muscle physiology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
skeletal muscle structure
muscle fibers that are long and cylindrical, fused cells with many nuclei, arranged along axis (parallel)
satellite cells- differentiate into muscle for growth or repair
fibers bundles into fascicles surrounded by connective tissue sheath
sarcolemma
cell membrane
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
endoplasmic rediculum
concentrates and sequesters calcium (important for contraction)
unique features of muscle fibers
myofibrils- rod like organelle used for contraction
transverse tubules-allow action potentials to penetrate nearer to internal structure or fibers
lots of mitochondria
glycogen granules
myofibrils
fiber contractile structures
thin filaments =actin
thick filaments= myosin
tropomyosin and troponin (regulatory proteins)
accessory proteins = titan and nebula
Sarcomere
contractile unit of the myofibril
that shortens during muscle contraction, composed of alternating thick and thin filaments
steps leading to skeletal muscle contraction
events at neuromuscular junction
excitation-contraction coupling
contraction-relaxation cycle
molecular contraction
contraction of muscle cells due to actin and myosin sliding past each other
sliding filament theory of contraction- overlapping actin and myosin myofibrils
myosin crossbridges move actin filaments
myosin heads bind to actin and calcium signaling initiates a power stroke where myosin pulls the actin back
power stroke
myosin crossbridge swivels and pulls actin towards M line
end of power stroke
myosin releases actin and resets and binds another actin
heads are not released in unison
initiation excitation-contraction coupling
acetylcholine is released from somatic motor neuron
ACh initiates an action potential in the muscle fiber
action potential in t-tubule alters conformation of DHP receptor
DHP receptor opens RyR releasing calcium from SR
calcium binds to troponin, allowing myosin-actin binding
power stroke of myosin head
actin filament slides toward center of sarcomere
calcium is pumped back into SR
dec in free cytostolic calcium causes calcium to unbind from troponin
tropomyosin re-covers brining site, causing myosin heads to release. elastic filaments pull filaments back to relaxed position
skeletal muscle contraction needs steady supply of ATP
glucose is most rapid and efficient store of energy
anaerobic or aerobic
phosphocreatine is backup energy
fatty acids can also be energy source
phosphocreatine
backup energy source of muscles
created from phosphorylation of creatine by creatine kinase
created when muscles are at rest to store for use later
causes of muscle fatigue
central fatigue due to CNS (psychological effects and protective reflexes)
peripheral fatigue due to neuron or muscle worked too hard (most common)
slow twitch fibers
rely on oxidative phosphorylation
resistant to fatigue
have more myoglobin, so darker in appearance
fast twitch fibers
develop tension faster
pump calcium into the SR more rapidly
fast twitch oxidative-glycolytic fibers or fast twitch glycolytic fibers
summation
stronger contraction when the muscle does not relax completely between action potentials
tetanus
summation causes maximal contraction
motor unit
one motor neuron and its muscle
mechanics of body movement
two types: isotonic and isometric contractions
isotonic contractions
move loads
isometric contractions
create force without movement
classification of smooth muscle
by location, contraction patter, and communication with neighboring cells
classify smooth muscle by location
vascular (blood vessels)
gastrointestinal
respiratory (trachea and bronchi)
urinary (bladder, ureter, urethra)
reproductive (ovaries)
ocular (eyes)
classify smooth muscle by contraction pattern
phasic- undergo periodic contraction and relaxation cycles
tonic- continuously contracted
classify smooth muscle by communication with neighboring cells
single unit smooth muscle- more common, forms wall of internal organs, gap junctions
multi unit smooth muscle- cells not electrically linked and must be stimulated independently (iris and ciliary)
12 major differences between smooth and skeletal muscle
smooth muscles must operate over a range of lengths
within an organ, the layers may tun in several directions
smooth muscle contract and relax much more slowly
smooth muscle uses less energy to generate and maintain a given amount of force
smooth muscle can sustain contractions for extended periods without fatiguing
smooth muscles have small, spindle-shaped cells with a single nucleus
the contractile fibers are not arranges in sarcomeres
contraction in smooth muscle may be initiated by electrical or chemical signals or both
smooth muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system
smooth muscle lacks specialized receptor regions
the calcium for contraction comes from the extracellular fluid as well as from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
the calcium signal initiates a cascade that ends with phosphorylation of myosin light chains and activation of myosin ATPase
myosin phosphorylation
inc cytosolic calcium released from the SR initiates contraction
calcium binds to calmodulin, initiating a cascade which results in the phosphorylation of myosin light chains (MLC)
myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) dephosphorylates myosin
calcium in smooth muscle contraction
sarcoplasmic calcium release activates:
ryanodine receptor (RyR) calcium release channel
IP3 receptor channel
calcium-induced calcium release (CICR)
store-operated calcium channels
cell membrane calcium entry
voltage-gated calcium channels
ligand-gated calcium channels
stretch-activated calcium channels
chemical signaling in smooth muscle
autonomic neurotransmitters and hormones: antagonistic control by sympathetic and para
chemical signals can have different effects (EPI) f
paracrine signals: histamine constricts smooth muscle in airways and nitric oxide relaxes smooth muscles of blood vesselso
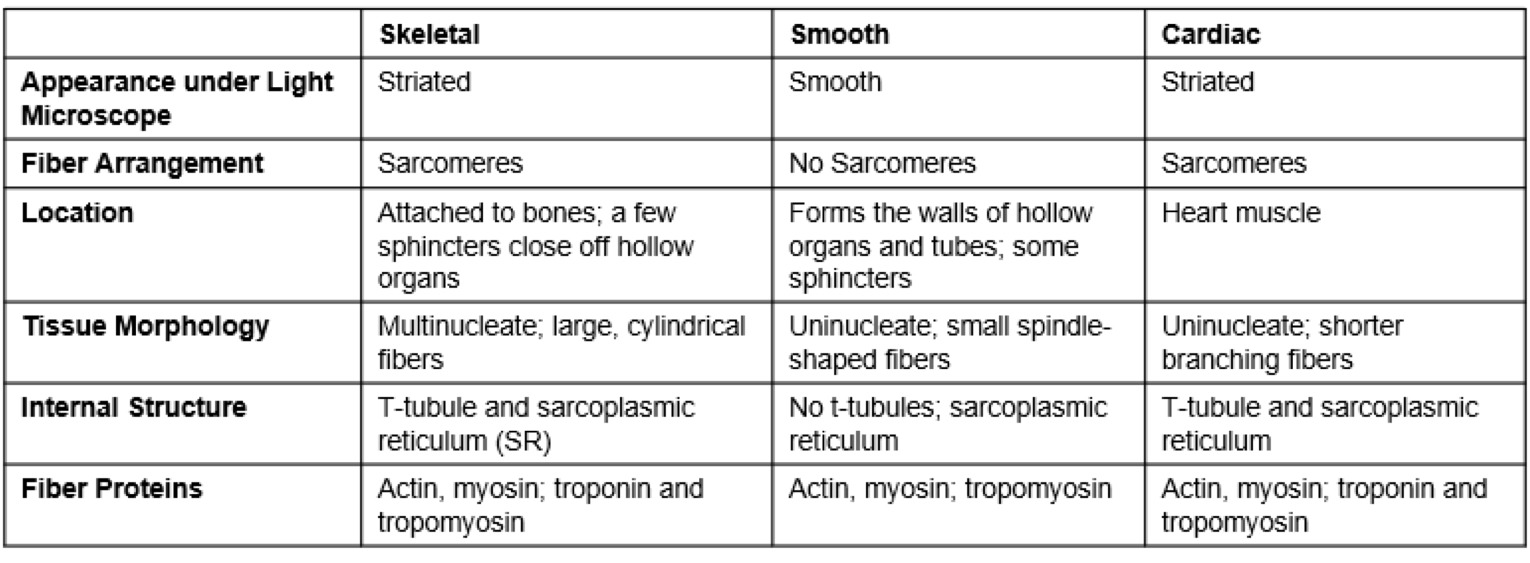
compare muscle types
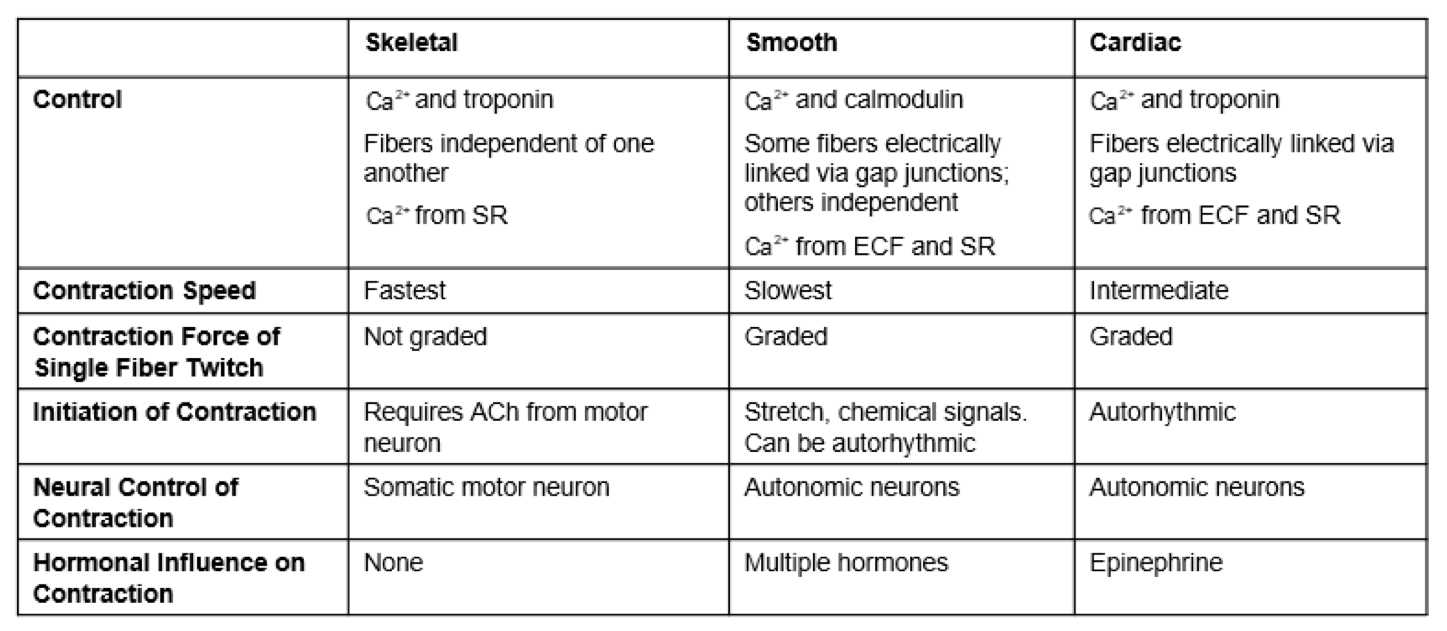
compare muscles