BUDGETING
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
It is a forecasting tool to determine future sources and uses of resources
Budgeting
It is a quantitative expression of what management wants to attain. It also serves as a guideline to attain desired outcomes or objectives.
Planning
Budget Cycle
Planning
Negotiation and Approval
Implementation
Review
Advantages and Uses of Budgets
Define goals and objectives
Think about and plan for the future
Means of allocating resources
Uncover potential bottlenecks
Coordinate activities
Communicate plans
Sources of Information for Preparing Budgets
Past company records
Benchmark with industry competitors
Standards developed by company
It is carefully predetermined price, cost, or quantity based on efficient operations and usually expressed on a per unit basis
Standard
These standards allow allowance for down-time and rest periods
Attainable (Practical)
These standards assume 100% efficiency
Theoretical (Ideal)
Budgets are determined based on standard costs and usually stated on a per unit basis (T/F)
False (total amount)
It is the understatement of revenues and overstatement of expenses making the budget targets easily attainable
Budgetary Slack
It is the sum total of all divisional budgets that is prepared by all the divisions.
Master Budget
Two Major Composition of Master Budget
Financial Budgets (Balance Sheet Budget)
Operating Budgets (Income Statement Budget)
In preparing the Master Budget what is the first budget that is being prepared?
Sales Budget
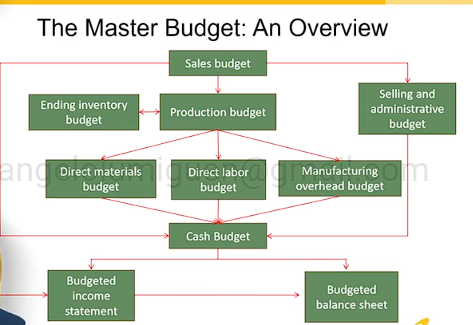
The last budget that being prepared
Budgeted Statement of Cashflow
It includes (1) cash, (2) capital expenditures, (3) balance sheet, and (4) cash flows
Financial Budget
Steps in Preparing the Operating Budget
Step 1: Revenues budget, in units to determine production budget then converted to money for the Sales budget
Step 2: Production budget (in units)
Step 3: Direct materials usage and purchase budgets
Step 4: Direct labor budget
Step 5: Manufacturing overhead budget
Step 6: Ending inventories budget
Step 7: Cost of Goods Sold budget
Step 8: Non-manufacturing costs budget
Step 9: Budgeted Income Statement
Major Components of Budget Committee
Marketing Manager
Production Manager / Industrial Engineer
Purchasing
Human Resource
Treasurer / Cash Budget
Controller - head
It is the budget that supports Total Quality Management. It is defined as a budgeting technique focusing on continuous improvement from a service or product perspective.
Kaizen
It is a planning system under which costs are associated with activities, and expenditures are then budgeted based on the expected activity level.
Activity-based budgeting
Common in both Kaizen Budgeting and Activity-based Budgeting
Increase in quality, efficiency, and speed, while decreasing the cost
This budget is prepared for a single level of output (normal capacity)
Static (Fixed) Budget
A Master Budget is an example of what type of budget?
Static Budget
This is the only budget that is adjusted to actual level of output
Flexible Budget
It is a budget that starts from zero regardless if there is a prior budget or actual operations from the prior year
Zero-based Budget
This budget is prepared on a monthly or quarterly basis
Continuous/Sliding/Rolling/Perpetual Budget
It is a budget that is prepared with the full cooperation and participation of the managers at all levels.
Participative Budget