Physical geography - earthquake,tsunami,volcano
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Fault
crack in the earth’s surface where movements have occurred.
Three type of fault
Normal fault, reverse fault, strike-slip fault
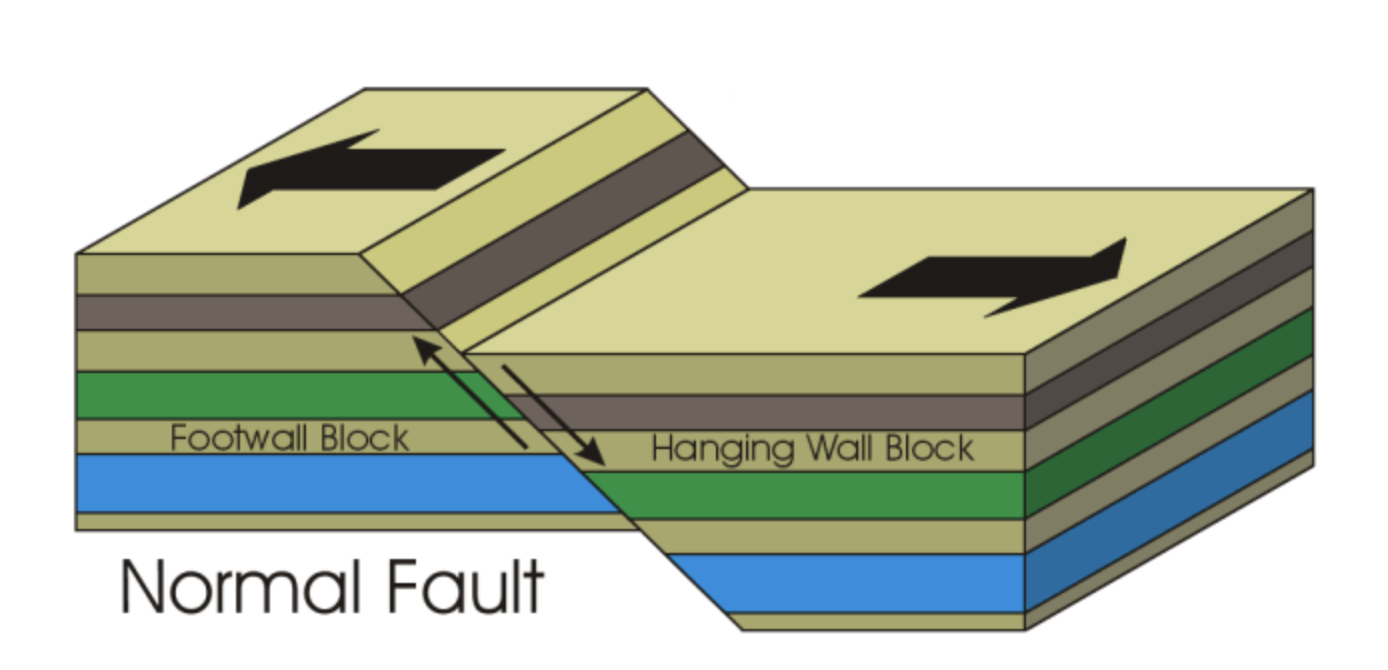
Type of fault: Normal fault
When rock is stretched apart or in tension, one side of the fault slips down relative to the other. Hanging wall moves down
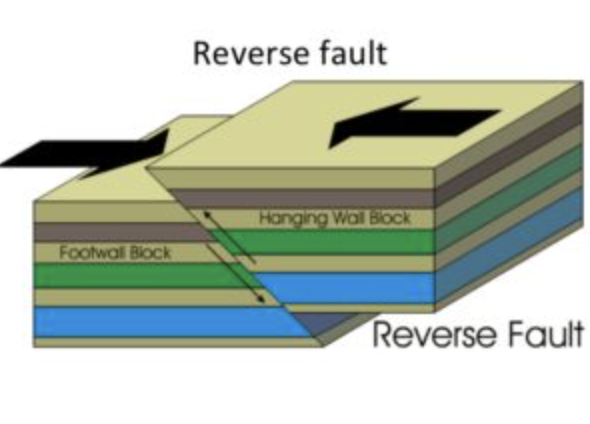
Type of fault: Reverse fault
when rock is compressed(pushed) together
Type of fault: Strike-Slip
Two plates slide past each other- go on opposite direction. Usually shallow earthquake
Measuring earthquakes
Measure in Richter Scale (amount of energy released) x3
Earthquake waves
Primary, Secondary,Love wave
Type of wave: Primary (p) Wave
It is fastest —> first waves to be felt.
Pushing/pulling, back and forth
Travel through solids and liquid
Type of wave: Secondary (S) waves
Move slowly and more destructive
Move up and down or side-to-side
Only travel through solids
Type of waves: Surface (Love) Waves
One the surface —> most destructive
Move like waves in water
Focus
Below the surface where the quake occurs
Epicenter
Above the focus
Liquefaction
The shaking makes water in the soil ries, filling the spaces between paticle. Building and roads sinks
Effects of earthquake (negative)
Fire
Landslides/debris flows/avalanches
Dam Failure
Tsunamis
Tsunami
Huge ocean movement caused by sudden movement under water(Earthquake)
Volcano
Opening in Earth’s crust where magma,gases,ash erupt. Occurs at tectonic plate boundaries and hotspots
Three types of volcano
Shield
Composite
Cinder
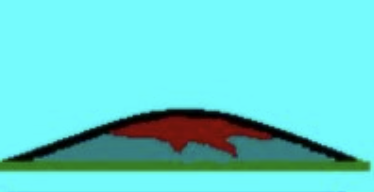
Shield
Wide, gently sloping with thin and runny lava
Low voscosity
Non-explosive
Largest
Happen in divergent
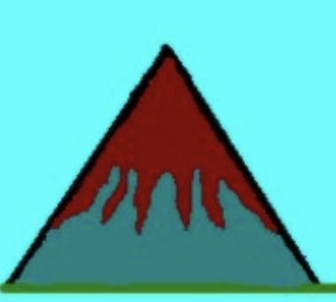
Composite
Steep conical shape with mostly ash and rock
Built from layer
Viscous (Sticky)
Send pyroclastic flows
Convergent
Cinder cone
Small steep volcanoes which erupt out of one central vent
Built from pyroclastic material (ash, lava fragment, and volcanic rock)
More viscosity
Short live and explosive
Hot spots
Unique volcano regions (not a plate boundaries)
Hot rock rises due to buoyancy creating mantle plume
Mantle plume —> magma
How does volcanoes formed
When magma rise to earth surface
High pressure to low pressure
Principle of density
Hot spots
Convergent/divergent
How are volcanoes formed
Subduction: When oceanic plate sinks, it’s under high pressure and the rock melts. Melted rocks lots of silica rise to mantle. Pressure begins to build in magma chamber.
Divergent: as plate separates, magma rise upward to fill thje gaps. Colls and solidifies creating new crust
Type of eruption: explosive
Magma is high viscosity
High gas and silica content
ex) composite, cinder
Mt st Helens
Type of eruption: effusive
Magma is low viscosity
Low gas contents
ex) shield
Lava
Molten rocks hat flows on the surface
forms various structure
Tephra
Fragmented volcanic material
Form pyroclastic flows and ash clouds
Volcanic gases
water vapor, CO2, sulfur dioxide
Create acid rain and affect climate
Igneous rock
Form when lava or magma cools and solidifies
lahar
Volcanic mudflow carrying debris,water,rock
Travels a great distance
Pyroclastic flow
Rapidly moving clouds of gas, rock, ash
Extreamly fast and extreamly dangerous
Ash fall
Free-falling ash can damage infrastructure
Caldera
Large hallow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption