Physical science
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:40 AM on 6/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
* Telling time
* Navigations
* Architecture
* Navigations
* Architecture
Role of Skies to Early Humans
2
New cards
Models
is a representation of a system, made of the composition of concepts which are used to help people know, understand, or simulate a subject the model represents.
3
New cards
Models
illustration to understand of something
4
New cards
* Geocentric Models
* Heliocentric Models
* Heliocentric Models
Models of the Universe
5
New cards
Geocentric Model
Earth centered universe
6
New cards
Geocentric Model
the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets all circled Earth.
7
New cards
Geocentric Model
Earth is the center of the universe
8
New cards
* Pythagorean model
* Eudoxus’ model
* Aristotle’s model
* Ptolemy’s model
* Eudoxus’ model
* Aristotle’s model
* Ptolemy’s model
What are the models under Geocentric Model?
9
New cards
* Copernicus’ model
* Brahe’s model
* Brahe’s model
What are the models under Heliocentric Model?
10
New cards
Pythagorean Model
Proposed by Pythagoras
11
New cards
Pythagorean Model
Earth is round. saang model siya nabanggit?
12
New cards
Pythagorean Model
basic and pinaka maling model sa lahat
13
New cards
Pythagorean Model
Earth is the center of the universe and everything rotates around it based on the relationship to musical sounds and numbers.
14
New cards
Eudoxus’ model
same lang ng sinabi ni Pythagoras pero nilagyan niya lang ng distinction ang bawat spheres/bawat layer ng spheres na pinrovide ni Pythagoras. Sinabi niya na bawat sphere ay may special properties or special heavenly body na andun sa sphere na yun.
15
New cards
Eudoxus’ model
Uses a series of 27 concentric spheres on which the Sun, moon and the planets moved in perfect circular motion.
• 1 sphere for fixed stars
• 3 spheres for the sun
• 3 spheres for the moon
• 4 spheres for the 5 planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Saturn and Jupiter)
• 1 sphere for fixed stars
• 3 spheres for the sun
• 3 spheres for the moon
• 4 spheres for the 5 planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Saturn and Jupiter)
16
New cards
Eudoxus’ model
Meant to answer the problem of Plato regarding motions of planets
17
New cards
Eudoxus’ model
What model is that?
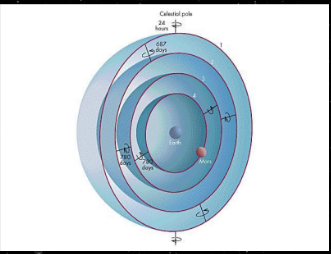
18
New cards
Eudoxus’ model
What model is that?
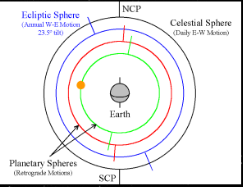
19
New cards
Pythagorean Model
What model is that?
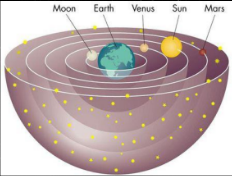
20
New cards
Aristotle’s model
Proposed by Aristotle.
21
New cards
Aristotle’s model
Added 27 buffering sphere between celestial spheres of Eudoxus.
22
New cards
Aristotle’s model
Earth – Moon – Mercury – Venus – Sun – Mars – Jupiter – Saturn – Fixed Stars – Firmanent of Prime Mover
23
New cards
Aristotle’s model
The rotation of the firmanent is the force that causes the other inner spheres to move.
24
New cards
Firmanent
Heaven
25
New cards
Prime Mover
God
26
New cards
Ether
medium that causes the spheres to move.
27
New cards
Aristotle’s model
Sinundan lang din niya yung kay eudoxus ang ginawa niya inispecify lang niya na the spheres are parang yung mga spheres na ito dito lang lng nakalagay ang mga stars pero nakahiwalay talaga yung mga planet sa kanya. Sama-sama na lahat ng planet and sama-sama lahat ng stars tapos yung moon naandon sa spheres kasama nung planet.
28
New cards
Aristotle’s model
What model is that?
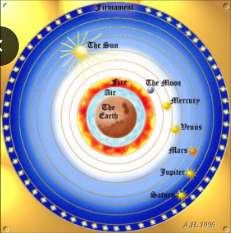
29
New cards
Ptolemy’s model
What model is that?
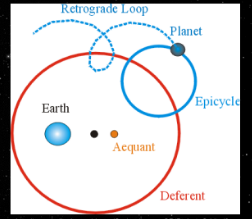
30
New cards
Ptolemy’s model
one of the important concept of geocentric kasi bibigyan niya ng importansiya yung notion ng planets. Binibigyan niya ng imprttance yung notion ng ibang heavenly bodies kung bakit nagkakaroon ng ganitong klasing pagbabago ng position yung heavenly bodies its because of the epicycle/retrograde.
31
New cards
Ptolemy’s model
Believed model for 14 centuries. Approved by the church due to biblical validity (“Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon", Joshua 10:12)
32
New cards
Epicycle
circle on which a planet moves.
33
New cards
Deferent
the path in which the center of the epicycle moves.
34
New cards
Equant
center of the deferent
35
New cards
Heliocentric model
Earth and Planets revolve around the sun
36
New cards
Heliocentric model
Sun is the center of the universe and Earth and other planets revolves around it.
37
New cards
Pyrocentric models
neither the sun nor earth is the center but a fire (Philolaus)
38
New cards
Pyrocentric models
Not accepted due to acceptance of Ptolemic model
39
New cards
Pyrocentric models
First heliocentric
40
New cards
Pyrocentric models
All stars, including the sun revolved around the fire All planets revolves around a star.
41
New cards
Copernicus model
Earth spins on its axis every day and revolves around the Sun like other planets; only the moon revolved around the Earth.
42
New cards
Copernicus model
Proposed by Nicolas Copernicus.
43
New cards
Copernicus model
lahat ng bagay nagmomove base sa center ng sun
44
New cards
1. Absence of stellar parallax
2. Lack of perceive motion of Earth
What are the 2 flaws in Copernicus model?
45
New cards
Brahe’s model
What is that model?
46
New cards
Galileo’s Evidences
ang tumulong para magprovide ng evidences/ magprovide ng other models para somehow maintindihan natin kung ano ba talaga ang mas tama sa dalawa heliocentric ba or geocentric
47
New cards
MOTION
the change of position of an object relative to a certain frame of reference (point).
48
New cards
frame of reference/reference frame
observer
49
New cards
Position
the location of an object with respect to a frame of reference
50
New cards
Frame of Reference
a system that allows an observer to specify quantitatively where and when something is observed
51
New cards
Kinematics
describes motions in terms of displacement, velocity and acceleration
52
New cards
Dynamics
relates force and motion
53
New cards
Translation
motion in a straight line
54
New cards
Kinematics
deals with the description of motion and describes motion mathematically
55
New cards
Dynamics
branch of physics that deals w/ study of how motion works or what is the cause of motion/bakit merong motion
56
New cards
Scalar quantities
are quantities that have only magnitude.
57
New cards
Vector quantities
are quantities that have both magnitude and direction
58
New cards
DISTANCE
(scalar) the length of the path by the body in moving from the initial to final position.
59
New cards
kasi inaalam lang natin kung gaano kahaba
why scalar yung distance?
60
New cards
DISPLACEMENT
(vector) distance measured in a straight line in a specified direction.
61
New cards
kasi aside from knowing kung gaano kahaba dapat alam mo kung saan pupunta
why vector ang displacement?
62
New cards
Speed
the measure of how fast or slow the body moves. (walang direction)
63
New cards
* Average Speed
* Instantaneous Speed
* Instantaneous Speed
Two types of speed
64
New cards
Average Speed
the total distance travelled by a body per unit of time
65
New cards
Instantaneous Speed
speed of an object in an instant (in a particular time).
66
New cards
VELOCITY
a speed in a given direction (may direction)
67
New cards
ACCELERATION
a measure of how fast the velocity changes with respect to time.
68
New cards
* Translatory/Translation Motion
* Circular Motion
* Circular Motion
TYPES OF MOTION
69
New cards
Translatory/Translation Motion
The motion in which all points of a moving body move uniformly along a straight line
70
New cards
* RECTILINEAR MOTION
* CURVILINEAR MOTION
* CURVILINEAR MOTION
TYPES OF TRANSLATORY MOTION
71
New cards
CURVILINEAR MOTION
If a body moves along a curved path
72
New cards
RECTILINEAR MOTION
If a body moves in a straight line
73
New cards
CIRCULAR MOTION
An object is said to be in circular motion when it moves around a fixed point called axis.
74
New cards
* REVOLUTION
* ROTATORY/ROTATIONAL MOTION
* RANDOM MOTION
* OSCILLATORY MOTION
* VIBRATORY MOTION
* PERIODIC MOTION
* ROTATORY/ROTATIONAL MOTION
* RANDOM MOTION
* OSCILLATORY MOTION
* VIBRATORY MOTION
* PERIODIC MOTION
TYPES OF CIRCULAR MOTION
75
New cards
REVOLUTION
When a body as a whole moves in a circular path
76
New cards
ROTATORY/ROTATIONAL MOTION
When a body undergoes translatory motion in such a way that its parts cover different distances in a given time
77
New cards
RANDOM MOTION
Irregular motion of a body in which the direction is not fixed
78
New cards
OSCILLATORY MOTION
When a body moves to and fro about a fixed point
79
New cards
VIBRATORY MOTION
Sometimes the whole object doesnot show to and fro motion but a part of it shows motion
80
New cards
VIBRATORY MOTION
Vibration
81
New cards
PERIODIC MOTION
When the same motion repeats itself after equal intervals of time
82
New cards
FREE FALL
Any object that is being acted upon only by the force of gravity
83
New cards
FREE FALL
As motion in translation or in rectilinear motion na kung saan ang isang object ay lumalaglag na walang istorbo/nababangga/obstruction/disturbance
84
New cards
PROJECTILE
When an object was thrown or projected at an angle (curvilinear motion)
85
New cards
PROJECTILE
Under the influence of gravity
86
New cards
Trajectory
The path followed by the projectile
87
New cards
* Law of Inertia
* Law of Acceleration
* Law of Action-Reaction
* Law of Acceleration
* Law of Action-Reaction
Newton’s three laws of motion
88
New cards
Law of Inertia
Newton’s first law of motion
89
New cards
Law of Inertia
An object at rest will remain at rest at a constant velocity unless influenced by an external force.
90
New cards
Law of Inertia
an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity unless influenced by an external force.
91
New cards
Law of Inertia
the tendency to resist change
92
New cards
Law of Acceleration
Newton’s second law of motion
93
New cards
Law of Acceleration
the ------ of a object is directly proportional to the force exerted on it.
94
New cards
Law of Acceleration
this law explains kung kailan gagalaw yung isang bagay na naka at rest
95
New cards
Law of Action Reaction
Newton’s third law of motion
96
New cards
Law of Action Reaction
every action has an equal and opposite reaction
97
New cards
Law of Action Reaction
Dapat may may dalawang na nag-iinteract or may dalawang force na opposing force. what law of motion yun?
98
New cards
Law of Action Reaction
kada apply mong force may bumabalik sayong force. what law of motion yun?
99
New cards
Law of Action Reaction
this law ang nagsasabi kung bakit nagkakaroon ng basic interaction sa universe
100
New cards
Law of Action Reaction
kada force merong equal pero opposite force na kokontra dun. anong law of motion yun?