Intro to Psychology
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mt1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Who is Rene Descartes?
Dualism - how the body and spirit interact. Pineal gland = where soul and body interact.
What did Hobbes have to say about Descartes’s philosophy?
Hobbes disagreed saying that the body and spirit (mind/brain) are connect, much like Hippocrates
What did Hermann von Helmholtz discover?
That signals through the nerves do not happen instantaneously → found out using frog legs.
What was significant about how Helmholtz discovered this phenomena (protopsychology)?
he didn’t just observe phenomena, he measured phenomena
his approach was empirical
Who is the founding father of psychology?
Wilhelm Wundt
Had the first psychology lab in the late 1880s in Germany
Made the first textbook, “Scientific study of the conscious experience (1897)”
What did Wundt practice?
Structuralism
Who developed introspection and what is it?
Wilhelm Wundt.
Introspection = to objectively observe your conscious experience.
What is structuralism?
Studying the basic building blocks of consciousness (thoughts, feelings, memories) → individual parts of the mind
What are the setbacks of structuralism?
Sample bias - educated (and rich) people were needed
Subjective
Can only access conscious experience
cannot be verified (behaviour can be observed and verified)
inconsistent results (hard to replicate introspection)
Who developed functionalism, and what is it about?
William James (also believed in introspection)
Functionalism = Understanding what the biological function of consciousness is (based on Darwin’s theory of evolution) → the mind as a whole
What is Gestalt psychology?
“The whole is greater than the sum of its individual parts”
“the whole” = perception
“individual parts” = sensation
Who is the founder of the clinical branch of psychology?
Sigmund Freud
Who came up with psychoanalysis, and the unconscious mind?
Freud
Who is Anna O and what did she suffer from? How is this person related to Freud?
Anna O suffered from hysteria (aphasia = inability to speak, paralysis on the right side of the body, disturbances in vision, hearing, and speech) with no physiological basis.
Found that free association helped with her symptoms.
What are Freudian slips?
When the superego’s energy slips and the id’s desires are said aloud (calling your boss dad).
What are the faults in Freud’s theory?
The theory couldn’t be proven false (unfalsifiable = scientifically insignificant)
Placed too much emphasis on sex
What did Freud do for psychology (positives)?
highlighted the importance of childhood
differed conscious and unconscious thought
how motivations can cause psychological conflict
What is the behaviorists perspective?
consciousness is flawed
primary mechanism is learning
believed in classical conditioning = dinner bell (learning)
believed in operant conditioning (punishing and rewarding behaviors causing them to be repeated/avoided)
→ the most effective form of therapy now
What is the humanists perspective?
Believed humans are good in nature, and you have the potential to grow
We have an intention to have positive growth (Maslow’s hierarchy of needs)
Who is Carl Rogers?
invented client-centered therapy = act as a mirror to help someone unravel/organized their jumbled thoughts
What are the components of client-centered therapy?
unconditional positive regard (you judge yourself so you need someone else to be that for you)
genuine
empathy
Give a timeline for the different psychology perspectives
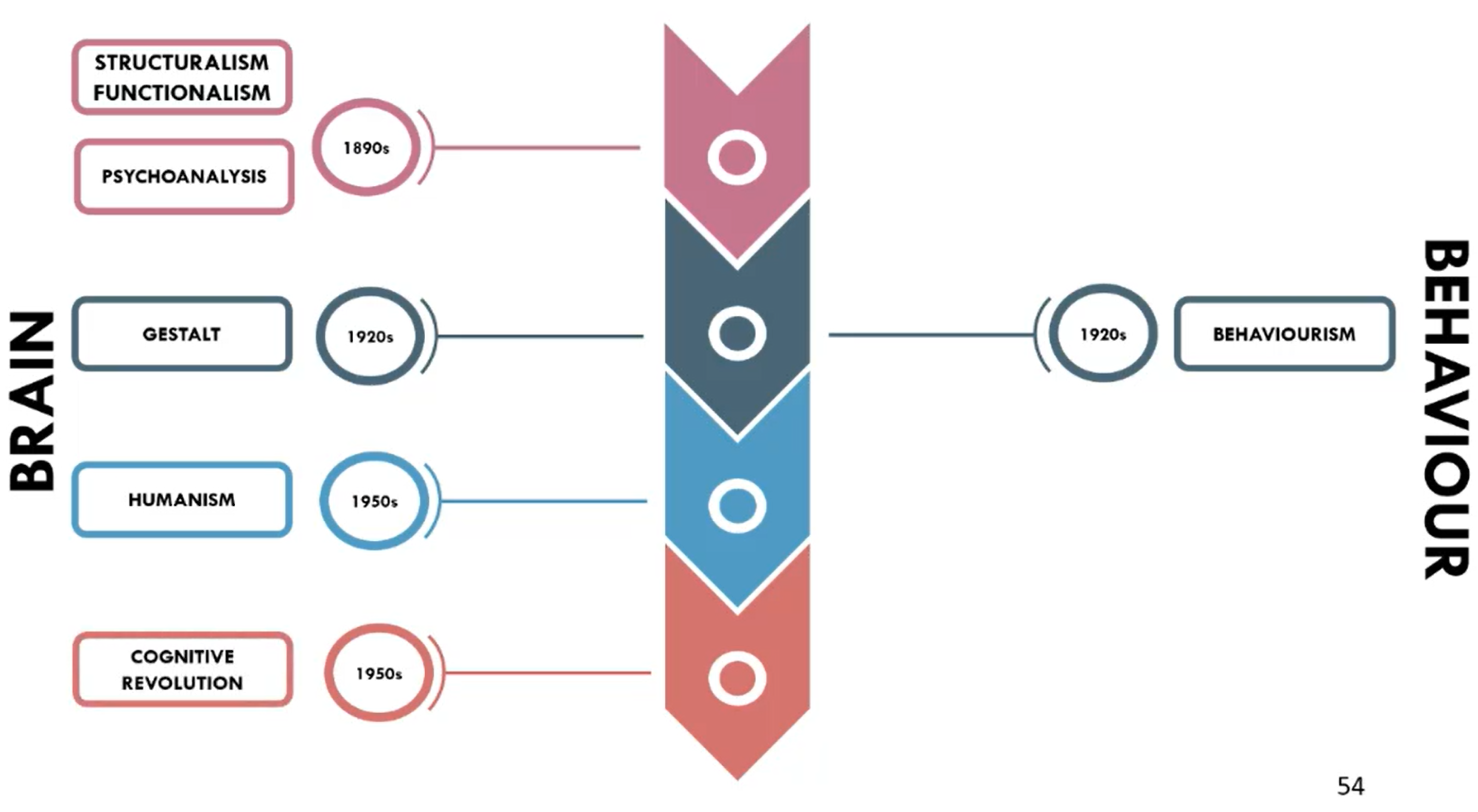
Describe cognitive revolution
placed emphasis on mental processes
linguistics (do languages shape thoughts?)
neuroscience (how does the brain work?)
collaboration across disciplines
Who is Bruno Bettelheim?
A holocaust survivor who came up with the diagnostic criteria for autism.
Why is feminist psychology important?
Before feminist psychology began the default was that males were dominant, and men assumed what women wanted (which was just not true).
Who is Karen Horney?
explain why women may have “penis envy” = men are more privileged in society and being a women meant being inferior in society
described “womb envy” and that men cannot give life (have children)
Who is Naomi Weisstein?
She stated the feminist approach was to free psychology of all gender biases (not put women above men), to study gender differences, and re-evaluate the contribution of women (e.g. Anna Freud)
What is Multicultural Psychology?
Explains how different events depend on cultural upbringing
Precedents of eating disorders differ by culture
Culture influences the types of hallucinations that people have
How culture and environment influence perception
What does WEIRD stand for?
Western Educated Industrialized Rich Democratic
Who is Cecil Sumner?
First African American to receive a PhD in America
What does biopsychology focus on?
Study of the brain and nervous system (sleep, sensation & perception, psychological disorders, development)
Focuses on immediate causes of behavior
What does evolutionary psychology focus on?
Focus on long-term biological causes of behavior
If behavior is determined by genetics, it will be shaped by its surroundings
What is the genetic cause of common behaviours in human cultures?
What is the McGurk effect?
Describes how what we see can alter what we are hearing, or vice versa
part of sensation and perception psychology
What is a Tritone Paradox?
When tones contain both a higher and lower frequency → brains have a preference of which to hear
What is developmental psychology?
developmental trajectories
cognitive, social, emotional, physical, moral psychology
neural blooming found during childhood and puberty