microeconomic decision makers
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
money
any commodity that could be used as a medium of exchange that is widely accepted for the purchase of goods and services
functions of money
medium of exchange, measure of value, store of value, standard of deffered payment
characteristics of money
durability, scarcity, uniformity, acceptibility, portability, divisibility, stability
whats banking?
helps people borrow, lend & carry out a range of other financial activities
commercial banks
business organisations which usually seek to make a profit
whats an overdraft?
enables a customers to spend more than what is in his/her account, up to an agreed limit. interest is changed on the amount borrowed
what needs to happen during bartering?
double coincidence of wants where both parties, the sellers & buyers have to agree to sell & buy each others commodities
what is bartering?
exchange of goods & services between two/more parties without the use of money
whats the problem with bartering?
lack of double coincidence of wants, lack of common unit of value, difficulty of future/deferred payments/difficulty of storage of value
borrowing from the bank
overdraft, loan, act as financial intermediaries, aid customers in making and reciving payments, buying & selling shares, providing insurance, exchange foreign currencies, provide financial planning advice
central bank
monetary authority that oversees and manages the nations money supply & banking system
funtions of central bank
governements bank, issuing currencies & coins, external functions, bankers bank, national debt management, lender of last resort
income
the amount of goods and services purchased depends largely on their level of income
ways people can earn income
interest on savings, rent, dividents, profit
disposible income
income earned by an individual after income tax & other charges have been deducted
what tends to happen when theres a rise in level of disposible income
theres a rise in spending and saving
what tends to happen when tax rates rise?
the level of disposible income decreases and therefore consumption decreases
current expenditure
money spent on goods & services consumed within the current year
capital expenditure
money spent on fixed items owned by individual/firm
factors that affect consumer spending
real income, unemployment, consumer confidence, interest rates, availability of credit, welfare benefits, tax rates, demographics, inflation & cost of living, house prices
house prices
Housing is the biggest form of wealth. When house prices are rising people are more confident to spend and they can also remortgage their houses. Rising house prices cause a wealth effect – with higher prices encouraging spending.
saving factors
interest rates, confidence, economic growth, availability of credit, wealth, consumer preferences, demographics
average propensity to save (APS)
it is the proportion of household disposible income that is saved. calculated by dividing savings by disposable income
borrowing
occurs when an individual, firm/the government takes out a loan, paying it back to the financial lender over a period of time with interest payments
mortgage
a loan specifically taken out to help buy a house
factors affecting borrowing
interest rates, availability of loans & overdrafts, consumer confidence, social attitudes
interest rates
paying back the amount borrowed from the bank plus interest this means high interest rate will increase the cost of borrowing and therefore reduce borrowing rates
social attitudes
some countries & some groups within countries are more concerned about the risks of getting into debt than others
wage factors
financial rewards that workers recive in return for their labour services. these are a major influence on their choice of occupation
earnings
the total pay a person recieves
wage rate
a payment which an employer contracts to pay a worker
wage
a payment for labour based on the amount of time worked
salary
an annual payment to a worker in exchange for their labour. even if you stay in work for longer than you need the money you earn stays the same
piece rate
a fixed amount paid per item produced/sold
commission
a percentage of the value of products/services sold
bonus
an additional lump sum of money paid during the year, usually dependent upon performance
profit related pay
additional payment on workers, based on the amount of profits made by the firm
share issue
workers recieve shares in the firm to give them incentive to work hard, so that the firm is profitable
what are the types of wage factors
wage, salary, piece rate commission, bonus, profit related pay, share issue
non wage factor
somethin other than pay that influences choice of occupation. while a person might be motivated to work in the short term by money, theyll want to also be motivated in the long term
fringe benefits
additional benefits provided to workers e.g. pensions, health insurance, company car
non wage factors
level of challenge, career prospects e.g. promotion, level of danger involved, length of training required, level of education required, recognition of the job, pension, working conditiond/hours, location, job security, personal satisfaction gained from the job, level of experience required
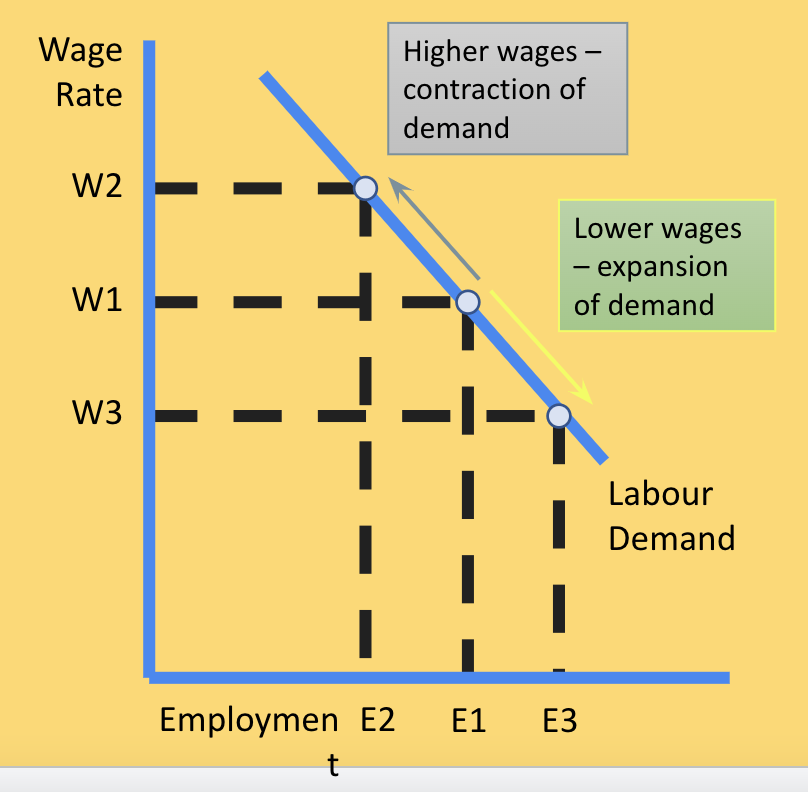
demand for labour
shows how many workers an employer is willing and able to hire at a given wage rate in a given time period. of the wage rate is high - its more costly to hire employess. when wages are low, labour becomes relatively cheaper than capital
non wage factors influencing labour supply
job risk, strength of vacation, career opportunitites, working conditions, anti social hours, quality of in work training, occupational pensions, living & working overseas
factors affecting wage determination
when the wage rate workers are willing to work for the wage rate that firms (employers) are prepared to pay
welfare benefits
it’s paid to unemployed workers which could discourage people from seeking employment this affects the number of people employed
changing social attitutes
more women are entering the workforce and delaying having families while more men choose to stay at home. this means many have to relp on immigration for workforces
geographical mobility
cost of living may vary between the regions making it uneconomical for a person to relocate there
bargaining power
refers to how much power a given person has on negotiation (wages). the more power the employer has on negotiation, the lower the wages are likely to be. this is reasons for differences in earnings.
minimum wage
some governments have introduced minimum wages in an attempt to raise the living standards of employees
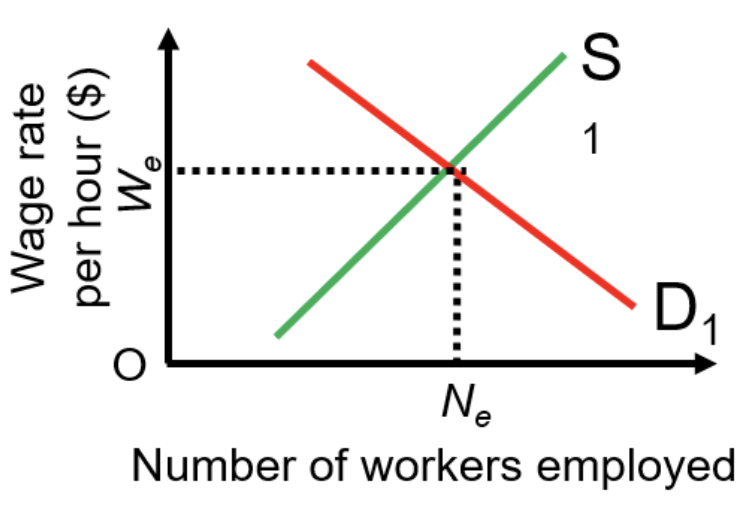
wage rate equilibrium
is the point where the supply of labor meets the demand for labor, resulting in a stable wage level.
public v private sector
private sector workers tends to recieve a higher wage than public but public sector workers may have greater non wage benefits
discrimination
sometimes workers get paid less because of discrimination, this can be due to gender, age race etc
changes in the demand for labour
if the demand for labour increases earnings are likely to rise, the wage rate may be pushed up & bonuses may be increased, more overtime may be available and it may be paid at a higher rate
demand for labour can be increased because:
increase in demand for the product - higher the demand for a product, greater number of workers employed, a rise in labour productivity, a rise in the price of capital
changes in supply of labour
a decrease in the supply of labour for a particular occupation/sector would be expected to raise the wage rate
a decrease in the supply for labour can be cuased by:
a fall in labour force, a rise in the qualifications/length of training required, a reduction in the non wage benefits, a rise in the wage/non wage benefits in other jobs
changes in the stages of production:
primary sector are usually paid less, the demand for primary has declined, demand for workers in the tertiary sector has increased, best paid workers are in tertiary
changes in bargaining power:
a change in unions bargaining power/willingness to take industrial action can affect earnings
changes in gov policy
raise in min wage, improved education can raise wages of skilled workers, gov policies on immigration, advances in tech
changes in public opinion
how occupations & thpse who take them can be viewed differently overtime
how does rate of interest affect saving?
when interest rates increase, saving increases as this means the bank will pay money to you for letting them use the money you saved on things the bank needs
Double coincidence of wants
A situation in which two parties each hold an item the other wants, making an exchange possible without the need for money.