Gr.10 Bio(Animal tissues, organs, organ systems)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Animal tissues
Tissue:
Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue
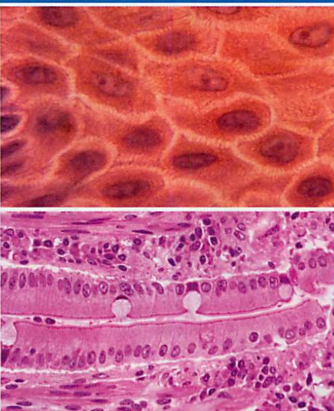
Epithelial Tissue
Function: lines body cavities and outer surfaces of body, protects organs, keeps organs in place, forms glands that produce hormones/enzymes/sweat.
Skin epithelia: Thin, flat cells that form sheets and act as a semi-permeable barrier between the inside and outside of the body.
Columnar Epithelia: Made of columns of cells that line the small intestine, stomach, and glands.
Connective Tissue
Function: supports and protects structures, forms blood, stores fat, fills empty space.
Bone: made of cells surrounded by calcium-hardened tissue through which blood vessels run, needed for movement/support/protection.
Fat: large/tightly packed cells, found under skin and around organs, needed for energy storage/paddling/insulation.
Blood: includes red blood cells/white blood cells/platelets within a straw-coloured liquid matrix called plasma, transports nutrients/oxygen, clots when skin is cut, attracts invaders(bacteria/viruses).

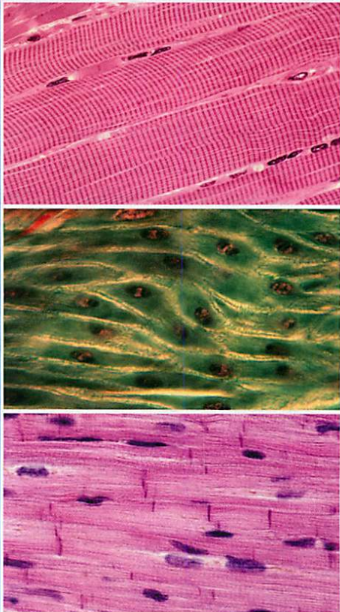
Muscle Tissue
Function: allows movement, designed to change shape, act by shortening and lengthening
Skeletal muscle: cells that line up in the same direction(makes tissue look striped), attaches to bone so the body can move, found in places where body needs support(limbs: arms, legs).
Smooth muscle: cells that are tapered at both ends(don’t look striped), contracts more slowly than skeletal muscle but its action is sustained for a long time, found in blood vessels and walls of internal organs(esophagus, stomach).
Cardiac muscle: cells w/nuclei that appear to be between cells, branched/unevenly striped, contracts as a unit, found in the heart.
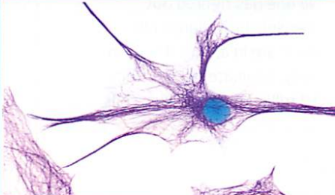
Nervous Tissue
Function: responds to stimuli, transports and stores information, coordinates body actions.
Specialized cells: cells called neurons, which have finger-like projects to receive and transfer signals.
Eg. brain and spinal cord, peripheral nervous system
Animal organs
Organ: a structure in an organism made of cells and tissues which perform specific functions.
Fun fact: there are 78 organs in the human body.
Skin
Tissues:
Epidermis: outer protective layer
Dermis: inner layer of skin
Function:
Protects cell from damage/infection.
Senses the environment(pain, pressure, heat, cold)
Releases excess heat by dilation of blood vessels
Cools body by sweating
Insulates body with layers of fat
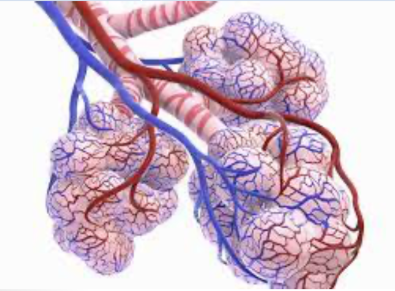
Lungs
Tissues:
Connective and epidermal
Function:
Allows intake of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide.
When we inhale, air passes into our lungs and eventually reaches the alveoli. Tiny thin-walled
blood vessels called capillaries surround the alveoli and allow for gas exchange through
diffusion. Air then leaves our lungs when we exhale.
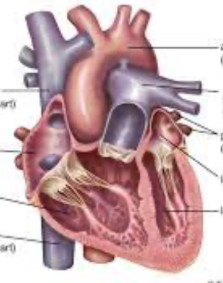
Heart
Component tissues:
All 4
Function:
Supplies blood to all parts of the body.
300 g. size of a fist.
Deoxygenated blood: flows from the body to the right side of the heart where it gets pumped to the lungs to be oxygenated.
Oxygenated blood: flows back to the left side of the heart which then pumps it out to the rest of the body.
Organs of digestion
Component tissues:
Epithelial, connective, muscle
Function:
Esophagus moves food along by peristalsis, the constriction and relaxation of smooth muscles in the esophageal walls.
Stomach churns food and mixes it with digestive juices and enzymes.
Intestines absorb nutrients and water.
Human organ systems
Muscular System
Organs: muscles, supporting structures
Function: Works with bones to move parts of the body.
Skeletal System
Organs: bones, cartilage
Function: supports, protects, and works with muscles to move parts of the body.
Nervous System
Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves
Function: detects changes in the environment and signals these changes to the body, coordinates responses, controls body functions.
Lymphatic System
Organs: thymus, spleen, lymph nodes
Function: protects body from diseases, absorbs/transports fats
Endocrine System
Organs: glands, pancreas, ovaries/testes
Functions: controls growth, development and metabolism, manufactures/releases hormones that act along with nervous system to keep various body systems in balance.
Excretory System
Organs: kidney, bladder, ureter, urethra
Functions: removes liquid wastes from the body.
Reproductive System
Organs: ovaries, uterus, testes
Functions: reproduction
Integumentary System
Organ: skin and associated structures
Structure: protects body from various things(injury, invasion by infectious organisms, abrupt changes in temperature)
Circulatory System
Organs: heart, blood, blood vessels
Function: Transport of materials(blood/nutrients/gases/wastes) within the body
Movement of oxygen from the lungs to all the body cells
Movement of carbon dioxide from all the body cells to lungs
Movement of nutrients from the small intestine to the body cells
Movement of waste products from the body cells to the kidneys and skins
Blood moving through the circulatory system!
Heart contracts —> produces pressure on blood —> blood moves thru the body
Valves(flexible flaps of tissues in heart/veins) open when blood pushes thru them but closes to prevent it from flowing backwards.
How blood moves:
Deoxygenated blood moves to heart’s right atrium (which receives blood from body).
From the right atrium blood moves to the right ventricle (which pumps blood to lungs) where blood eliminates CO2 and picks up oxygen.
Oxygenated blood goes to the left atrium (which receives blood from lungs) and then to the left ventricle (which pumps blood out to the rest of the body through a huge artery called the aorta)
This blood travels through the body becomes deoxygenated and goes back to the heart’s right atrium.
Deoxygenated blood: blood that returns from the body where body cells removed the oxygen and carries carbon dioxide waste from cellular respiration.
Blood
type of connective tissue
transport liquid pumped by the heart to all parts of the body
Composed of:
plasma: yellowish liquid that holds the blood cells, protein, and other constitutes of whole blood in suspension.
white blood cells: protect from infection.
platelets: allow for blood clotting
red blood cells: carry oxygen due to hemoglobin from the lungs to body cells.
Blood cells
Red blood cells: hemoglobin in the cell is iron-containing protein that transports oxygen to the tissues of the body.
White blood cells: fights diseases and foreign invaders.
Platelets: aid in blood clotting and are involved in repairing damaged blood cells.
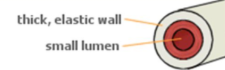
Artery
(Type of blood vessel)
Role: carries blood away from heart.
Structure: thick elastic wall, small lumen
Capillary
(Type of blood vessel)
Role: site of exchange between blood and cells/tissues
Bring blood into close contact w/tissues in the digestive system so that the blood can pick up nutrients from digested food.
Bring blood close to the alveolus where blood picks up oxygen.
Capillaries also deliver blood that is rich in oxygen/nutrients which picking up waste to transport to kidneys/lungs where they are removed from bloodstream.
Structure: single thick cell wall, smallest diameter (only 1 epidermal cell thick)
Red = oxygenated, going to body
Blue = deoxygenated, going to heart
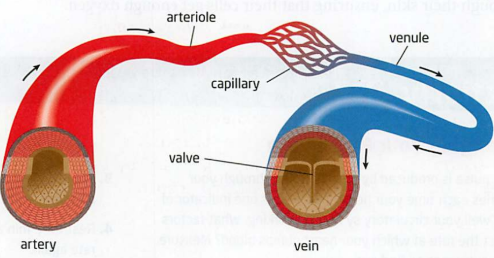
Vein
Role: carry blood toward the heart
Structure: thin wall, large lumen, valves present to help push blood back to heart
Respiratory System
Organs: trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles
Functions: gas exchange(bringing oxygen into the body and getting rid of the CO2), controls breathing
Working with other systems: when you breathe muscles contractions cause your rib cage to move up/down and your diaphragm to move down.
Respiratory system process
Air enters through nasal passages ad pharynx, then moves into trachea.
The epiglottis controls the passage: it opens for air and closes for food.
Air travels through the bronchi, which branch into smaller bronchioles that regulate airflow via muscle contraction.
Oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Carbon dioxide is expelled when the chest muscles and diaphragm relax during exhalation.
Body adjusts breathing rate based on carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
Gas exchange in respiratory system
Occurs in alveolus(plural = alveoli)
Oxygen gas and carbon dioxide diffuse through 2 thin walls: alveolus wall and capillary wall.
Oxygen gas diffuse from the air in the alveoli into the blood where it binds to the red blood cells.
Carbon dioxide leaves the blood and moves into the alveolus and is exhaled in the air we breathe.
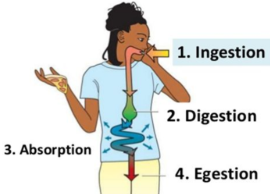
Digestive System
Organs: esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver
Function:
Ingestion
Digestion
Absorption
Egestion
Mechanical digestion:
Physical change
Biting, chewing, contractions, peristalsis
Occurs in mouth, esophagus, stomach
Chemical digestion:
Chemical change
Occurs in mouth, stomach, small intestine due to digestive enzymes