Week 1- Triage + Critical thinking
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Why is critical thinking important in veterinary medicine?
Understanding why you are performing actions improves patient outcomes and decision-making.
Define critical thinking.
A mental process of active perception, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation of information to guide actions.
What is the first rule of critical thinking?
Always know what normal is before identifying abnormalities.
What are the five steps of critical thinking?
Assess, Analyze, Plan & Prioritize, Implement, Evaluate.
What happens during the Assess step?
Physical exam, data collection, and consideration of patient preferences.
What happens during the Analyze step?
Determine if findings are normal, compare diagnostics to patient context, and alert the DVM to concerns.
What happens during the Plan & Prioritize step?
Determine what must be done first, set realistic goals, and prepare backup plans.
What happens during the Implement step?
Perform treatments or delegate tasks and follow up to confirm completion.
What happens during the Evaluate step?
Review outcomes, identify what worked or didn’t, and apply lessons to future cases.

What does the term triage mean?
Triage comes from the French word “trier”, meaning to sort or choose; it is the process of prioritizing patients based on urgency.
What is the goal of triage?
To rapidly identify and address life-threatening conditions before performing a full exam or diagnostics.
What is the Primary Survey?
A quick initial assessment focusing on major organ systems to identify immediate life-threatening problems.
Which four major body systems are evaluated during initial triage?
Respiratory, Cardiovascular, Central Nervous System (CNS), and Renal systems.
What tools are commonly used during triage?
Observation using the five senses (except taste), stethoscope, watch/timer, and thermometer.
What are the key components of respiratory triage?
Airway patency, breathing rate, breathing effort, and respiratory posture.
What questions should be asked when evaluating the airway?
Is the airway patent? Is there abnormal airway noise?
What are initial treatments for respiratory distress?
Establish or maintain the airway and provide supplemental oxygen.
List common upper airway emergencies.
Collapsing trachea, laryngeal paralysis, foreign bodies, allergic reactions with swelling, neoplasia, brachycephalic syndrome.
List common lower airway emergencies.
Feline asthma, pneumonia, pulmonary contusions, pulmonary edema, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, diaphragmatic hernia, pulmonary neoplasia.
What muscles are used during inhalation?
Diaphragm and external intercostal muscles.
What muscles are used during exhalation?
Abdominal muscles and internal intercostal muscles.
What cardiovascular parameters are assessed during triage?
Mucous membrane color and moisture, capillary refill time (CRT), pulse quality, and heart sounds.
Why should pulses be palpated while auscultating the heart?
To assess pulse quality and detect deficits or abnormalities in circulation.
What are initial treatments for cardiovascular compromise?
Supplemental oxygen, hemostasis, CPCR if needed, and IV fluids to optimize preload.
What gait observations are important during CNS triage?
Ability to walk, limb movement, coordination, and abnormal postures.
What abnormal head findings should be assessed during CNS triage?
Head trauma, head tilt, nystagmus (horizontal, vertical, or rotary).
What levels of consciousness are assessed during triage?
Alert, depressed, delirious, stuporous, or comatose.
What is the order of neurologic damage from least to most severe?
Conscious proprioception → motor function → superficial pain → deep pain.
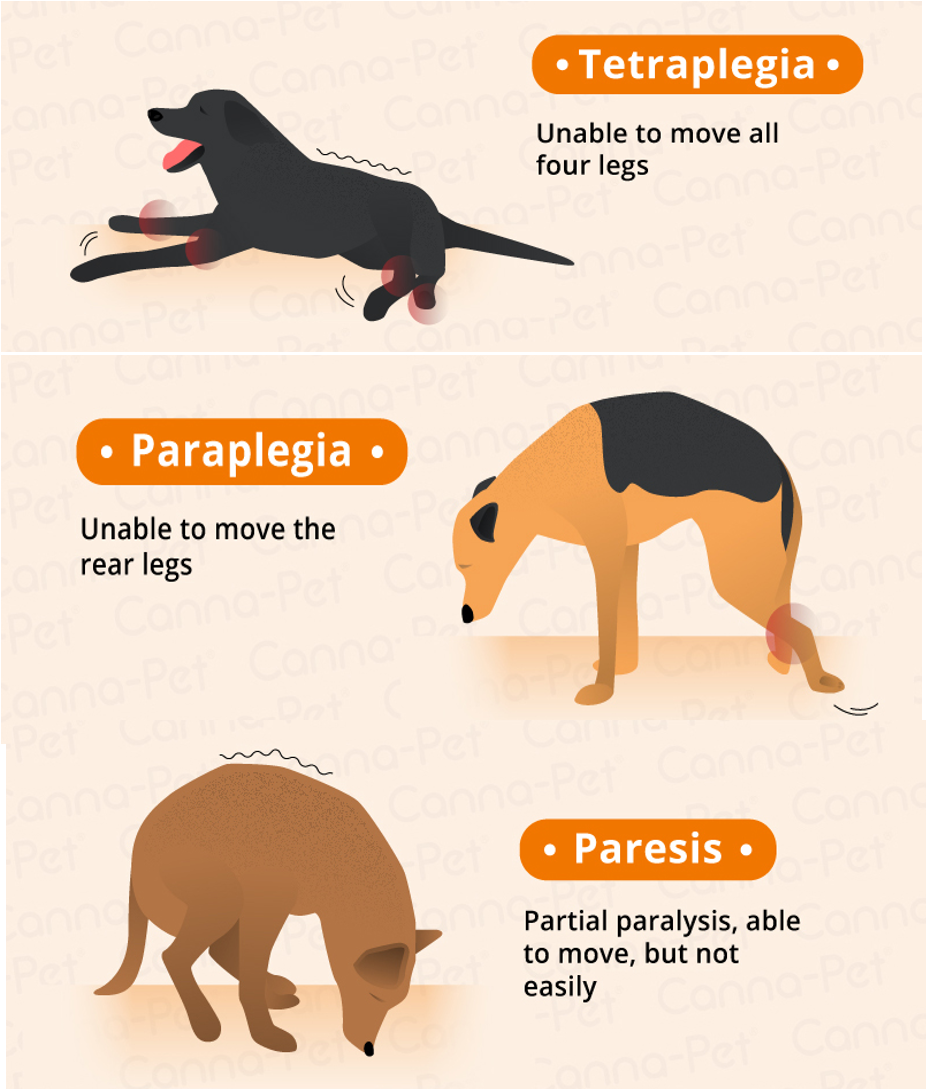
What is plegia?
Complete inability to voluntarily move a limb or limbs (paralysis).
What is paresis?
Weakness or difficulty moving limbs voluntarily.
List common CNS emergencies.
Seizures, head trauma, acute paralysis (IVDD, FCE, spinal injury), toxin exposure.
What are initial treatments for CNS emergencies?
Supplemental oxygen, anticonvulsants for seizures, detoxification protocols, and pain management.
What observations are important in renal triage?
Abdominal injury, dehydration, CNS abnormalities, and bradycardia due to hyperkalemia.
What does a firm, non-expressible urinary bladder suggest?
Possible urinary obstruction.
When are kidneys normally palpable?
In small dogs and most cats; assess for size and pain.
What are initial treatments for renal emergencies?
Monitor urine output and carefully manage fluid loss and replacement (with caution if obstruction).
List common renal emergencies.
Acute renal failure (toxins), chronic/end-stage renal failure, urethral obstruction, lower urinary tract trauma.
When is the secondary survey performed?
After initial triage and stabilization.
What occurs during the secondary survey?
Full history, complete physical exam, diagnostics, and ongoing monitoring