Unit 10: Invisible Astronomy
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What does the electromagnetic spectrum look like?
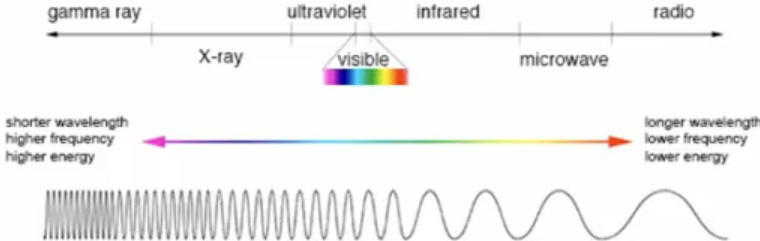
What are some radio wave advantages?
detected all day
detected on ground
reflected off metal
not absorbed by dust
emitted by distant young galaxies
What explains the fact that radio waves can be detected all day?
long wavelength
impervious to atmosphere & cloud molecules
Sun produces low radio emission
What explains the fact that the atmospheric opacity of gamma ray, X-ray, and UV waves is at 100%?
smaller particles than atmosphere
bounce away
What number is the approximate atmospheric opacity of UV waves becoming visible?
80%
What number is the approximate atmospheric opacity of visible light?
10%
What explains the fact that big telescopes are on mountains?
more thin atmosphere = more light
What explains the fact that infrared waves can touch the ground?
atmosphere contains certain molecules that efficiently block in specific spots
What number is the approximate atmospheric opacity of microwave & radio waves?
0%
What number is the limit to radio wavelengths that touch the ground?
50m
What explains the fact that radio waves beyond 50m don’t touch the ground?
reflect off upper atmosphere
What are commonly found in distant galaxies?
radio jet
What did military start to use leading to WWII?
radar
What was accidentally detected in the early 1930s by Karl Jansky?
1st radio light
What explains the method of discovering radio light?
Jansky worked at Bell Labs
investigated transatlantic telephone by radio waves
identified radio sources interfering with voice
What radio noise did Jansky find?
thunderstorm
sky hiss
rising & falling in strength every 24 hours
What did Jansky initially believe about the radio hiss?
come from Sun
What did Jansky finally believe about the radio hiss?
come from Sagittarius constellation / Milky Way disk
because Milky Way centre rises & sets
What was announced on May 5, 1933 in the New York Times?
Jansky’s discovery
“New Radio Waves Traced to the Centre of the Milky Way”
What did Grote Reber do in 1937?
built 10m dish in backyard by iron sheet
What did Grote Reber identify in 1937?
discrete radio emission
What was a diffuse radio source in Reber’s map?
Milky Way centre
What was a discrete radio source in Reber’s map?
2 unknown
What did Dutch astronomer Hendrik van de Hulst predict in 1945?
H naturally emits 21 centimetre radio wave when electron flips
What are “aligned poles?”
high E state
unnatural repulsion force
stable for 10 000 000 years
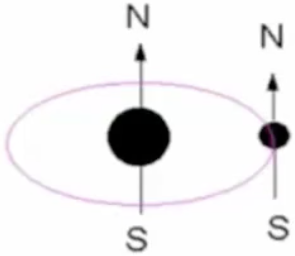
What are “opposite poles?”
low E state
natural attraction force
What process causes opposite poles?
electron flips
emits 21 centimetre wavelength energy
What was astronomers’ response to Hendrik van de Hulst’s prediction in the 1950s?
21 centimetre emission
strong along Milky Way disc
What did astronomers find about hydrogen in our Galaxy?
21 centimetre radio emission map = Galaxy hydrogen map
What was the key result of the Dutch astronomers’ 21 centimetre map in 1958?
H is arranged in discrete locations
→ spiral arms
What is Earth’s Universe address?
Earth
Solar System
Orion Spur Arm
Milky Way
Local Group
Local / Virgo Supercluster
What is the nearest discrete radio emission source?
Sun
What did English radar engineer Stanley Hey detect in 1942?
radio from solar flare
What is a “solar flare?”
radiation eruption tracing magnetic field line from sunspot
What caused Stanley Hey to detect radio from solar flare?
English radar sites tracking enemy planes were interfered by radio emission
What did Stanley Hey initially conclude about the interfering radio emission?
enemy defence
What did Stanley Hey finally conclude about the interfering radio emission?
radio surge matched solar flare
→ related to Sun magnetic field
What happens what atoms fly through magnetic fields?
radiate & trace magnetic field line
What explains the Sun’s differential rotation?
fluid body
What is “differential rotation?”
rotation speed decreases with latitude
closer to equator = quicker spin
What explains Earth’s magnetic field being a big bar magnet?
core = spinning iron sphere
What is Sun’s magnetic field?
un/twisting field every 11 years
What did German astronomer Samuel Schwabe track over 2 decades?
visible sunspot number reaches hundreds from handfuls every 11 years
What is a “solar minimum?”
few sunspots

What is a “solar maximum?”
many sunspots

What process causes sunspots to appear in pairs?
magnetic field comes out surface
loses heat
magnetic field goes in surface
What was discovered about Sun radio emission in the 1850s?
magnetic storm & aurora followed Sun cycle
What causes magnetic storms & auroras?
charged particles by sunspots
What are the name origins of “aurora?”
Roman dawn god
What are the word origins of “borealis?”
the south
Latin
What is a “magnetic storm?”
sudden & temporary magnetic field scramble
What causes magnetic storms?
solar wind of charged particle distorts Earth magnetic field
What is an “aurora?”
charged solar wind particle glow
What causes auroras?
solar charged particle wind follows Earth magnetic field to pole & smash Earth atmosphere
What is a “radio array?”
multiple radio dishes
What detected the most distant observed object?
radio array
What are radio arrays’ advantages?
cheap
practical
What is the “SKA?”
Square Kilometre Array
radio array with most dishes
see 50x further
What did English radio astronomers Jocelyn Bell Burnell & Antony Hewish detect from supernova remnant cores in 1967?
pulsar
What did Jocelyn Bell Burnell & Antony Hewish initially conclude about the radio source that pulsed radio emission?
intelligent life
What did Jocelyn Bell Burnell & Antony Hewish finally conclude about the radio source that pulsed radio emission?
radio light pulse
What is a “pulsar?”
neutron stars pulsing radio light
What produces magnetic fields?
spinning charged particles
What causes pulsars?
neutron star sucks charged particles from gas cloud
… accelerates
… shoots out radio beams
radio beams sweep circle
magnetic axis is not always aligned with spin axis
… aim at Earth
What was found about binary pulsars in the 1980s?
tick slower when close to centre of mass
What is “time dilation?”
time slows down in strong gravity field
What explains time dilation?
more gravity = slower time
What explains why one would see the opposite of GR’s prediction if pulsars spin slower due to star gravity?
gravity causes pulsar to speed up
What did Stanley Hey identify about radio galaxies & quasars in 1946?
1st radio source from galaxy
What was the 1st radio source from galaxy?
Cygnus A
What is a “radio galaxy?”
(typically) giant elliptical with radio jet
What causes radio jets?
galaxy nucleus
What is a “Seyfert galaxy?”
radio- loud / bright spiral
What did American astronomer Martin Schmidt investigate in the 1960s?
star-like spectra at same coordinates as strong radio sources
What are “quasars?”
Quasi-Stellar Radio Source
huge redshifted galaxy
What is the “Doppler Effect?”
larger shift = faster object
What is “Hubble’s Law?”
higher recessional speed = more distant object
What causes quasars?
bright star-like appearance = huge swirling matter
What was proposed about binary star system black holes?
black hole can accrete companion star matter & form swirling disc around black hole
black hole’s spin produces magnetic field
→ radio lobe
What is an “accretion disc?”
disc around supermassive black hole at galaxy centre
What would the space immediately surrounding a black hole have?
near infinite gravity
What do radio galaxy images reveal?
huge hot gas & dust disc around dark object
What explains why only distant quasars are seen?
young phase
denser galaxy core
→ more black hole fuel
accretion disc disappears
→ stable galaxy
What do nearby galaxies emitting radio jets suggest about black holes?
temporarily reactivated
What causes temporarily reactivated black holes?
galaxies interact
gravitation pull pushes stuff towards hibernating black hole
What explains why most galaxies have a quiet central black hole?
consumed all nearby matter
What is “Sagittarius A?”
brightest Galaxy radio source
What is the Milky Way supermassive black hole size?
6 light hours
1 000 000 000 kilometres
What explains why x-ray has to be observed from space?
can’t penetrate Earth atmosphere
What did NASA launch in the late 1970s?
Einstein Observatory
1st x-ray space observatory
What is the strongest galactic x-ray source, discovered in the 1960s?
Cygnus X-1
What causes accretion discs to glow?
high speed
What is a “stellar mass black hole?”
black hole from single dead star
What is in the most steeply curved space around the stellar mass black hole?
x-ray
high energy radiation
What is the process of detecting black holes?
search for companion star
bright x-ray source
accretion disc
What did Canadian astronomer Tom Bolton find about Cygnus X-1 in 1972?
binary system