Unit 5: Heredity
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
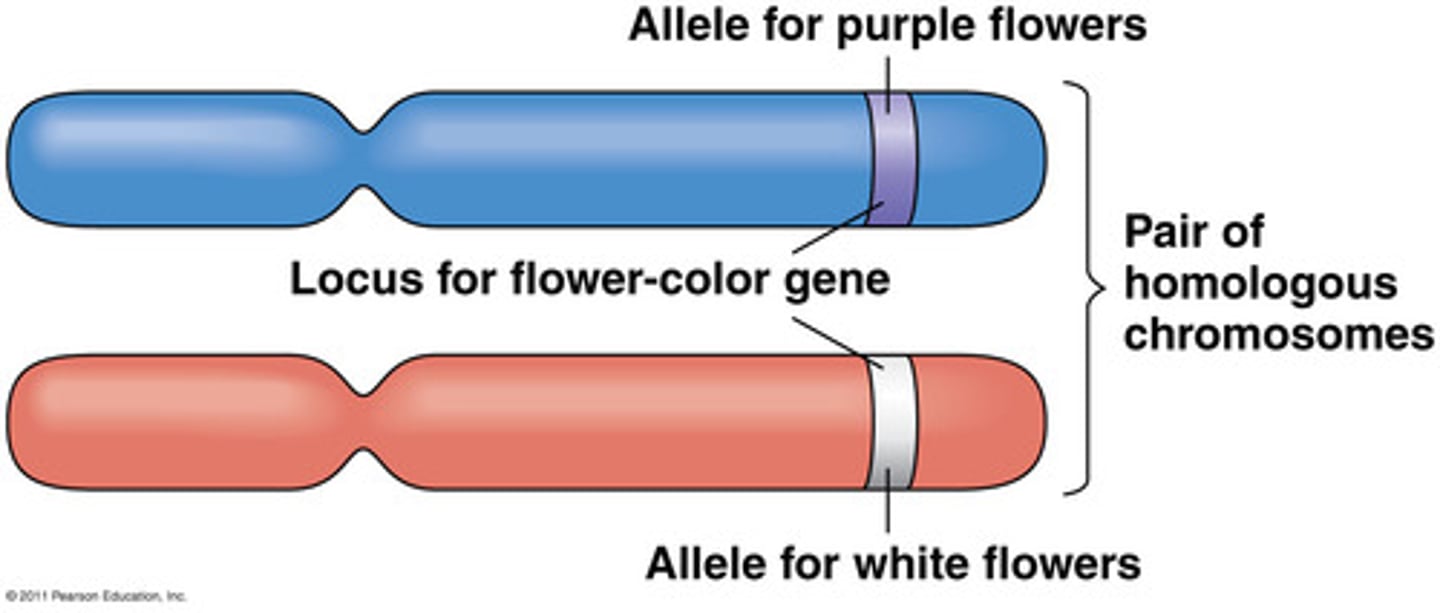
Allele
A version of a gene found at a specific location on a chromosome
Autosome
A chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
Barr body
An inactivated X chromosome found in the cells of female mammals
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA)
DNA located in the chloroplast, usually inherited from the mother in plants
Codominance
A form of inheritance where both alleles are fully and equally expressed
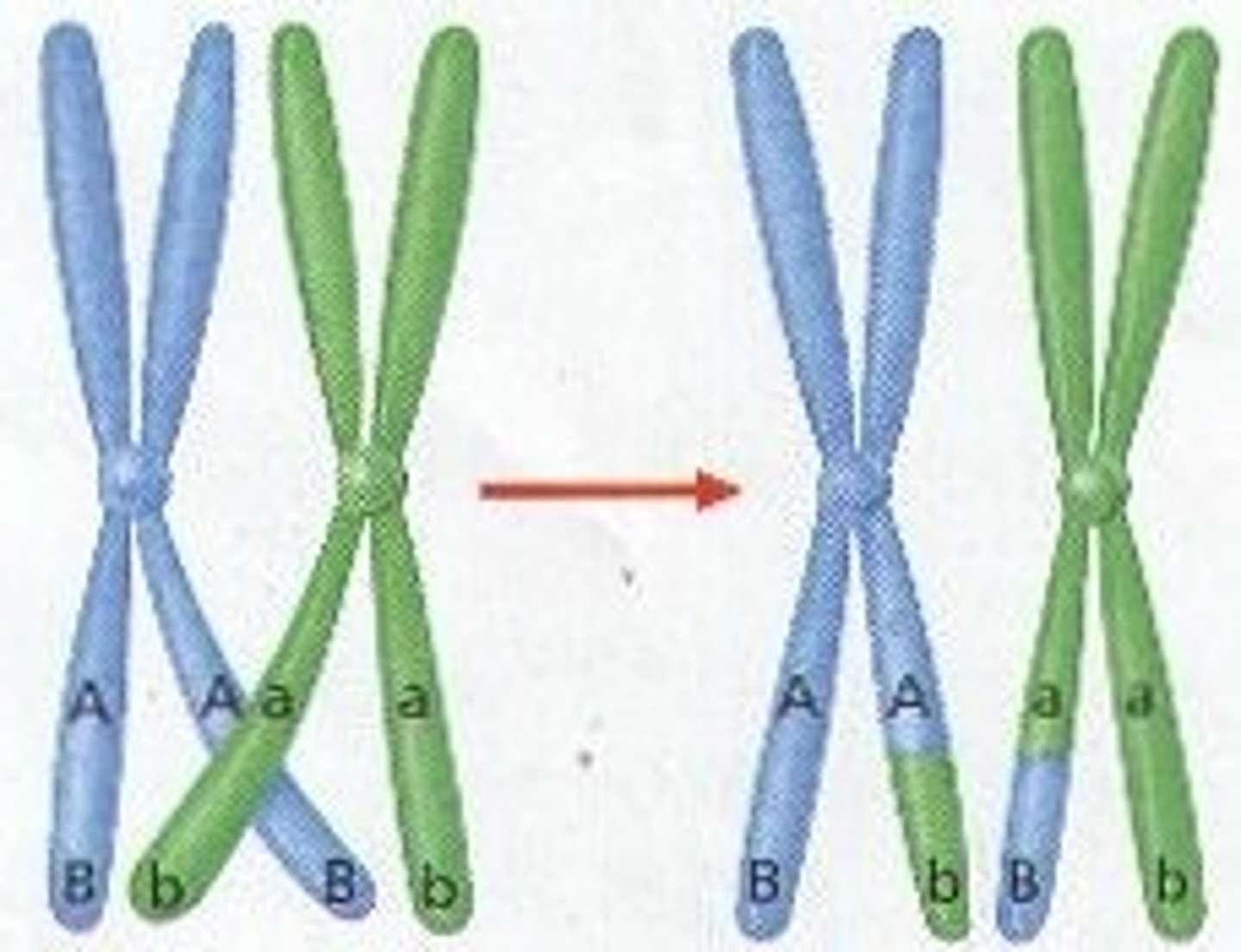
Crossing over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
Daughter cell
A new cell formed as a result of cell division
Dihybrid cross
A genetic cross involving two traits
Diploid
A cell that contains two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
Dominant
An allele that is expressed even if only one copy is present
Epistasis
A phenomenon where one gene affects the expression of another gene
Fertilization
The fusion of a sperm and an egg to form a zygote
Gamete
A haploid sex cell such as a sperm or egg
Genetic disorders
Diseases or conditions caused by changes or mutations in DNA
Genetic diversity
The total variety of genetic characteristics in a population

Genetic linkage
The tendency of genes located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together
Genetics
The study of heredity and variation in living organisms
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism in terms of its alleles
Haploid
A cell containing only one complete set of chromosomes
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a gene
Homozygous dominant
Having two identical dominant alleles for a gene
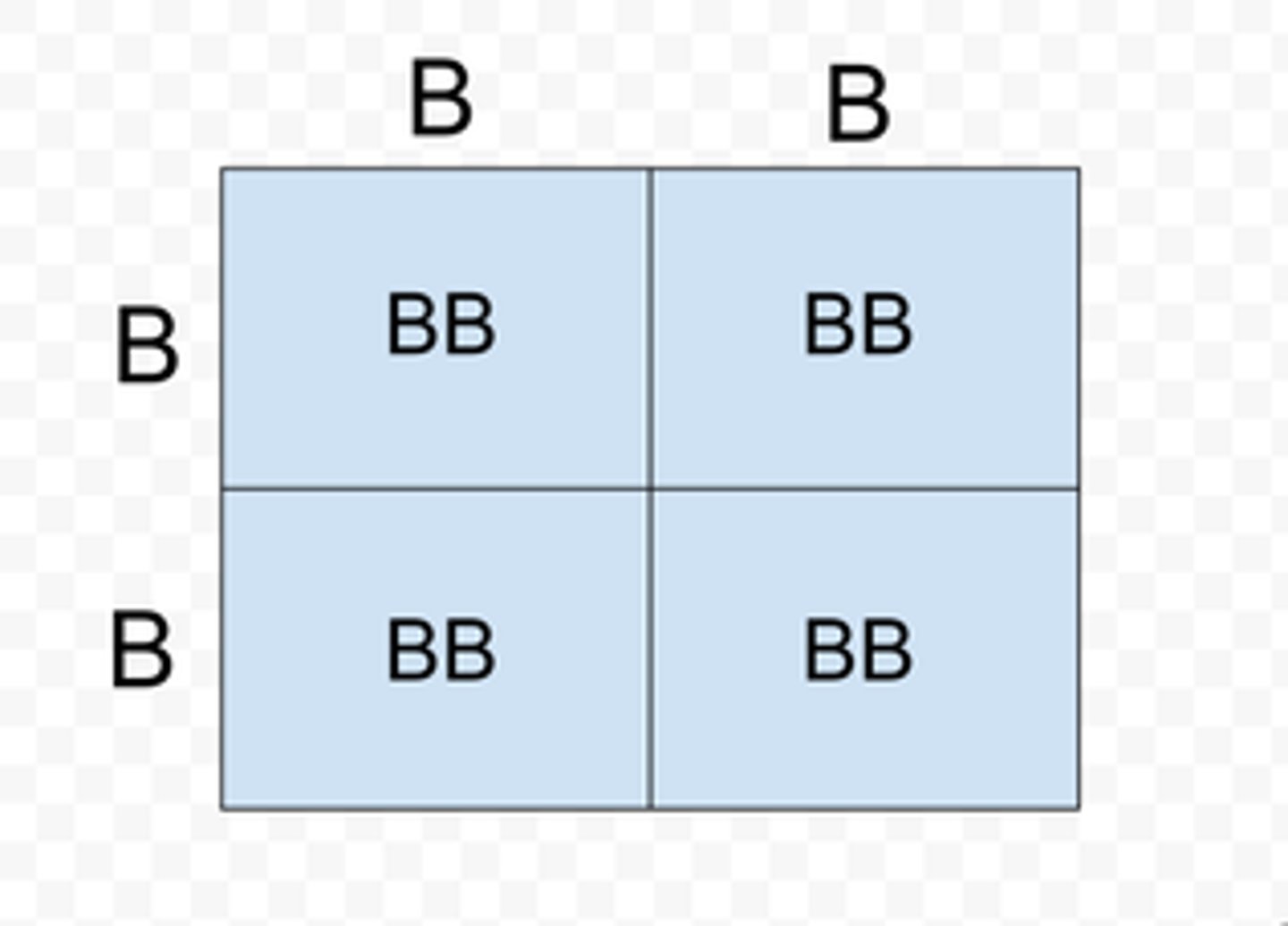
Homozygous recessive
Having two identical recessive alleles for a gene
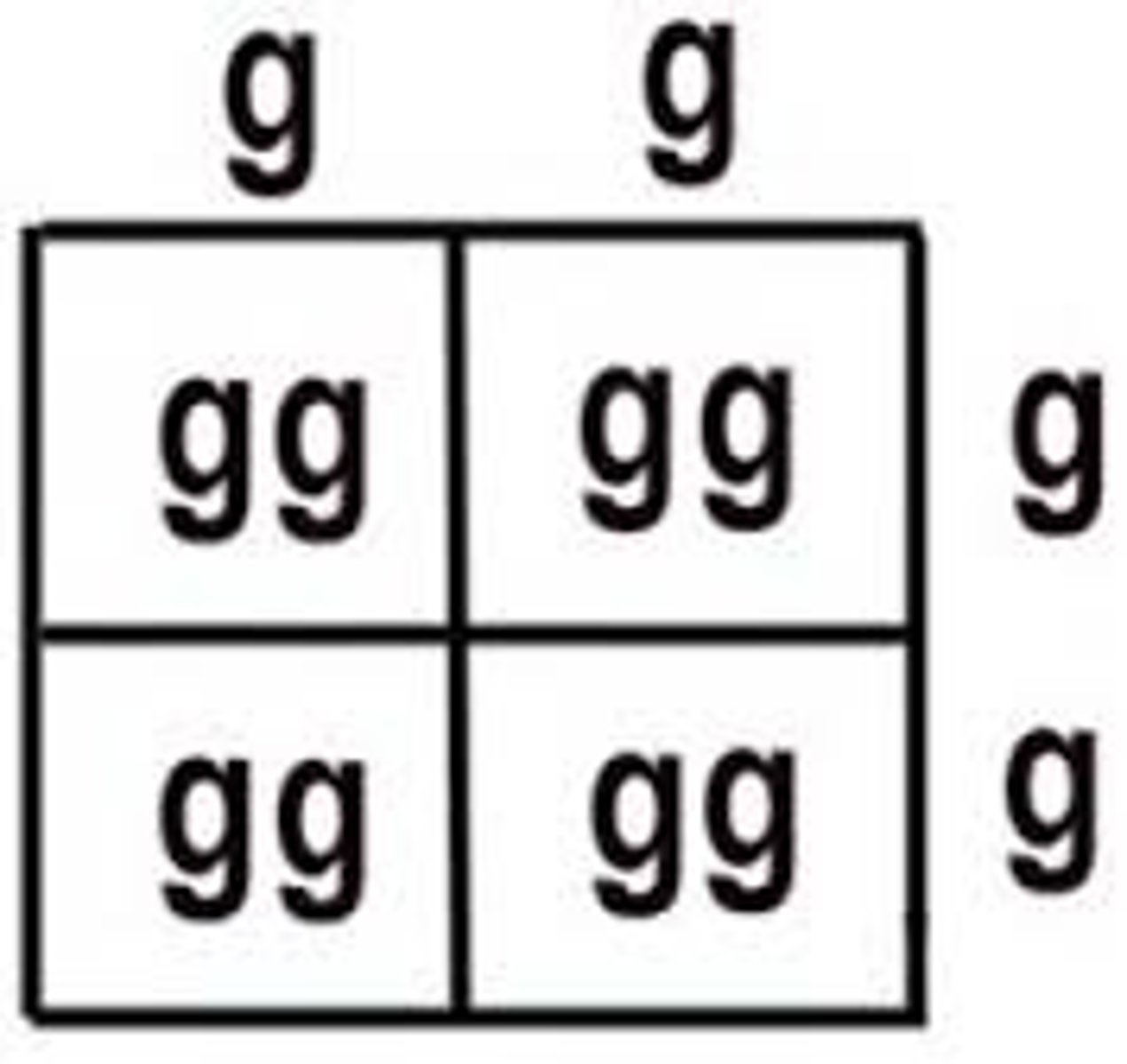
Incomplete dominance
A form of inheritance where the phenotype is a blend of both alleles
Karyotype
A picture showing an organism's chromosomes arranged in pairs
Law of independent assortment
Mendel's principle that genes for different traits are inherited independently
Law of segregation
Mendel's principle that two alleles for a gene separate during gamete formation
Lethal allele
An allele that can cause the death of an organism if present in a certain genotype
Linkage map
A genetic map showing the relative locations of genes on a chromosome
Linked genes
Genes located close together on the same chromosome that are inherited together
Locus (loci)
The specific physical location of a gene on a chromosome
Map unit
A unit of distance on a chromosome equal to a 1 percent recombination frequency
Meiosis (I and II)
The two-part cell division that results in four genetically unique gametes
Mendels Laws
The foundational principles of heredity established by Gregor Mendel
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
DNA found in mitochondria that is inherited from the mother
Monohybrid cross
A genetic cross involving one trait
Monosomy
A condition where an individual has only one copy of a chromosome instead of two
Multiple alleles
More than two possible alleles exist for a gene in a population
Non nuclear inheritance
The inheritance of DNA found outside the nucleus such as in mitochondria or chloroplasts
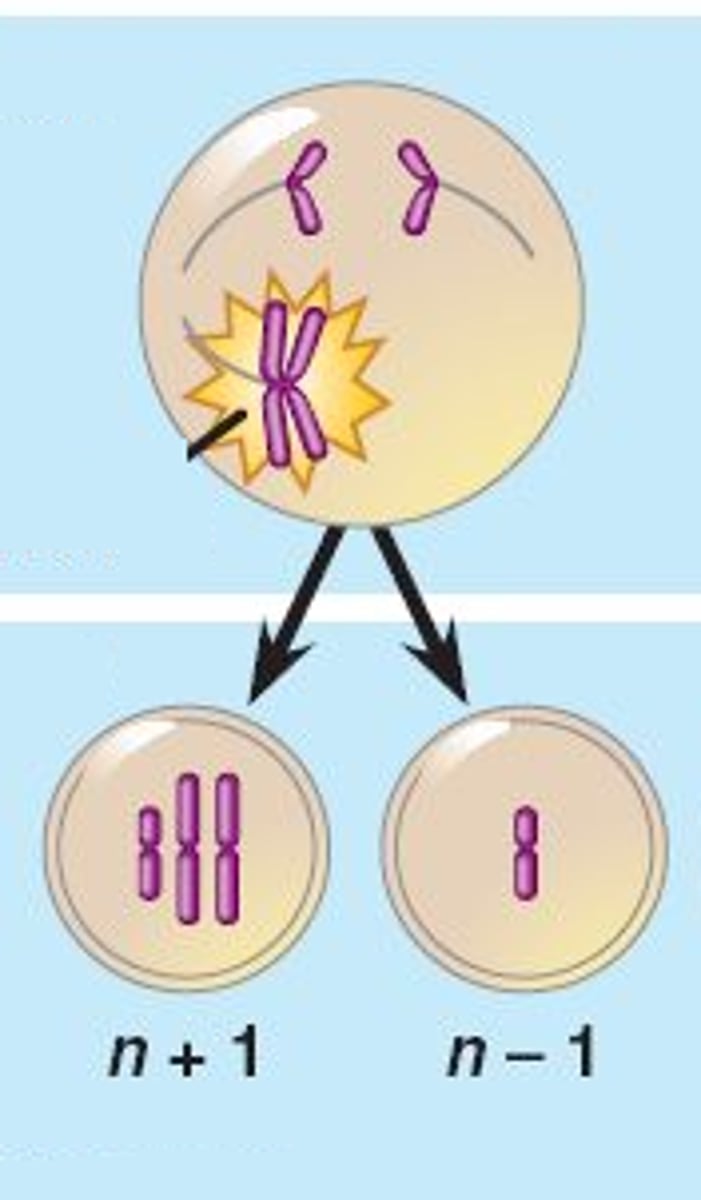
Nondisjunction
The failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis
P F1 F2 Generations
The parental first filial and second filial generations used in genetic crosses
Pedigree
A diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations
Phenotype
The observable traits or characteristics of an organism
Phenotypic plasticity
The ability of one genotype to produce different phenotypes in different environments
Polygenic inheritance
A trait controlled by two or more genes
Polyploidy
A condition in which an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes
Punnett square
A chart used to predict the genetic outcomes of a cross
Random assortment
The random distribution of chromosomes into gametes during meiosis
Recombinant chromosome
A chromosome that has undergone crossing over and contains genes from both parents
Recombination
The rearrangement of genetic material through crossing over or independent assortment
Rules of probability
Mathematical principles used to predict the likelihood of genetic outcomes
Sex chromosome
A chromosome that determines an individual's biological sex
Sex linked trait
A trait associated with a gene carried on a sex chromosome
Sexual reproduction
Reproduction involving the combination of genetic material from two parents
Somatic cell
Any body cell that is not a gamete
Test cross
A genetic cross used to determine an unknown genotype by crossing with a homozygous recessive
Tetrad
A group of four chromatids formed during meiosis by the pairing of homologous chromosomes
Trait
A specific inherited characteristic of an organism
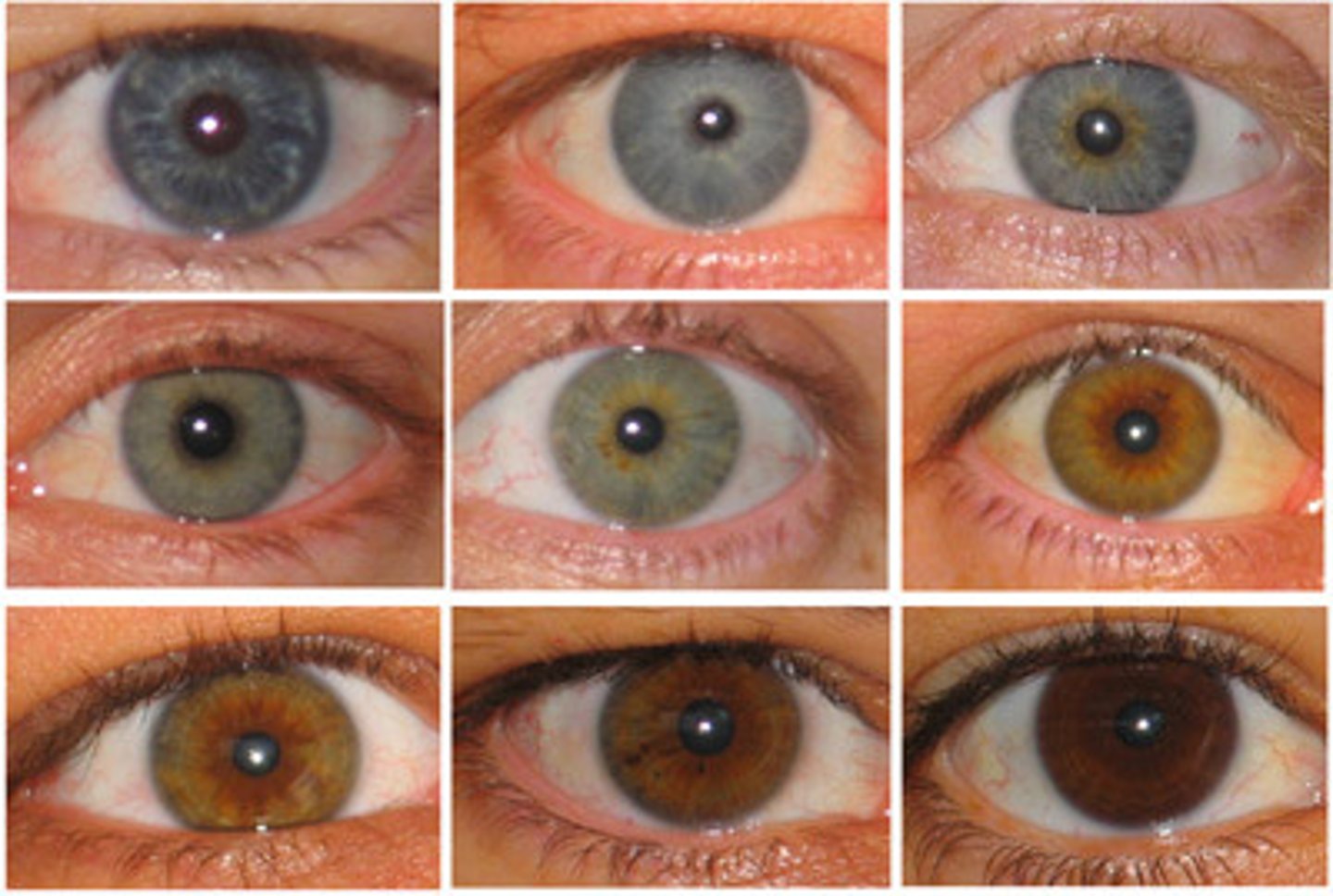
Trisomy
A condition where an organism has three copies of a chromosome instead of two
True breeding
Organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves when self fertilized
X chromosome
A sex chromosome found in both males and females
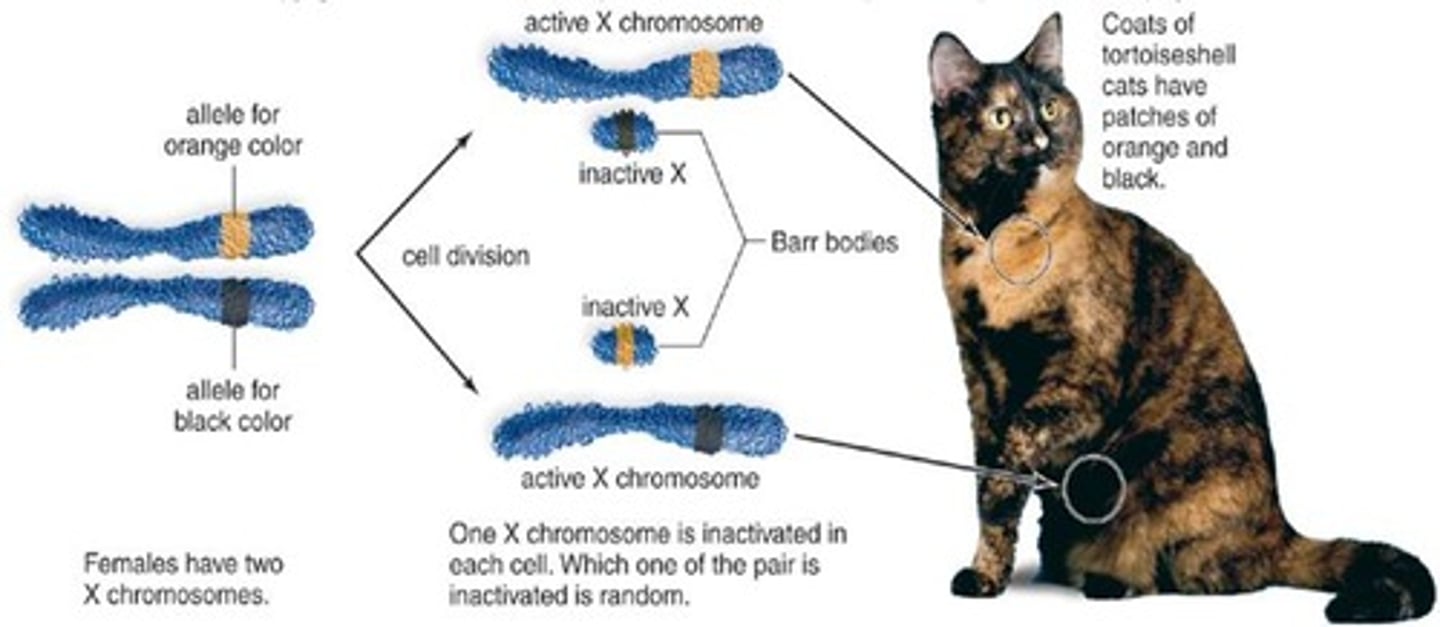
X Inactivation
The process by which one of a female's X chromosomes becomes inactive
X linkage
A gene located on the X chromosome
Y chromosome
The sex chromosome found only in males
Zygote
A fertilized egg cell formed by the fusion of a sperm and an egg