Work, Energy Power
1/13
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Work done
Work done = force × distance moved in the direction of the force
W=Fx
Units: joules(J, =Nm)
Gravitational potential energy
The capacity for doing work as a result of an objects position in a gravitational field
Unit: joules(J, =Nm)
Equation for gravitational potential energy
Ep = mgh
Kinetic energy
Energy associated with an object as a result of its motion
Units: joules(J, =Nm)
Ek α m
Ek α v²
Equation for kinetic energy
Ek = ½ mv²
Power
Rate of work done
Unit: watts(W, =Js-1)
Equation for power
P=W/t
P=E/t
Equation for power in terms of force and velocity
P=Fv
Efficiency
Efficiency = (useful output energy) / (toatal output energy) × 100
Smooth surface
A surface with no friction.
The principle of conservation of energy
The total energy of a closed system remains constant - energy cannot be created nor destroyed
Deriving the equation for kinetic energy
v2 = u2 + 2as and F = ma and u = 0
v2 = 2(F/m)s = 2 (Fs)/m = 2 Ek/m (since Fs = work done)
So Ek = ½ mv2
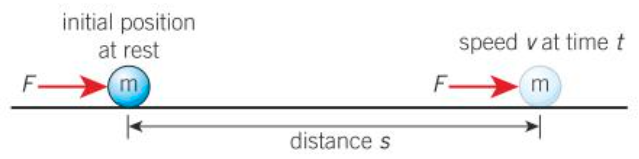
Deriving equation for gavitational potential energy
Work done = Force × distance = weight × height = (mg)h
So Ep = mgh
Deriving P=Fv
Power = Work done / time = (Force × distance) / time = Force × (distance / time) = Force × velocity
So P=Fv