Patho Exam 1
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
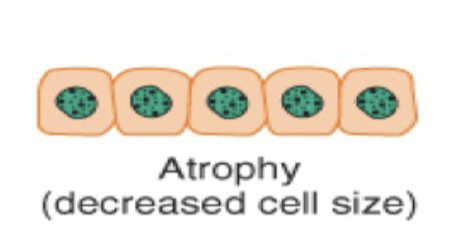
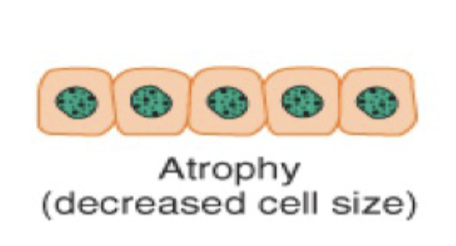
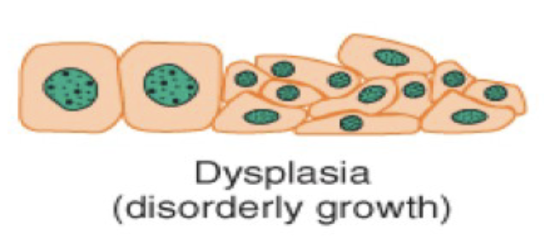
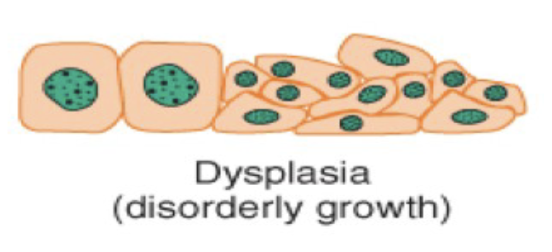
Atrophy is a type of cellular adaptation where there is a _____ in cell size due to ____ synthesis or increased _____ _____, or both.
a decrease in cell size due to protein synthesis or increased protein catabolism or both.
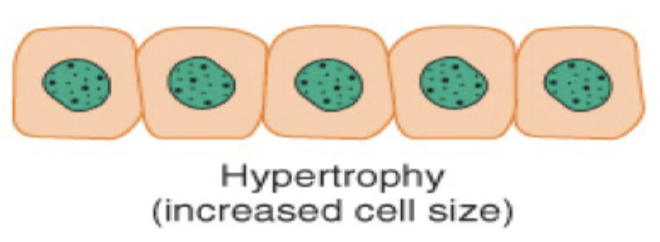
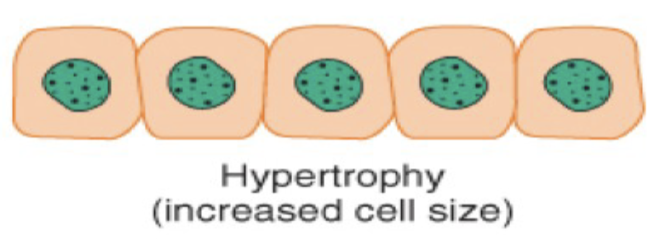
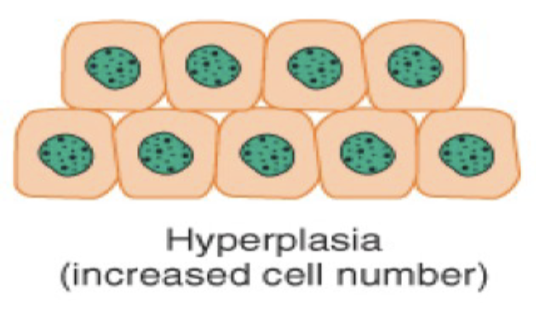
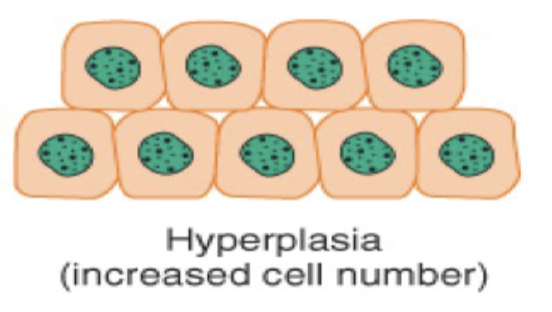
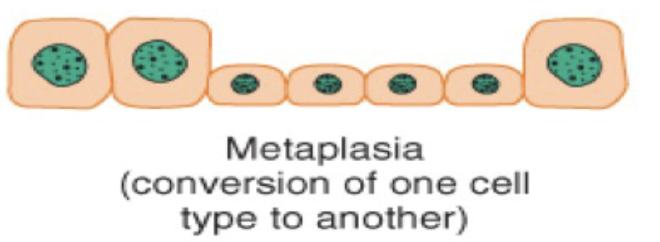
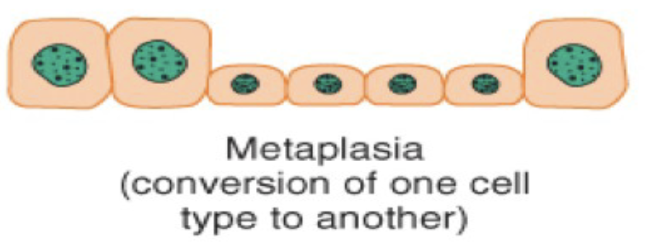
Metaplasia is a cellular adaption with the ____ of one ____ ____ to another.
the conversion of one cell type to another.
What is the most important risk factor for Down Syndrome?
increased maternal age
A provider notes that a group of institutionalized people develop similar respiratory symptoms due to what type of necrosis?
caseous necrosis
What type of pathologic atrophy occurs with prolonged bedrest?
decreased muscle size atrophy
What type of cells responds to parasitic infection?
eosinophils
____ is a protein synthesized by the liver, as are all ___ ____ except for immunoglobulins, and is catabolized by all ____ active tissues.
albumin, liver, plasma proteins except for immunoglobulins, and catabolized by all metabolically active tissues.
Oncotic/ osmotic pressure is induced by ____, notably ____.
proteins, albumin
Intracellular fluid is ____ the cell while extracellular fluid lies ____ of the cell.
within, outside
Aging adults experience ____ free fat and ____ mass, and renal decline.
decreased free fat and muscle mass, and renal decline
____ pressure pushes water out of capillaries (____).
Hydrostatic, (filtration).
Hydrostatic pressure is higher during ____.
filtration
**water** molecules
Forces favoring filtration:
_____ hydrostatic pressure ( ____ pressure)
_____ (in between capillaries, space between cells) oncotic pressure (water- pulling)
capillary hydrostatic pressure (blood pressure)
interstitial (space between cells) oncotic pressure
* capillary ____ pressure (water- pulling)
* interstitial ____ pressure
* interstitial **hydrostatic** pressure
A low level of ADH results in ____ urine production.
____ - ____ system (RAS) is triggered by a drop in ____ ____ and a drop in ____ volume.
renin- angiotensin system (RAS), drop in blood pressure, fluid
____ also releases ____.
**liver**, **angiotensinogen**
____ then acts on angiotensinogen to form ____ I.
ACE (angiotensin- ____ ____) release from ____.
ACE acts on angiotensin to form ____ II.
____ II also acts directly on blood ____ stimulating ____ (narrowing).
**angiotensin** II, blood **vessels** stimulating **vasoconstriction**
Angiotensin II acts on the ____ gland to stimulate the release of ____.
(RAS system)
Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to stimulate reabsorption of ____ and ____.
salt and water
BNP increases _____ excretion.
fluid
ANP BNP system works by increasing ____ (which decreases ____ volume), performing ____ (which decreases ____ ____), and decreasing ____.
GFR- glomerular filtration rate, blood, vasodilation, blood pressure, renin
The solution with the higher solute concentration is _____.
The solution with the lower concentration is _____.
The solution with the same concentration is _____.
hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic
Edema is the accumulation of _____ within the _____ spaces.
Edema is caused by an increase in _____ _____ pressure, a decrease in plasma ____ pressure, an increase in ____ permeability, and ____ channel obstruction (lymphedema).
fluid, interstitial
capillary hydrostatic pressure, plasma oncotic pressure, capillary permeability, and lymph channel obstruction.
in the heart: peaked _ waves, _fib or ____ standstill, hypotension, ___cardia.
in the GI tract: diarrhea and ____ bowel sounds.
neuromuscular: paralysis in ____ extremities, increased ____, profound muscle ____.
diarrhea and **hyperactive** bowel sounds
paralysis in **lower** extremities, increased **DTR** (deep tendon reflex), profound muscle **weakness**
Hypokalemia (low potassium) is categorized by (think low and slow):
in the heart: flat _ waves, __ depression, and prominent _ wave.
muscular: decreased ___, muscle ____, and flaccid ____ (paralyzed limbs).
GI tract: decreased _____, _____ to absent bowel sounds, _____, abdominal _____, paralytic ileus, paralyzed intestines.
flat T waves, ST depression, prominent U wave.
decreased DTR, muscle cramping, and flaccid paralysis.
decreased motility, hypoactive to bowel sounds, constipation, abdominal distention (enlargement) paralytic ileus, paralyzed intestines.
____ “red and rosy”
____ “waterbed skin”
___ ___ fever
____ (hyper thirst)
neuro: ____ & ____
moans, groans and stones
_____ of the thumb, flexion of the _____ joints, extension of the _____ joints, and flexion of the _____.
24- hour urine osmolality range is ___-___ mOsm/kg of water.
500-800 mOsm/kg of water
Random urine osmolality range is ___-900 mOsm/kg of water.
300-900 mOsm/kg of water