MOD 2 - Data Acquisition Methods
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Three methods of acquiring data (Types of Scans)
Localizer Scans
Sequential Scans
Helical Scans
Types of Data Acquisition of Sequential Scans
Continuous = one slice abuts the next
Gapped = taken when a survey of an area is needed, and imaging of every part of the region is not required
Overlapping = rare, because they raise patient dose and don’t provide additional diagnostic info
Benefit vs. Disadvantage of Sequential Scans
Benefit = very slightly improved spatial resolution due to perpendicular slices (not helical), and the patient is stationary
Disadvantage
excessive scan time (significant when using contrast media, breathing instructions)
inability to create MPR's from raw data (must be helical)
Slice misregistration (when a patient breathes differently with each data acquisition)
data gaps
Helical Scans (spiral)
The most common method
Requires continuous tube/detector activation and rotation while the table feeds through the gantry at a prescribed speed
Volume of data / Feature of Helical Scans
the result of helical data acquisition (an unsliced loaf of bread) which can be reconstructed
Pitch - Helical Scans
= Table movement per rotation/ beam width (or detector collimation)
= Describes the table movement throughout a helical scan acquisition
pitch<1 = anatomy scanned multiple times (tabled slower)
pitch>1 = data gaps are created (table faster)
Pitch = 1 = table feed and beam collimations are identical
Most Common Pitch
1-1.5
Types of MDCT Detector Arrays
Fixed
Adapted
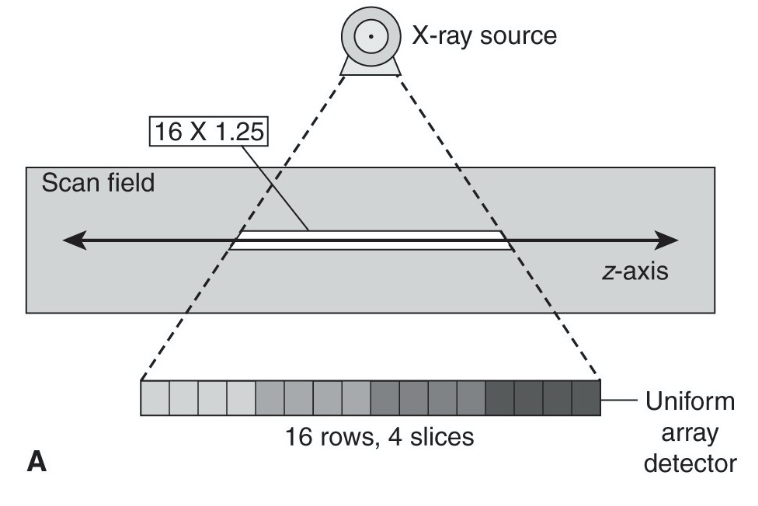
Fixed MDCT
contain multiple rows of detectors of the same dimension
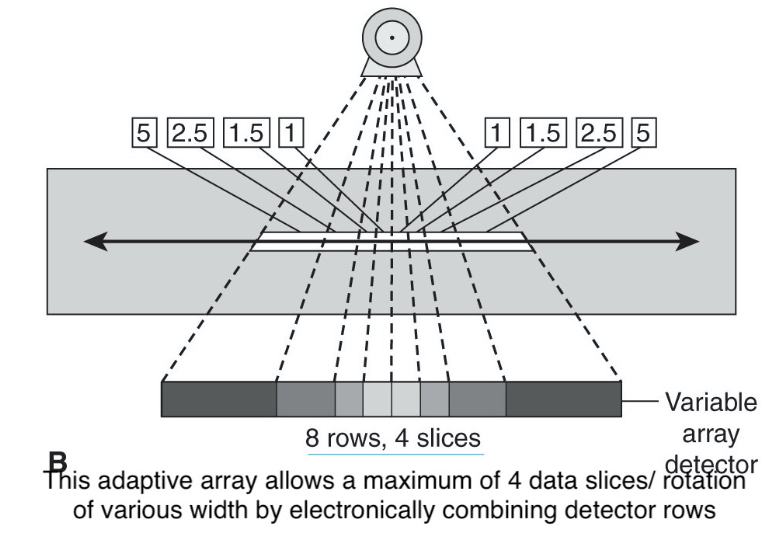
Adaptive MDCT
contain detector rows of varying dimensions (in the z-axis)
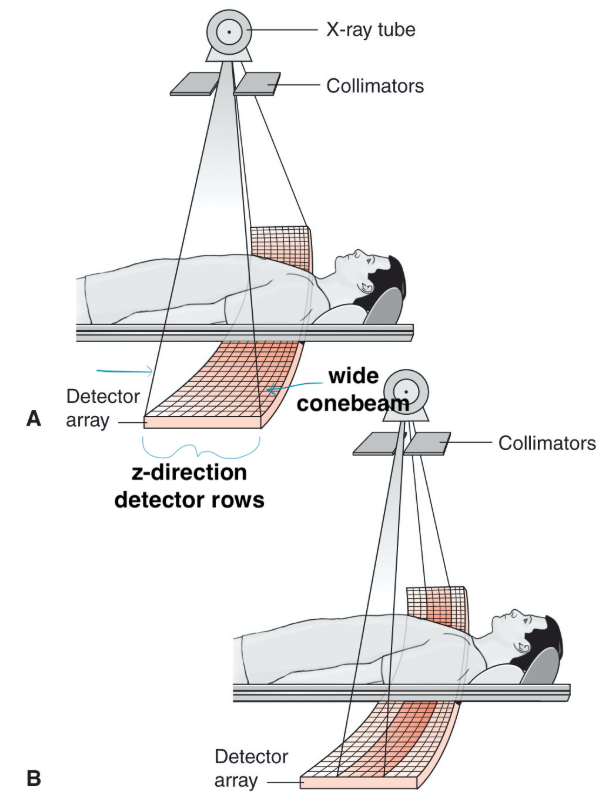
MDCT Advantage
= ability to acquire multiple/longer/faster discrete slices of data with each gantry rotation
however, a wider beam decreases IQ; hence, maximum collimation is limited in areas that require high IQ
only when speed is prioritized, the full detector array will be activated
Advanced Data Acquisition Methods
Dual Source CT
Dual Energy CT
Dynamic CT
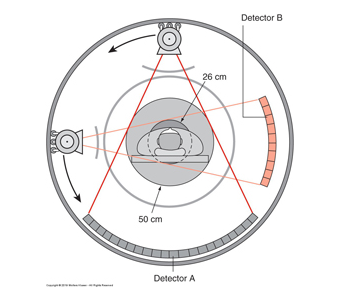
Dual Source/ Focal Spot CT
= incorporates two sets of tube-detector arrays within the gantry
Pro and Con of Dual Source CT
Pro = increased scan speeds/ temporal resolution, high-powered scanning for bariatrics
Con = practically, the second detector array is restricted by the size available in the gantry. Therefore, one detector array covers the entire scan field of view, whereas the second detector is limited to a smaller, central field of view
Dual Energy CT (Spectral Imaging)
= done by operating the tube(s) at two different energies
Function of the Dual Energy CT
allows for tissue differentiation through software analysis
useful when the identification of a particular substance in the body benefits diagnosis
Dynamic CT
= continuous scanning of the same region by continuously scanning with the table stationary
Function/Benefit of Dynamic CT
Common for blood flow evaluation, aka perfusion study
Brain perfusion scans which are performed to evaluate the extent of brain tissue involvement during/following ischemic stroke events.
Spectral Detector CT (SDCT)
uses a dual-layer detector to perform spectral (dual-energy) imaging