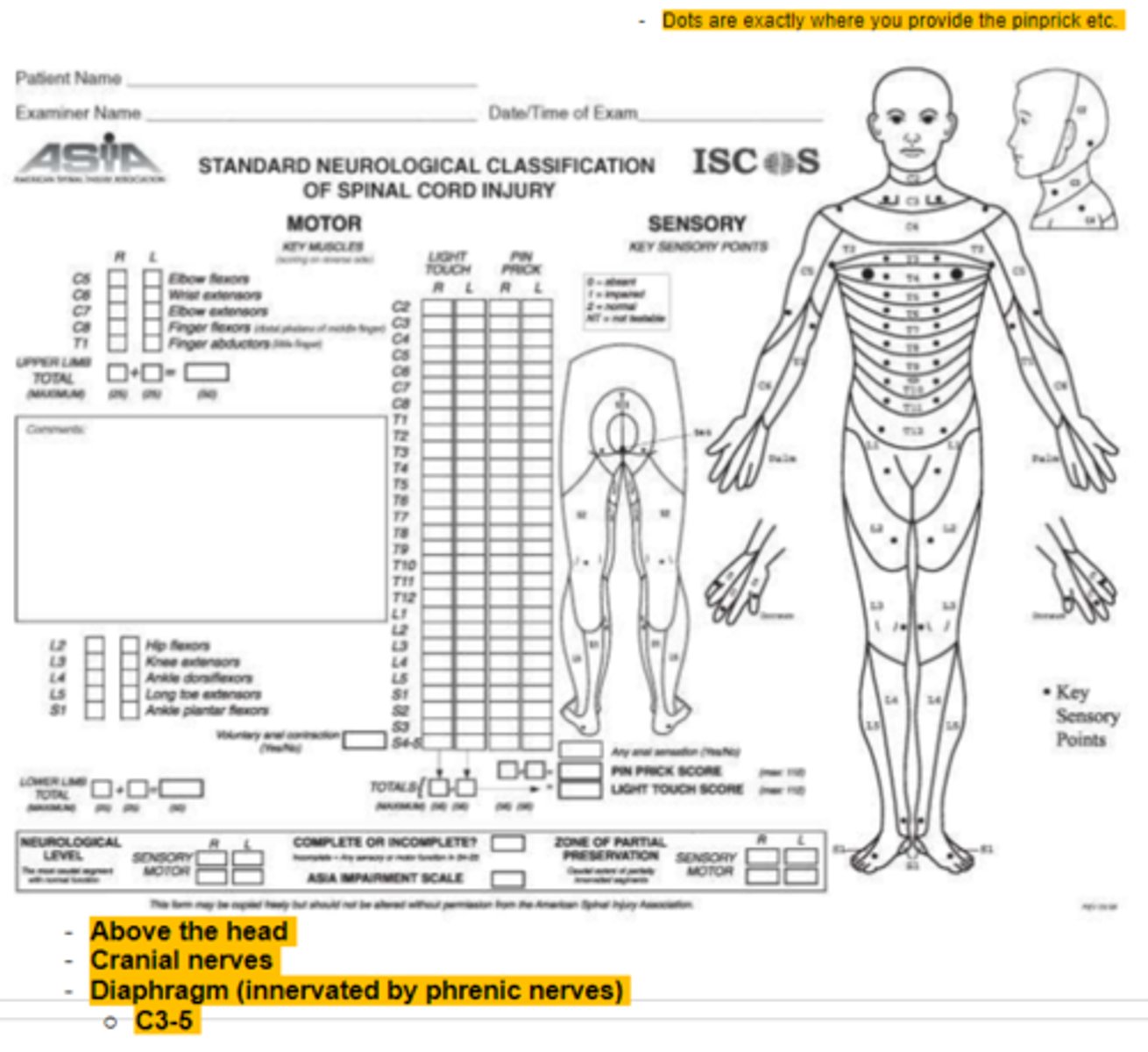
Key Muscles for ASIA testing
C5 - elbow flexors
C6 - wrist extensors
C7- elbow extensors
C8 - finger flexors
T1 - finger abd
L2 - hip flexors
L3 - knee extensors
L4 - Ankle DF
L5 - Long toe extensors
S1 - Ankle PF
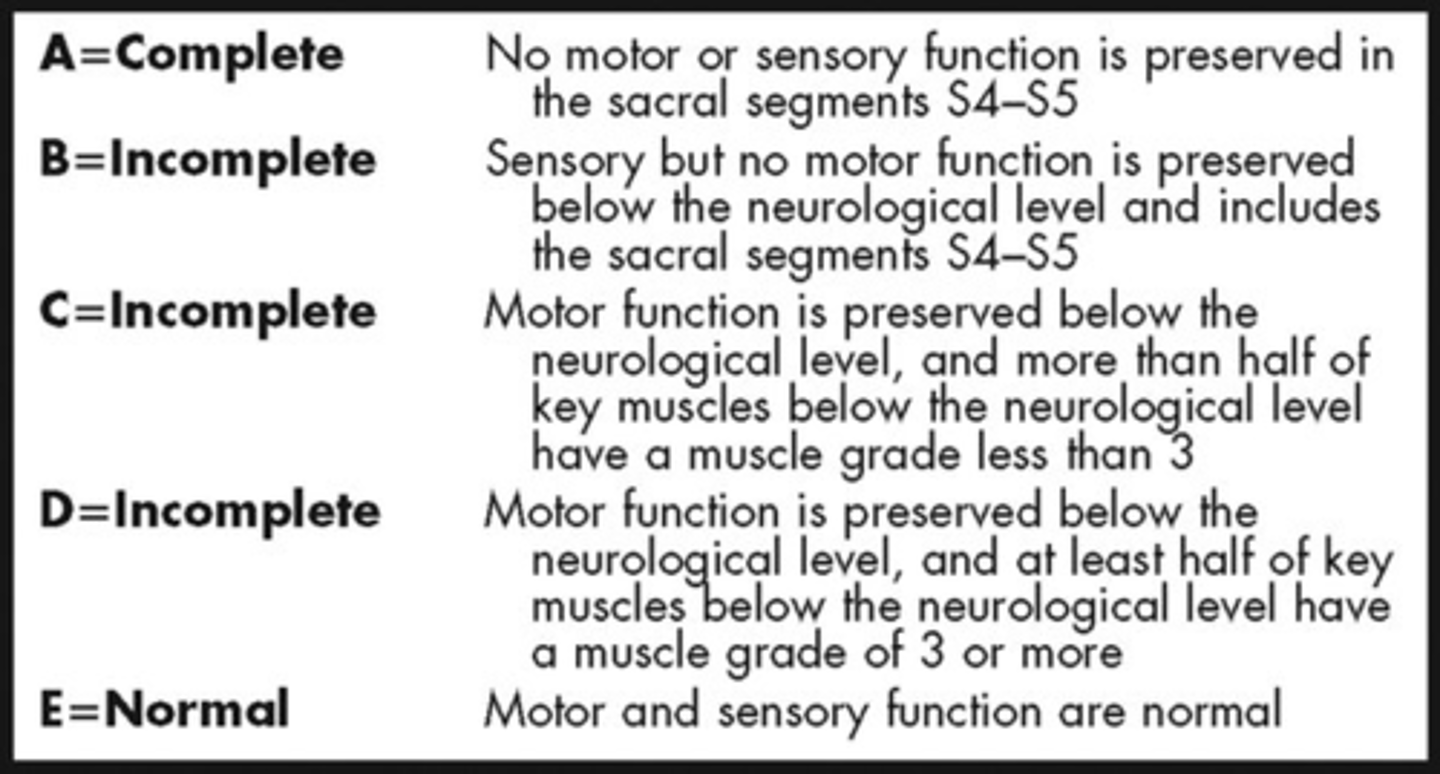
ASIA A
Complete - no sensory or motor function is preserved in sacral segments (S4-5)
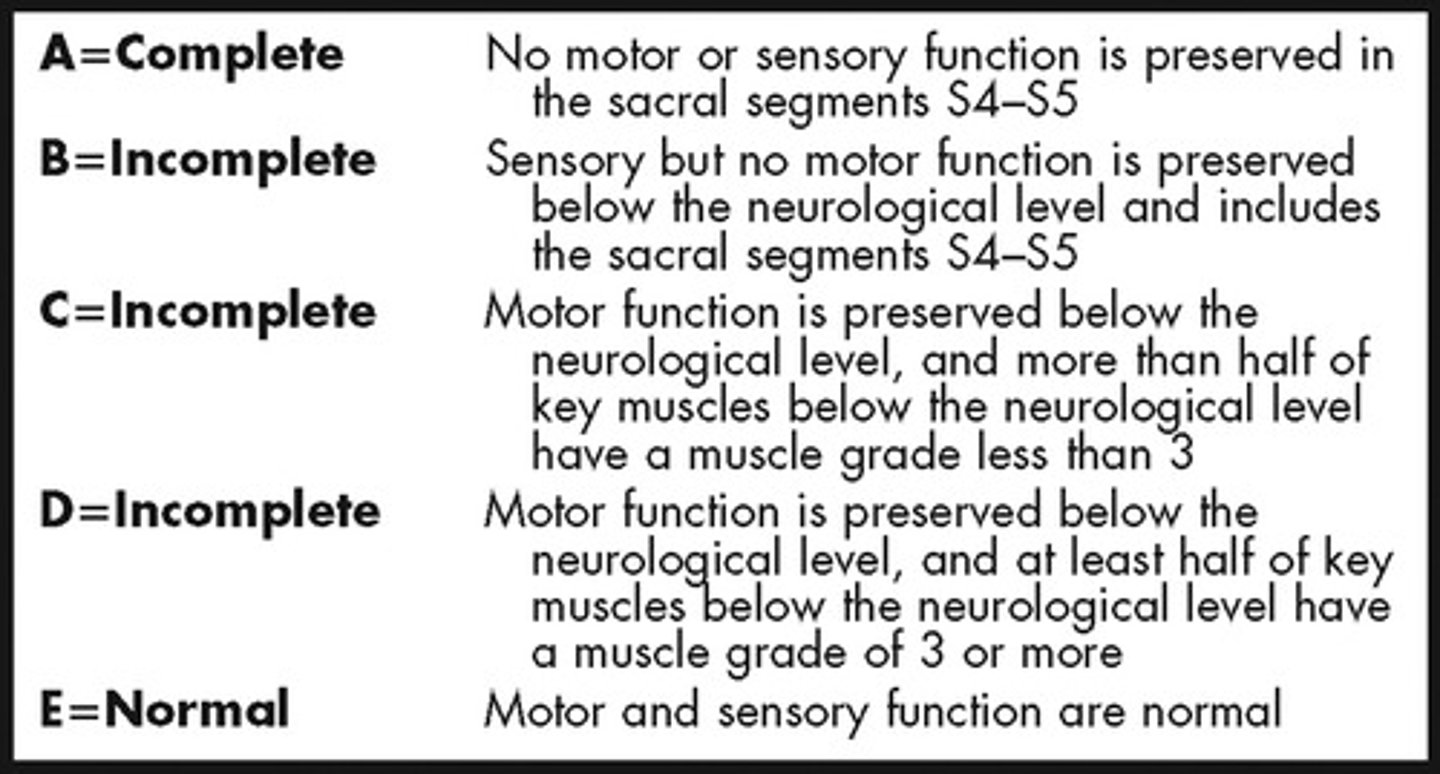
ASIA B
Sensory incomplete
-Sensory but not motor fxn is preserved below NLI and includes sacral segments S4-S5
(so they have to have LT/PP of sacral segments or DAP)
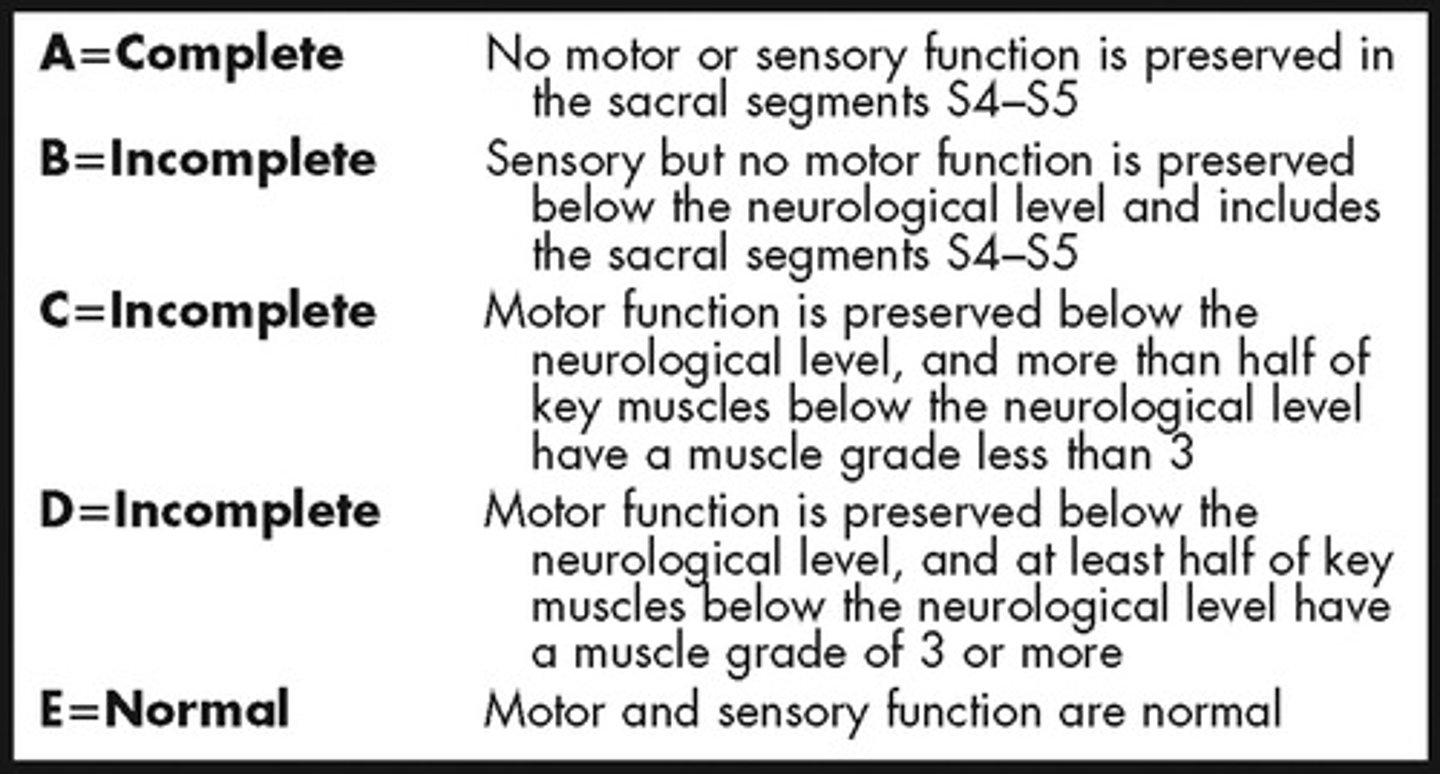
ASIA C
Motor incomplete
-Motor fxn preserved in most caudal sacral segments for VAC
OR
-pt meets criteria for sensory incomplete status (S4-S5 for LT, PP or had DAP
AND pt has some sparing more than three levels below IL motor level on either side for less than half of key muscles below NLI have muscle grade > or = to 3
ASIA D
Motor Incomplete
Motor fx preserved below the neurological level muscle grade > or = to 3 in more than half key muscles
Key Sensory Points
C2 - behind the ear
C3 - supraclavicular fossa (midclavicular line)
C4 - AC joint
C5 - radial side of antecubital fossa
C6 - dorsum hand on proximal phalanx of thumb
C7 - dorsum hand on proximal phalanx of middle finger
C8 - dorsum hand on proximal phalanx of little finger
T1 - ulnar side of antecubital fossa
T2 - apex of axilla
T3 - Midclavicular line @ 3rd ICS
T4 - 4th ICS @ nipple line
T5 - 5th ICS (midway btw T4 and T5)
T6 - 6th ICS @ level of xiphisternum
T7 - 7th ICS (midway btw T6 and T10)
T8 - 8th ICS (midway btw T6 and T10)
T9 - 9th ICS (midway btw T8 and T10)
T10 - 10th ICS @ umbilicus
T11 - 11th ICS (midway btw T10 and T12)
T12 - Midpoint of inguinal ligament
L1 - Midway btw T12 and L2
L2 - Mid-anterior thigh
L3 - Medial femoral condyle
L4 - Medial malleolus
L5 - Dorsum of foot on 3rd MTP
S1 - Lateral heel
S2 - Popliteal fossa
S3 - Ischial tuberosity
S54-S5 - perianal area
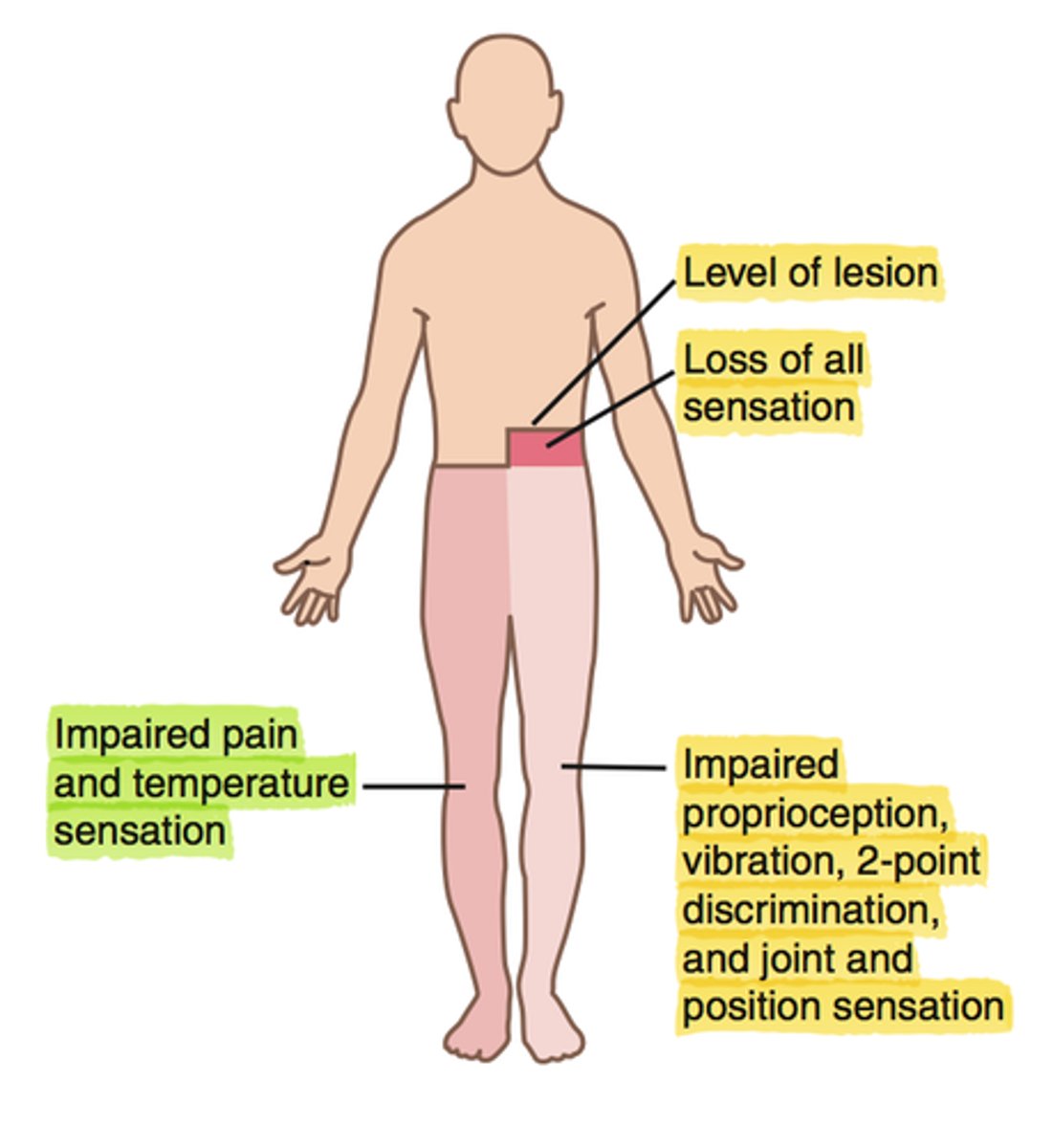
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
What: Hemisection of the spinal cord due to GSW or stab
Results:
Ipsilateral deficits
-loss of sensation (LT, proprioception, vibratory sense) (dorsal columns) and paralysis of muscles (corticospinal tract)
Contralateral deficits
-Loss of pain and temperature (spinothalamic tract) but does not start until SEVERAl segments below)
Anterior Cord Syndrome
What: due to hyperflexion injury of C-spine
(The head goes anterior to flex C-spine)
Preservation of proprioception, vibratory and discriminatory sense
Results:
-Loss of motor function (anterior corticospinal tract)
-Loss of pain and temp (spinothalamic tract ant/lateral)
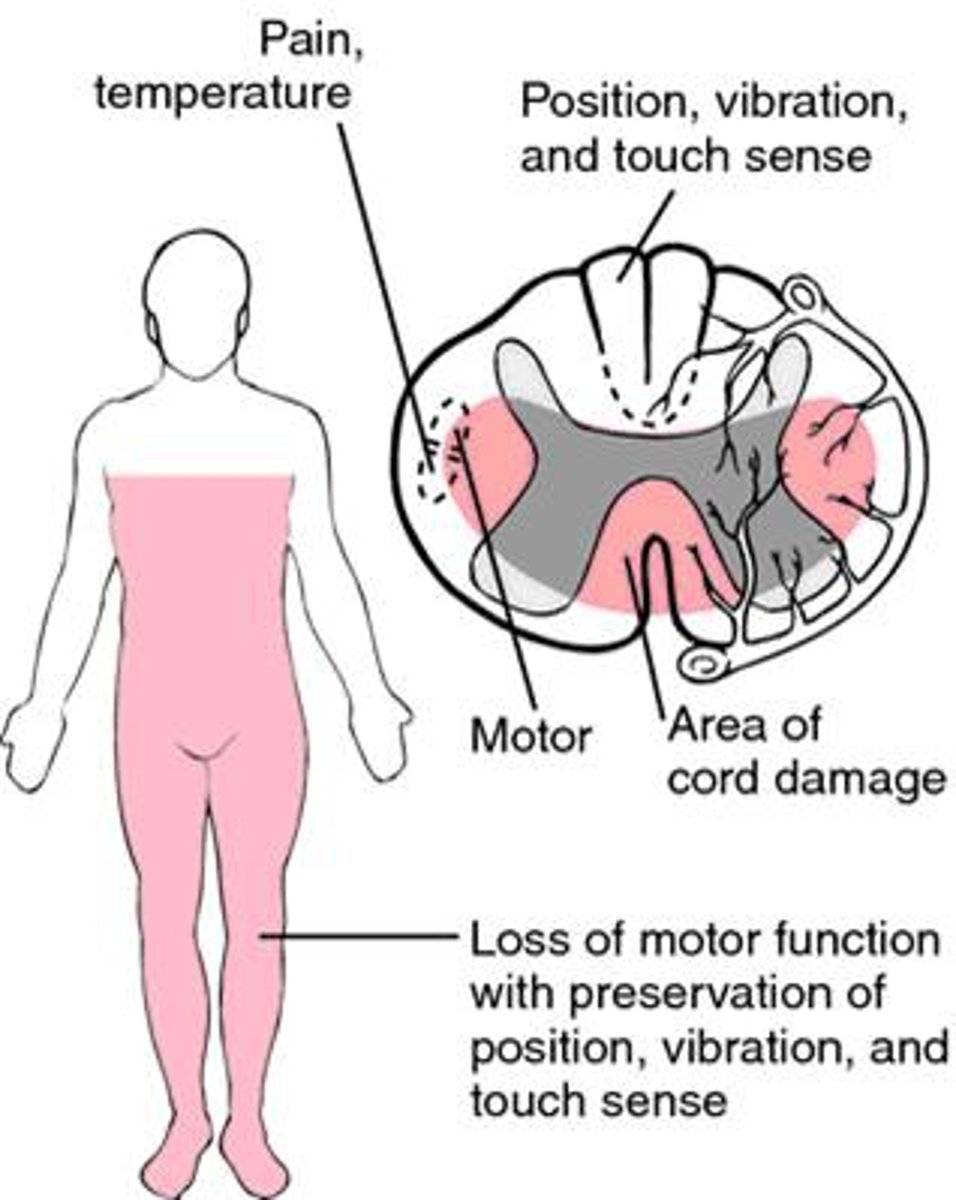
Central Cord Syndrome
What: Caused by hyperextension injuries, congenital or degenerative narrowing of the spine
(whiplash)
Walking quads - most common incomplete SCI syndrome
Results in:
-UE > LE in involvement
-Sensory impaired but < than motor impaired
- Preservation of sacral tracts (sexual and B&B preserved)
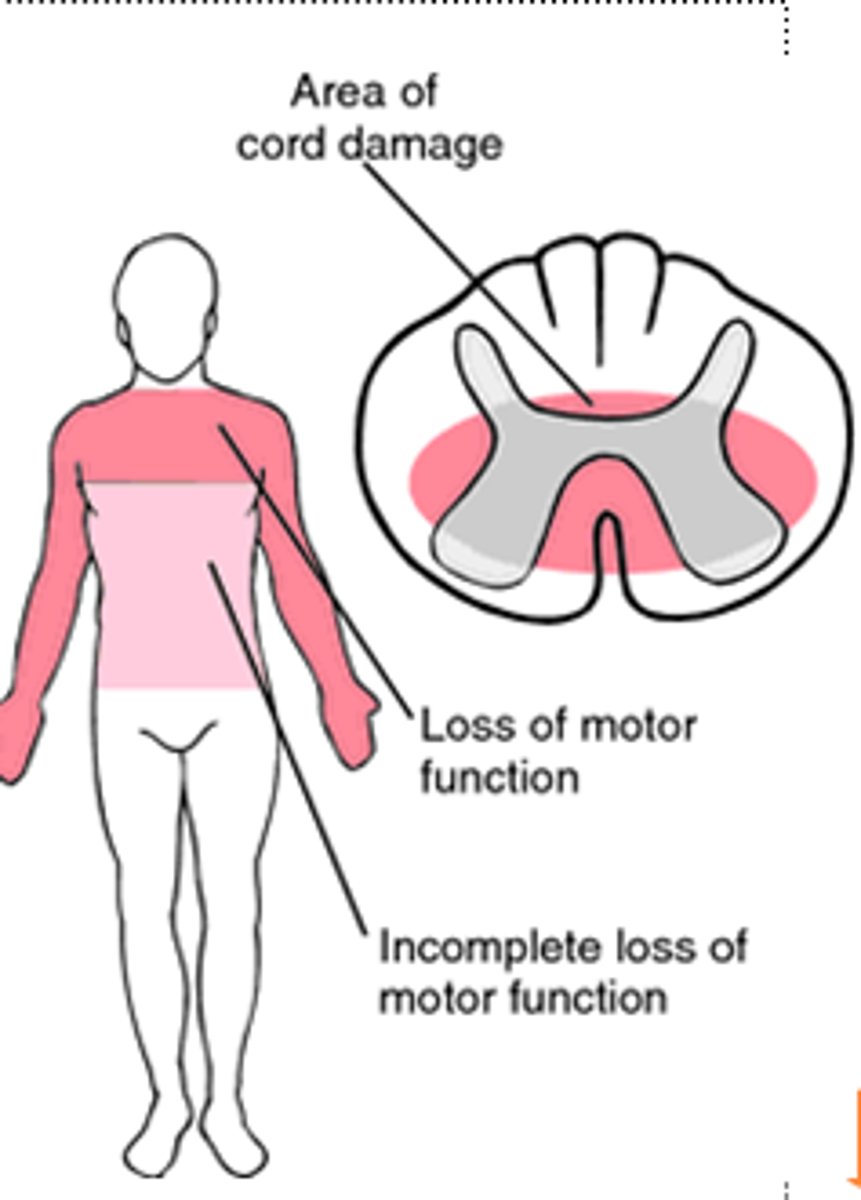
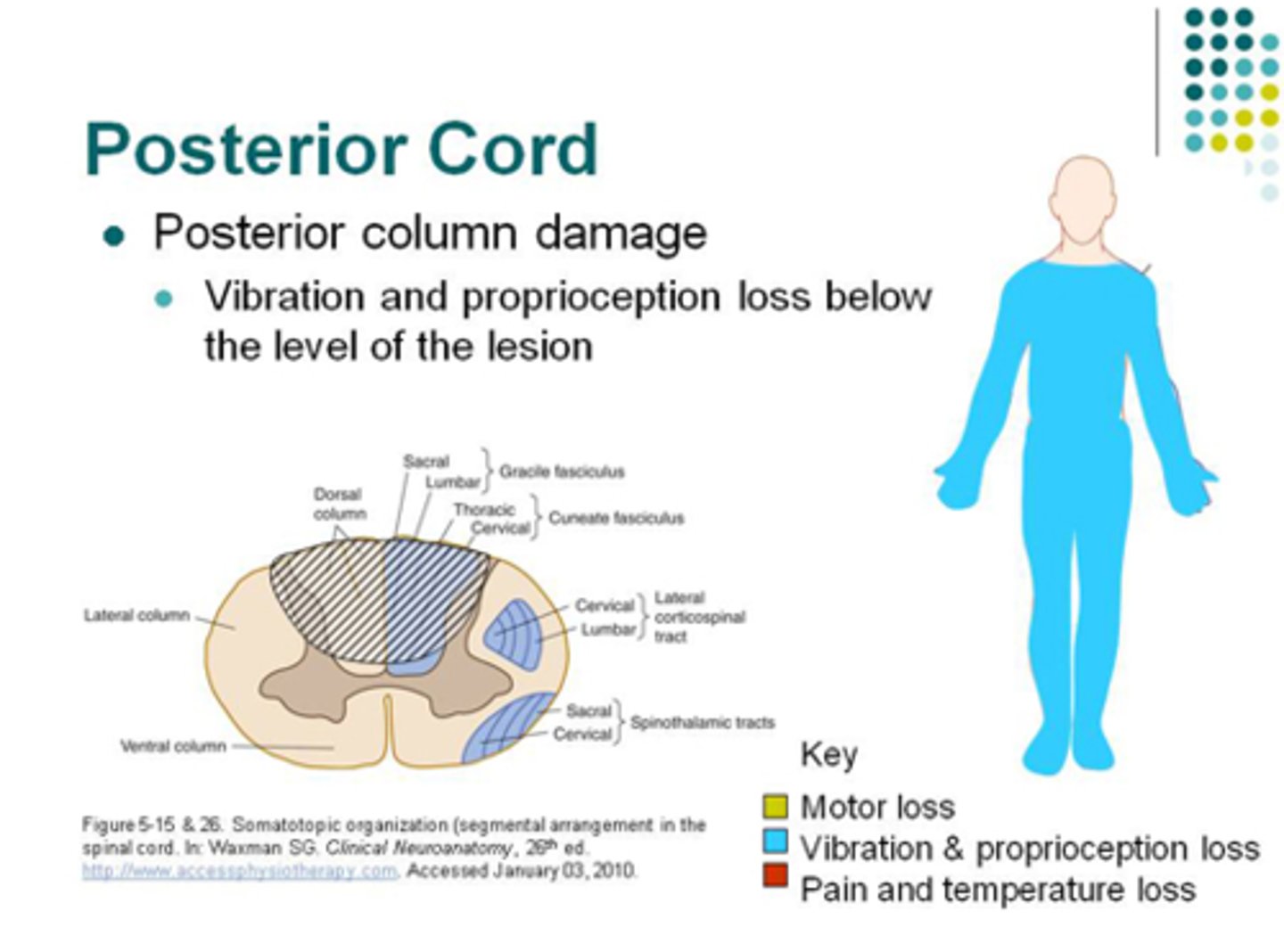
Posterior Cord Syndrome
What: rare syndrome when posterior spinal artery is compressed
Results in:
-Loss of proprioception, pain, 2-point discrimination, and stereognosis
Motor is preserved
Conus Medullaris Injury
What: injury at L1-L2 caused by disc herniation, trauma or tumor
Clinical Presentation
-Bilateral and symmetrical loss of sensation in saddle distribution
-symmetrical motor loss
Results in:
-Mixed UMN and LMN signs (areflexic B&B and saddle anesthesia)
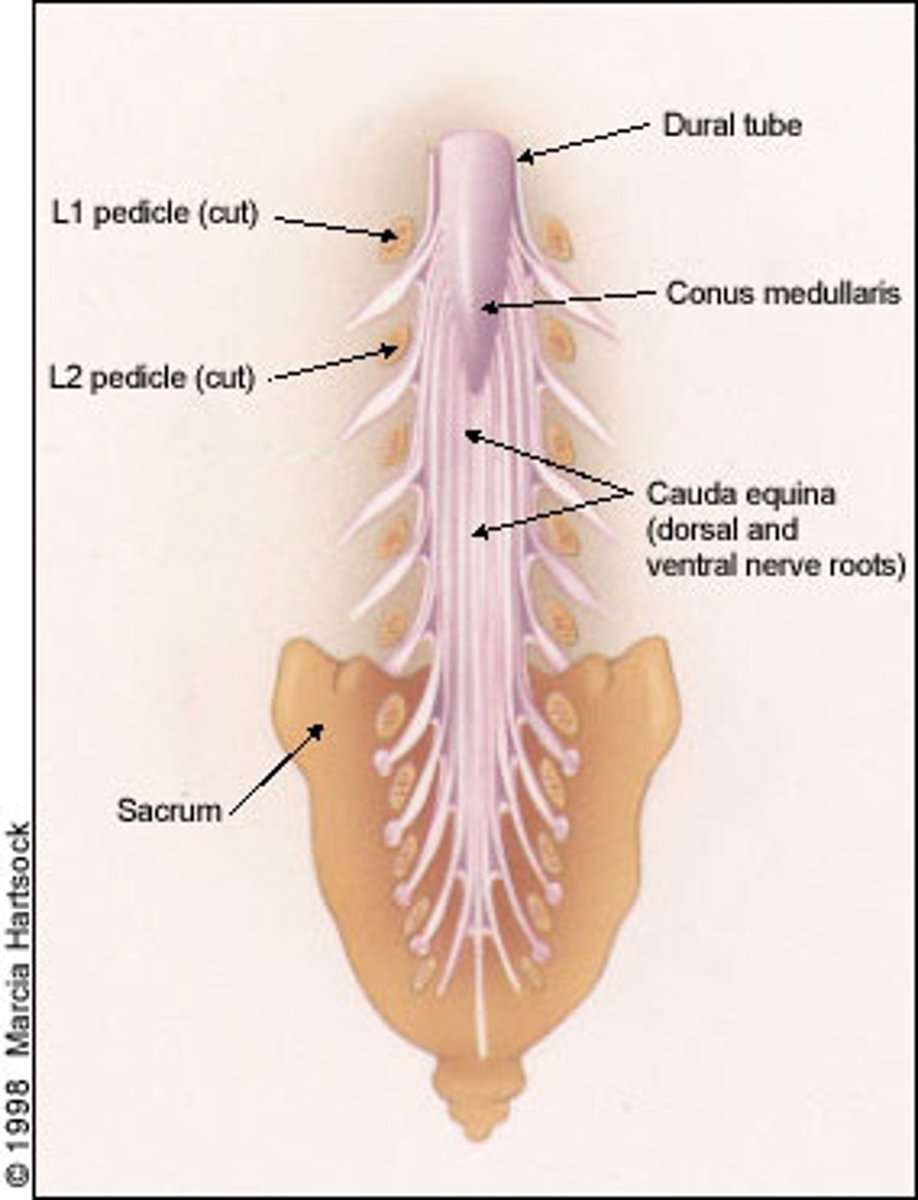
Cauda Equina Syndrome
What: Injury below L1-2
Clinical Presentation
-Unilateral and asymmetrical loss of sensation and motor
Results in:
LMN injury and S&S
Spinal Shock
The period of altered reflex activity immediately after a traumatic SCI
Autonomic Dysreflexia
What: Occurs in SCI pt with NLI T6 and above; is LIFE THREATENING
Results in:
-Noxious stimuli triggers sympathetic surge
-Signal cannot pass down due to NLI
-brain decreased HR but elevate BP presists
-elevation of BP (from 90-110 SBP to 250-300 SBP)
Unregulated PSNS control above lesion = bradycardia, nasal congestion and flushing
uncontrolled below lesion = goose bumps, cold and clammy
Steps for treating AD
1. Sit them up!
2. Loosen tight clothing
3. Check BP every 5 min
4. Check bladder then bowel
5. Check body for any other irritating stimuli
6. Apply nitropaste 1 in above injury and wipe off when resolved
What SCI level can breath without ventilator briefly?
C4- glossopharyngeal breathing
What SCI level can use manual w/c on level surfaces?
C5
What SCI level is the first level someone can indep transfer with level surfaces and have the POTENTIAL to be independent?
C6
Transfer using Sideboard
What SCI level can consistently be independent living?
C7
What SCI level is a community ambulator?
T8
What is the first SCI level to drive?
(low effort) C5 or C6 (for sure independent)
What is the first SCI level to stand outside bars with braces/RGO?
C8
Micturition is controlled by :
S2, S3, S4
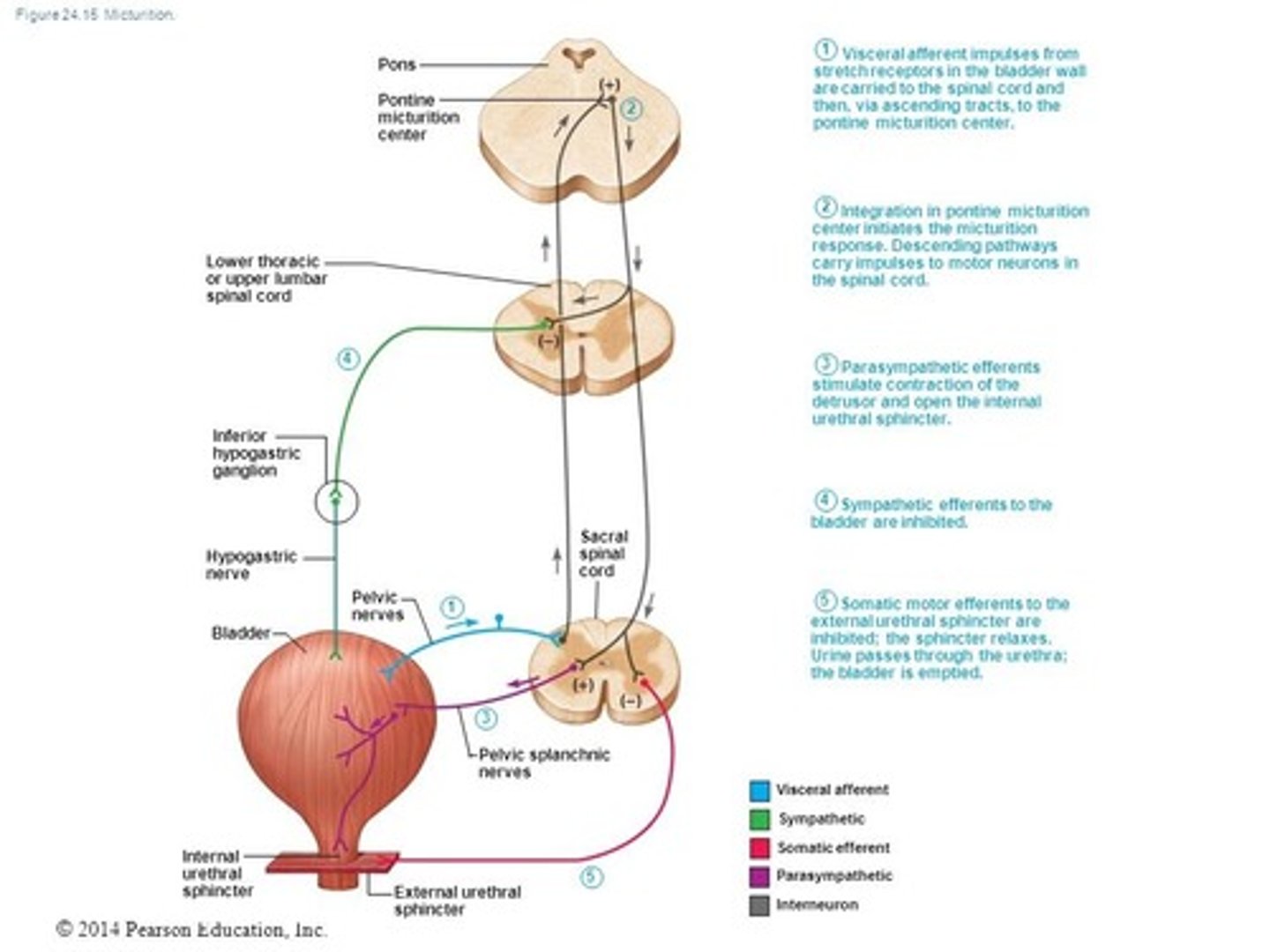
UMN Bladder
-Spastic or hyperreflexic bladder
-Lesion: Above conus medullaris and sacral segments (T11-T12 and above)
-Bladder will reflexively empty in response to certain level of filling pressure
-Dyssynergia: detrusor is hyperreflexive but sphincter may have increased tone
Tx: Intermittent cath, indwelling cath
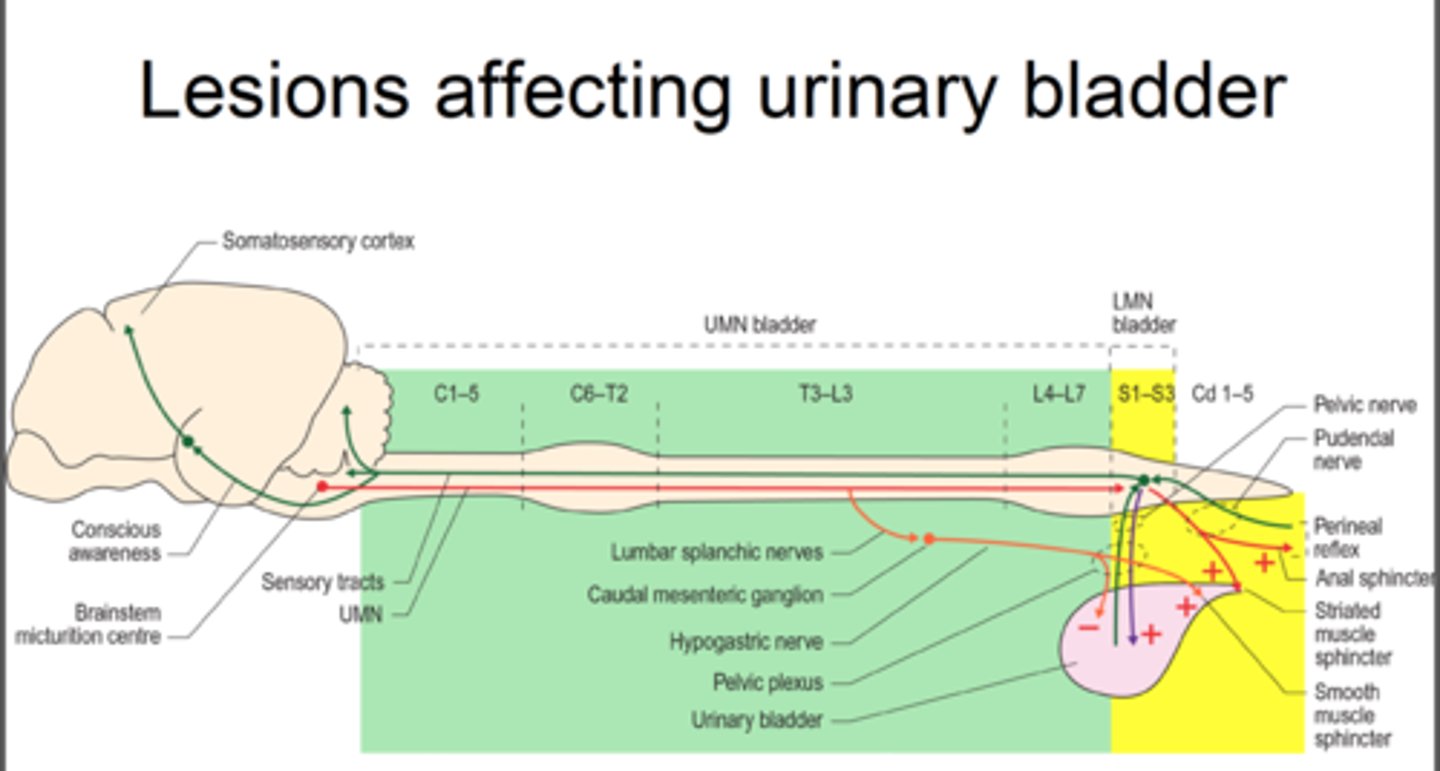
LMN Bladder
-Essentially flaccid and no reflex action of detrusor muscle
-Involving T12/L1 and below
-Bladder empties with increased intra-abdominal pressure
(can use Valsalva or Crede's maneuver) to empty
-Have high residual urine volume (can't get it all out)
Tx: Still will intermittent cath to keep volumes below 500-600 mL

2 bladder dysfunction
1. Failure to store: areflexive sphincter and spastic detrusor
2. Failure to empty: areflexive bladder and sphincter that is unable to relax
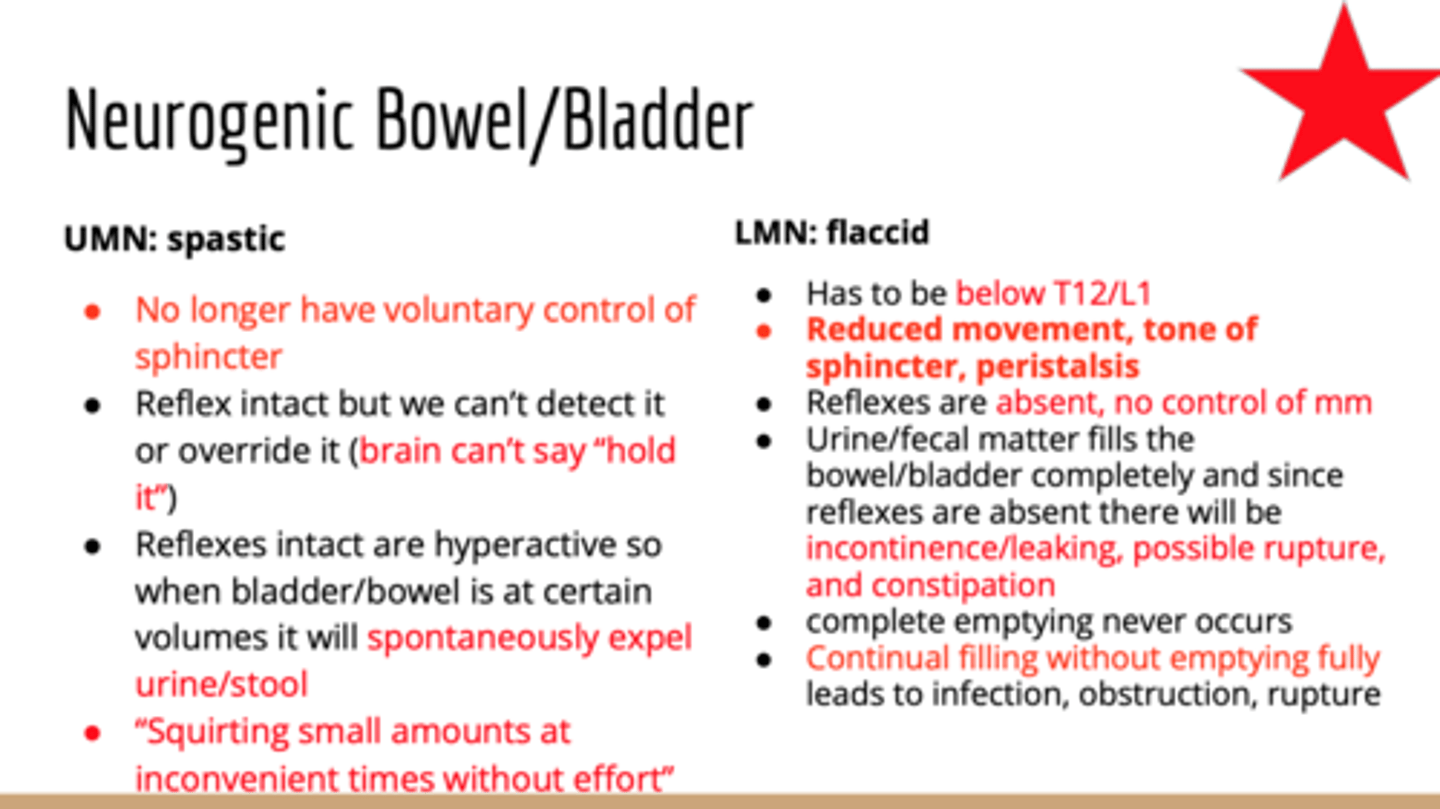
UMN Bowel
-Reflex/spastic bladder with lesion above S2
-PSNS and internal sphincter connections from S2-4 are intact so reflex defecation when rectum filled with stool
Tx:
-Digital stimulation to manual stretch anal sphincter
-Then add valsalva and/or abdominal massage for evacuation
-Empty daily or every other day
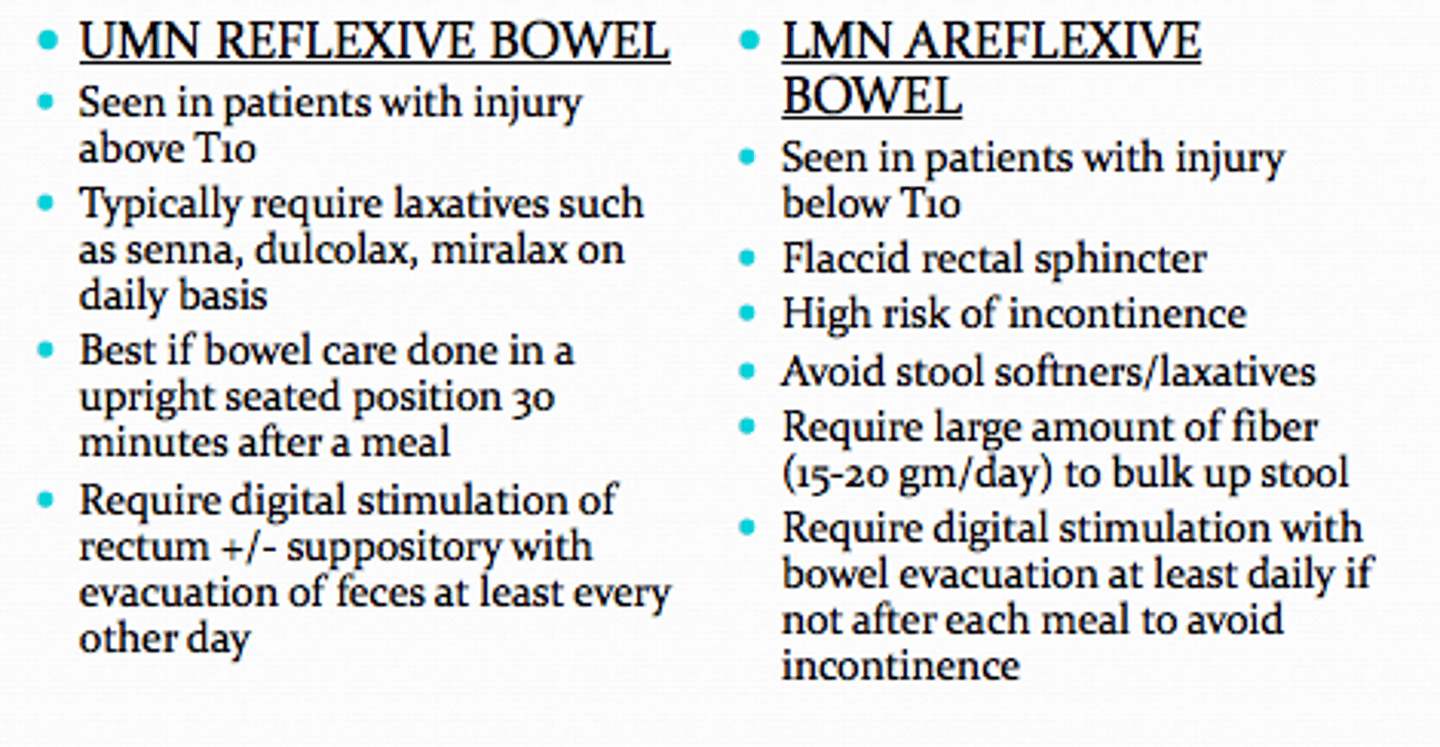
LMN Bowel
-Flaccid/areflexive bowel (lesions below cauda equina)
-Feces can be impacted
Tx:
-manual evacuation and gentle valsalva
-Emptied 1x/day or 2x/day
Lhermittes' Sign
flexion of neck= electric shock in extremities in pt with MS
If the NPTE stem of the questions talks about a female, btw 20-40 yo, who is very active and has sudden unrelenting fatigue, think
MS most likely
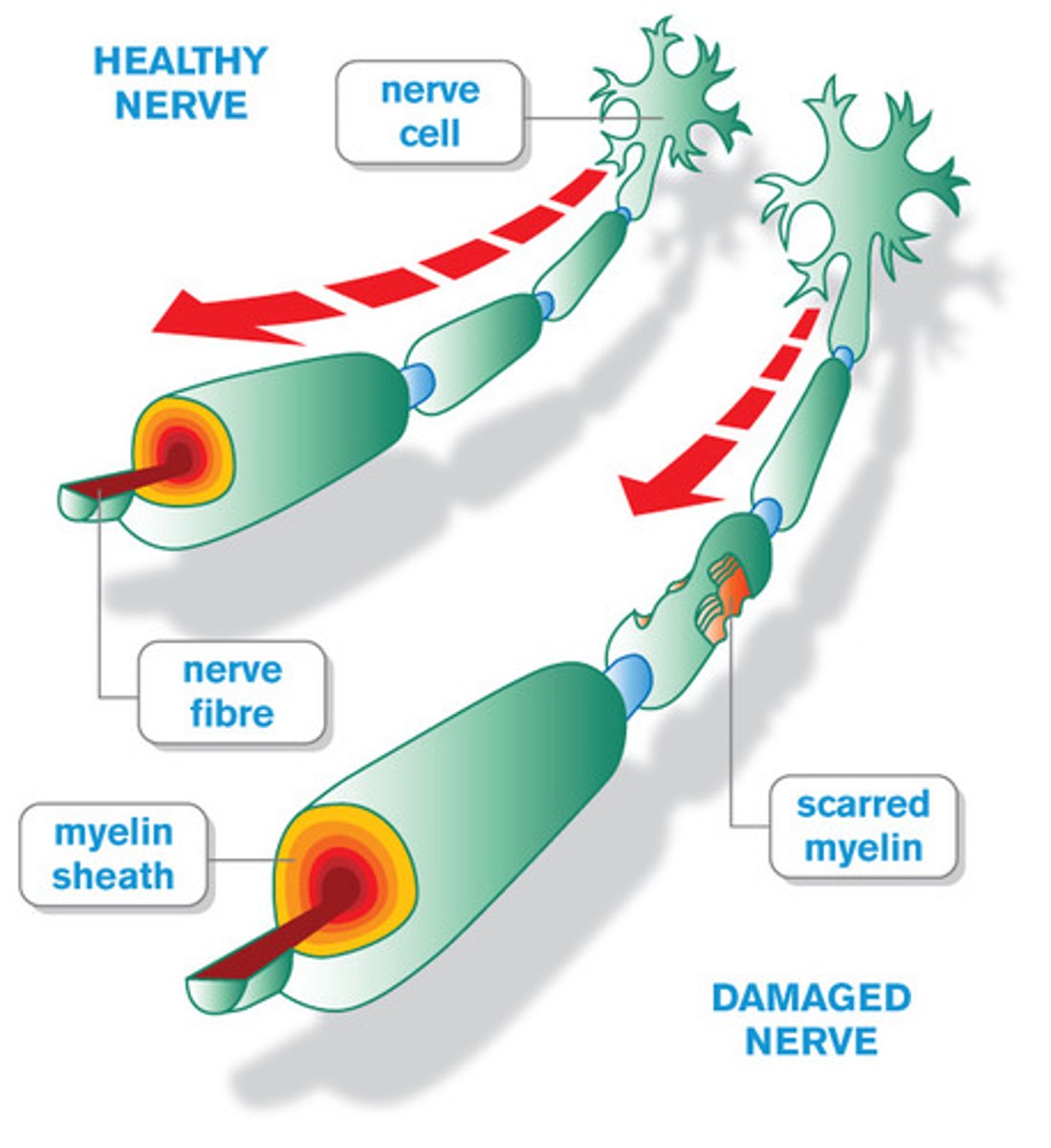
MS can have 2 CN involvements with condition, what two nerves?
Optic nerve = vision issues
Trigeminal nerve = eating, shaving and touch to face may trigger painful episode
What is defined as a MS exacerbation?
Neurological symptoms lasting >24 hours (new or recurrent)
-can last days to weeks to months
Pool therapy for MS patients, water temp must be
< 85 degs

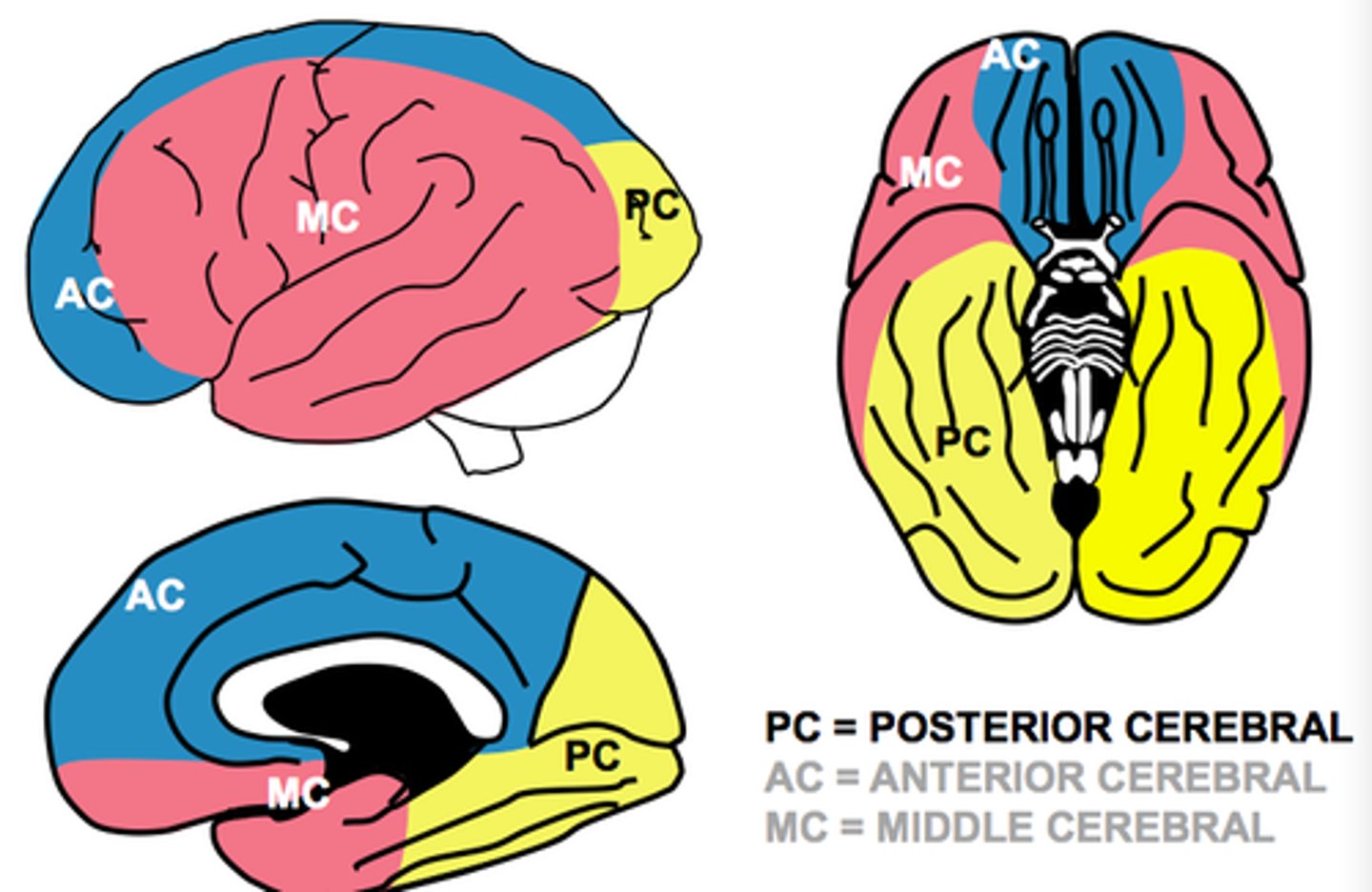
Anterior Cerebral Artery CVA
Results in:
-CL motor and sensory loss (LE > UE)
-Sensory loss (LE>UE)
-Memory and behavioral impairments due to frontal lobe involvement
-Urinary incontinence (bladder/genitals on homunculus)
-Problems with imitation, bimanual tasks and apraxia
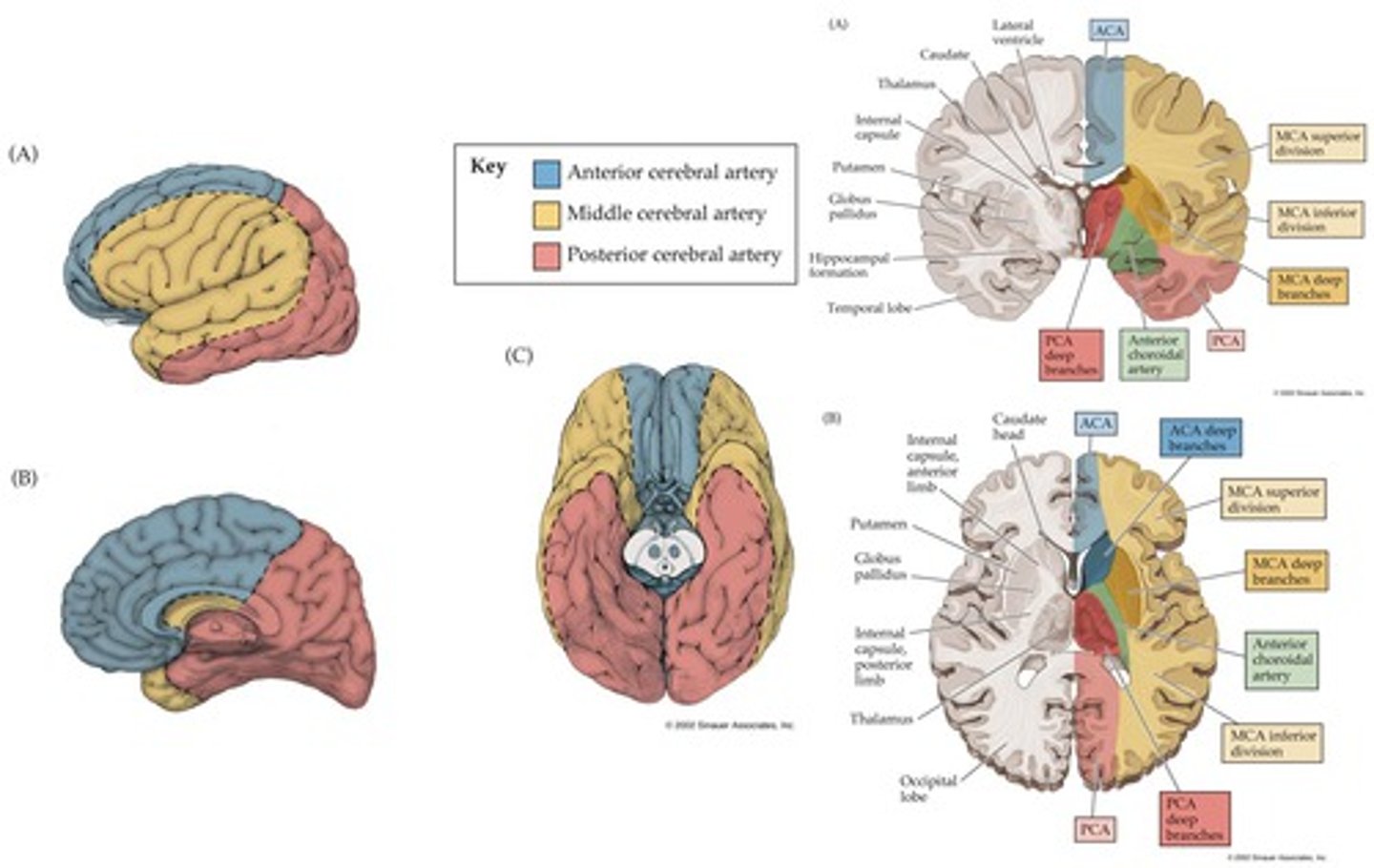
Middler Cerebral Artery CVA (most common)
Results in:
-CL motor and sensory loss involving UE and Face (UE>LE)
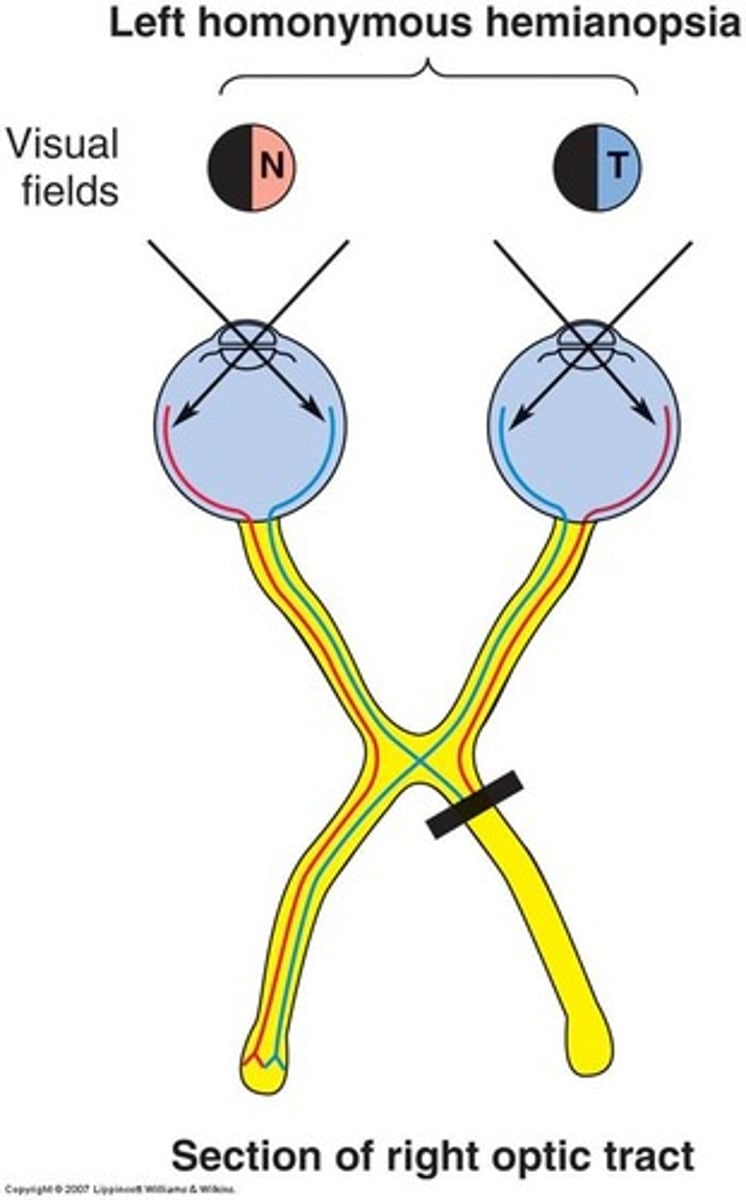
-CL homonymous hemianopsia
-If L CVA = aphasia
-If R CVA = perceptual problems (UL neglect, depth perception, spatial relations agnosia, apraxia)
Posterior Cerebral Artery CVA
Results in:
-CL homonymous hemianopsia
-Memory deficits
-Visual agnosia
-Prosopagnosia (difficulty naming people on sight)
-Central poststroke (thalamic pain)
Agnosia
inability to recognize an object by sight, touch or hearing
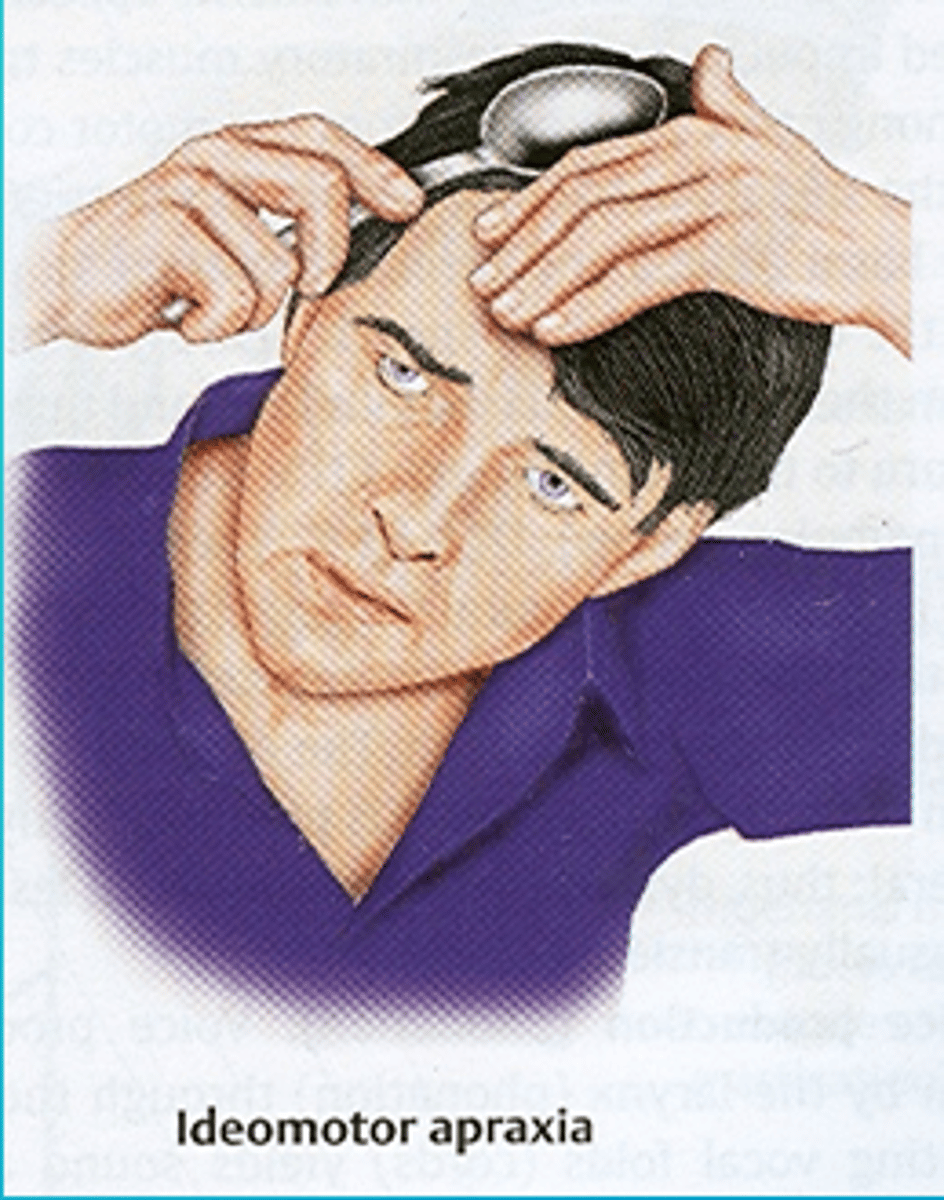
Apraxia
inability to carry out learned sequential movements on command

ideational apraxia
an impairment in the ability to carry out a sequence of actions because they do not recognize what to do with the object on command
Absolutely don't have the ability to do the task on command or on their own

ideomotor apraxia
the inability to carry out a simple motor activity in response to a verbal command, even though this same activity is readily performed spontaneously when provided with the object
Has the motor ability to do the task but not on command and only on their own

Form discrimination
unable to discriminate objects of similar shape/form

Figure-ground discrimination
inability to visually distinguish a figure from the background in which it is embedded
(example: buttons on a shirt)
R CVA clinical presentation
-L sided weakness/paralysis
-L neglect, spatial perceptual problems
-Poor judgement, (impulsive)
-Shortened attentions span and short-term memory loss
-Communication problems due to weakness in face
-Cognitive problems
R CVAs are like toddleRs - impulsive and no regard to safety
L CVA clinical presentation
-R sided weakness/paralysis
-Aphasia
-Personality changes - cautious, disorganize behavior
-Difficulty with new information, generalizing or conceptualizing
-Decreased memory
L CVA are like oLd people - slow and cautious people
UE flexion synergy pattern
-Scapular retraction, elevation or hyperextension
-Shoulder ABD/ER
-Elbow flexion
-Forearm supination
-Wrist and finger flexion
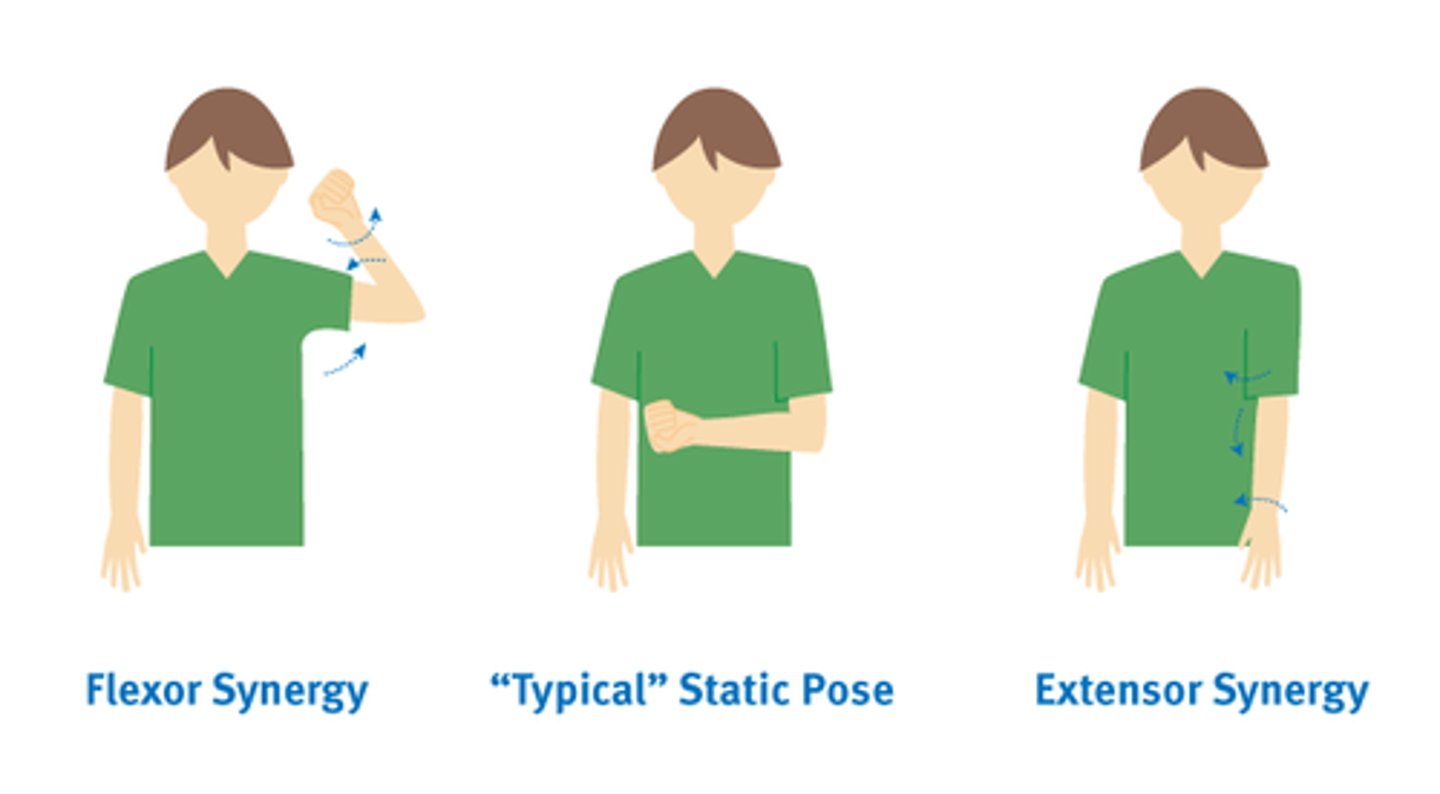
LE extension synergy pattern
-Hip ext/ADD/IR
-Knee extension
-Ankle PF, Inv
-Toe extension
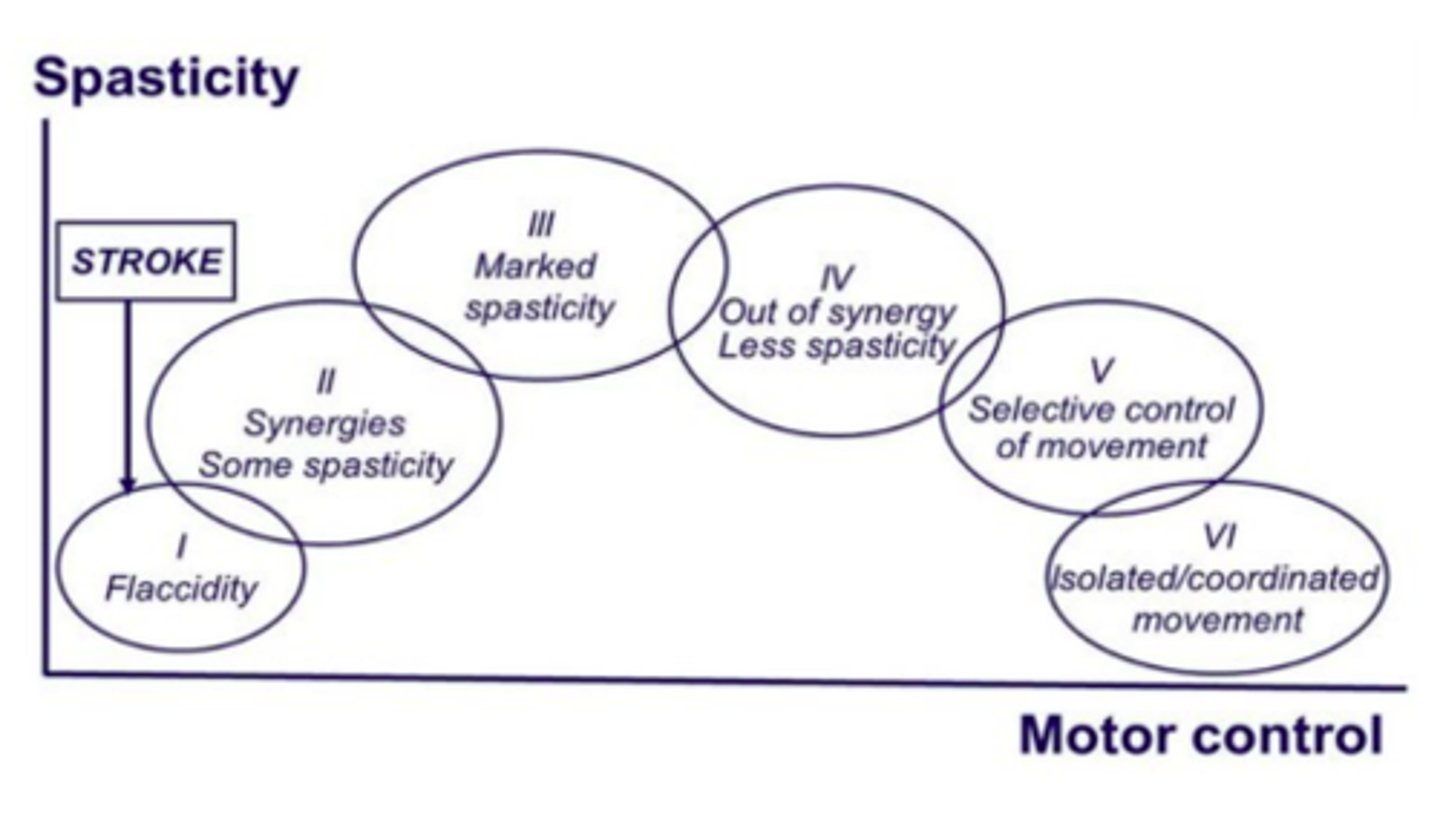
What stage of the brunnstrom's stages does spasticity peak?
Stage 3
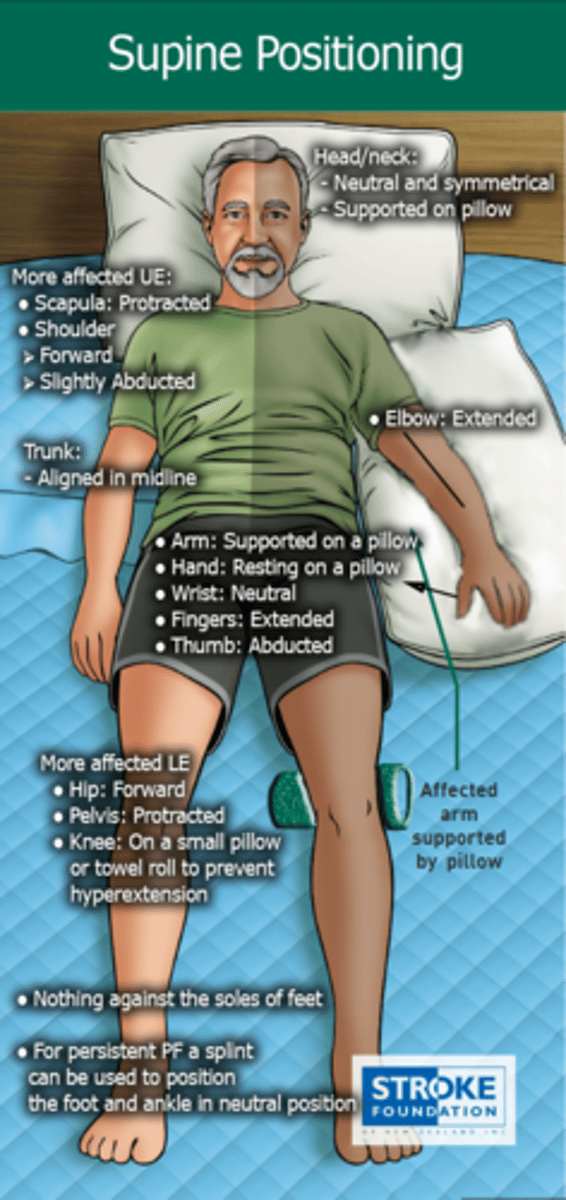
Supine Positioning for CVA pt in bed
Head/neck: Neutral
Trunk: midline
More affected UE:
-Scapular protraction
-Shoulder forward and slight ABD
-Arm supported on pillow
-Elbow extended
-Hand on pillow w/ neutral wrist, fingers extended and thumb ABD
More affected LE:
-Hip forward
-Knee on small pillow to prevent hyperextension
-Nothing against soles of feet
-Can splint for PF persisting
Side-lying on more affected side positioning for CVA pt in bed
Head/neck: neutral
Trunk: midline
More affected UE:
-Scapular protraction
-Shoulder forward
-Arm in slight ABD and ER
-Elbow extended
-Forearm supinated
-neutral wrist, fingers extended and thumb ABD
More affected LE:
-Hip extended
-Knee flexed and supported by pillows
(Alt: slight hip and knee flexion with pelvic rotation)

Side-lying on LESS affected side positioning for CVA pt in bed
Head/neck: neutral
Trunk: midline; small pillow under ribs to elongate side
More affected UE:
-Scapular protraction
-Shoulder forward
-Arm supported on pillow with
-Elbow extended
-Forearm supinated
-neutral wrist, fingers extended and thumb ABD
More affected LE:
-hip flexion and knee flexion but all on pillow

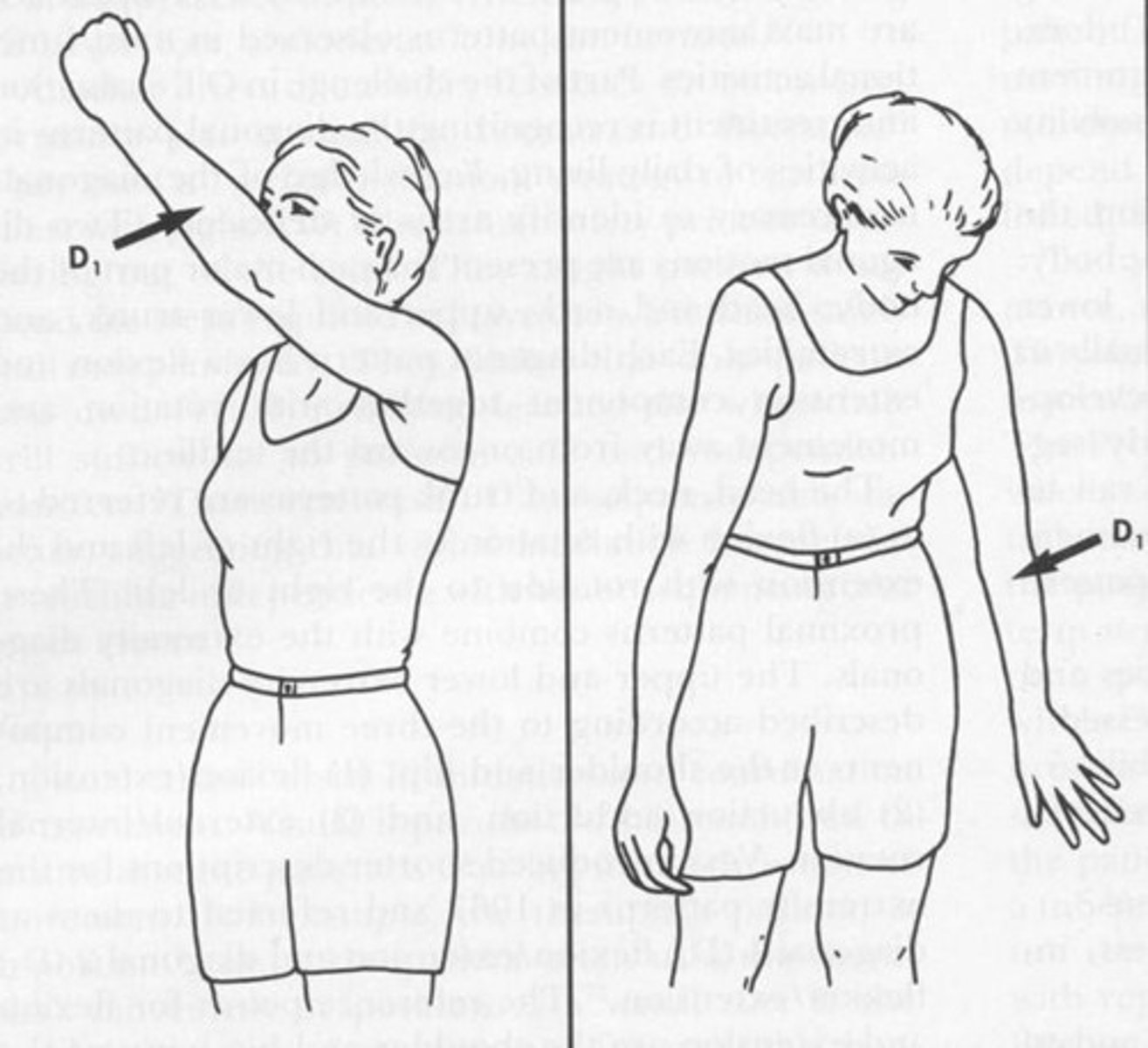
UE D1 flexion
Shoulder: Flex, ADD and ER
Forearm: supinated
Wrist: radially flexed
(Putting on a seat belt or eating)
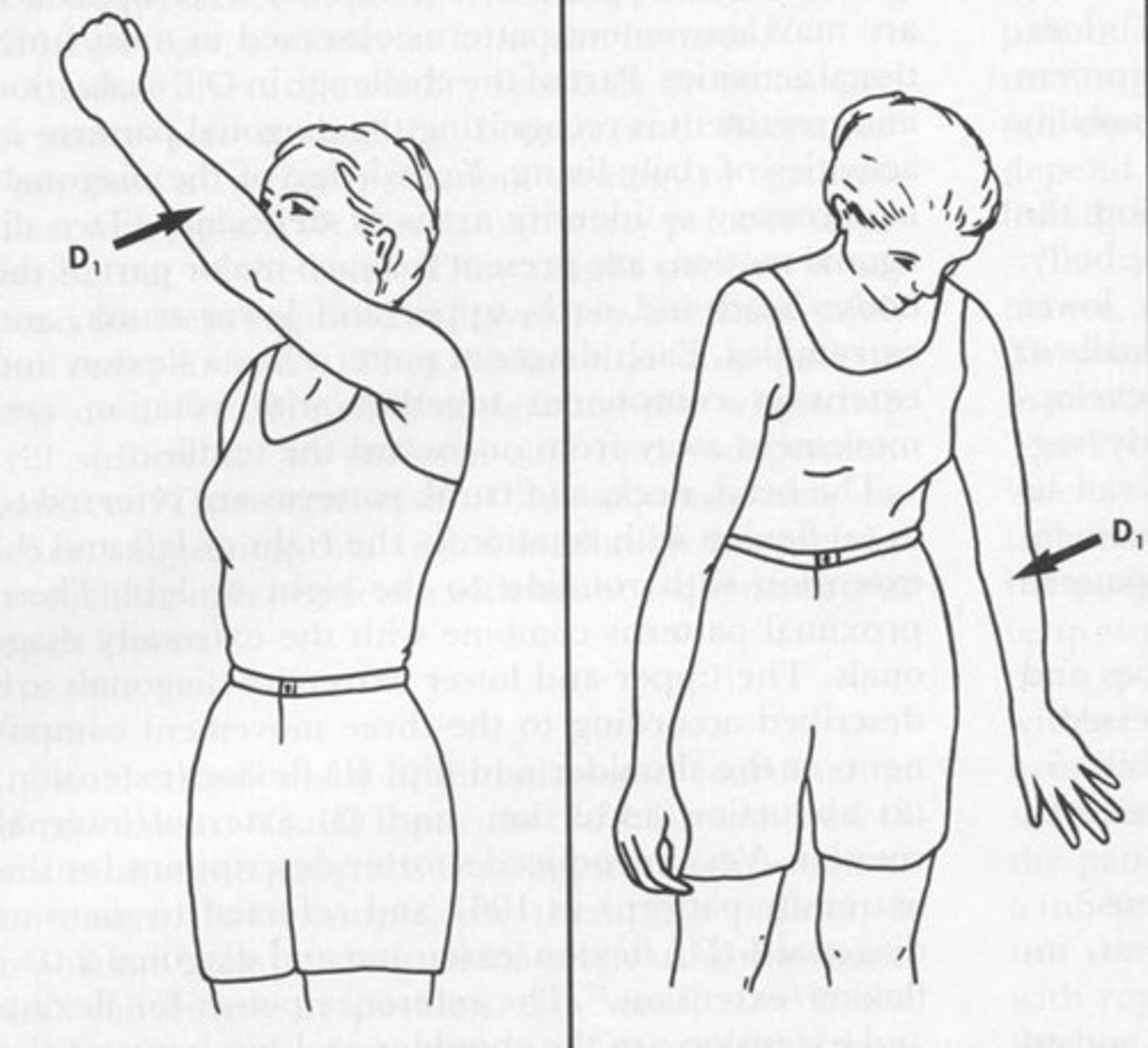
UE D1 Extension
Shoulder: Ext, ABD and IR
Forearm: pronated
Wrist: ulnarly extended
(pushing away the bad food)
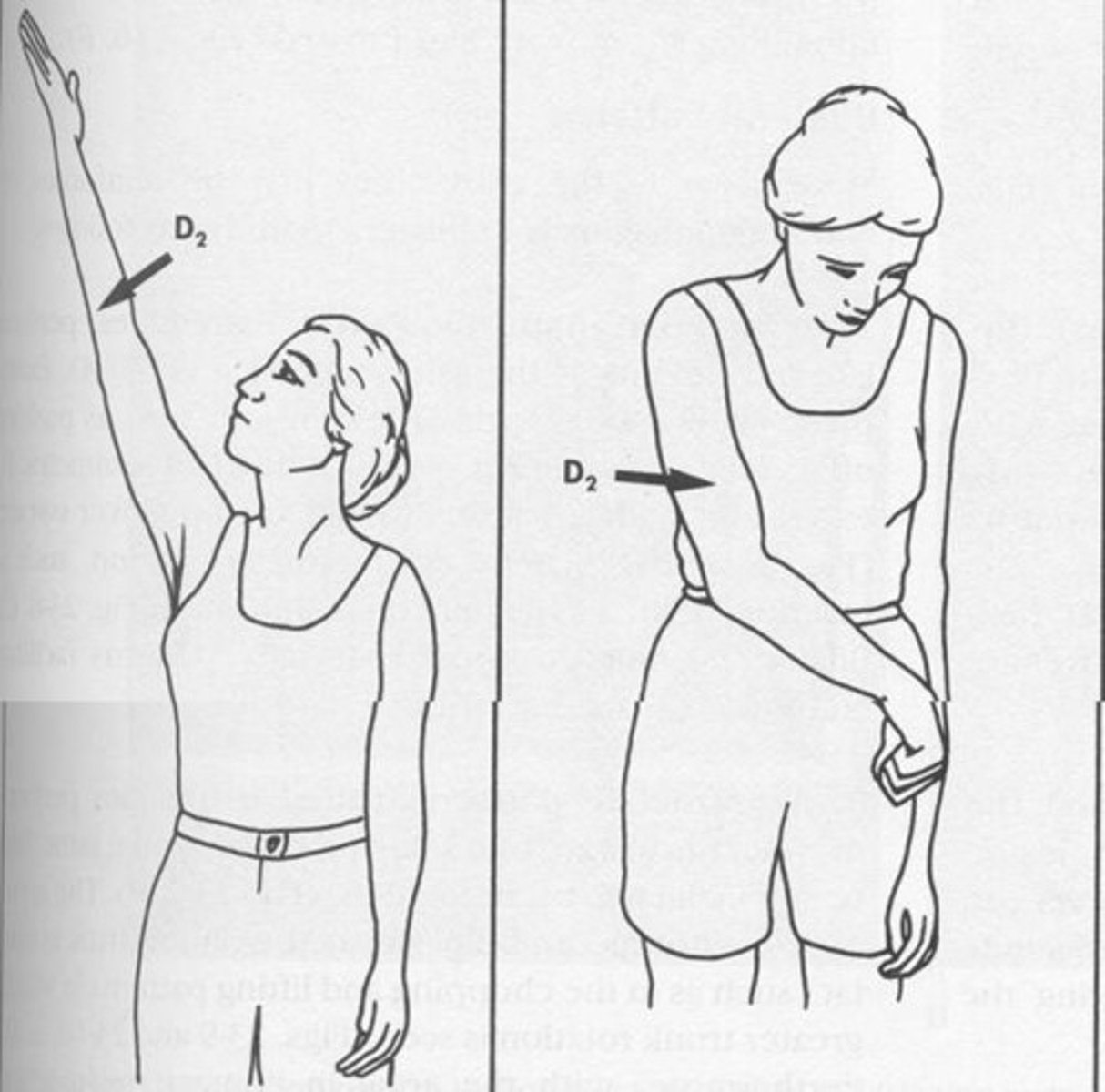
UE D2 Flexion
Shoulder: Flex, ABD, and ER
Wrist: radially extended
(Draw your sword)

UE D2 Extension
Shoulder: Ext, ADD, and IR
Wrist: ulnarly flexed
(Putting sword back)
Head/neck and trunk chop
Lead arm= Weak arm begins in D1 Flex --> D1 ext
Strong arm = holds from the top of the wrist and moves into D2 ext
Remember: we don't chop our legs
So Chops only happen for weak arm doing D1 flex<>ext
(used as HEP PNF)
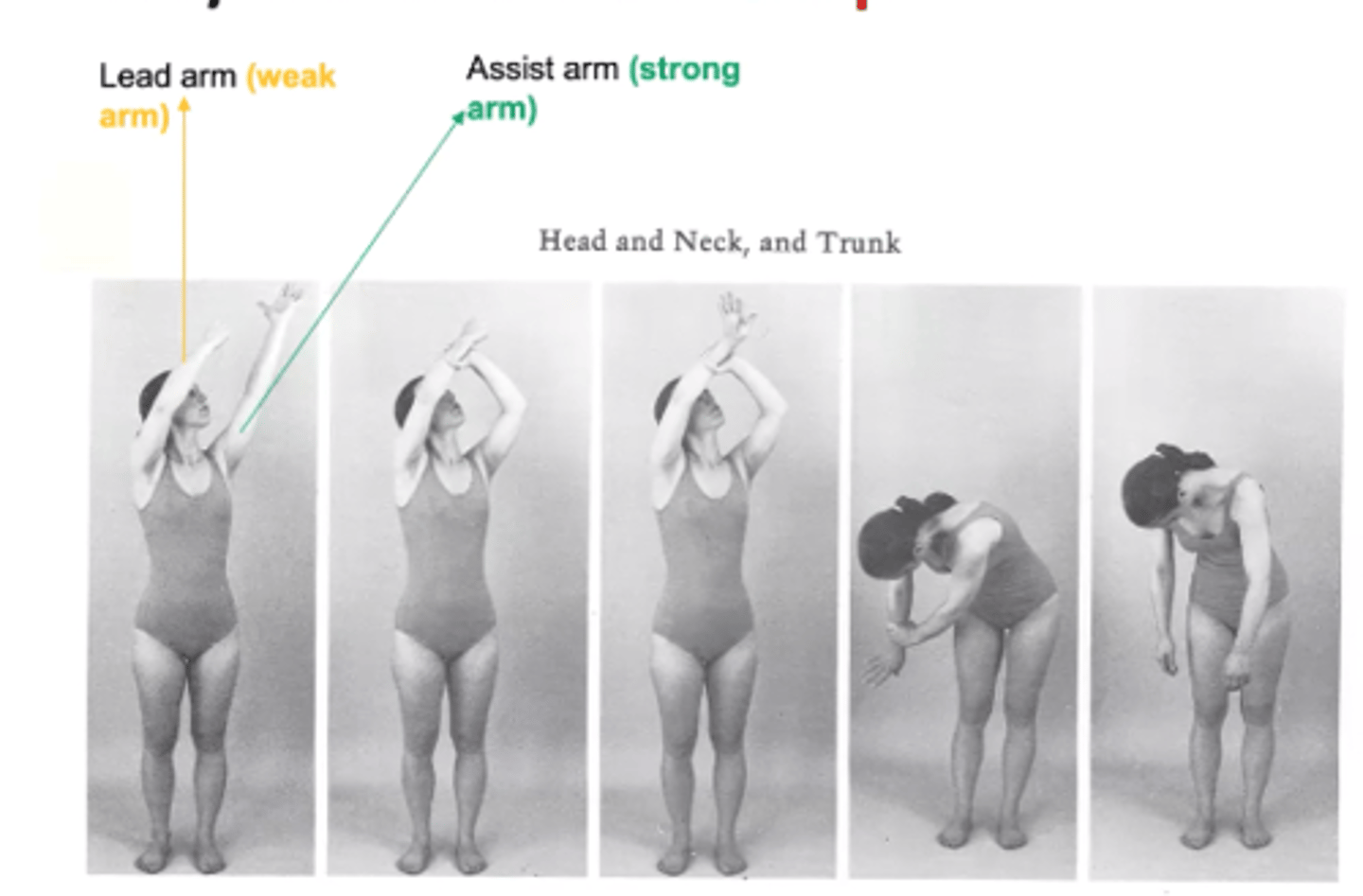

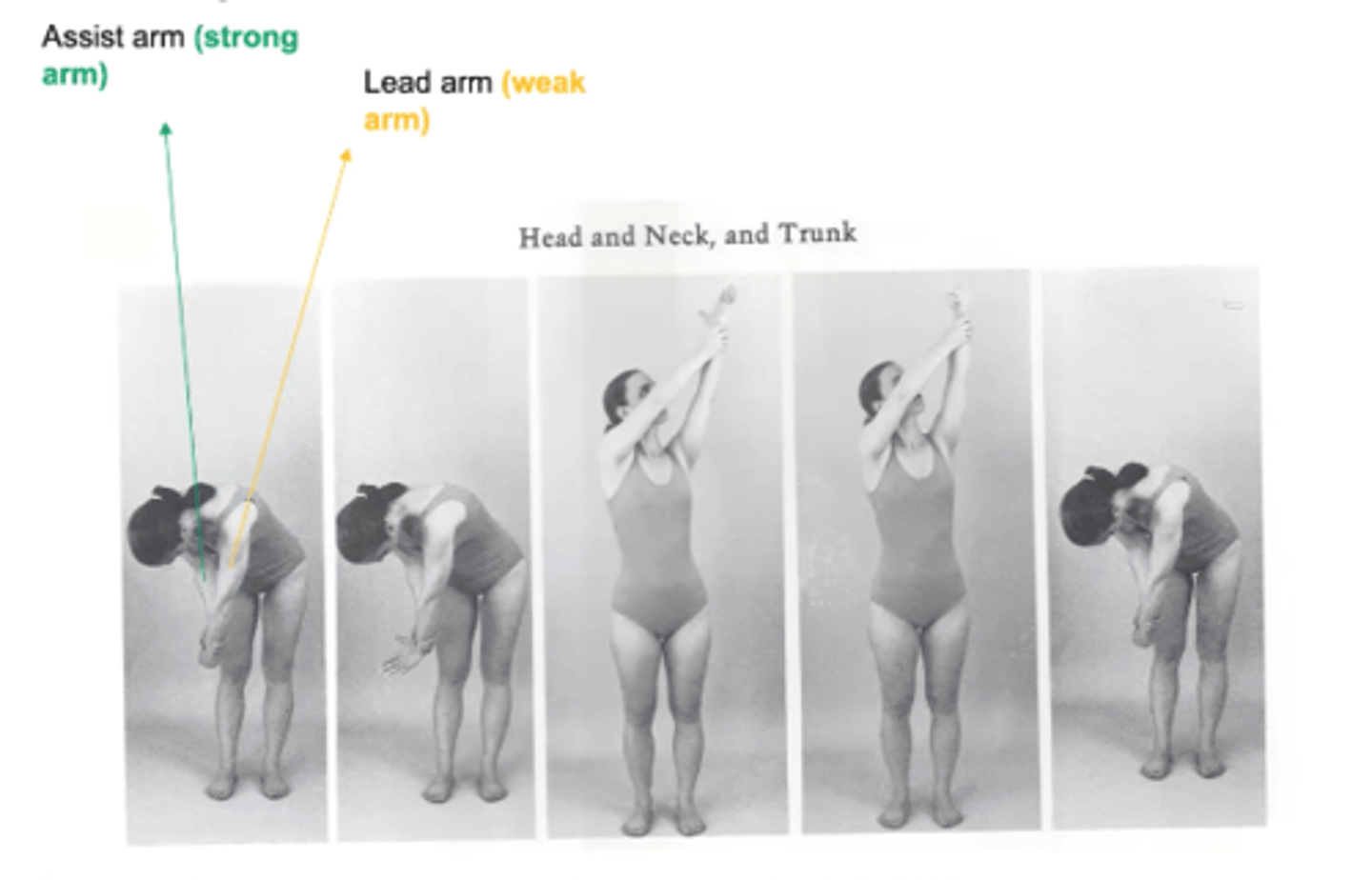
Head/neck and trunk lift
Lead arm = weak arm begins in D2 extension --> D2 flex
Strong arm = holds from underneath wrist and moves into
D1 flex
Remember: we would want to lift our sword up until the end of battle
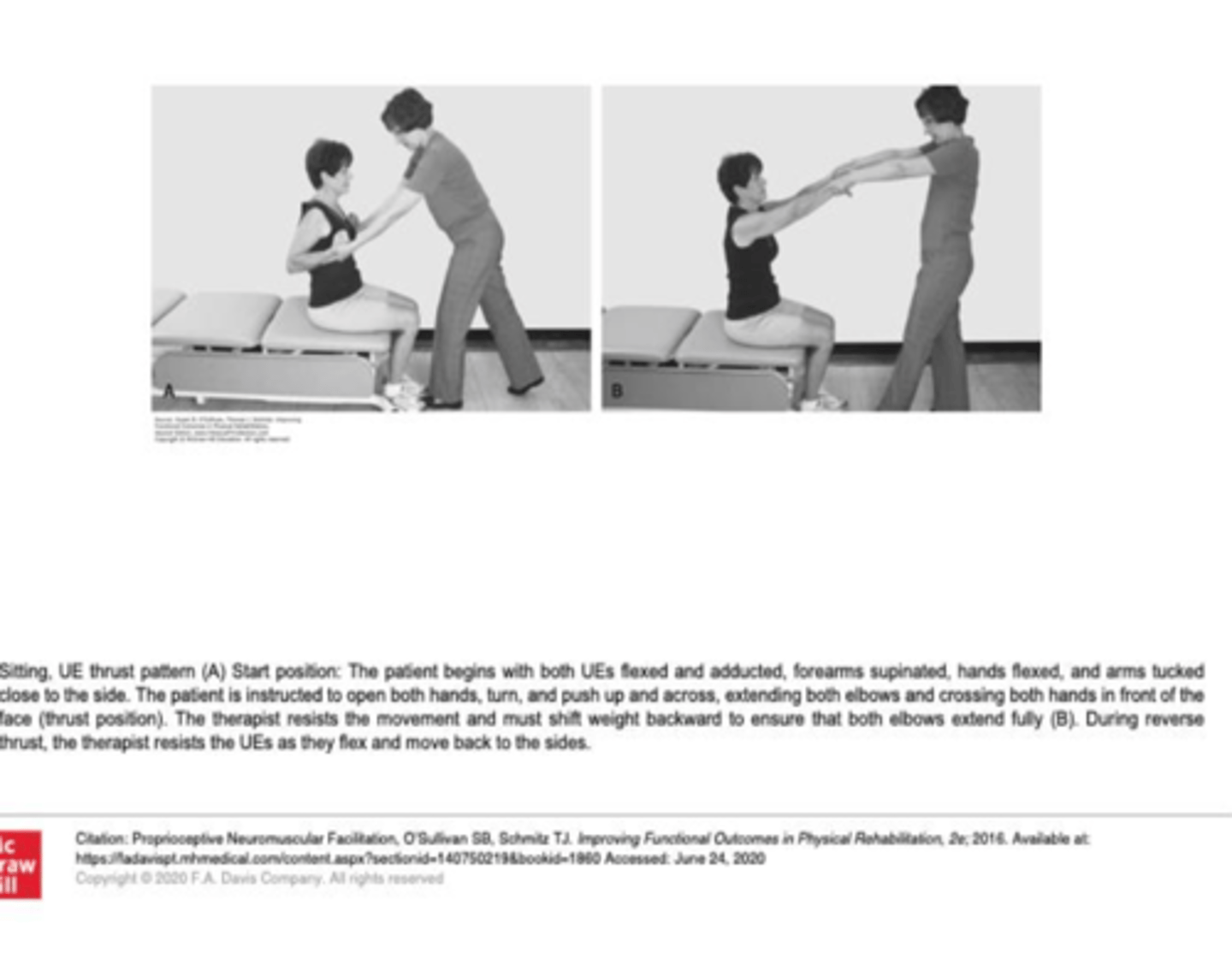
UE Thrust Pattern
Both UEs flexed and ADD, forearms supinated and hands flexed and arms tucked close to side
Pt asked to thrust out and PT resists motion out and back in
LE D1 Flexion
Hip: Flex, ADD, ER
Knee: Ext or flex
Ankle: DF, Inv
Toe: extension
Hacky sack

LE D1 Extension
Hip: extension, ABD, IR
Knee: flex or ext
Ankle: PF, Ev
Toe: flex

LE D2 Flexion
Hip: flex, ABD, IR
Knee: flex
Ankle: DF, Eve
Toe: Flex
(pee on the firehydrant)
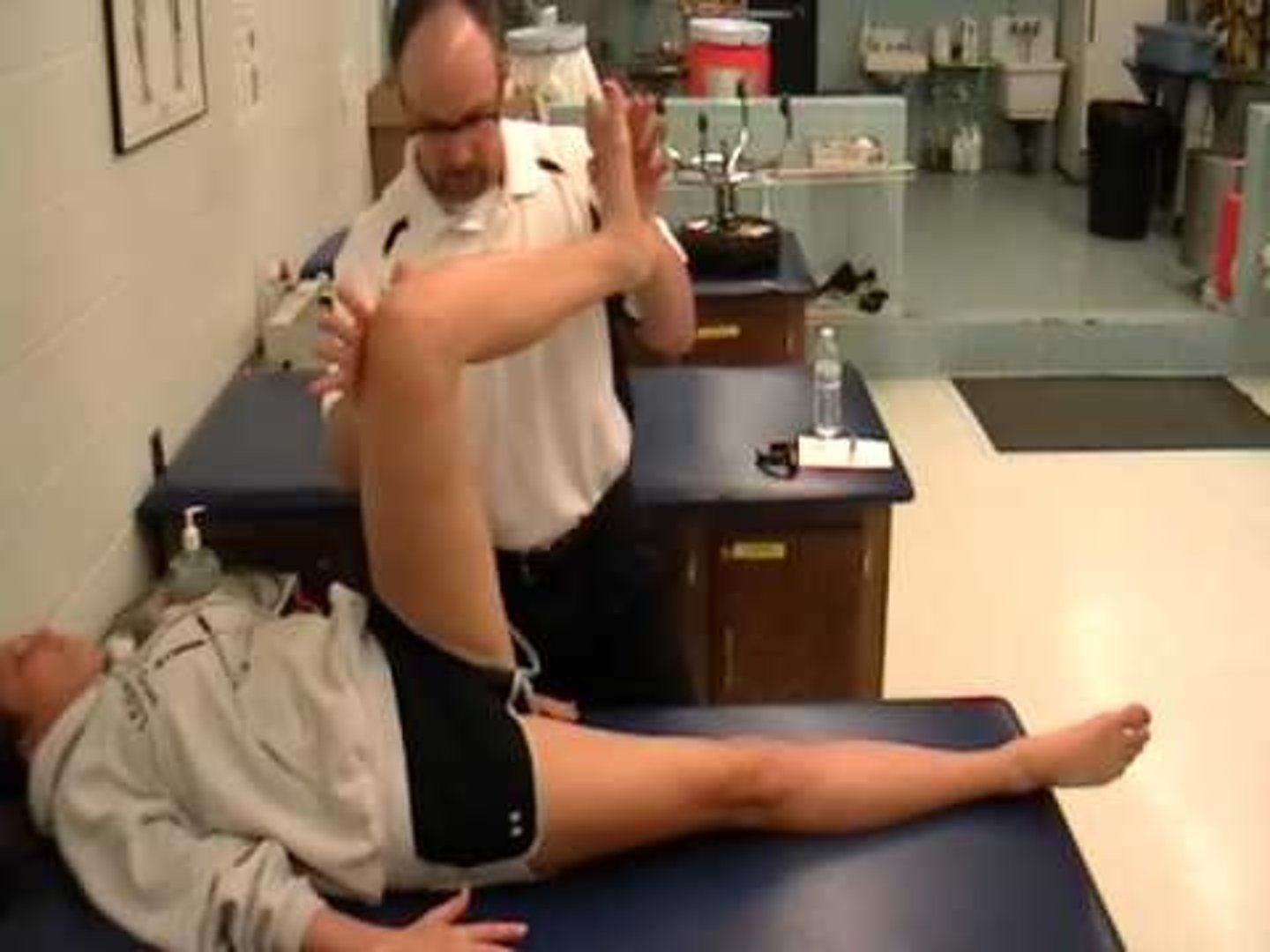
LE D2 Extension
Hip: ext, ADD and IR
Knee: flex or ext
Ankle: PF, Inv
Toe: flex
(Image: R leg)
Can kind of think like crossing legs to not pee

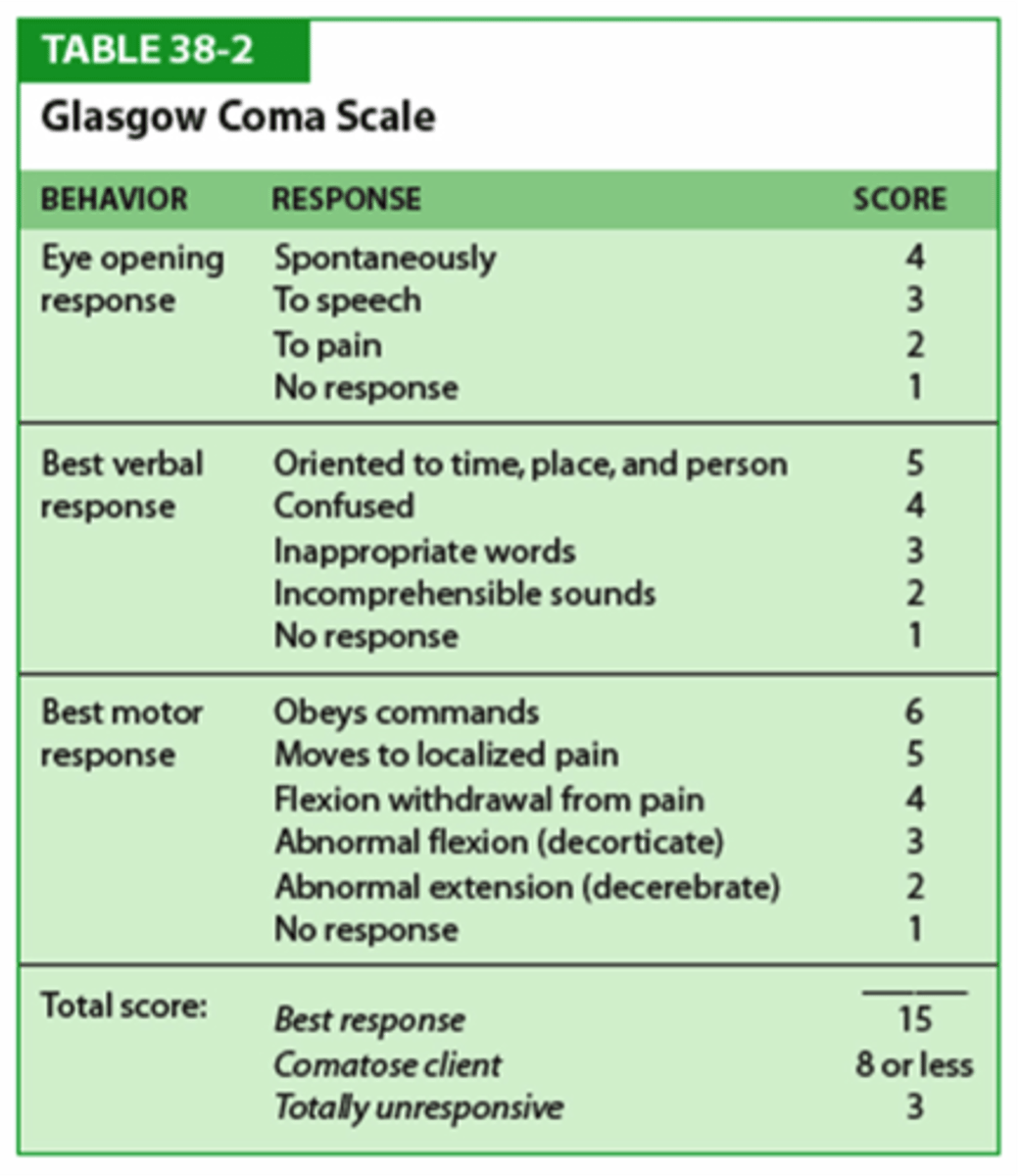
GCS measures
Level of consciousness
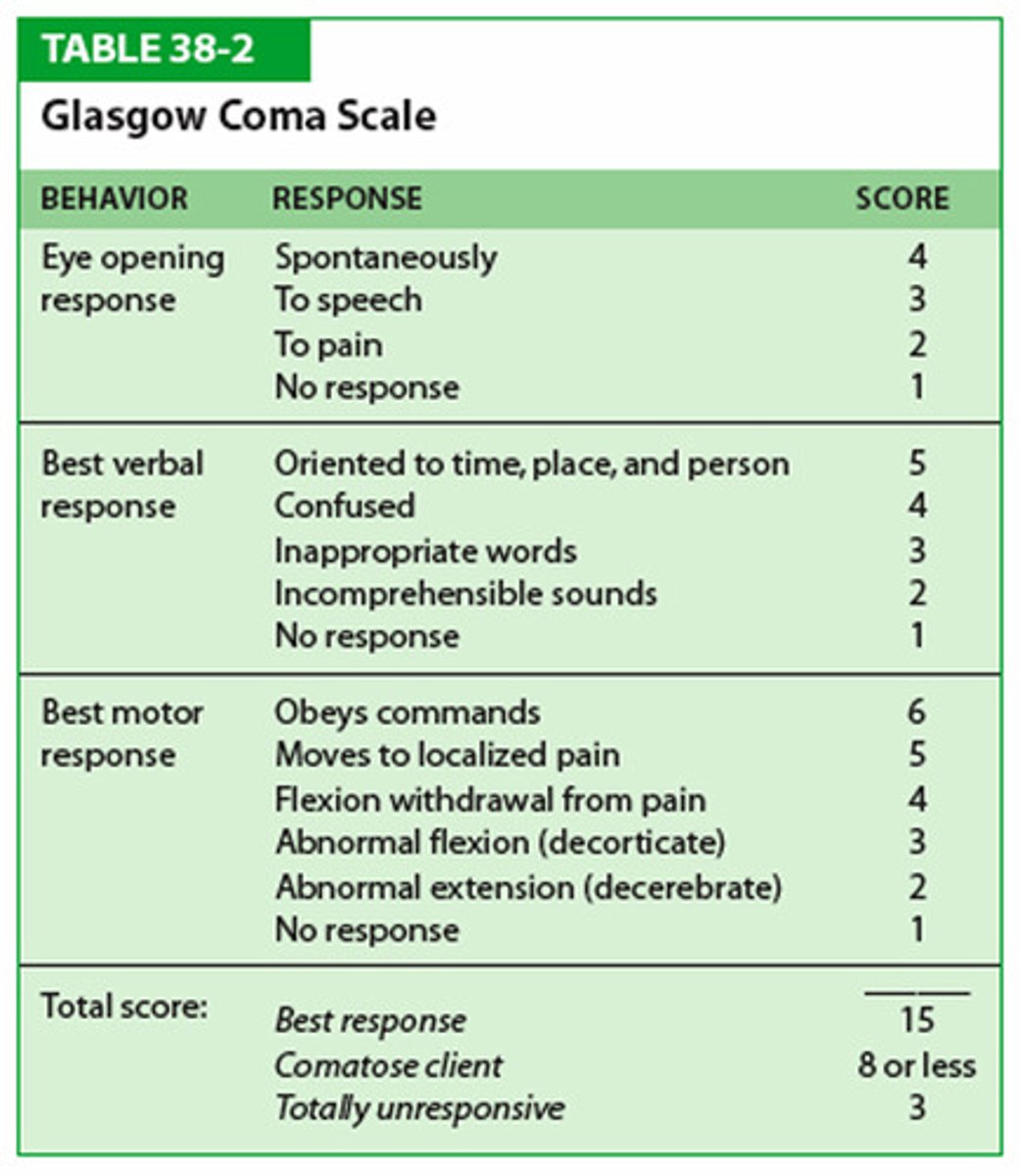
GCS Scores
- 8 or less, Severe
- 9-12, Moderate
- 13-15, Mild
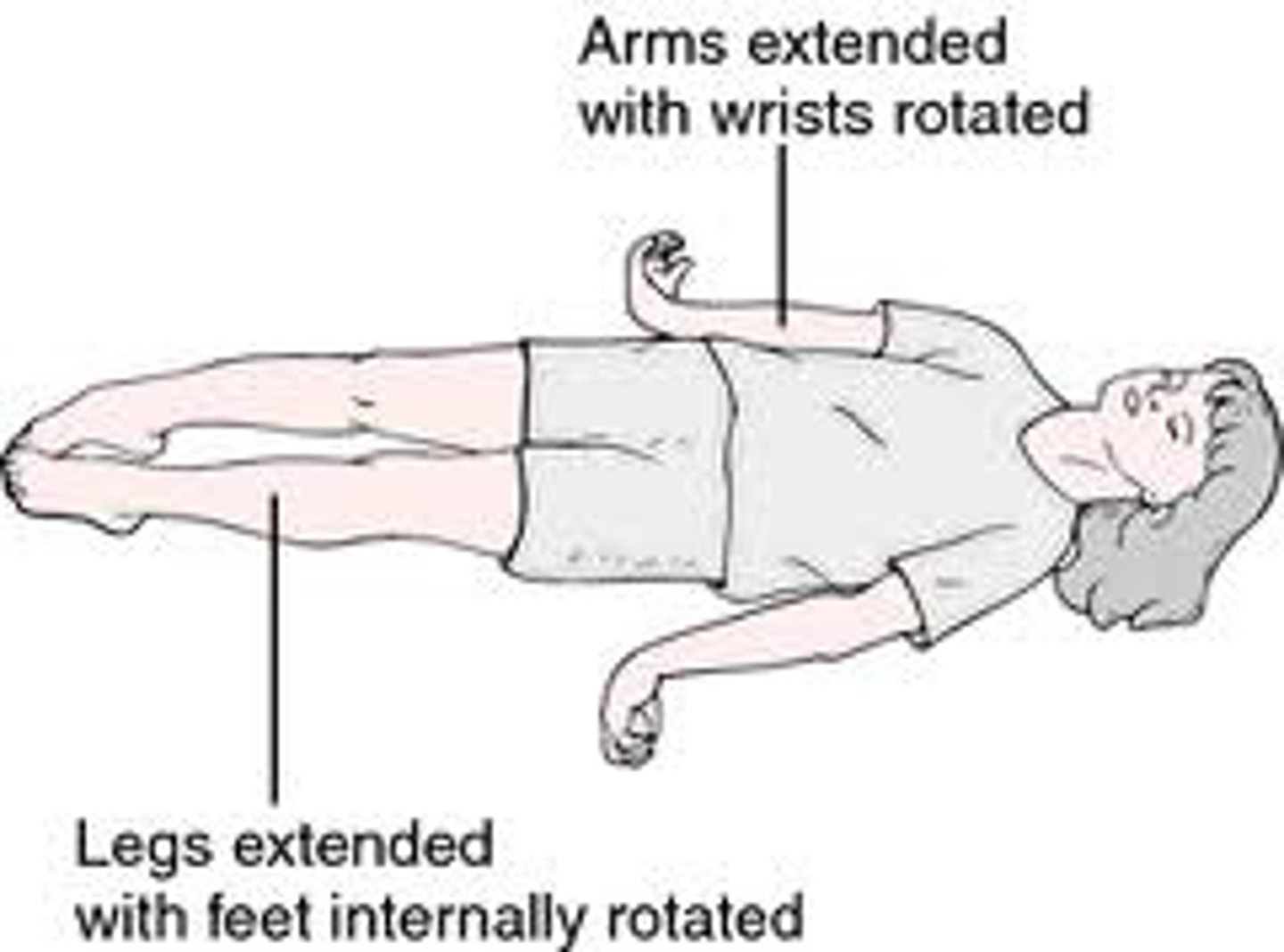
Decordicate posturing
UE: arms are flexed/adducted with the wrists and fingers are flexed
LE: legs are extended with feet plantar flexed
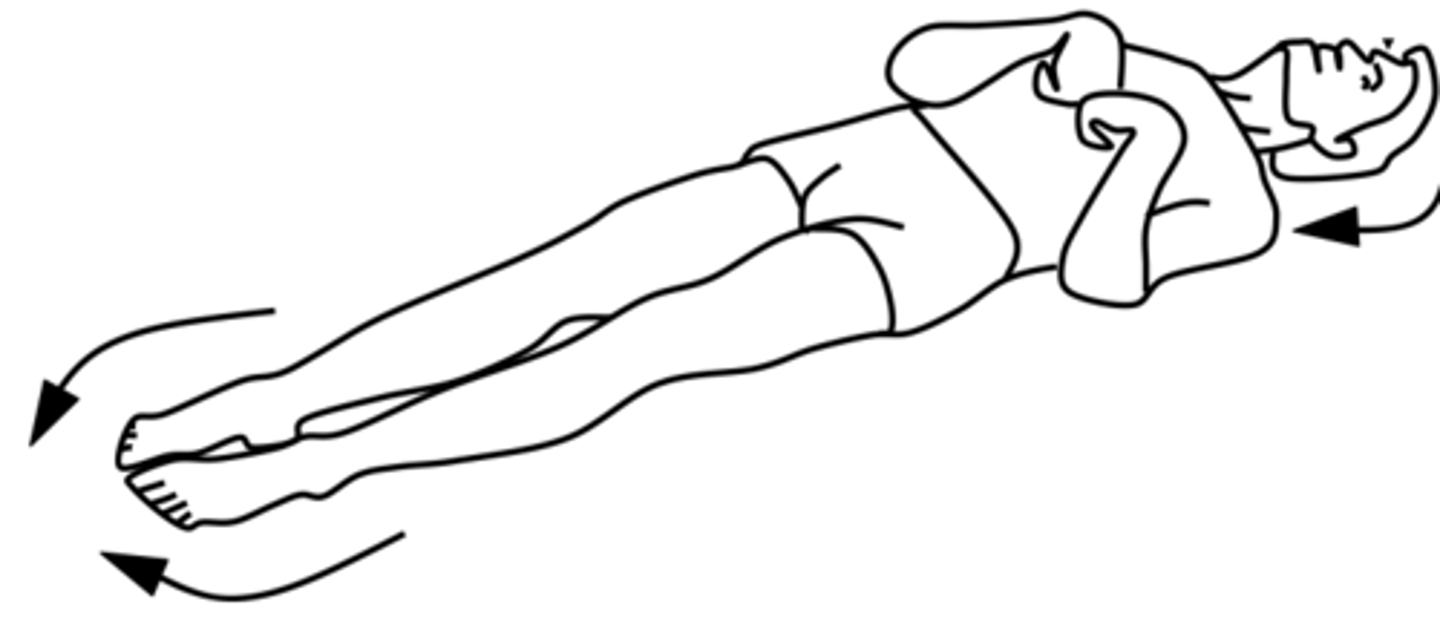
Decerebrate posturing
-"extensor posturing";
-abduction of arms, elbow and wrist extension and extension and PF of legs
Think decerebrate has a lot of e's for extension of all extremities
Rancho IV
Confused and agitated
-alert and has increased state of activity
-may be aggressive of flight behavior
-absent short-term memory
-unable to really cooperate with treatment
Tx:
-calm area for tx
-be calm and consistent (same time, place, PT)
-know when to stop
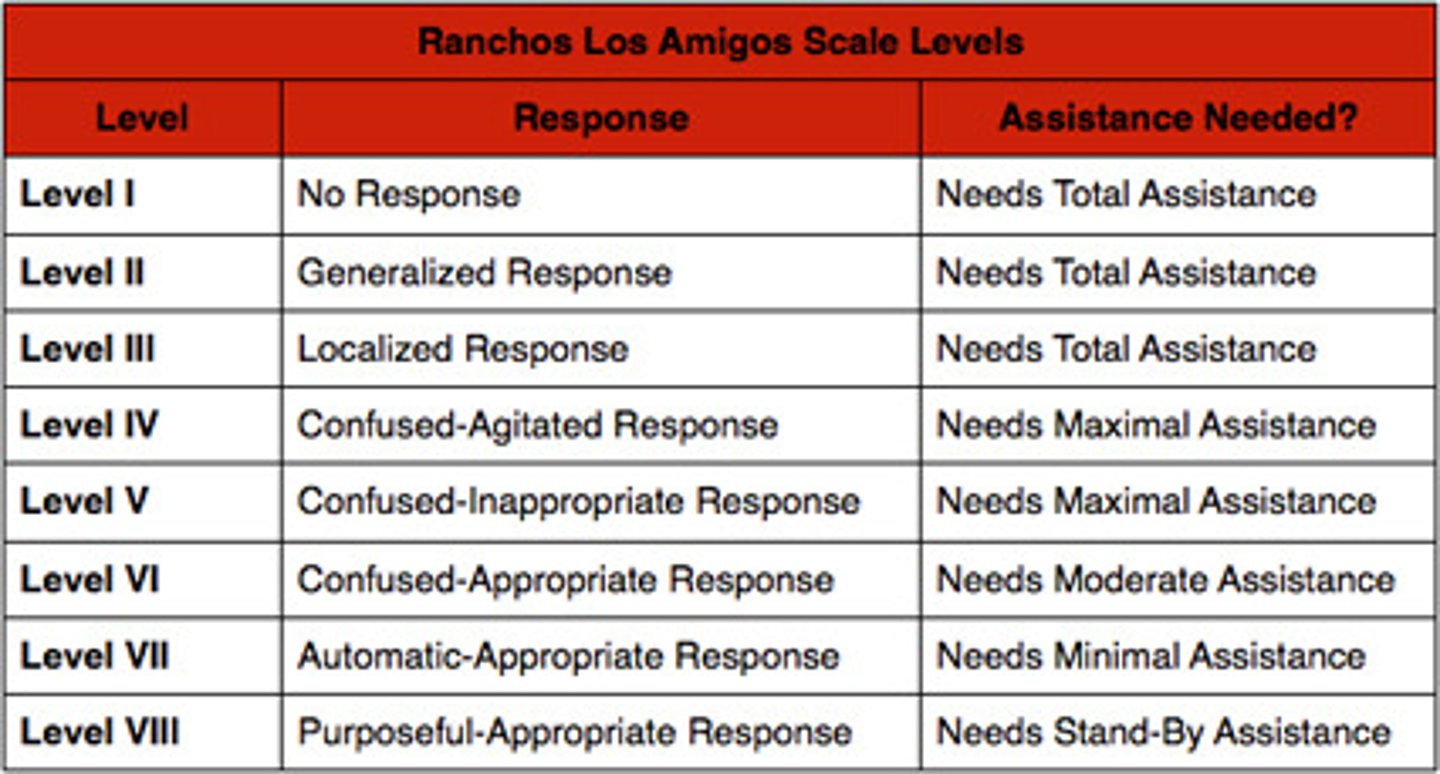
Rancho V
Confused, inappropriate, non-agitated
-unable to learn new info
-frequent brief periods
-consistent with simple commands
-inappropriate use of objects
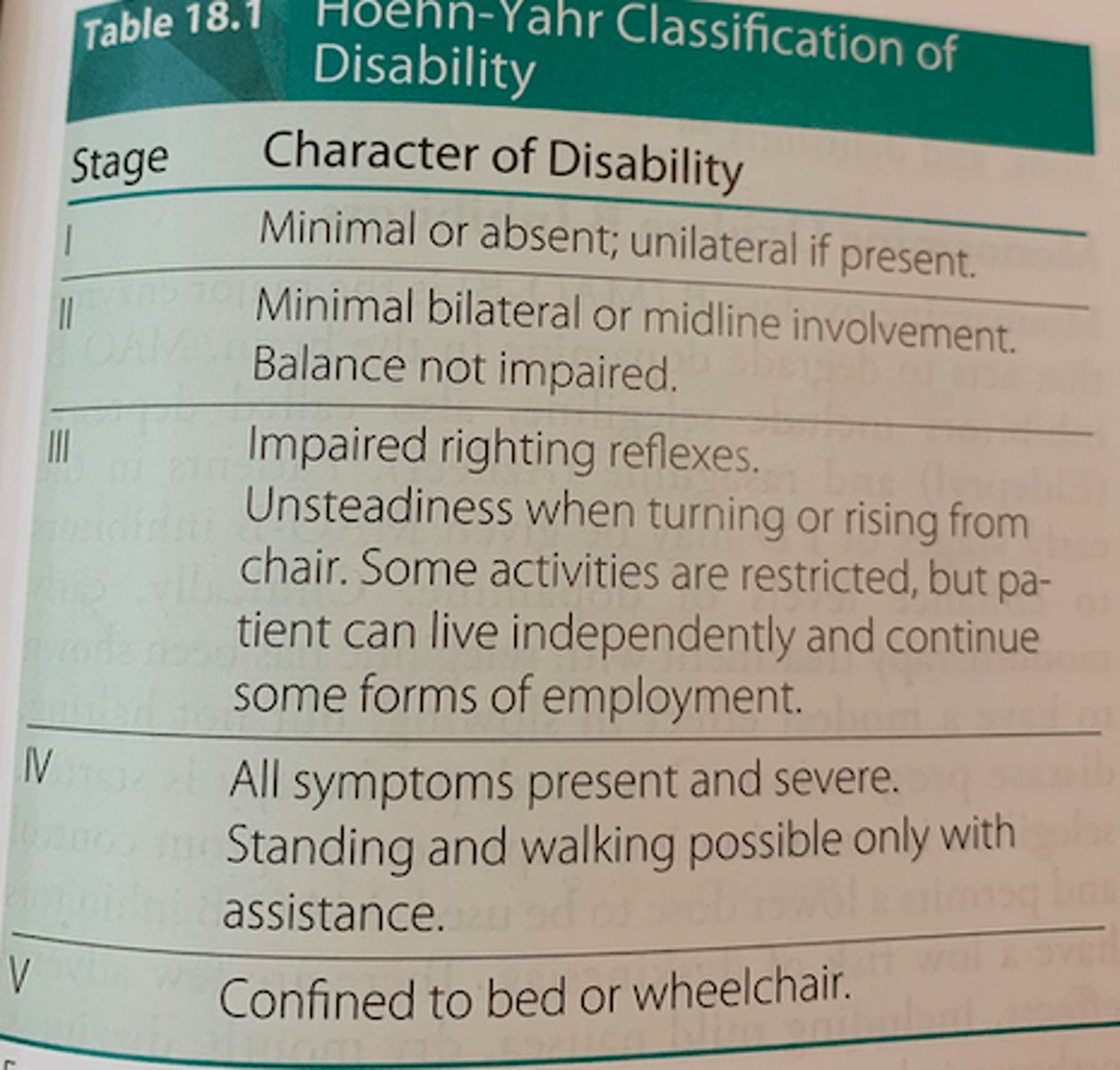
Hoehn and Yahr Scale
I - minimal or absent; UL if present
II - Minimal BL or midline involvement; balance not impaired
III - Impaired righting reflexes, Unsteadiness when turning or rising from chair, Some activities restricted but can live indep
IV - All symptoms present and severe, standing and walking possible with assitance
V - confined to bed or w/c
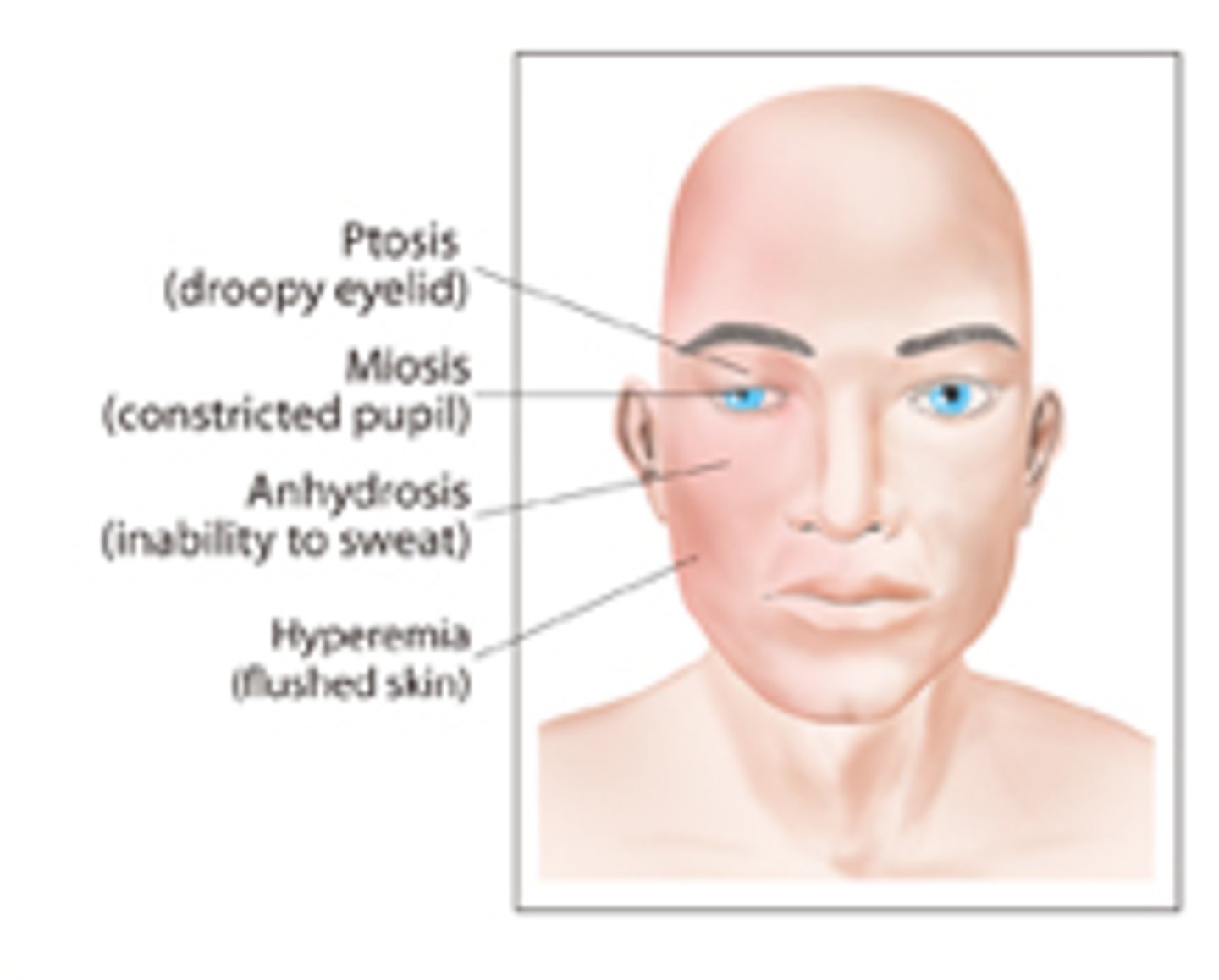
Horner's Syndrome
What: Stroke of vertebrobasilar artery
Clinical Presentation:
-miosis (pupil constriction)
-ptosis (droppy eyelid)
-Decreased sweating
-Dsyphagia and dysphonia
-Impaired thermal sense over 50% of body
Vertebral Arteries supplies
Cerebellum: Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA)
Medulla: Medullary Artery
Basilar arteries supplies:
Pons: pontine arteries
Internal ear: Labyrinthine arteries
Cerebellum: Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (AICA)
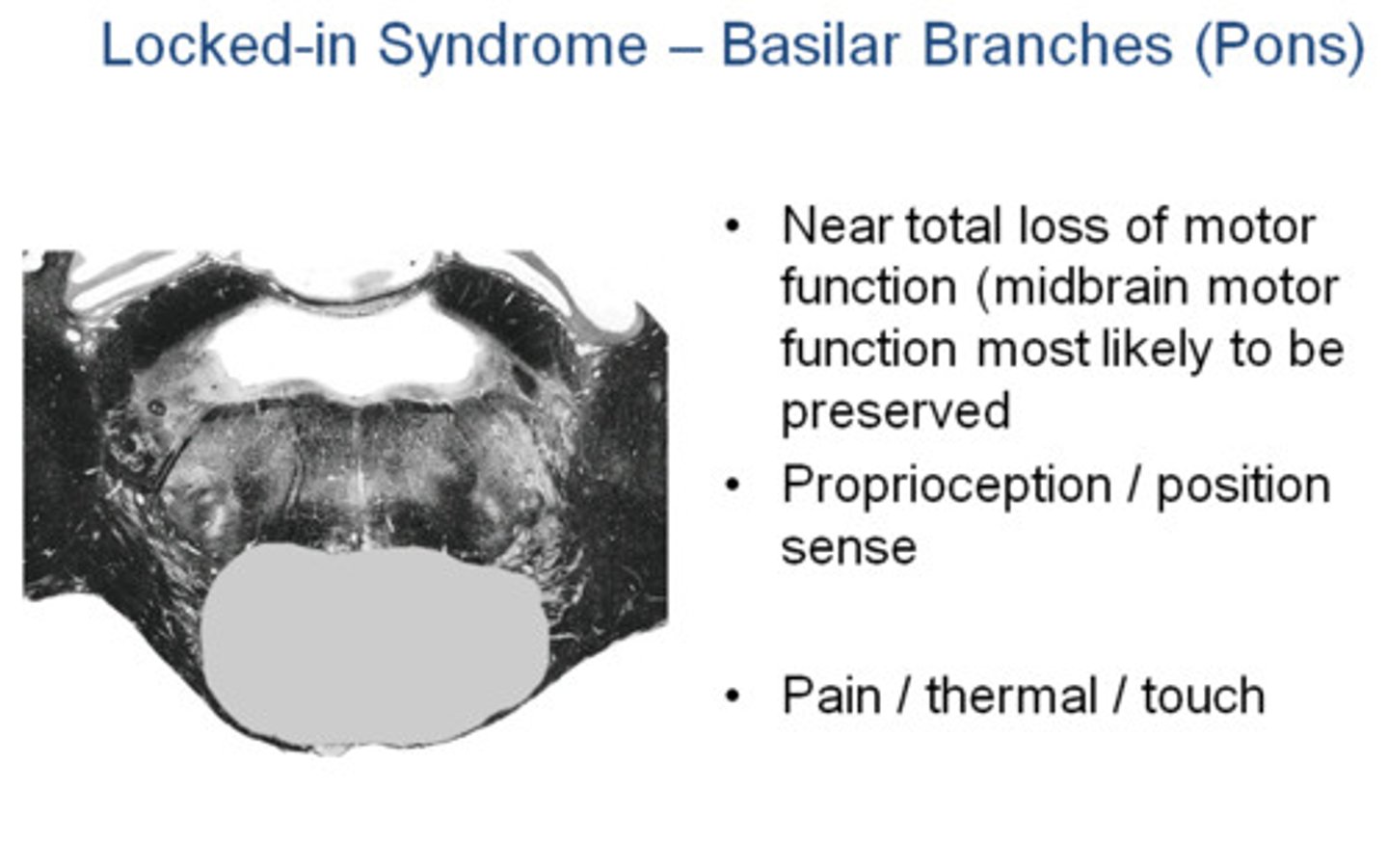
Locked-in syndrome
What: Caused by thrombosis and BL infarction of ventral pons
Presentation:
-acute hemiparesis progressing to tetraplegia and lower bulbar paralysis (CN V-XII)
-Mutism
-Cannot move or speak but alert and oriented
-Vertical eye movement and blinking preserved
Important muscles for each SCI level:
C2-3: part diaphragm, neck extensors, facial muscles
C4: diaphragm, traps (sip and puff)
C5: 3BIRDS - Biceps, Brachioradialis, Brachialis, Infrasp, Rhomboids, Deltoid, Supinator
C6: PET SLIP - P Major, ECR, T minor, SA, LD, Infrasp, Pronator
C7: FEET- FCR, EBP, Extrinsic finger ext and Triceps
C8: wrist flexion and finger flexion, hand instrisics
T1-6: hand intrinsics, full UE use, PHYSIOLOGICAL walking (RGOs)
T8-T12: abdominal muscles, KAFO's
L1-L2: iliopsoas, community ambulation, needs w/c
L3-L4: quadriceps, indep ambulation with (K)AFOs and crutches
Brown POT
Brown Sequard Syndrome = Pain and Temp lost on the Opposite side of the injury
SCI ASIA scale simplified
A- complete loss
B- Incomplete, Sensory (+) but motor (-)
C- Incomplete, Sensory (+) and Motor (+) but LESS than 50% mm have MMT >3/5
D- Incomplete, Sensory (+) and Motor (+) but MORE than 50% mm have MMT >3/5
E- E is ME = Normal
SCI below T10 has
mostly normal respiration
Spastic Bladder (UMN)
-Pt with injury ABOVE S2
Tx
-intermittent catheterization every 3-6 hours (4 hours optimal)
-Suprapubic tapping
Flaccid Bladder (LMN)
-Pt with injury BELOW S2
Tx
-intermittent catheterization every 3-6 hours
-valsalva or crede's maneuver
Key Muscles for C5 SCI = 3BIRDS
3B - biceps, brachioradialis, brachialis
I- Infraspinatus
R- Rhomboids
D- Deltoid
S- Supinators

Key Muscles for C6 SCI = PET SLIP
P- Pec Major
E- ECR
T- Teres minor
S- Serratus Anterior
L- Lat Dorsi
I - Infraspinatus
P- Pronator

Key Muscles for C7 SCI = FEET
F- FCR
E- EPB and EPL
E- Extrinsic finger ext
T- Triceps
SCI C1-C2 respiratory
-Relies on ventilator
-But has some innervation of: Upper Traps, SCM, Neck extensors, Facial muscles
SCI C3-C4 respiratory
-Relies on ventilator
-But has some innervation of diaphragm, scalenes and levator scapulae
C4 can do glossopharyngeal breathing