Principles of Chemistry I: Bond Strength and Molecular Structure
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Bond Energy
Energy needed to break one mole of bonds.
Enthalpy (H)
Measurement of energy in a thermodynamic system.
Endothermic Process
Absorbs heat from surroundings during reaction.
Exothermic Reaction
Releases heat; ΔH is negative.
Lattice Energy (ΔH lattice)
Energy to separate one mole of ionic solid.
Born-Haber Cycle
Series of steps to form ionic solids.
Ionization Energy (IE)
Energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
Electron Affinity (EA)
Energy change when an electron is added to an atom.
Bond Dissociation Energy (D)
Energy needed to break a bond in a molecule.
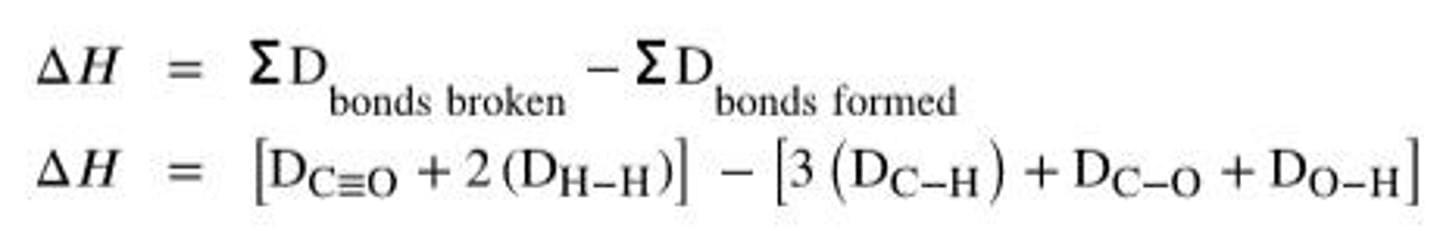
Covalent Bond
Chemical bond formed by sharing electron pairs.
Single Bond
One pair of shared electrons between atoms.
Double Bond
Two pairs of shared electrons between atoms.
Triple Bond
Three pairs of shared electrons between atoms.
VSEPR Theory
Predicts molecular structure based on electron repulsion.
Bond Length
Distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Bond Angle
Angle between two bonds including a common atom.
Molecular Polarity
Distribution of electrical charge across a molecule.
Regions of Electron Density
Includes lone pairs and bonding pairs around atoms.
Repulsion Order
Lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bonding > bonding-bonding.
Terminal Atom Locations
Positions of atoms in linear and planar geometries.
Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometry
Five regions of electron density around a central atom.
Octahedral Geometry
Six regions of electron density around a central atom.
Lewis Structure
Diagram showing bonds and lone pairs in a molecule.
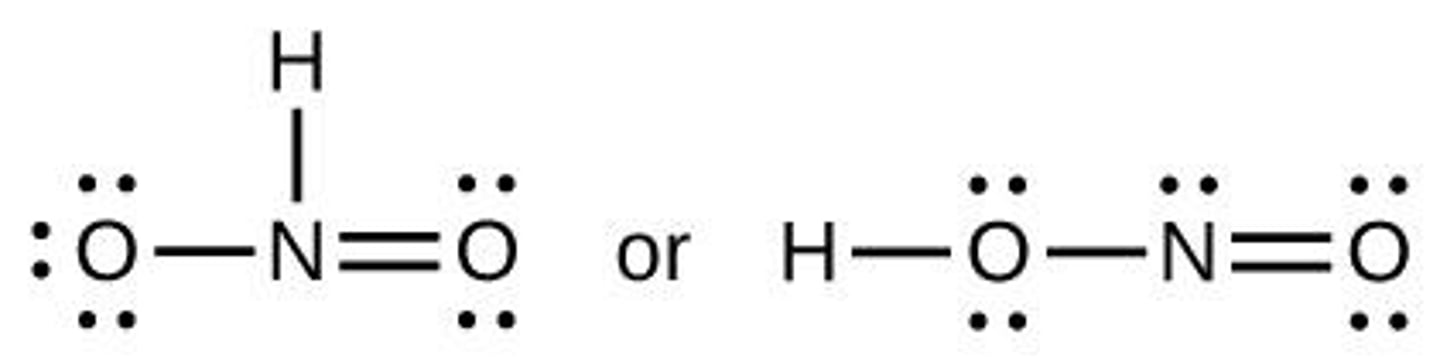
Average Bond Energy
Mean energy required to break bonds in a molecule.
ΔH for Reactions
Sum of bond energies broken minus formed.
Molecular Structure Prediction
Determining shape based on electron pair arrangements.
Bond Strength
Energy required to break a bond; stronger bonds require more energy.
Crystal Type Constant (C)
Constant in lattice energy formula based on crystal structure.
Interionic Distance (Ro)
Distance between ions in a crystal lattice.
CO2
2 regions of electron density
BCl3
3 regions of electron density
H2O
4 regions of electron density
Electron-pair geometry for CO2
linear
Electron-pair geometry for BCl3
trigonal planar
Electron-pair geometry for H2O
tetrahedral
Number of Lone Pairs for CO2
4
Number of Lone Pairs for BCl3
0
Number of Lone Pairs for H2O
2
Molecular Structure for CO2
linear
Molecular Structure for BCl3
trigonal planar
Molecular Structure for H2O
Bent
Regions of electron density for N
4
Regions of electron density for CH2
4
Regions of electron density for CO2 (in multicenter molecules)
3
Regions of electron density for OH
4
Electron-pair geometry for N
Tetrahedral
Electron-pair geometry for CH2
Tetrahedral
Electron-pair geometry for CO2 (in multicenter molecules)
Trigonal Planar
Electron-pair geometry for OH
linear
Number of Lone Pairs for N2
2
Number of Lone Pairs for CH2
0
Number of Lone Pairs for CO2 (in multicenter molecules)
0
Number of Lone Pairs for OH
2
Molecular Structure for N2
linear
Molecular Structure for CH2
Tetrahedral
Molecular Structure for CO2 (in multicenter molecules)
Trigonal Planar
Molecular Structure for OH
Bent
Bond dipole moment formula
µ= bond dipole moment; Q= magnitude of the partial charges; r: distance between charges
Definition of a Polar molecule
A molecule with a separation of charge, depending on its molecular structure and the polarity of each of its bonds.
Definition of a Nonpolar molecule
A molecule without a separation of charge.
Dipole moment
Measures the extent of net charge separation in the molecule as a whole.
Avogadro's Number
6.02214179 × 10^23.
Definition of a mole
The amount of a substance containing the same number of discrete entities as the number of atoms in a sample of pure carbon-12 weighing exactly 12 g.
Molar mass
The mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance, expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol).
Saccharin
Artificial sweetener with formula C7H5NO3S.
Molar Mass
Mass of one mole of a substance, measured in g/mol.
Percent Composition
Percentage by mass of each element in a compound.
Empirical Formula
Simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound.
Molecular Formula
Actual number of atoms of each element in a compound.
Molarity (M)
Moles of solute per liter of solution.
Dilution
Process of reducing solution concentration by adding solvent.
Solvent
Component of solution present in greater concentration.
Solute
Component of solution present in lower concentration.
Aqueous Solution
Solution where water is the solvent.
Concentration
Relative amount of a component in a solution.
Mass Percentage
Mass of component divided by total mass, expressed as %.
Volume Percentage
Volume of solute divided by total volume, expressed as %.
Mass-Volume Percentage
Ratio of solute mass to solution volume, expressed as %.
Parts per Million (ppm)
Mass of solute per million parts of solution.
Parts per Billion (ppb)
Mass of solute per billion parts of solution.
Molecular Mass
Mass of one molecule, measured in amu.
Formula Mass
Sum of atomic masses in a chemical formula.
Stoichiometry
Calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
Gas Composition
Percentage of different gases in a mixture.
Concentration Units
Various ways to express solution concentration.
Dilution Equation
n1 = n2; relates concentrations before and after dilution.
Hydrochloric Acid
Aqueous solution of HCl, commonly used in labs.
Physiological Saline
0.9% (m/v) NaCl solution for medical use.
Ethanol Production
Bacterial fermentation process producing ethanol and gas.
Chemical Reagents
Substances used in chemical reactions for analysis.
Chemical Analysis
Determining the composition of substances.
Concentration Calculation
Computing concentration based on mass and volume.