Foundations of American Democracy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Bicameral legislature
two-house legislature.
Checks and balances
system in which each branch of government can limit the power of the other two branches, e.g., presidential veto of a congressional law.
Commerce clause
gives Congress the power to regulate commerce among the states, with foreign nations, and among Indian tribes. Granted through Article 1, section 8 of the Constitution.

Confederation
system in which sovereign states are only loosely tied to a central government, e.g., the U.S. under the Articles of Confederation.

Direct democracy
a system in which the people rule themselves.

Elite democracy
a model of democracy in which a small number of people, usually those who are wealthy and well-educated, influence political decision making.

Federalism
constitutional sharing of power between a central government and state governments.
Federalist Papers
group of 85 essays written by Madison, Hamilton, and Jay for the purpose of persuading the people of New York to adopt the Constitution.

Formal amendment
a change in the actual wording of the Constitution. Proposed by Congress or national convention, and ratified by the states.

Indirect democracy
a system in which the people are ruled by their representatives. Also known as representative democracy, or republic.
Informal amendment
a change in the meaning, but not the wording, of the Constitution, e.g., through a court decision such as Brown v. Board of Education.

Limited government
a principle stating that the government is only allowed to do things that the people have given them the power to do.

Natural rights
the rights of all people to dignity and worth.

Participatory democracy
a model of democracy in which citizens have the power to decide directly on policy and politicians are responsible for implementing those policy decisions.

Pluralist democracy
a model of democracy in which no one group dominates politics and organized groups compete with each other to influence policy.
Popular sovereignty
principle in which ultimate political authority rests with the people.

Republicanism
a form of government in which power is vested in the people and is exercised by the people through representatives chosen by the people.

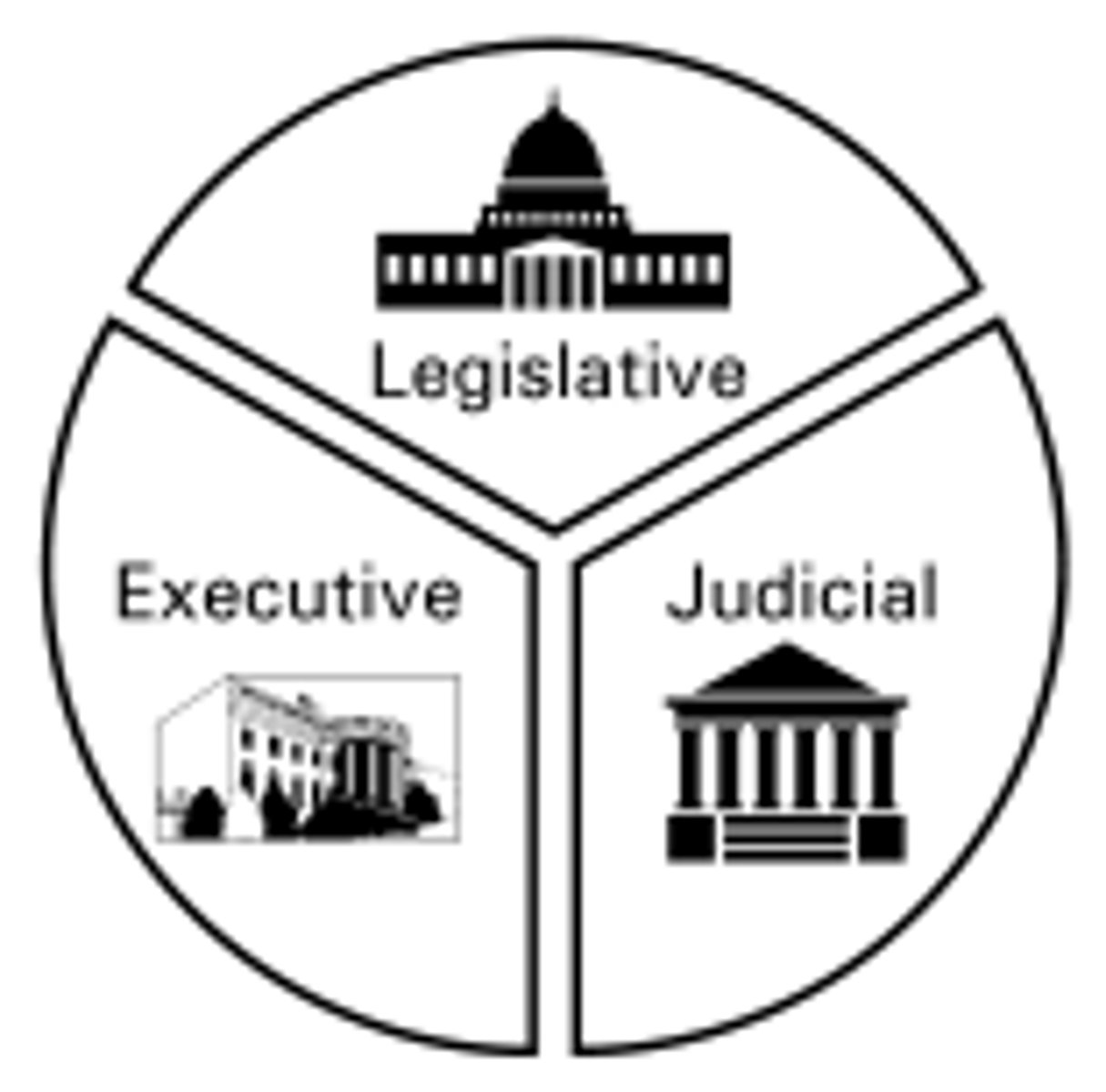
Separation of powers
principle in which the powers of government are separated among three branches: legislative, executive, judicial.

Shays' Rebellion
1786 revolt by Massachusetts farmers seeking relief from debt and foreclosure that was a factor in the calling of the Constitutional Convention.

Social contract
an implicit agreement among the members of a society to cooperate for social benefits, for example by sacrificing some individual freedom for state protection.

Supermajority
a majority greater than a simple majority of one over half, e.g., 3/5, 2/3.

Supremacy clause
gives national laws the absolute power even when states have created a competing law.
Unicameral legislature
one-house legislature.

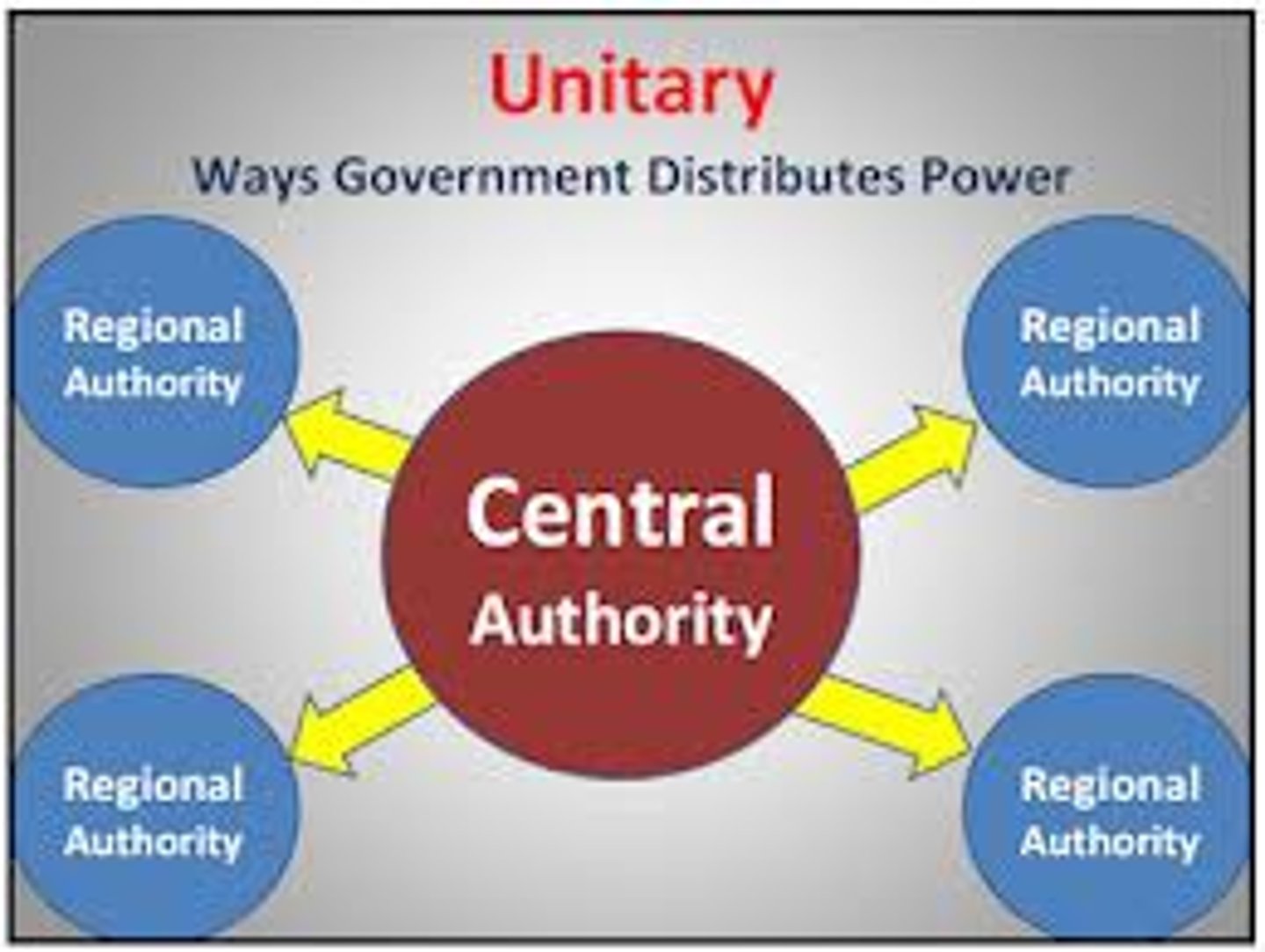
Unitary system
a system of political organization in which most or all of the governing power resides in a centralized government (in contrast to a federal system).