Ch. 19 Gastrointestinal and Urologic Emergencies
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
what does the liver do?
assists in digestion
secretes bile
filters toxic substances produced by digestion
creates glucose stores
produces substances necessary for blood clotting and immune function
what does the gallbladder do?
it’s a reservoir for bile
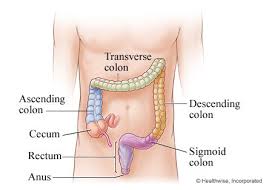
small intestine
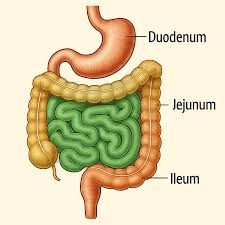
colon (large intestine)
food not broken down and used moves into the colon as a waste product
water is absorbed and stool is formed
urinary system
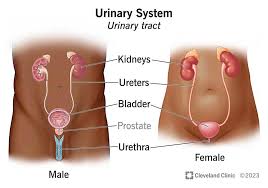
a normal adult forms ____ to ____ of urine per day
1.5 to 2 L
peritoneum
covers the organs of the abdomen
parietal peritoneum: lines the walls of the abdominal cavity
visceral peritoneum: covers the organs
the presence of foreign material can irritate the peritoneum, causing peritonitis
acute abdomen
the sudden onset of abdominal pain
often associated with severe, progressive problems requiring medical attention
ileus
paralysis of muscular contractions that normally propel material through the intestine
peritonitis
any foreign material, such as blood, pus, bile, pancreatic juice, or amniotic fluid, can cause irritation of the peritoneum
can cause: ileus; diverticulitis; cholecystitis; acute appendicitis
usually associated with nausea and vomiting
fever may or may not be present
emesis
vomiting
diverticulitis
inflammation in small pockets at weak areas in the muscle walls of intestines
cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
nerves that supply the peritoneum
parietal peritoneum: same nerves that supply the skin of the abdomen
these nerves can easily identify and localize a point of irritation
visceral peritoneum: the autonomic nervous system
these nerves are less able to identify and localize pain
referred pain
results from: the connection between the body’s 2 separate nervous systems
description: pain felt in an area of the body other than the area where the cause of pain is located
common causes of acute abdomen
ulcers
gallstones
pancreatitis
appendicitis
gastrointestinal hemorrhage
esophagitis
esophageal varices
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
gastroenteritis
diverticulitis
hemorrhoids
ulcers
protective later of the mucous lining erodes, allowing acid to eat into the organ
common causes: Helicobacter pylori bacteria; chronic use of NSAIDs
signs/symptoms: gnawing pain in the stomach; nausea, vomiting; belching; heartburn
complications: hematemesis; melena; peritonitis
gallstones
may form and block the outlet from the gallbladder
if blockage is not relieved, inflammation can occur
signs/symptoms: constant, severe pain in the right upper or midabdominal region that may refer to the right upper back, shoulder, or flank; nausea, vomiting; indigestion; bloating; gas; belching
pancreatitis
inflammation of the pancreas
common causes: an obstructing gallstone; alcohol abuse
signs/symptoms: severe pain in the upper left and right quadrants that can radiate to the back; nausea, vomiting; abdominal distension; tenderness
complications: sepsis or hemorrhage
appendicitis
inflammation or infection in the appendix
signs/symptoms: initial pain that is generalized, dull, and diffuse, which may center in the umbilical area; pain later localizes to the RLQ; may have referred pain; nausea, vomiting; anorexia; fever, chills; rebound tenderness
complications: abscess; peritonitis; shock
gastrointestinal hemorrhage
symptom of another disease, not a disease itself
may be acute or chronic
location: upper or lower gastrointestinal tract
common causes: esophagitis; esophageal varices; Mallory-Weiss tear; inflammation; diverticulosis; diverticulitis; cancer; hemorrhoids
signs/symptoms: hematemesis; melena; bright red stools
esophagitis
occurs when the lining of the esophagus becomes inflamed by infection or acids from the stomach
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
signs/symptoms: pain with swallowing and feeling like there is something stuck in his or her throat; heartburn; nausea, vomiting; sores in the mouth
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach opens, allowing stomach acid to move up into the esophagus
also referred to as acid reflux disease
signs/symptoms: burning sensation in chest; nausea, vomiting; sores in the mouth
esophageal varices
amount of pressure within blood vessels surrounding the esophagus increase - result of liver failure
common causes: alcohol in industrialized countries; viral hepatitis in developing countries
pts will initially show signs of liver disease
rupture of varices is far more sudden
signs/symptoms: sudden onset discomfort in the epigastric region or sternum; difficulty swallowing; vomiting of bright red blood; hypotension; signs of shock
complications: significant blood loss
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
junction between the esophagus and the stomach tears
common causes: violent coughing or vomiting
signs/symptoms: signs of shock; upper abdominal pain; hematemesis; melena
gastroenteritis
can be caused by infection or by noninfectious conditions
signs/symptoms: diarrhea with blood and/or pus; abdominal cramping; nausea, vomiting; fever; anorexia
complications: dehydration and shock
diverticulitis
lack of fiber in the diet causes the consistency of stools to become more solid, requiring more intestinal contractions and increasing pressure in the colon
bulges in the colonic walls result from increased intestinal contractions
fecal matter becomes caught in the bulges, allowing bacteria to collect, and resulting in inflammation and infection
signs/symptoms: abdominal pain localized more in the LLQ
complications: perforation of the intestinal wall leading to severe infection and shock
hemorrhoids
created by swelling and inflammation of blood vessels surrounding the rectum
common causes: conditions that increase pressure on the rectum or irritation of the rectum
signs/symptoms: painless, bright red bleeding during defecation
cystitis
bladder inflammation, aka UTI
common causes: bacterial infection
signs/symptoms: midline lower abdominal pain; blood in the urine; an urgency and frequent urination; pressure and pain around the bladder
complications: kidney infection
kidneys
play a major role in maintaining homeostasis
eliminate waste from the blood
when kidneys fails → uremia results
kidney stones can form and cause blockage
acute kidney failure
sudden decrease in function
common causes: hemorrhage; dehydration; trauma; shock; sepsis; heart failure; medications; drug abuse; kidney stones
reversible with prompt diagnosis and treatment
chronic kidney failure
progressive and irreversible damage
common causes: diabetes; hypertension
signs/symptoms: lethargy; nausea; headaches; cramps; edema in the extremities and face; seizures; coma
will eventually require treatment with dialysis
the pts have an increased risk of heart failure and cardiac arrest
kidney stones
can grow over time, and if a stone passes into the ureter, it can cause a blockage
pressure will build up behind the kidney stone and cause swelling in the kidney
pts may initially report vague discomfort in the flank, but the pain can become intense and radiate to the groin
pts are often agitated and restless
may report nausea and vomiting
female reproductive organs
abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
pulsating mass may be felt - difficult to detect
back pain with a tearing sensation
use extreme caution on these pts
hernia
description: protrusion of an organ or tissue through a hole or opening into a body cavity where it does not belong
common causes: congenital defects; a surgical wound that has failed to heal; a natural weakness in an area such as the groin
may not always produce a noticeable mass or lump
reducible hernia: pose little risk, can be pushed back into cavity
incarcerated hernia: cannot be pushed back, compressed by surrounding body tissue
blood supply is compromised
serious signs/symptoms: a formerly reducible mass is no longer reducible; pain at the hernia site; tenderness when the hernia is palpated; red or blue skin discoloration over the hernia
SAMPLE history
nausea and vomiting
changes in bowel habits
urination
weight loss
belching or flatulence
pain
other signs or symptoms
concurrent chest pain
treatment for acute abdomen
treat the pt for shock even when obvious signs are not apparent
position pts who are vomiting to maintain a patent airway
providing low-flow oxygen may decrease nausea and anxiety
adverse effects of dialysis
hypotension
dysrhythmias
chest pain
muscle cramps
nausea and vomiting
hemorrhage from the access site
infection at the access site
management of a dialysis pt
manage the XABCs
provide high-flow oxygen if indicated
manage any bleeding
position the pt sitting up in case of pulmonary edema or supine if the pt is in shock
transport promptly
strangulation
complete obstruction of blood circulation in a given organ as a result of compression or entrapment; an emergency situation causing death of tissue
uremia
severe kidney failure resulting in the buildup of waste products within the blood
eventually brain functions will be impaired