HSS1101: Viruses
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HSS1100
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Basic components of viruses
Nucelic acid: infectious genetic material
Protective coat (capsid)
Surface antigens: Protein or carb. Highly variable
5 Steps for virus replication
Adsorption - Viruses adsorb to receptors on the cell surface.
Penetration and uncoating - The virus enters the cell, the protein coat is lost and the nucleic acid released; it becomes undetectable (eclipse).
Synthesis of nucleic acid and protein - The viral nucleic acid redirects the cell metabolism to produce viral protein and nucleic acid.
Assembly-Maturation - Viral components are assembled to form mature (infective) virus particles.
Release - Newly formed virus particles are released by either lysis (destruction) of the cell or budding through the cell membrane
Main approaches to viral diagnosis
A. Detection of viruses in clinical specimens.
B. Detection of the immune reactions triggered by the virus in the patient, i.e., detection of antibodies in the patient's blood.
Detection of viruses in clinical specimens
AKA direct detection
Visualization of electron microscopy (E.M.)
Effect after inoculation into cell cultures: this requires multiplication, i.e., time
Direct detection of viral antigens in clinical specimens themselves by immunological methods
Direct ELISA: detects Antigen (more colour = more Ag) ex. pregnancy + steroid tests
Visualization by electron microscopy
method for dection of virus in clinical specimens
since viruses are invisible by light microscopy and very high magnification required.
Only used for a few viruses which happen to be present in very large numbers in clinical specimens
Cytopathic effect
visible modifications of infected cells caused by virus
An effect after inoculation into cell cultures
hemagglutination
An effect after inoculation into cell cultures
Some viruses agglutinate red blood cells added to the cell cultures
Immunofluorescence
An effect after inoculation into cell cultures
will reveal the presence of viral antigenic material within the infected cell culture, even if there is no visible damage caused by the multiplying virus
Detection of immune reactions triggered in the patient's immune system
i.e. detection of antibodies in patient’s blood
AKA indirect detection
Immunity tests
presence or absence of antibody against a given virus
a method for detection of immune rxns triggered in patient’s immune system

Diagnostic tests
a method for detection of immune rxns triggered in patient’s immune system
rise in antibody or high antibody titer against a given virus = evidence that this particular virus has recently caused a viral illness
5 common Respiratory viruses
A group of viruses which are found mainly in the respiratory tract and produce respiratory tract disease. They belong to different virus families
Includes:
influenza viruses
parainfluenza viruses
respiratory syncytial viruses
rhinoviruses
coronaviruses
Influenza virus
Has 2 types
Grow easily in certain cell cultures
produce a haemagglutinin (i.e. agglutinate red blood cells)(diagnostic)
Frequent recombination leads to
high antigenic variability
pandemics
2 types of influenza viruses
Influenza virus A: causes major epidemics
influenza virus B: causes milder disease; occasionally occurs in epidemics
Clinical presentations of influenza viruses
fever, variable respiratory symptoms
Infants and elderly more susceptible
Diagnosis of influenza virus
Throat washings, naso-pharyngeal aspirate inoculated into cell culture
Serum of influenza virus
Paired sera (acute and convalescent stage)
Prevention of influenza virus
Annual vaccination especially for high risk groups
antivirals are available for type A influenza
Parainfluenza
Infants and young children
Age 5-12
Respiratory infection that could have serious complications
Clinical presentations:
Croup (barking cough, high pitch sound on inhalation)
Bronchiolitis, bronchopneumonia
No vaccine
Respiratory Syncytial Viruses (RSV)
Major respiratory pathogen for children < 5 years
Clinical presentation:
Pneumonia and bronchiolitis; occasionally fatal
Epidemics
Vaccine available
Antiviral: Ribavizine
Rhinovirus
Common colds
> 100 serotypes; no cross-immunity
Repeated infections
Coronavirus
Member of coronaviridae family
RNA virus
Enteric viruses
Enterovirus = Enteric virus
Infect intestinal / lymphoid cells
Poliovirus, coxsackievirus
Multiply in GI tract, but RARELY cause gastroenteritis
Infection via respiratory or GI tract
Spread to other target organs in body
95% inapparent infection, 4-5% minor illness, 1% serious illness
Enteroviruses
Polioviruses
Coxsackieviruses
Viruses of Diarrhea
Rotavirus
Norovirus
5 Virus causing rashes
Measles
Varicella
Rubella
Herpes Simplex Virus
Papilloma virus
Poliovirus
Humans are the ONLY natural host
Types 1, 2 and 3
Causes poliomyelitis
Highly infectious, invades the host nervous system and can cause total paralysis in as little as a few hours
Transmission via fecal-oral route
Poliovirus Diagnosis
Isolation from stool samples (up to 5-6 weeks after infection), CSF and pericardial fluid
Serology: acute and convalescent phases
Carriers with inapparent infection are able to spread the disease to susceptible individuals
Polio prevention
2 types of Vaccination
Salk vaccine
Sabin vaccine
Salk Vaccine
Killed/inactivated vaccine; does not produce local immunity in GI of host (IgA)
Virus can still colonize host GI tract and SPREAD to the community!!!
used for immunocompromised
Sabin Vaccine
Most common
live-attenuated host will produce IgA and IgG, so is protected against intestinal colonization and virus can NOT replicate and spread
Oral administration
Coxsackieviruses
Groups A and B
Seasonal variation
Diagnosis by stool sample and paired sera (same as polio)
NO VACCINE
Clinical presentation of coxsackieviruses
aseptic meningitis
herpangina
small blister-like bumps or ulcers that appear in the mouth, usually in the back of throat or the roof of the mouth
hand-foot-and-mouth disease, pericarditis and myocarditis
Pleurodynia: Severe, sharp, and stabbing pain in the lower chest or upper abdomen.
Comes in waves, lasting 15 to 30 minutes

Rotavirus
Virus causing epidemics of diarrhea of infants (6mo.-2yrs), during winter months.
The virus multiplies in the small intestine, producing a loss of fluids and electrolytes, as well as a transient malabsorption of fats and sugars.
Highly infectious
Diagnosis of Rotavirus
EM or immunological testing of virus from stool samples (within 3 days)
Epidemiology of rotavirus
Short incubation (2-3days)
Fecal-oral route, aerosols (explosive diarrhea), fomites
Outbreaks in daycare centres, children’s hospitals
Prevention of rotavirus
Rapid diagnosis and isolation of patient
Proper handwashing
Vaccine available
Clinical manifestations of rotavirus
acute gastroenteritis diarrhea, fever
Norovirus
Causes outbreaks of gastroenteritis in 18 yrs+, in any season.
problem in cruise ships
Diagnosis of norovirus
first exclude bacterial cause, then can be differentiated from bacterial gastroenteritis
diagnosis via stool/vomit sample by examining for virus antigenic material(immunofluorescence)
Epidemiology of norovirus
VERY CONTAGIOUS; survives well on objects/environment – Fecal-oral route; food-borne outbreaks
Prevention of norovirus
handwashing and isolation of infected individuals
no vaccine
Measles
One of the highest infectivity rates
Lifelong immunity after natural infection +survival
Complications: secondary bacterial infections, e.g., bronchopneumonia – Encephalitis (rare) – Exacerbation of TB and leukemia
Clinical manifestion of measles
Koplik spots
rash first appears behind ears, forehead and nostrils then spreads to whole body; BLOTCHY appearance

Diagnosis of measles
Serological
Confirmation of Suspected Case:
IgM Ab in single blood specimen against measles OR a rising
IgG Ab titer against measles in paired blood
Immune status
Circulating measles specific Ab IgG
Treatment of measles
Passive immunization
Immunoglobulin: can suppress disease if given within 5 days of contact with virus
Active immunization
Live attenuated vaccine: very effective, widely used. Administer after 12 months of age
Rubella
AKA German measles
Mild disease, however extremely dangerous in non- immune pregnant women, because it can produce birth defects in the offspring.
Clinical manifestation
similar to measles but milder
usually enlargement of cervical, retro auricular (behind the ears) and sub-occipital lymph nodes.
lifelong immunity
Epidemiology and Immunity of Rubella
pre-vaccine era, seen in school children during winter in spring, outbreaks every 7-10 years, lead to life-long immunity
Now most cases (60%) are seen in those 15 years and older
Lab diagnosis of Rubella
Suspected cases: detection of rubella specific IgM or rising Ab titer in paired sera
Immunity status: detection of circulating Rubella Ab (IgG)
Prevention of congenital rubella
Check immune status of women of childbearing age
Diagnosis in hospitals
Rubella serology screening of men and women starting work in hospitals
Vaccination of non-immune
Isolation of rubella cases in hospitals
Vaccination is live-attenuated and is NOT admnistered to pregnant women
Varicella
AKA chickenpox: Varicella Zoster Virus(VZV)
Clinical manifestations of varicella
childhood febrile illness with characteristic rash
Successive crops of fresh vesicles appear within 3- 4 days of onset
In non-immune adults, occasional pneumonia, may be fatal
Vaccine available
Herpes Zoster (shingles)
LIMITED rash, along trajectory of ONE nerve
Late recurrence of latent VZV (chicken pox) infection
Prevention of varicella
vaccine; detection of susceptible persons by serological methods
Chicken pox vs. Shingles vaccine

Diagnosis of Varicella
ID of virus particles in pustules by EM or immuno methods, followed by cell culture
Herpes Simplex Virus
Widespread
Become LATENT after initial infection; lesions reappear periodically
High percentage of inapparent infections
Epidemiology of HSV
HSV1: “cold sores” oral and ocular lesions; transmitted via oral and respiratory secretions
HSV2: “herpes genitalis” associated with genital tract; infected females can transmit to the newborn
Diagnosis of HSV
ID of virus particles by EM or immuno methods; cell cultures; Serology NOT useful
Clinical manifestation of HSV OTHER THAN cold sores
Genital infections: recurrent in both sexes
Herpetic encephalitis: RARE (see CNS viruses)
Neonatal Herpes: acquired during birth from asymptomatic mother; difficult to prevent; can result in death or severe sequelae (see CNS viruses)
Herpetic Whitlow: affects fingers, occupational hazard of health care workers; nosocomial infections in neonates
Corneal and Conjunctival Infection: can cause ulceration of cornea and blindness
Treatment/prevention of HSV
Antivirals; C-section for symptomatic mothers; vaccines coming soon
Papilloma Virus
Cause different types of warts
Common warts on hands and feet
Genital warts: sexual transmission, asymptomatic carriers
Some types associated with cancer: cervix, vulva, penis
Diagnosis of Papilloma Virus
immuno techniques and DNA hybridization techniques; no cell cultures available
Prevention of papilloma virus
Vaccine
Gardasil
Viruses that causes GLANDULAR ENLARGENMENT
Mumps
Epstein-Barr Virus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Hepatitis A, B, C
Mumps
Childhood disease
bilateral inflammation of parotid glands
many inapparent infections
Clinical manifestations of mumps
meningitis, orchitis (can lead to sterility), ovaritis
Epidemiology of Mumps
spread by salivary and respiratory secretions; incubation 18-21 days
Prevention of Mumps
MMR vaccine (live, attenuated)
Infectious Mononucleosis
AKA Epstein-Barr Virus
Mild disease; children and young adults; can be prolonged and debilitating
Transmission by saliva (kissing disease)
affects lymph nodes
Latent virus
Chronic disease (rare) or asymptomatic shedding (common) for lifetime of host
NO VACCINE
5 Symptoms of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
lymphadenopathy, fever, sore throat, atypical lymphocytes, enlargement of liver and spleen
viruses that affect lymph nodes
Infectious mononucleosis
Measles
Rubella
Hepatitis
Chicken pox/shingles
HIV
Cytomegalovirus
Diagnosis of EBV
blood picture (increase in atypical lymphocytes)
Monospot Test (detects RBC agglutination)
Presence of EBV antigens
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
usually asymptomatic and latent BUT dangerous for
Pregnant women: neonatal infection with jaundice, enlarged liver and spleen, intellectual deficiency and motor disorders
Transplant patients: disseminated infection can cause transplant rejection
AIDS and other immunocompromised patients: frequent infection, GI tract ulceration and retinitis
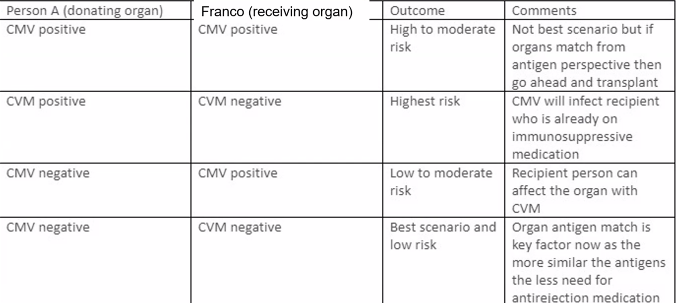
Diagnosis of CMV
Isolation of virus from urine, blood, organ biopsies (slow process, but accurate)
CMV antigen detection, DNA hybridization and PCR in leucocytes much faster
Serology screening for donors and recipients before transplant
Treatment/Prevention of CMV
Match CMV immune status between donor and recipient in transplants
Preventative administration of antivirals
Universal precautions to prevent transmission
NO VACCINE
Hepatitis Virus
AKA inflammation of liver
Malaise, fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite and jaundice
Hep A, B most common and well characterized
Hep C, E, G less common
Other viruses and bacteria can cause hepatitis as a complication of infection
Diagnosis: serological
Hepatitis A
Mainly children and young adults
Sporadic cases and small epidemics
Epidemiology of Hep. A
Transmission by fecal-oral route
food borne illness
Incubation 15-50 days
Stools infectious 2-3 weeks before onset
Mild or inapparent infection in children
No chronic hepatitis
Life-long immunity
Diagnosis of Hep. A
Suspected clinical cases: detection of IgM
Immunity: detection of IgG (before travel)
Prevention of Hep. A
Vaccine for high risk populations
Commercial γ-globulin for prevention after exposure
Hepatitis B
Sporadic cases; all ages
Epidemiology of Hep. B
Contaminated blood/blood products; saliva, urine, semen
Avg. incubation 90 days
Infective serum 30-60 days before onset of symptoms
Carriers
Clinical Manifestation of Hep. B
More severe than HepA
Chronic hepatitis and chronic carrier-state
Diagnosis of Hep. B
Blood test for HepB surface antigen (HBsAg)
Antibodies are produced several months after onset of symptoms
Used as markers of infection and immunity
Prevention of Hep. B
Universal precautions for blood and body fluids
Proper handling of needles
Screening
Vaccination
HepB immunglobulins after exposure
HepB carriers
Hepatitis C
Epidemiology:
Blood and sexual transmission
Initially mild disease but can cause chronic hepatitis
Diagnosis:
Serological
Prevention:
Same as HepB
Treatment/cure?
Epclusa (sofosbuvir-velpatasvir)
Hepatitis Delta agent
Epidemiology:
Blood and sexual transmission
“Viroid”-relies on HepB presence for replication in cells
Increases severity of HepB infection
Diagnosis:
Serological
Prevention:
Vaccination against HepB
Hepatitis E
Transmission via fecal-oral route
Incubation 15-50 days
Symptoms similar to HepA BUT 20% mortality in pregnant women
Endemic in India, Pakistan, Nepal, Burma, North Africa and Mexico
Yellow Fever Virus
Haemorrhagic fever with hepatitis
Endemic in Africa, South America and Caribbean
Mortality rates as high as 50%
Transmitted by mosquito
Travellers to endemic countries receive live attenuated vaccine
Clinical manifestations of viruses affecting CNS
Aseptic meningitis
Encephalitis
Meningo-encephalitis
Poliomyelitis
Slow progressive, persistant infections
General Diagnosis of viruses affecting CNS
Always first exclude possibility of bacterial or fungal infection*
Lumbar puncture X4
Other specimens
Blood, urine, aspirates,
throat swabs
stools, sera
CNS viruses with human reservoir
Usually an extension of a primary infection in another part of the body
Mumps-aseptic meningitis in children
Enteroviruses-aseptic meningitis in infants and children
HSV1-RARE cause of herpetic encephalitis in young adults
HSV 1 or 2-RARE cause of meningo-encephalitis in neonate or young adult
Vaccination for mumps, measles and polio (entero)
CNS viruses with animal reservoir
RARE: Humans are accidental or dead-end hosts(AKA humans are not preferred host)
Arbovirus:
Rabies virus
Arbovirus
over 200 different types
Tropical rainforest areas
Encephalitis
E.g. West Nile
control mosquito pop.
get rid of stagnant water around the house
Rabies virus
Fatal, acute encephalitis
Infects mammals, transmitted via saliva
Long incubation (30-60 days)
Combined active and passive immunization
Prevention by vaccination of wildlife and pets
HIV and AIDS
Severe immunosuppressive condition;
often fatal;
predisposition to opportunistic infections and cancers
HIV causes depletion in helper T-cells making the host very susceptible to other infections
Frequent antigenic changes
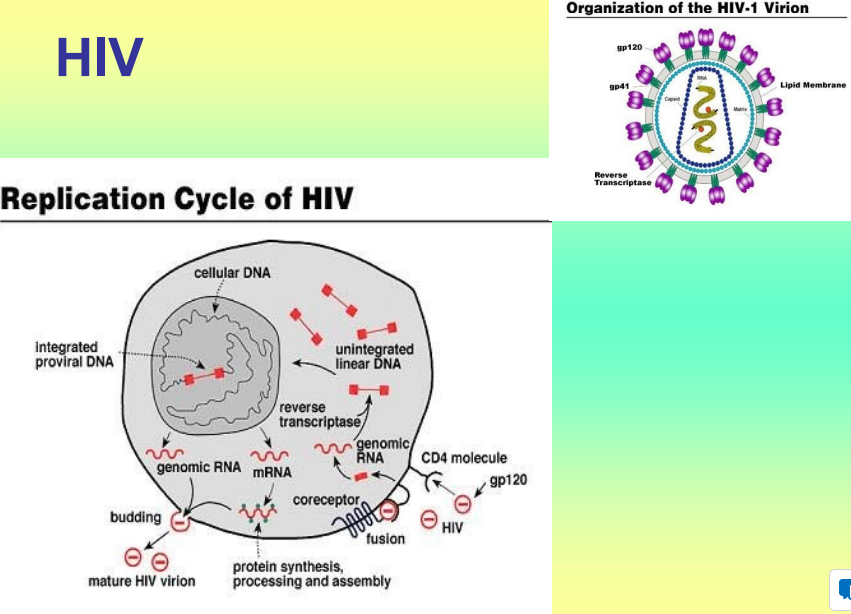
HIV inactivation
Virus often protected by living inside cells, protect it from disinfecting action
Transmission of HIV
Sexual, blood/blood products, congenital, organ transplants, sperm donation
Lengthy asymptomatic period increases spread of disease