Fundamentals of Enviornmental Biology: Exam 3
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Human Population Growth
Growth rate is slowing down, but the other graph shows it’s still continuing to grow
World population reached 6 billion. in October. 1999 and is more than 8 billion. now
What type of growth is the human population experiencing?
Exponential Growth
Issues of Population Growth
Easier spread of diseases
Run out of resources
Space problems
Getting rid of waste
Benefits of Population Growth
Diversity
Population Doubling Time
70 years/growth percent = doubling time in years
Current world growth rate is 0.85% (was 1.0%)- world doubling time: 82 years
Current US growth rate is 0.54% (was 0.57%)- US doubling time: 130 years
Limits of Population Growth in Human History
War
Genecide
Natural Disasters
Diseases
Demographics
The study of the human population
What did an increase in women’s rights lead to?
Decrease in birth rates
Children in lower birth rate societies face a smaller pool for reproduction, fewer working class, impact family’s name
Benefits: More resources, financial stability, more attention
Thailand- Successful family planning
Increased availability of contraceptives
Increased contraceptive use from 15 to 70% among married couples, now 80%
Population growth rate dropped from 6.1 to 1.6%, currently listed at 0.3%
Egalitarian relationship between men and women
Buddhism “many children make you poor”
Economic development
Thailand- Unintended Consequences
Currently working to reverse the declining birthrate through improved welfare structure and social supports, including increased parental leave, more childcare options, and other considerations.
India- Off to a bad start
Pushed sterilization instead of contraception in the 70’s
Not reversible
Expensive
Improved the situation in the
90’sEducation and contraception
Improved the situation of women
India- Changing Attitudes
Now considering replacement level population growth as a positive thing
Looking to turn population growth into economic growth, moving toward smaller cities and increased job opportunities in technology
Continued pressure on employment, resources, and environment
China- The One Child Policy
Initiated in 1979, ended 2016
May have two if first is female or disabled
Birth spacing of 3-4 years
Fines for more children
Denial of promotions, etc.
Increased tuition for schooling
Subject to discrimination for some ethnic groups
Now can have 3
China- Results of the One Child Policy
Distorted sex ratio
Resisted by rural families
Unreported children vs. infanticide
Increased death rate for females
China- Demographic Challenges
Birthrate dropped to 1.3 births per woman in 2020
Population dropped for the 1st time in 2022
India surpassed China in 2023
Aging population affects workforce, and social programs
Global Citizen
Is aware of the wider world and has a sense of their own role as a world citizen
Respects and values diversity
Is willing to act to make the world a more equitable and sustainable place
Takes responsibility for their actions
Worldview
The way a person sees and understand the world
Anthrocentric
(Human), makes human needs and wants the primary focus for decision-making
Biocentric
(Living), all living things (plants and animals) are considered
Ecocentric
(Ecosystem), both living and non-living aspects are included in any decisions being made about the region
Ecological Footprint Calculation
Approximates the amount of ecologically productive land and sea area required to sustain a population, manufacture a product, or undertake certain activities, by accounting for the use of energy, food, water, building material, and other consumables.
Ecological Footprint Averages
US- 7.8 gha per person
Canadians- 8.4 gha
Italians- 4.5 gha
Pakistanis- .8 gha
Qataris- 15 gha
Global average is 2.6 gha per person
Soil
Is more than dirt; made up of worms, rocks, moisture, organic material, decomposing material, bacteria, nitrogen
What role does soil play in an ecosystem?
Offers nutrients, air, water to protect roots, recycles carbon + nutrients, buffers temperature, regulates flow of rainwater
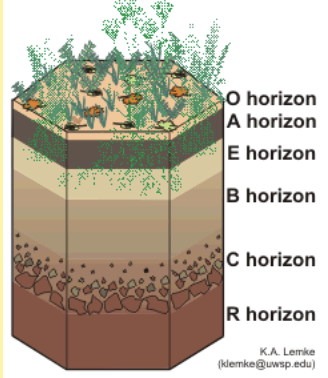
Soil Horizons
O- litter layer high in organic matter with no minerals or rock particles
A- topsoil layer rich in humus and finely decomposed rock with little or no clay
E- contains decomposed minerals, but little clay or organic matter
B- decomposed minerals and clay
C- slightly decomposed rock
R- bedrock
Erosion
The weathering away of natural materials which are then moved away
Caused By: wind, rain, compacting material, agriculture, acid rain, deforestation
Terracing
A sloped hillside that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces which resemble steps
Strip Cropping
Cultivating a field partitioned into long, narrow strips which are alternated in different crops
Crop Rotation
Growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons
Contour Planting
The farming practice of plowing and/or planting across a slope following its elevation contour lines
No-till-farming
A technique for growing crops or pasture without disturbing the soil
Windbreak/Hedgerow
One or more rows of trees or shrubs planted in such a manner as to provide shelter from the wind
Deposition/Sedimentation
The other side of erosion where all the sediment is washed in
Desertification
When land that is not a desert becomes a desert
Caused By: lack of water, overgrazing, extremes in weather
Soil Degradation
Prevention: Being mindful of pollution, planting techniques, doing no ill planting, and being aware of drainage systems
Improve: Add fertilizers, composting
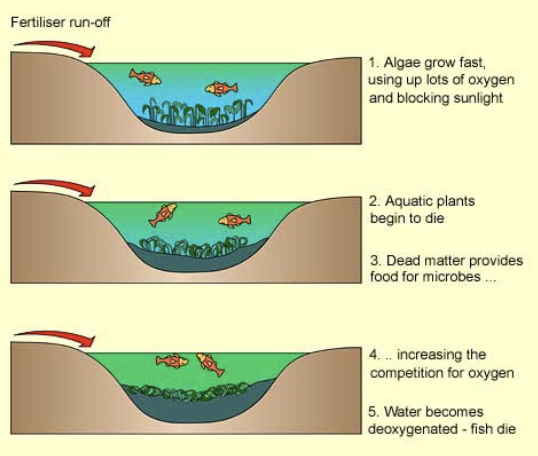
Fertilizers
If it runs out, it causes eutrificaion for aquatic ecosystems. causing fish to die
Can have too many nutrients
Pest
An animal or bug interfering with what’s trying to grow
Weed
A plant that interferes with what’s trying to grow
We regulate with chemicals
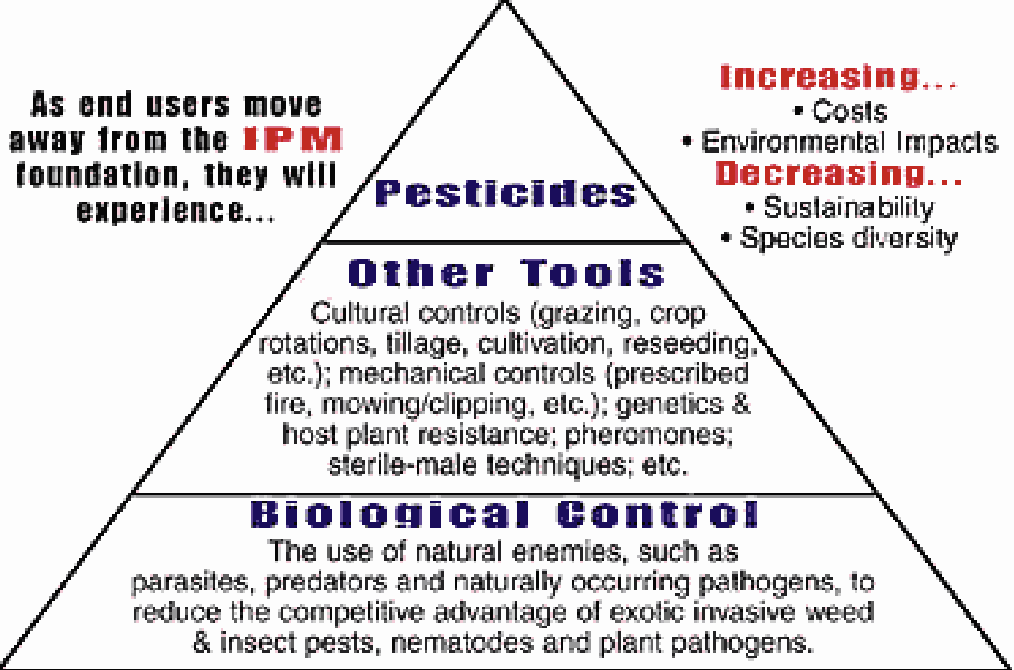
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
We try to use a variety of means to control these pests; bottom uses biological control, middle is other tools, top is pesticides
Reduce chemical use as much as possible
Pesticides and Resistance
Natural selection and survivial of the fittest can cause resistance
Biocontrol
Uses natural pests, those that feed off of what’s harming your garden; does not use chemicals (natural predators, parasites, fungi, and natural chemicals such as pheromones)
Mechanical/Physical Control
Crop rotation, mowing; not able to spread to other materials
Biotechnology can include:
Genetically modified organisms
Breeding programs
Biopesticides
Biofertilizers
What are some common toxins found in the environment?
Oil, waste, fossil fuels, carbon dioxide, acid migraine
Natural Toxins
Naturally occurring chemical components of fruits and vegetables serve as defense mechanisms against herbivorous animals, insects, bacteria, and fungi
EX) venom, pesticides
Synthetic Toxins
Posions we’ve created by chemical processes rather than being derived from natural sources
Chemicals we’ve produced
Carcinogens
Chemicals that cause cancer
EX) Benzene, asbestos, many smoke compounds, formaldehyde, radication, vinyl chloride, dioxin, mercury
Mutagens
Chemicals that cause mutations of DNA in organisms
EX) Nitrous oxide, UV radiation, alpha and gamma radiation, bromine, and some viruses
Teratogens
Chemicals that cause harm to unborn organisms
EX) Aflatoxin, alcohol, atrazine, benzene, caffeine, cannabis, DES, lead, thalidomide, mercury
Allergens
Substances that trigger the immune system to respond unnecessarily
EX) Pollen, dust, animal dander, poison ivy, mold, and foods
Neurotoxins
Chemicals that affect the function of the nervous system
EX) Snake, spider, pufferfish, and scorpion venoms, carbon monoxide, red tides, molds, bacteria, bees, and red pepper
Endocrine Disruptors
Chemicals that interfere with or mimic hormones
EX) DES, DDT, dioxin, PCBs and many pesticides and plasticizers
Which ecosystems have a high level of toxins?
Aquatic
Bioacculmation
Occurs when levels of toxin build up in a single organism over time
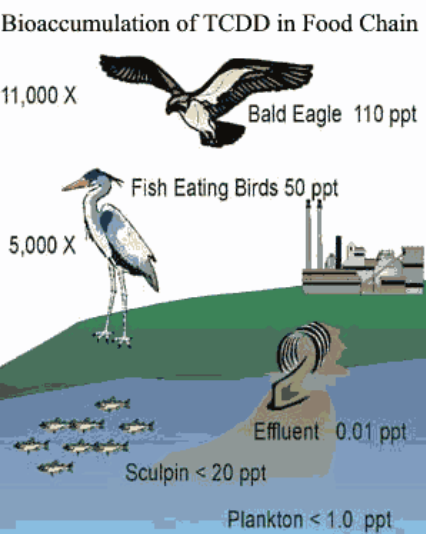
Biomagnification
Occurs when toxins increase in concentration as they move up the food chain
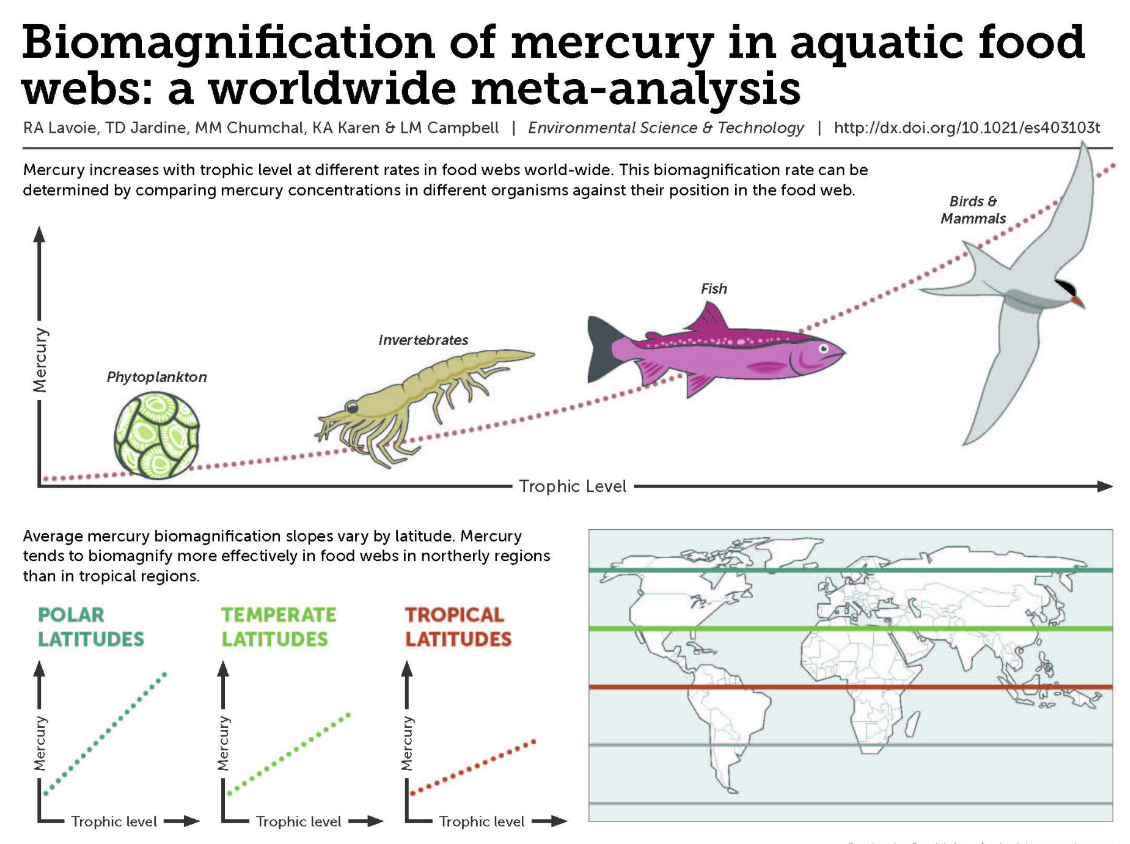
Is there a higher level of mercury in colder or hotter water?
Colder
Chemical Hazards
Enters the environment as a chemical and causes harm to what’s there
EX) Oil spills, pesticides, fertilizers, acid mine, drainage, and DDT
Physical Hazards
Events such as natural disasters
EX) Hurricane Katrina, flooding, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, diseases
Biological Hazards
Damage caused by the interaction between organisms
EX) Diseases
Socioeconomic Hazards
Cultural or lifestyle-based effetcs on the ecosystem
EX) Pollution
Additional Natural and Man-Made Health Threats
Visible lights produce electromagnetic radiation
Radiation occurs from nuclear power sources and weapons
Indoor health threats such as radon and lead posiniong pose environmental risks