Chapter 18, Lesson 2: Erythrocytes
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 18, Lesson 2 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Erythrocytes
Also called red blood cells, they transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
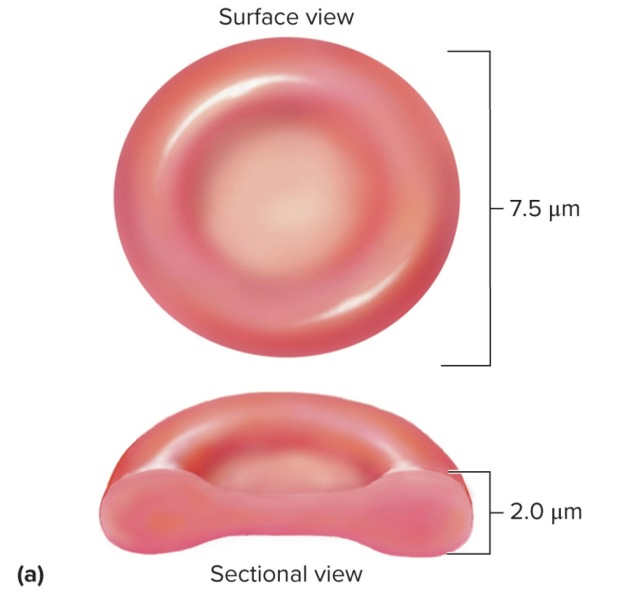
Erythrocyte structure
Discoid with a biconcave shape and no organelles with anaerobic fermentation for ATP and no protein synthesis or mitosis
Hemoglobin
Particle that makes up 33% of an erythrocyte’s cytoplasm; gives a red pigment and aids in oxygen and carbon dioxide transport
Glycolipids
Particles on the outer surface of an erythrocyte for blood typing
Hemoglobin structure
4 proteins consisting of a heme group with iron to carry oxygen and globins binding with carbon dioxide
Hematocrit (packed cell volume)
The percentage of whole volume composed of red blood cells; typical values for men are 42-52% and women are 37-48%
Hemoglobin concentration
How much hemoglobin is in a whole blood sample; typical values for men are 13 to 18 g/dL and women 12 to 16 g/dL
Red blood cell count
Blood cells in a sample; men have 4.6 to 6.2 million per microliter and women have 4.2 to 5.4 million per microliter
Gender erythrocyte differences
Women have lower values due to androgens, periodic menstrual losses, and hematocrit being inversely proportional to body fat
Erythropoiesis
Erythrocyte production; occurs at a rate of 3 to 5 days at 1 million per second for a lifespan of 120 days
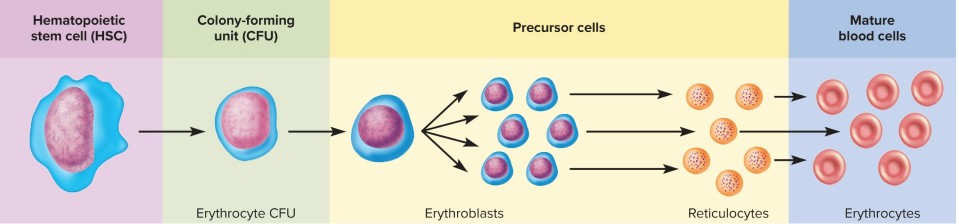
Erythrocyte production
Stem cell forms colony-forming units
Hemoglobin is synthesized as nucleus is discarded
Polyribosomes disintegrate, creating erythrocytes
Reticulocytes
Immature erythrocytes with polyribosomes
Erythrocyte homeostasis
Maintained through a negative feedback loop; lower counts can result in hypoxemia (oxygen deficiency) but is replaced in 3 to 4 days by kidneys to increase counts in blood loss, high altitudes, exercise, or emphysema
Iron
Used heavily for erythropoiesis but lost through daily life with low absorption
Vitamin B12 and folic acid
Used for rapid cell division and DNA synthesis
Vitamin C and copper
Cofactors for enzymes synthesizing hemoglobin
Erythrocyte death
Membrane proteins deteriorate
Cell ruptures in spleen and liver
Macrophages digest and separate particles; heme becomes biliverdin
Primary polycythemia
Erythrocyte excess with cancer in bone marrow
Secondary polycythemia
Polycythemia from all other causes
Anemia
The deficiency of erythrocytes or hemoglobin, could cause hypoxia or reduced viscosity:
hemmorhagic (bleeding)
hemolytic (destroyed)
insufficient synthesis
Sickle-cell disease
A hereditary hemoglobin effect prominent in Africa, the Middle East, and India where cells are sickle-shaped and cannot carry oxygen as well