Chapter 6 pt 1, chapter 7 pt1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Long bone
length greater than width
ex humerus

irregular bone
doesn’t fit other classification of a bone
flat bone
what kind of bone is this?
short bone
same length and width
cube shaped
sesamoid bone
small round bone that is embedded in a tendon or muscle
Projections
part of bone that extends outward from main structure
muscle/ligament/tendon attachment
articular surfaces
when two bones join together (like joints)
depression and openings
passage ways
hollow in a bone
sutures
fused bones together
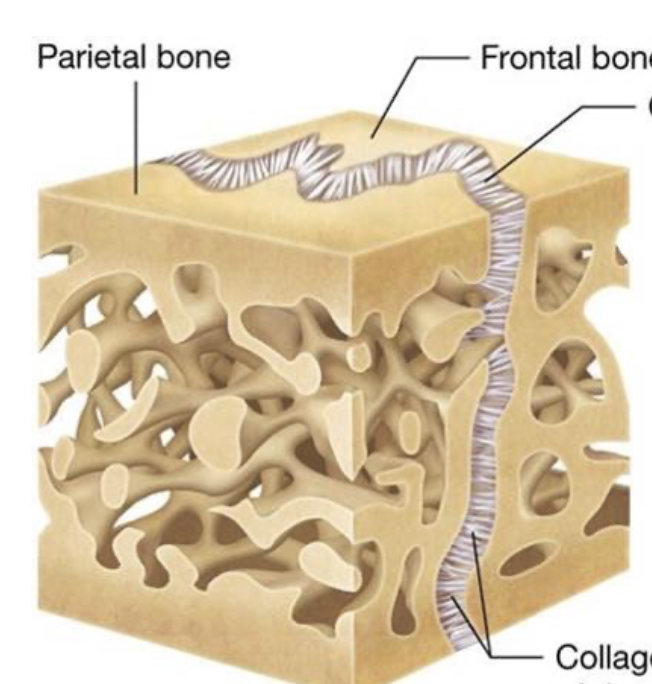
dense regular ct
protection
cranial bone
encloses brain
attachment site for head and neck muscles
facial bones
form framework of face and contains cavities for special senses (taste,smell,hear)
provide openings for food and air
anchor facial muscle
frontal bone
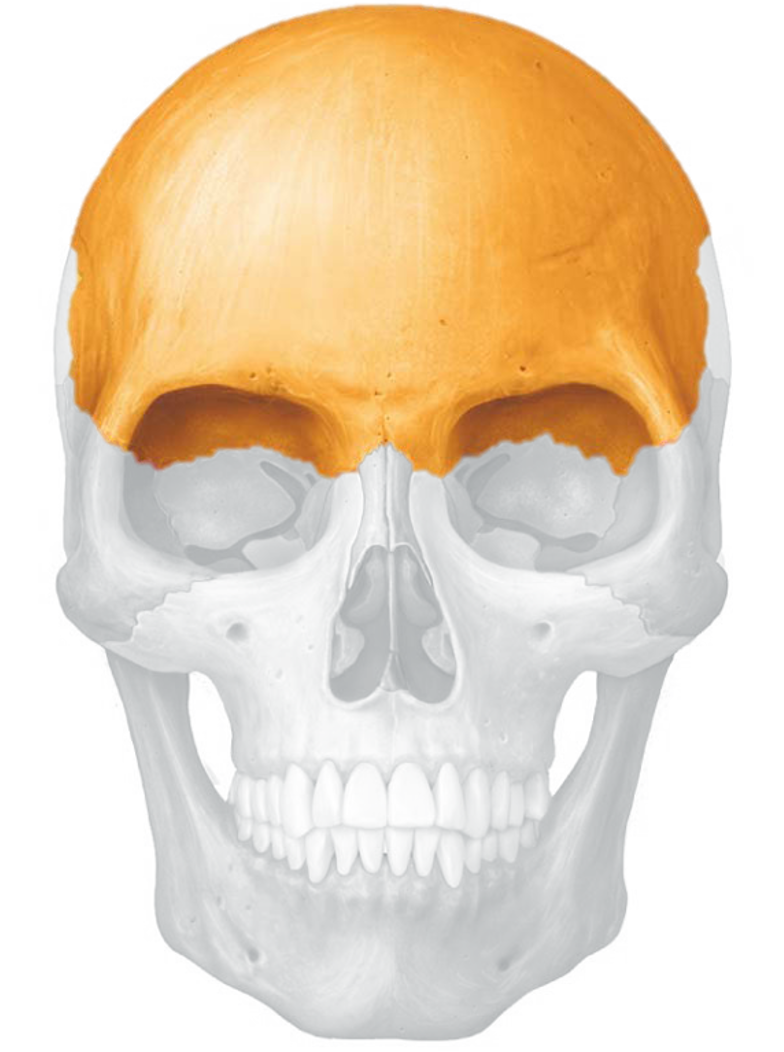
Parietal bone
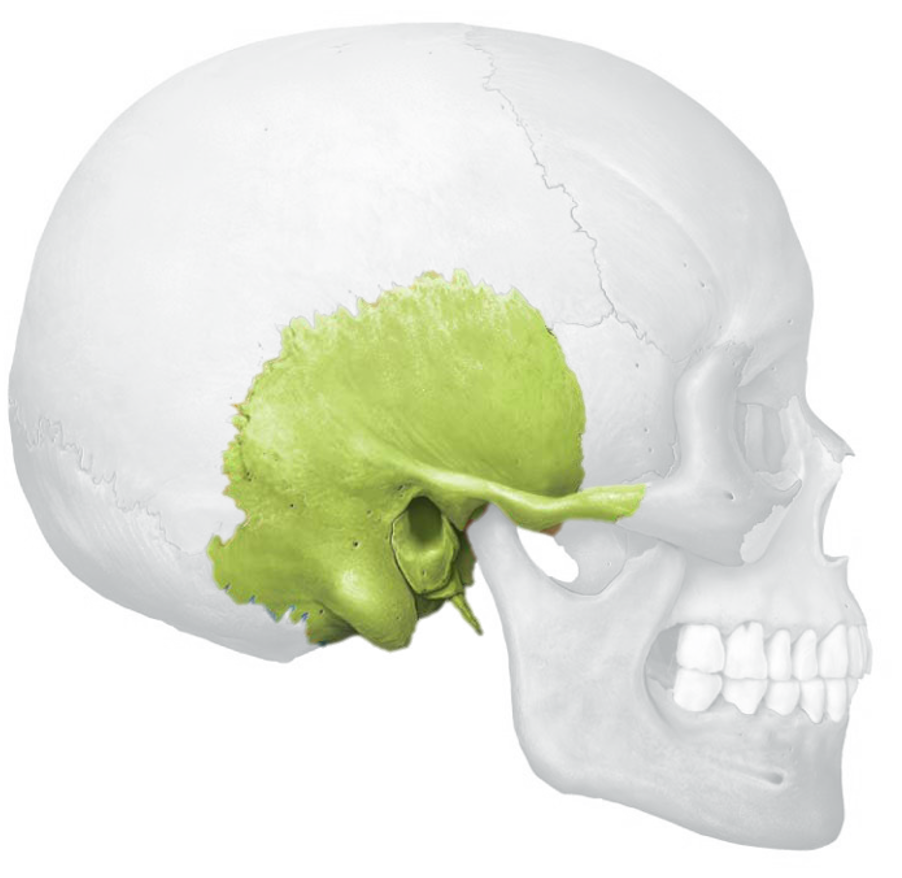
temporal bones
occipital bone
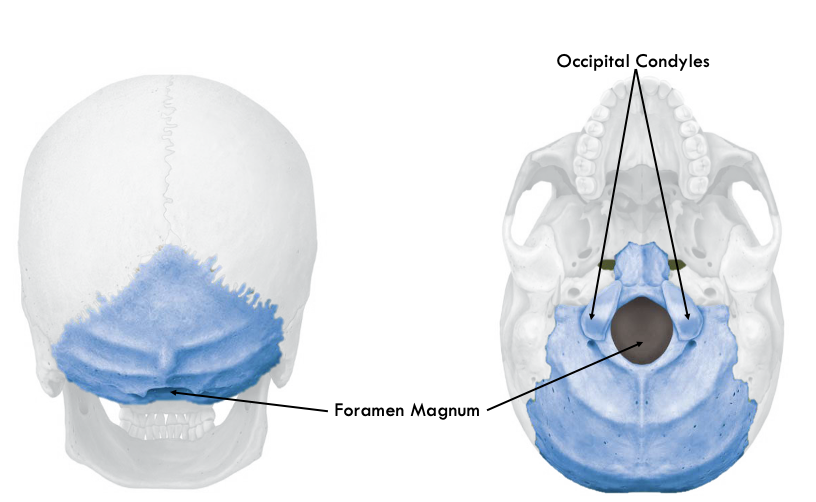
Occipital condyles
two knobs on occipital bone that connects skull to first vertebra
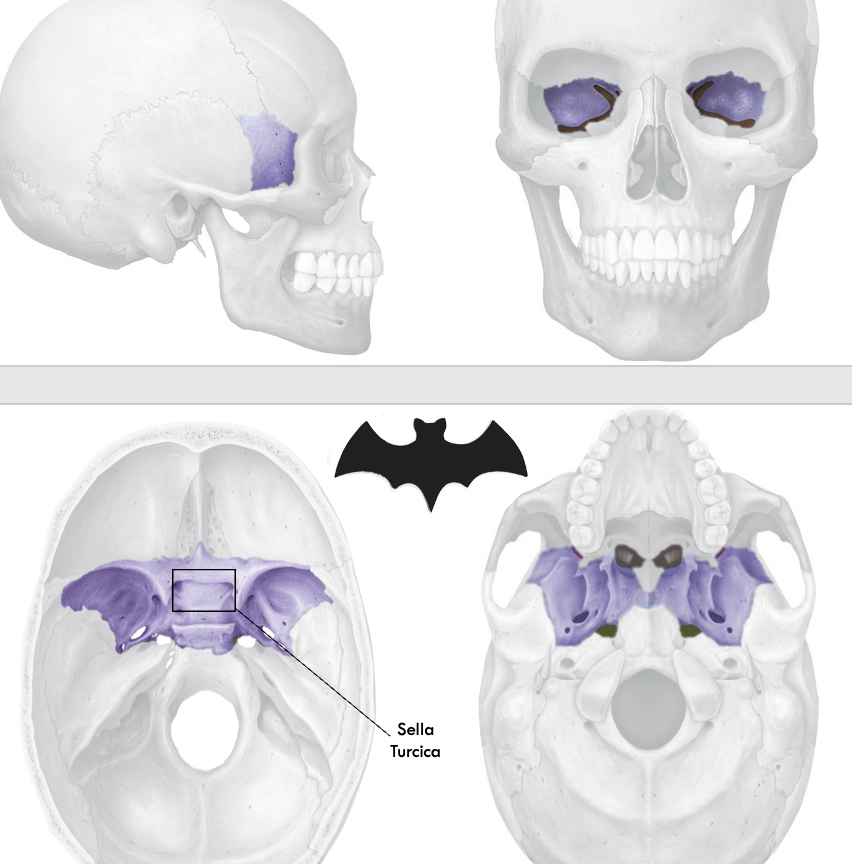
sphenoid bone
ethmoid bone
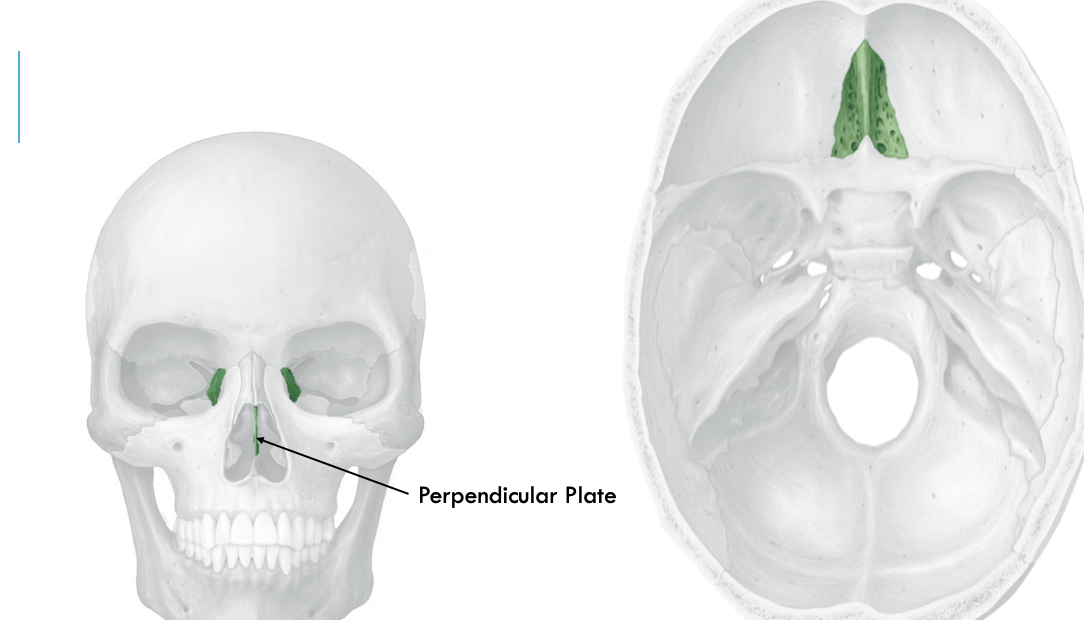
perpendicular plate
forms nasal septum (divides nasal cavity to left/right path)
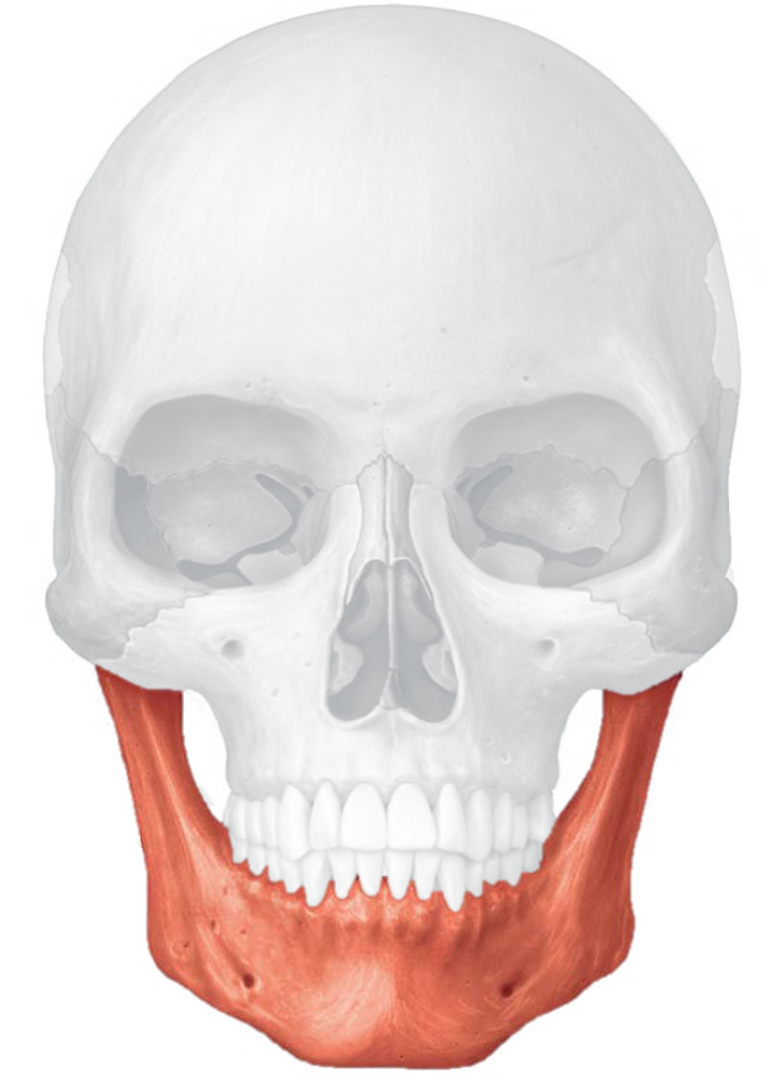
mandible
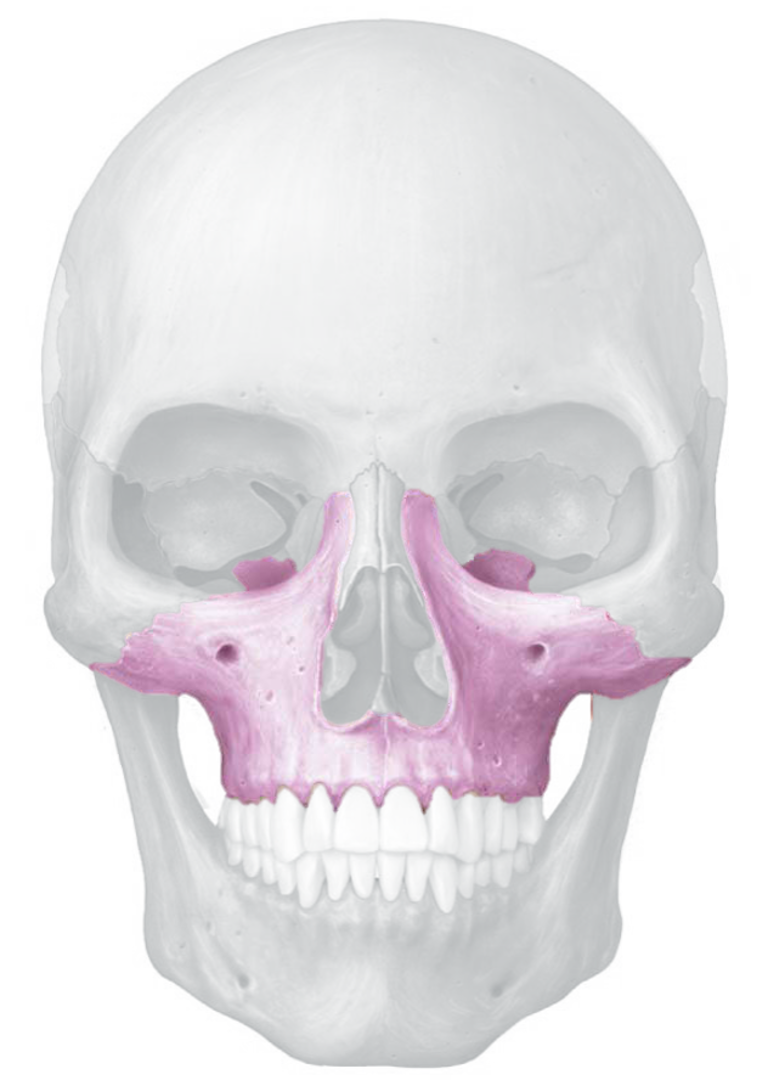
maxillae bones
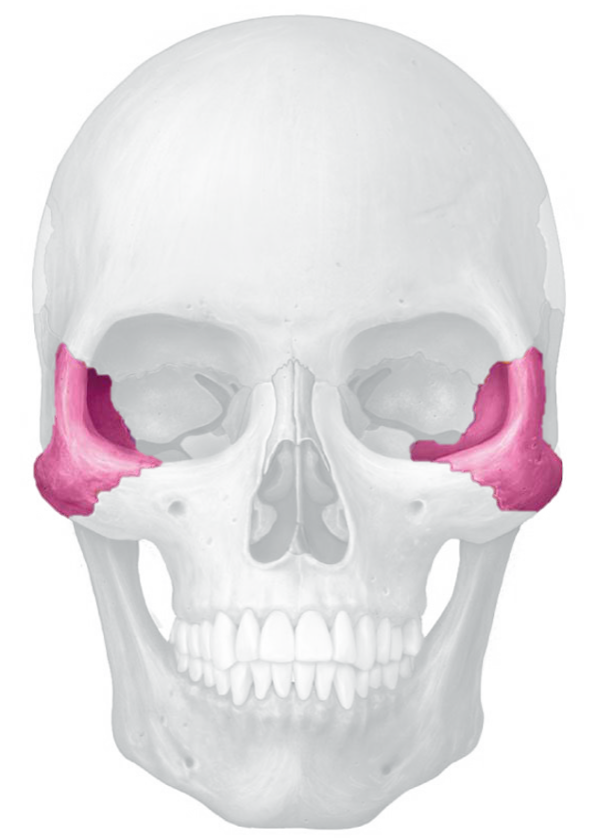
zygomatic bones
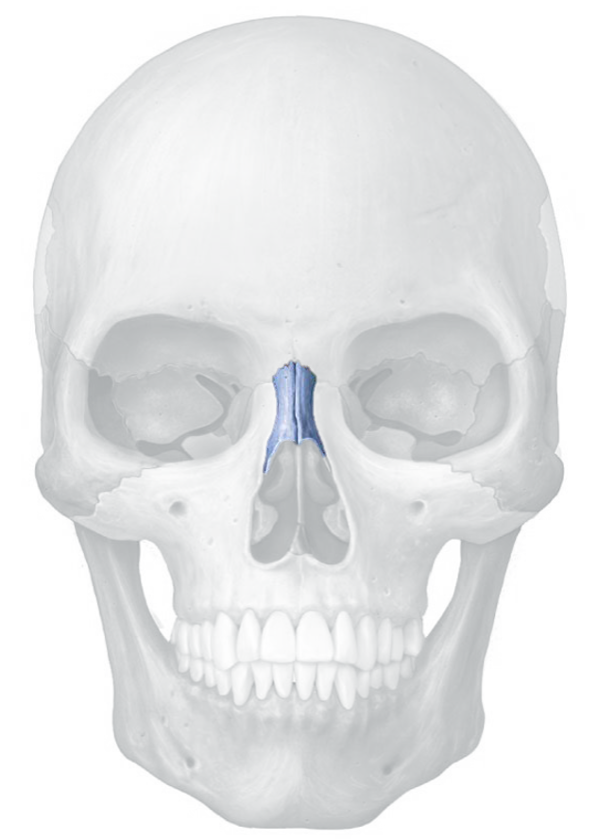
Nasal bone
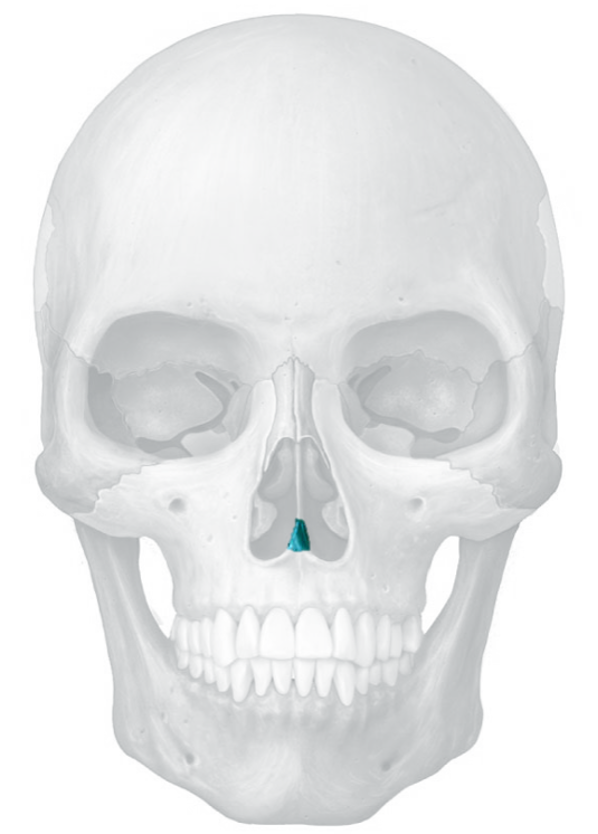
vomer
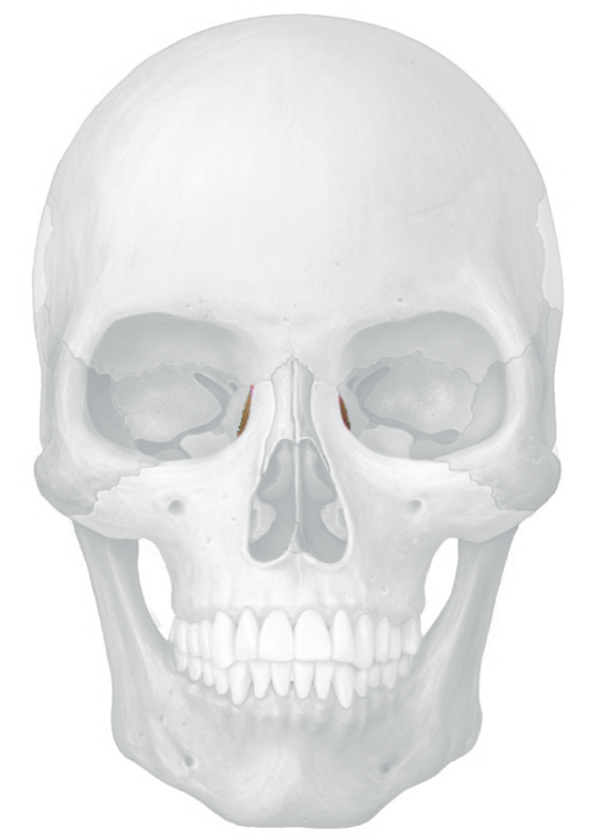
lacrimal bones
palatine bones
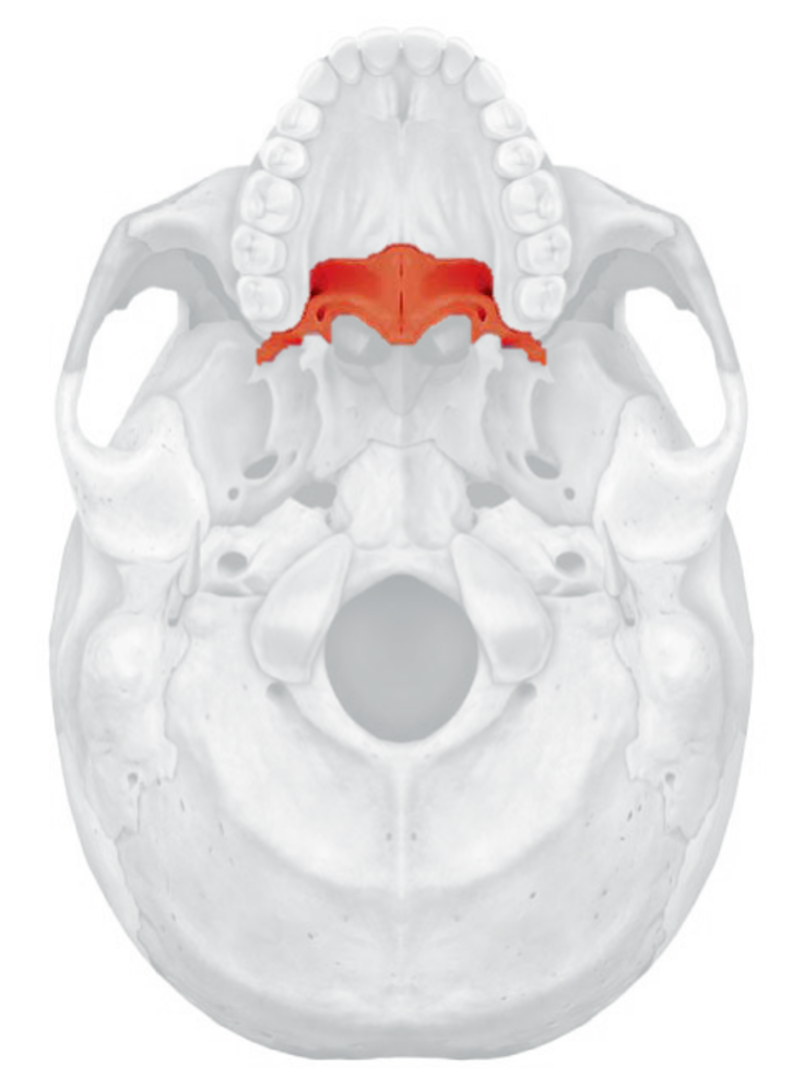
inferior nasal conchae
Nasal septum
divides Right and left nasal cavity
Palatine and maxilla bone
Whats in the oral cavities’ hard palate?
mucous membrane
whats in the oral cavities’ soft palate?
paranasal sinuses
Air filled spaces
Location: Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxillary bone
Function:
Warm and humidify air taken in
Lighten skull (if bones didn’t have air filled space, it would get too heavy)
Enhance resonance of voice
Vertebral column
Supports weight of trunk
Protect spinal cord
Ribs and muscle attachment
Cervical
7 vertebrae
Secondary curvature: not born with this, develops later in life
Develops 6 months of age, cannot not hold up head before.
Thoracic
12 vertebrae
primary curvature: born with this curvature
Lumbar
5 vertebrae
secondary curvature: develop around 1 year of age (start of walking)
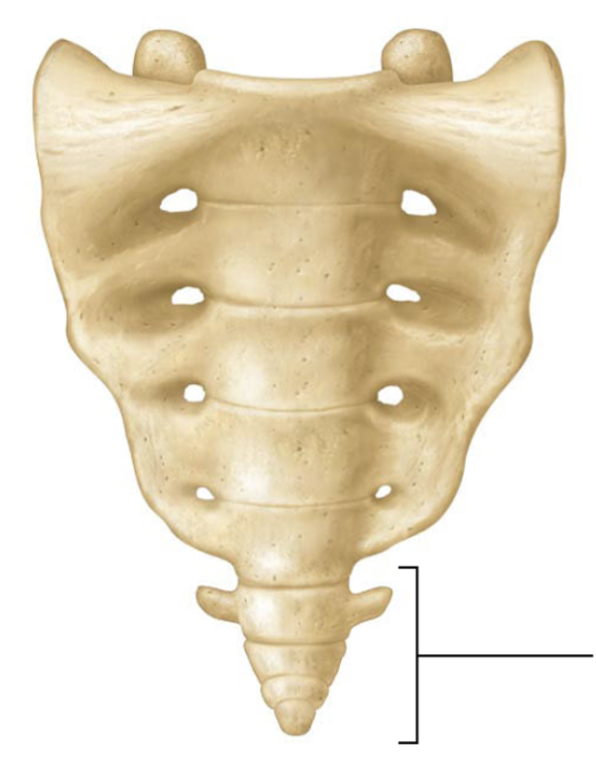
Pelvic
sacrum and coccyx
primary curvature
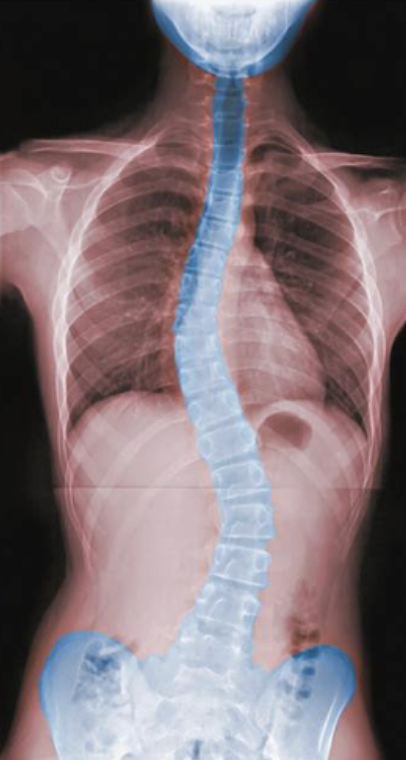
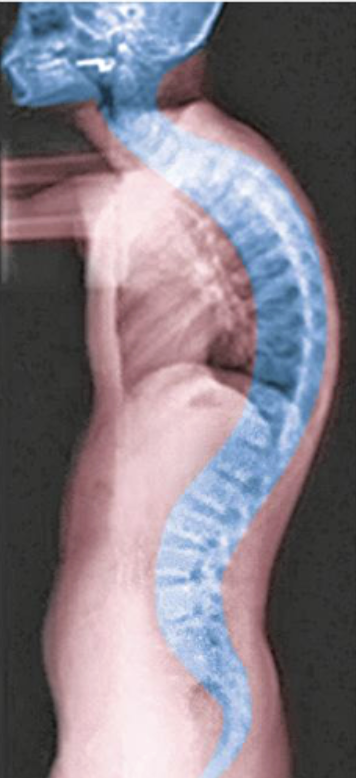
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature
lordosis
Exaggerated cervical or lumbar curvature
Happens when a lot of weight is pushed on vertebral
Ex. pregnancy
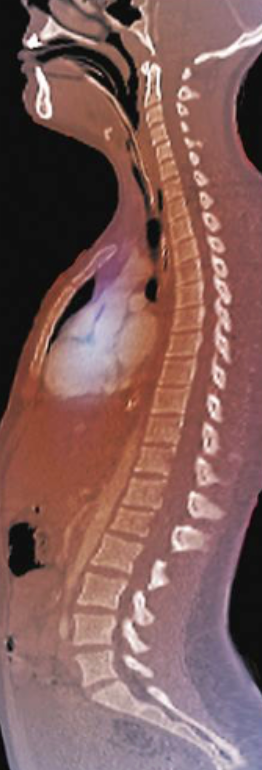
kyphosis
Exaggerated thoracic curvature
Ex. hunch back
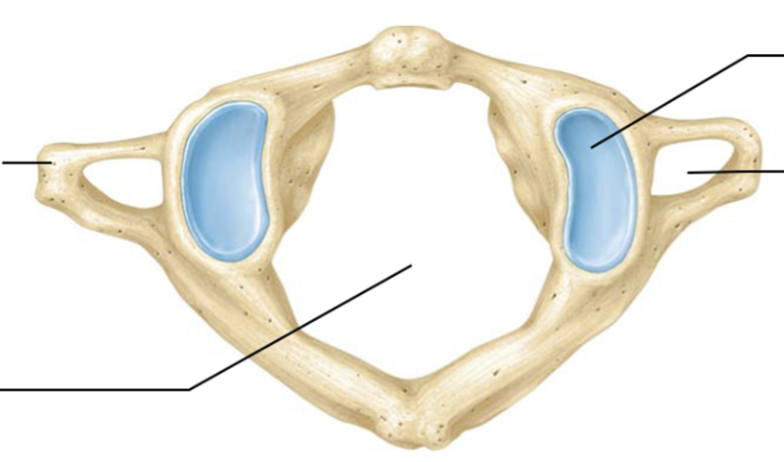
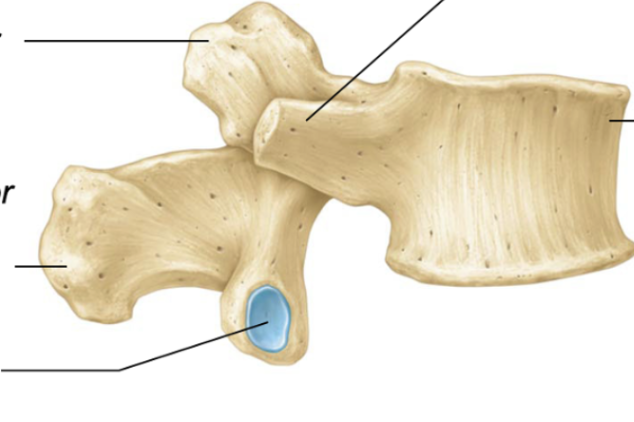
Vertebral foramen
opening/hole where spinal cord passes through
annulus fibrosis
Acts like a barrier to keep inner part in
nucleus pulposus
absorbs any shock/stress
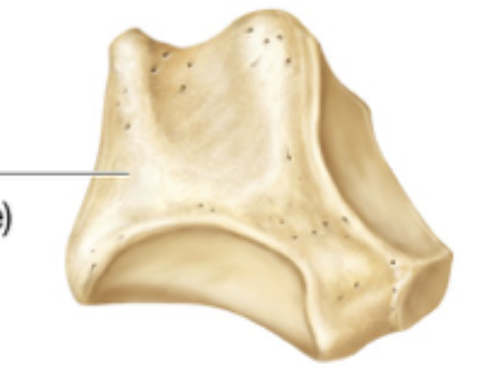
Atlas cervical vertebra
No vertebrae body
No spinous process
Still contains transverse foramen
Allows us to shake out head yes
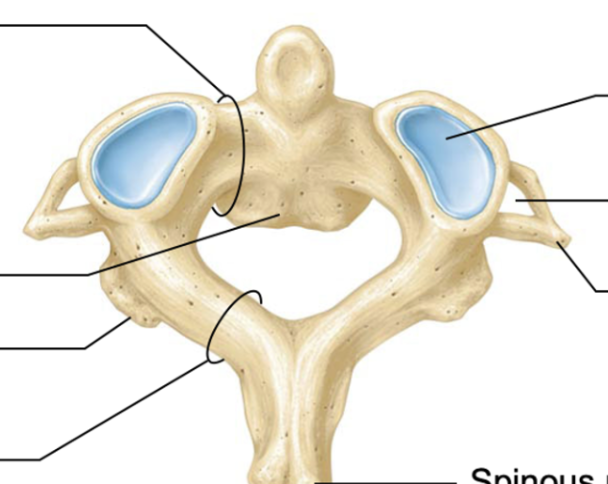
Axis cervical vertebra
allows us to shake our head no
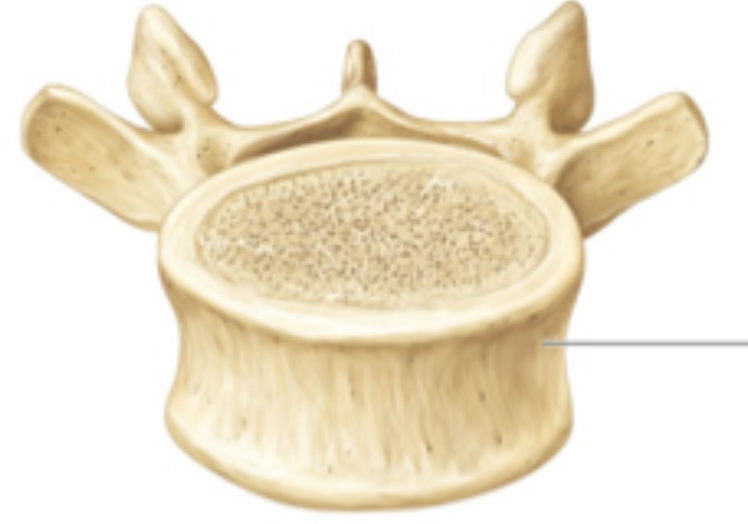
thoracic vertebrae
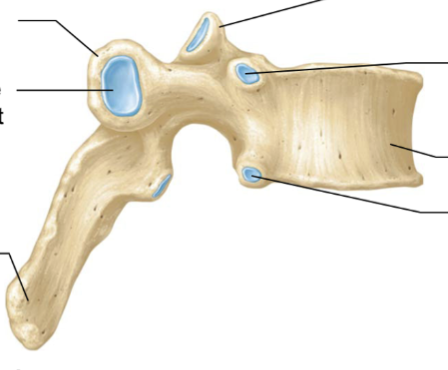
lumbar vertebrae
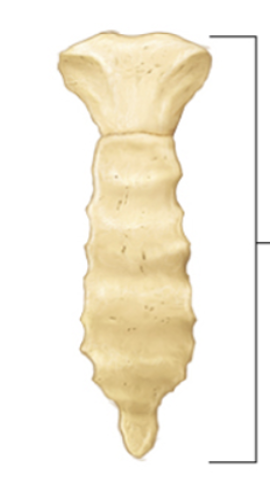
coccyx
vertebrosternal
connects to vertebrae and sternum
vertebrochondral
connects to vertebrae, dont connect to sternum
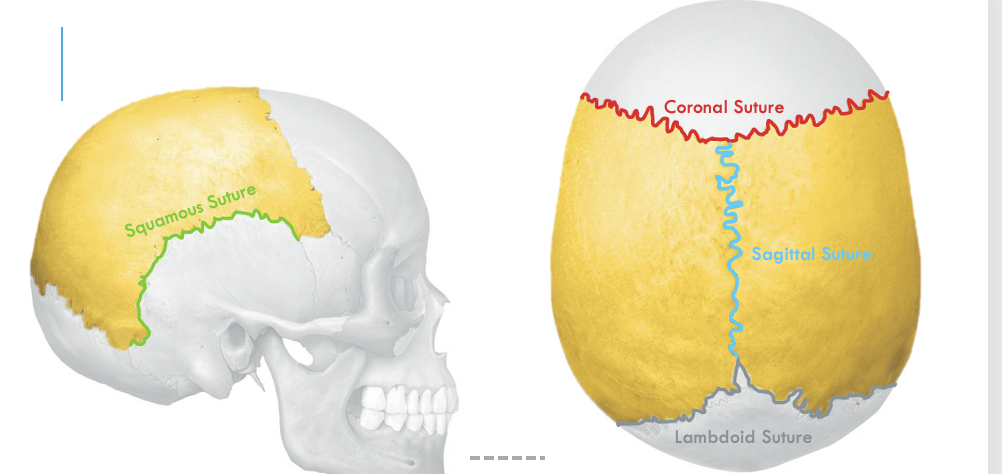
squamous suture
connects to temporal bone
sagittal suture
connects and left and right parietal bone
coronal suture
connects parietal bones with frontal bone
lambdoid suture
connects parietal bones to occipital bone
sella turcica
Depression in the center of the bone for the pituitary gland to sit inside of it.