Mendelian Genetics - Monohybrids (10/28-10/30)
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Recommended: Learn mode but only with Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Pangenesis (Hint: 3)
Theory of Inheritance
Proposed by the Greek physician Hippocrates
“Seeds” produced by all parts of the body are collected in the reproductive organs then passed to the offspring at the moment of conception
Preformationism (Hint: 2)
Theory of Inheritance
Homunculus that simply develop in the womb
Homonculus
“Little man” that early microscopists thought they saw in the sperm
Blending Theory (Hint: 2)
Theory of Inheritance
Factors that control heredity traits are malleable and can blend together from generation to generation
Gregor Mendel (Hint: 3)
The father of Genetics
Austrian monk that worked with pea plants in the monastery garden
Published his findings from crossing plants in 1866 in a manuscript call Experiments in Plant Hybridization
What are the 2 Reasons for the Success of Gregor Mendel’s Experiment?
Model choice
Experimental (empirical) approach
Model Choice (Hint: 4)
Pea plants
Readily available and easy to grow
Rapid generation time and produce many offspring
A number of varieties available
Experimental (Empirical) Approach (Hint: 2)
Take detailed records of crosses
Use math to interpret results
Trait (Hint: 3)
The specific property of a character
Examples:
Round vs. wrinkled
Eye color is a characteristic and blue and brown are traits
Characteristic/Character (Hint: 3)
Morphological trait of an organism
Overarching category
Example: Seed shape/color
Gene
An inherited factor (region of DNA) that determines a characteristic
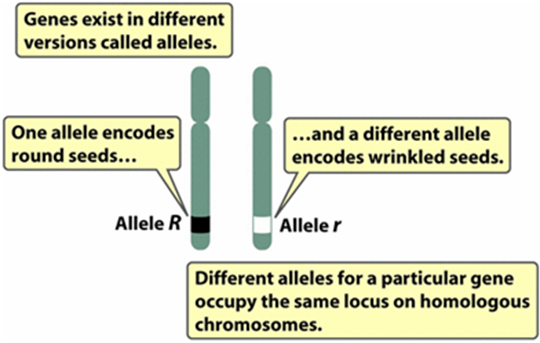
Allele
One of two or more different forms of a gene
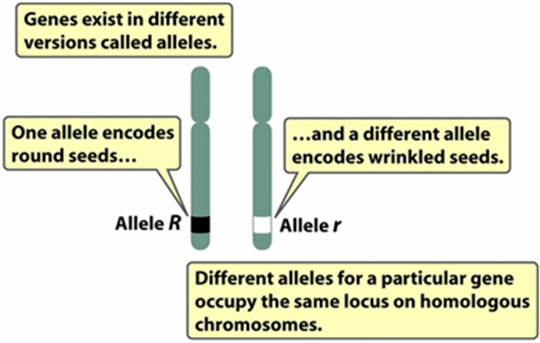
Locus
Physical location on a chromosome occupied by a gene
Genotype (Hint: 2)
The set of alleles possessed by an individual organism
Individuals carry 2 alleles of a gene
Phenotype (Hint: 2)
The physical appearance or manifestation of a trait associated with a particular genotype
The genotype is inherited, not the phenotype
Heterozygote
2 different alleles at a locus
Homozygote
2 of the same allele at a locus
Pure/True Breeder (Hint: 3)
Strain that produces the same trait over several generations
Homozygous for the given trait
Example: Always produces green seeds
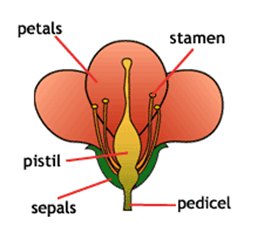
Stamen
Male reproductive organ of a flower that produces pollen
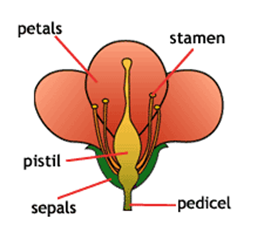
Pistil
Female reproductive part of a flower that produces ovules
Hybridization
The mating or crossing of 2 individuals with different traits for a character
Hybrid (Hint: 2)
The offspring of such a cross
Example: Round seeds x Wrinkled seeds
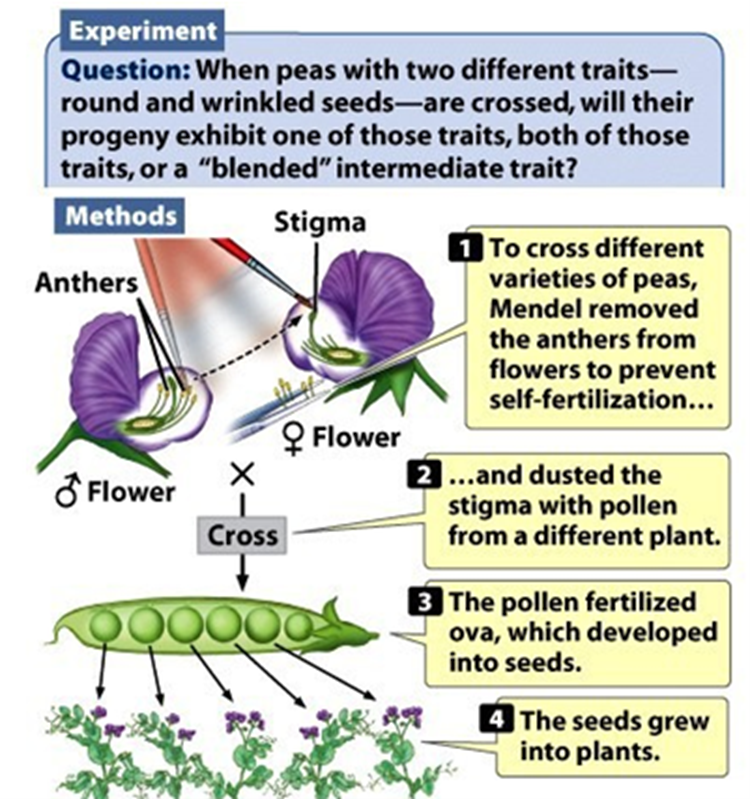
Cross-Fertilization (Hint: 2)
Pollen and eggs are from different plants
Remove stamen and dust the pistil of another flower
Self-Fertilization (Hint: 2)
Pollen and eggs are from the same plant
Occurs without manipulation in peas
Monohybrid Cross (Hint: 3)
Cross 2 variants of a single characteristic (pure breeders)
How Mendel started
Example: Plant height (tall x dwarf)
P Generation (Hint: 3)
The parental cross
Cross fertilization
Use true breeding individuals (homozygous)
F1 Generation
The result of the P generation cross
F2 Generation
The result of crossing individuals in the F1 generation
The Principle of Segregation (Hint: 5)
Mendel’s First Law
Each individual possesses 2 alleles for each character
Each allele separates during the formation of gametes
Each allele is separated in equal proportions (50/50)
Meiosis underlines this principle

Dominance (Hint: 3)
Used when 2 different alleles for a single character are found in the same individual
1 allele is dominant and its phenotype is expressed
The other allele is recessive and its phenotype is not expressed
Dominant (Hint: 2)
Phenotype is expressed
Capital letter
Recessive (Hint: 2)
Phenotype is not expressed
Lower case letter
Punnett Square (Hint: 2)
A grid that can be used to predict the outcome of a simple genetic cross
Originally proposed by the English geneticist Reginald Punnett
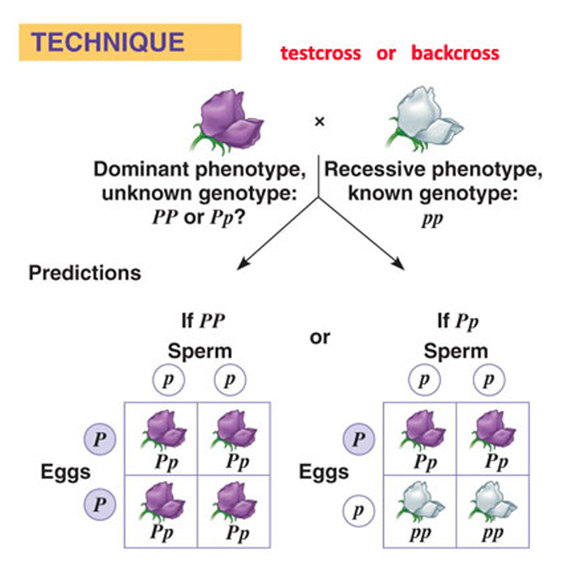
Back Cross
A cross between an F2 genotype and either of the parental genotypes
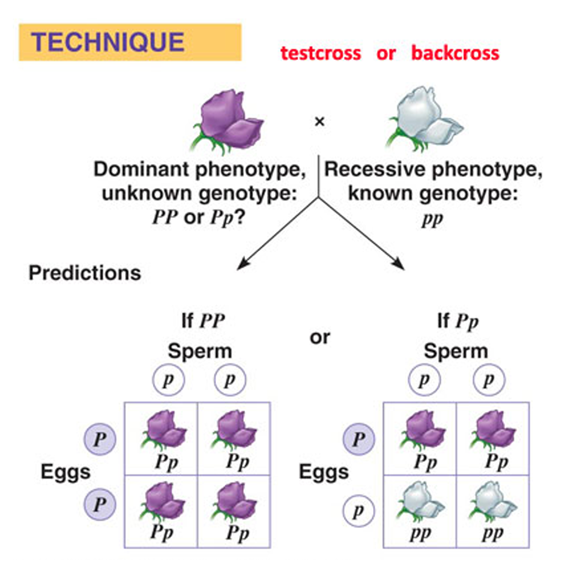
Test Cross
An individual of unknown genotype (A_) is crossed with an individual homozygous recessive (aa) for the given trait to reveal the unknown genotype
What types of crosses did Mendel perform?
Monohybrid Crosses
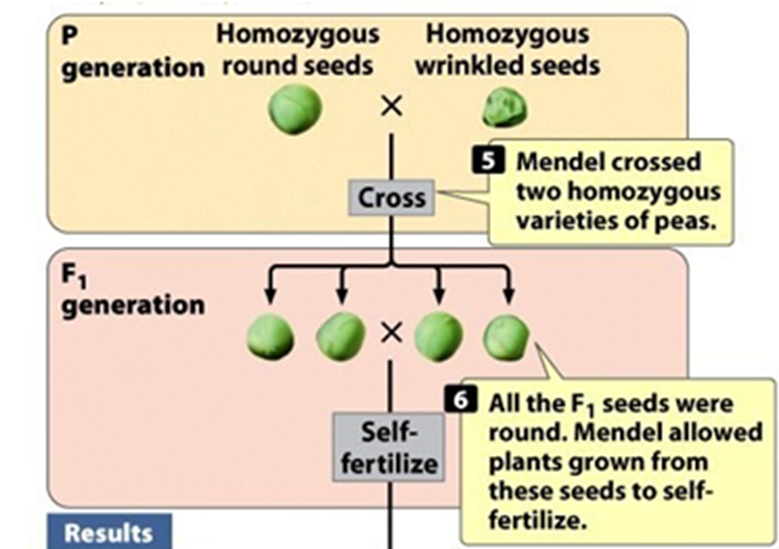
What did Mendel observe for the characters in the F1 generation?
For all 7 characters only 1 of the 2 parental traits was observed
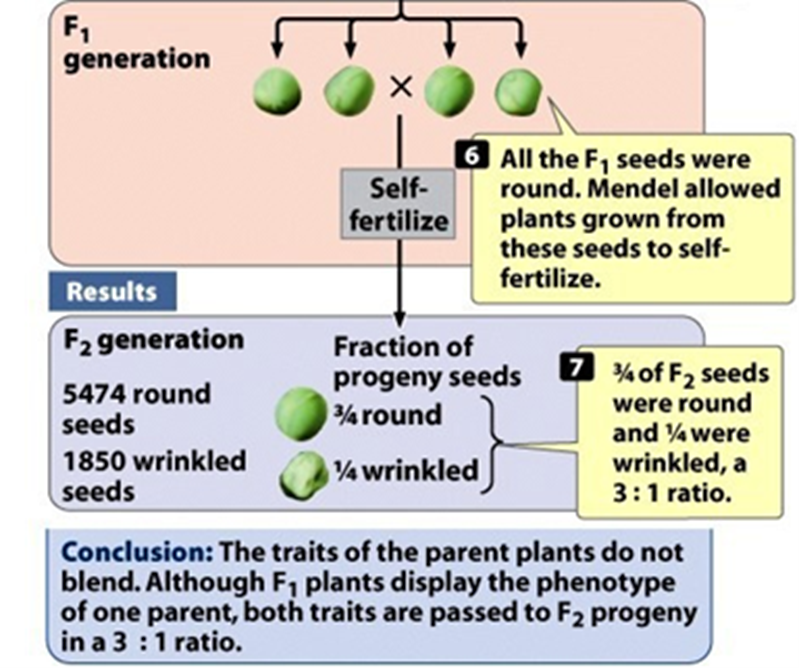
What did Mendel observe for the characters in the F2 generation?
Showed a 3:1 ratio of the 2 parental traits
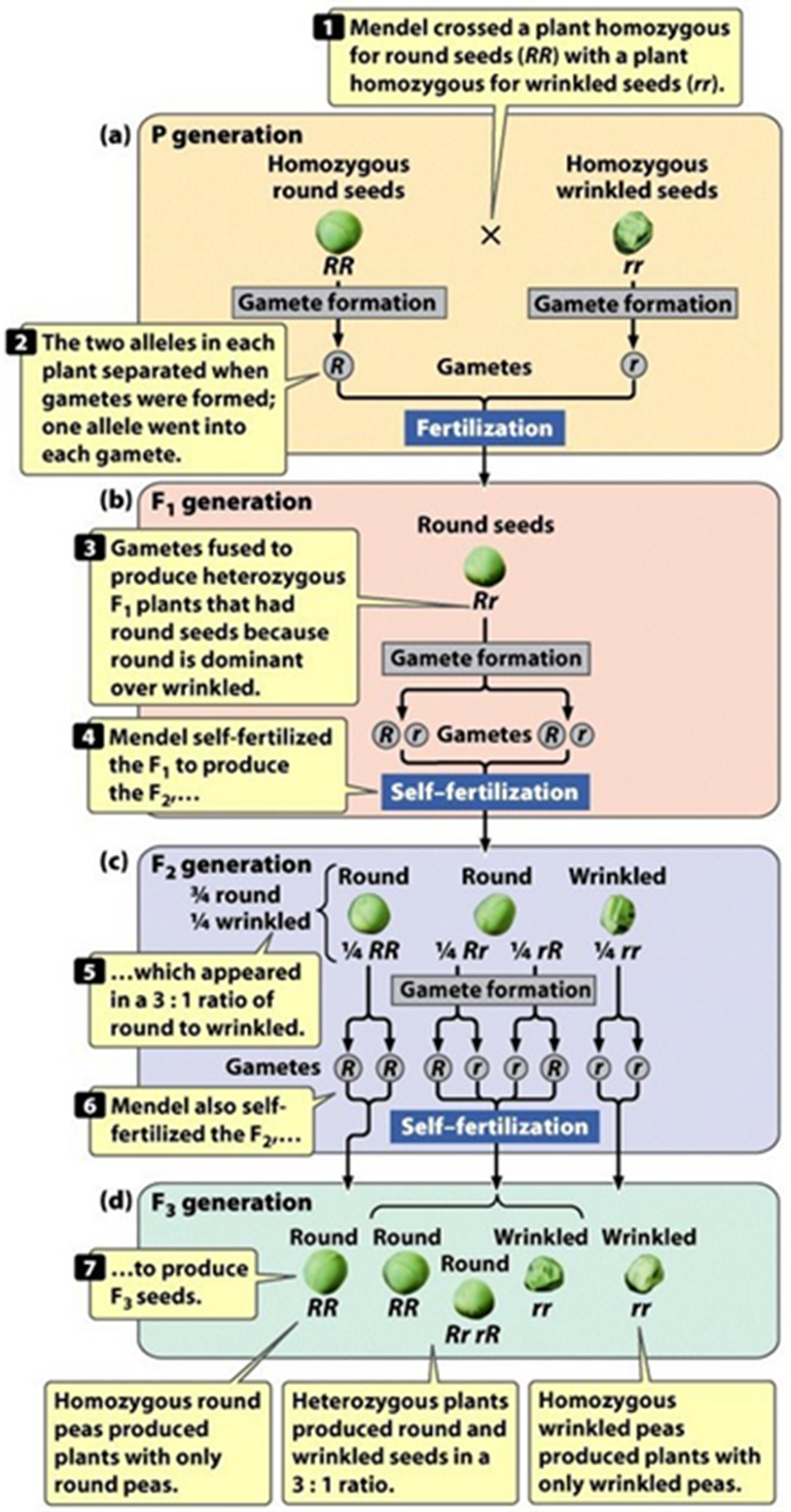
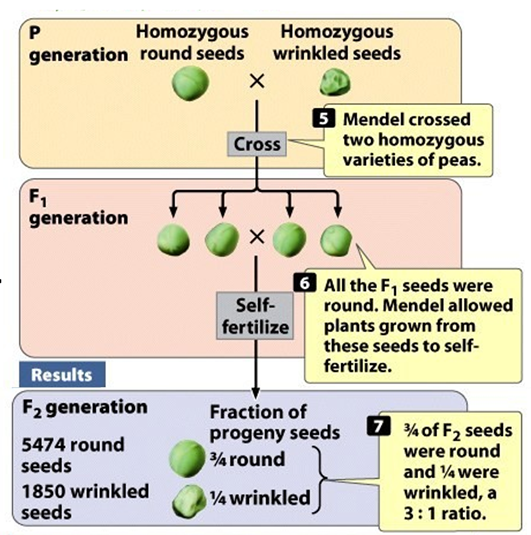
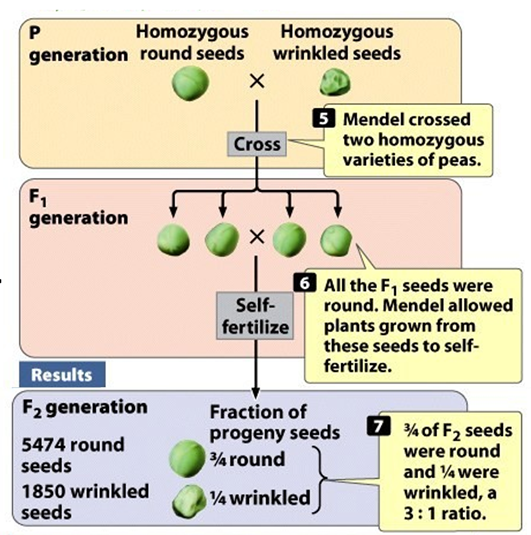
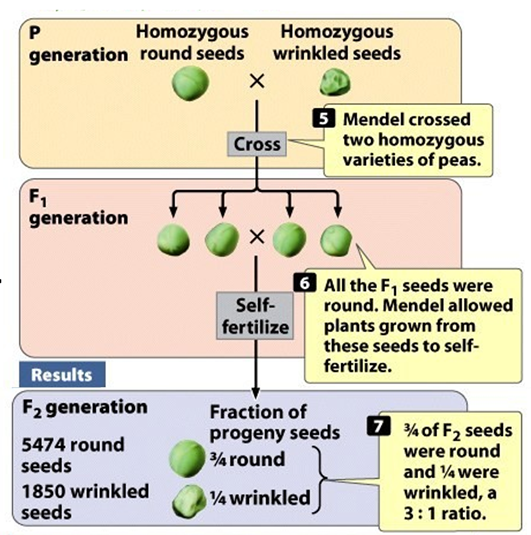
Describe the Mendel Experiment and Results (Hint: 7)
Mendel crossed a plant homozygous for round seeds (RR) with a plant homozygous for wrinkled seeds (rr)
The two alleles in each plant separated when gametes were formed and one allele went into each gamete
Gametes used to produce heterozygous F1 plants that had round seeds because round is dominant over wrinkled
Mendel self-fertilized the F1 to produce the F2 which appeared in a 3:1 ratio of round to wrinkled
Mendel also self-fertilized the F2 to produce the F3 seeds (Homozygous round peas produced plants with only round peas
Heterozygous plants produced round and wrinkled seeds in a 3:1 ratio;
Homozygous wrinkled peas produced plants with only wrinkled peas)