Unit 4 AP Stats
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Random Process
We are aware of possible outcomes but have no clue what the outcome will be (results determined by change)
There is a sense of predictability that occurs in the ____ run.
long
Patterns of random occurrences may include _____ or runs of outcome that appear to be non-random.
strings
Outcome
Result of a trial of a random process (ex: heads)
Event
A collection of outcomes (results of a trial of a random process ex: roll a prime # (2,3,5))
Simulation
A way to model random events
Law of Large Numbers
Simulated probability gets closer to theoretical probability as the number of trials increases (variability from true probability is decreased)
Conducting a simulation (with random num gen) Describe the process for FRQs
Describe how the random digits will imitate the trial (what digits represent which outcomes). Also determine what will be recorded from each trial
Perform many trials of the simulation
Calculate the relative frequency of successful trials to get a calculated probability
Sample Space of Random Process
The collection of all possible non-overlapping outcomes ex: (roll a dice= [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
Probability of an event A
P(A)
Interpret Probability
Probabilities of events in repeatable situations can be interpreted as the relative frequency with which the event will occur in the long run.
Interpret Probability of P(Jazz) = 0.205
If we were to randomly select many individual albums sold this year (with replacement), the relative freq. of jazz albums selected would be approx. 0.205.
Valid probability distribution
Sum of all probabilities is 1
Complement of an event A is the event that A…
doesn’t happen
Complement of A is denoted by:
A’ or A^c
Probability of complement of A =
P(A’) = 1 - P(A)
Mutually Exclusive Events (Disjoint)
Cannot occur at the same time
Joint Probability
Probability of the intersection of two events
P(A^B)
Probability of A and B
P(AUB)
Probability of A or B
P(B|A)
Probability of B given A (Conditional probability)
Multiplication Rule
P(A^B) = P(A) * P(B|A)
Conditional Probability Rule
P(B|A) = P(A^B)/P(A)
How do you know if events A and B are independent?
They are independent only if by knowing whether or not Event A has occurred (or will occur) doesn’t change the probability that Event B will occur.
What are some equations that help prove the independence of events?
P(A|B) = P(A)
P(A|B’) = P(A)
P(A^B) = P(A) * P(B)
Union of Events
The probability that A or B (or both) will occur
Addition Rule
P(AUB) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A^B)
Random Vars
They are numerical outcomes of random behavior (represented with capital letter)
Example of Random Var
X = # of children in a randomly selected household
Discrete Random Var
Can only take a countable number of values (X = num of children in randomly selected household)
Continuous Random Var
Can take on an infinite # of values (W = time it takes to run a mile)
Probability Distribution
Display of entire set of values with their associated probability.
Describing a probability distr.
Shape
Center (median)
Spread (common to use SD but can use range)
Can make histogram for shape (ex: skewed)
Mean of a Random Var
Take the sum of each x value times the probability of each x value
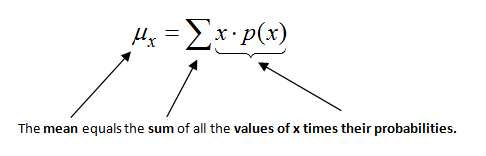
Interpreting Mean
In the long run, if many prairie dogs are randomly selected, the average # of pups per litter will be about 2.66 pups.
Standard Deviation of Random Var
The sum of (each x val - mean)² times P(x val))
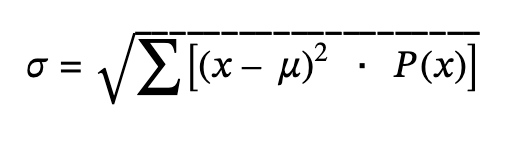
Interpret SD
The number of prairie dog pups in randomly selected litters will generally vary form the mean of 2.66 pups by about 1.267 pups.
Standard deviation is the ______ ____ of the variance.
square root
When a question asks you to calculate/interpret the expected value for something they mean…?
Find the mean!
Interpretations of random variable parameters should use appropriate ____ + include _____ of the population.
units, context
Transforming Mean of Random Var
a + b(mean)
Transforming SD of Random Var
|b|(mean)
Binomial Setting
Two possible outcomes (success, fail)
Independent trials of same random process
Fixed # of trials, n
Each trial has the same probability of success
Independent trials
Knowing that one outcome doesn’t help us to predict another outcome
Binomial Random Var
Random variable in binomial setting
What are two ways that you can find probabilities using binomial random variables?
Use simulation to estimate probabilities
Use the binomial probability formula to calculate probabilities
Binomial probability formula
(n combination x) (p^x)(1-p)^n-x
n = number of trials
p = probability
Calculator Function for Combination
MATH, PRB, nCr
Binompdf/Binomcdf
2nd, DISTR
Difference between cdf and pdf
Pdf finds exact probability at x = # while cdf finds cumulative probability up to x = #
Mean of binomial random var
mean = np
SD of binomial random var
SD = sqr(np(1-p))
Interpret mean of bin rando var
In many random samples of 40 cell phone owners, the BTB team can expect an avg of 8.4 people to have a cracked cellphone screen.
Interpret SD of bin rando var
In many random samples of 40 cell phone owners, the number with cracked phones will typically vary from the mean of 8.4 by about 2.58 phones.
Geometric Setting
Two possible outcomes
Independent trials
Each trial has same probability of success
BUT there isn’t a fixed # of trials!
Geometric distribution formula
P(X=x) = ((1-p)^x-1)(p)
Mean of geo distr
1/p
SD of geo distr
sqr(1-p)/p
Interpret geo mean
Over many seasons, we expect it will take 2.44 storms on average to get the first hurricane.
Interpret geo SD
Over many seasons the number of tropical storms it takes to get the first hurricane will differ by about SD from mean of ___.