DIalation Topic 7.1
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
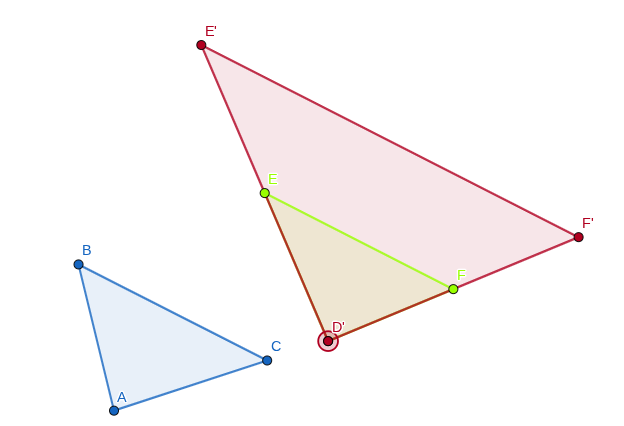
What is this image show this problem that △DEF dialates to △D’E’F’?
A) From △DEF dialates to △D’E’F’ is the scale factor of 1.5.
B) From △DEF dialates to △D’E’F’ is the scale factor of 2.
C) From △DEF dialates to △D’E’F’ is scale factor of 1/4.
D) From △DEF dialates to △D’E’F’ is the scale factor of 1/8.
The answer is B.
It explains that △DEF dialates to △D’E’F’ is the scale factor 2.
DE ≆ D’E’, EF ≆ E’F’, and DF ≆ D’F’. All for the sides are not equal. But, ∠D ≅ ∠D’, ∠E ≅ ∠E’, and ∠F ≅ ∠F’. All are the angles are congruent.
The (x,y) numbers for △ABX is A(1,2), B(3,3), and X(4,0). The dialation of the scale factor is 2.
What is the new (x,y) numbers for △A’B’X’?
A) The new (x,y) numbers for △A’B’X’ is A’(2,4), B’(6,9), and X(3,0).
B) The new (x,y) numbers for △A’B’X’ is A’(2,4), B(6,6), and X’(8,0).
C) The new (x,y) numbers for △A’B’X’ is A’(2.2,4.5), B(6.5,6.5), and X’(8.5,0).
D) None of the above.
The answer is B.
Step by step is
A(1,2), B(3,3), and X(4,0). Multiply by 2 from △ABX to △A’B’X’.
A(1 × 2, 2 × 2), B(3 × 2, 3 × 2), and X(4 × 2, 0 × 2).
The answers for this problem is the new (x,y) numbers for △A’B’X’ is A’(2,4), B(6,6), and X’(8,0).
What’s dialation?
A) It only moves the figure up, down, left, or right.
B) It flips the figure over a line.
C) It changes the size of the figure while maintaining its shape.
D) It rotates the figure around a fixed point.
C) It changes the size of the figure while maintaining its shape.
2. The value used to multiply the dimensions of a figure during a dilation is called the:
A) Translation value
B) Rotation angle
C) Scale factor
D) Reflection axis
C) Scale factor
3. If a figure is dilated with a scale factor of 1/2, what kind of transformation occurs?
A) An enlargement
B) A reduction
C) The figure remains the same size
D) A reflection
B) A reduction. Tha’s the answer.
4. A point P is located at (4, 8). If it is dilated by a scale factor of 0.5 centered at the origin, what are the coordinates of the new point P'?
A) (4.5, 8.5)
B) (2, 4)
C) (8, 16)
D) (4, 8)
5. A rectangle has vertices at (1, 1), (5, 1), (5, 3), and (1, 3). If it is dilated by a scale factor of 3 centered at the origin, what are the coordinates of the new vertices?
A) (1, 1), (5, 1), (5, 3), (1, 3)
B) (3, 3), (15, 3), (15, 9), (3, 9)
C) (4, 4), (8, 4), (8, 6), (4, 6)
D) (0, 0), (4, 0), (4, 2), (0, 2)
B) (3, 3), (15, 3), (15, 9), (3, 9)
Remember the scale factor of 3.
(1, 1) x 3, (5, 1) x 3, (5, 3) x 3, and (1, 3) x 3.
6. A square has a perimeter of 20 inches. If the square is dilated by a scale factor of 4, what is the perimeter of the new square?
A) 20 inches
B) 40 inches
C) 80 inches
D) 320 inches
C) 80 inches
SCALE FACTOR IS 4!
20 inches multiplies by the scale factor of 4, which is equal to the total amount of 80 inches! (read as 20 × 4 = 80.)