APUSH Final Review
1/399
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
400 Terms
Southwest Native American settlements
Pueblos, Hohokam, Anasazi.
Lived in caves and used irrigation
Northwest American Indian Settlements
Mainly near Pacific Coast
Permanent longhouses
Great Basin and Great Plains
Dry arid climate
Hunted Buffalo
Very few created permanent settlements as most migrated
Prince Henry the Navigator
finds long sea route around South Africa
Portuguese ruler
Treaty of Tordesillas
Signed by Spain and Portugal in 1491 where Portugal gets Brazil but Spain gets the rest of the Americas.
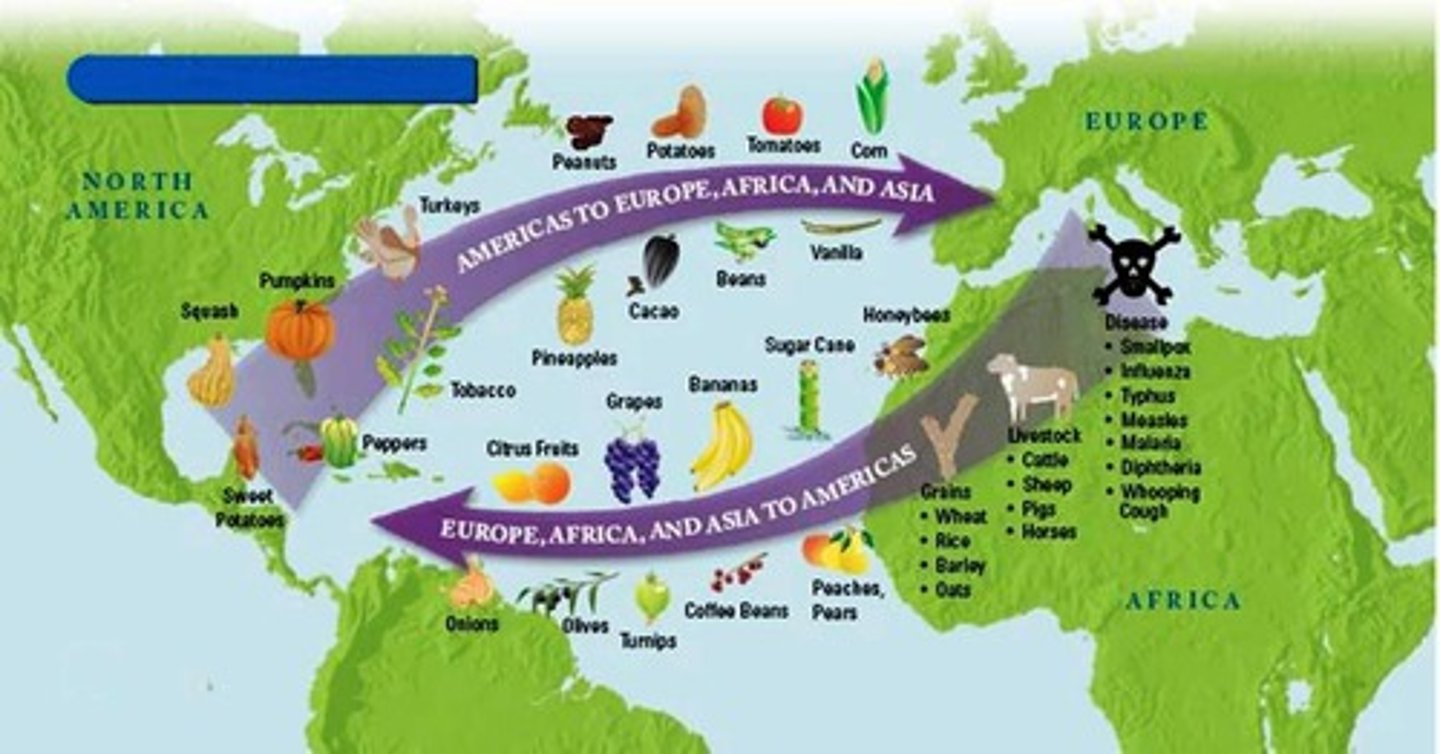
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
Resulted in population decline of Native Americans
joint stock companies
Limited liability for the individual shareholder.
Hernan Cortez
A Spanish Conquistador who defeated and conquered the Aztec Empire
Francisco Pizarro
Spanish explorer who conquered the Incas in what is now Peru and founded the city of Lima (1475-1541).
Encomienda System
Spanish gave their nobles land in America including the natives who lived on the land. As a result, the Natives were forced to work on the land.
Spanish Caste System
- peninsulares (born in Spain)
- creoles (born in colonies but European)
- mestizos (Spanish and native)
- mulattos (Spanish and African)
- Africans and native Americans
English Policy in Americas
came as families so intermarriage was rare
first worked with natives by trading but later pushed them out
French Policy in Americas
came to trade for fun and creating fur trading post in Great Lakes area
Wanted to convert natives to Catholicism and saw them as military allies.
Corporate colonies
operated by joint stock company like Jamestown
Royal Colonies
Colonies controlled by the British king through governors appointed by him and through the king's veto power over colonial laws. Like Virginia after 1624
Proprietary Colonies
Under authority of individuals who got charters of ownership from the king like Pennsylvania
Jamestown
The first permanent English settlement in North America, found in East Virginia in 1607
Had problems of dysentery and malaria and conflict between natives and settlers
Pocahontas helped make tobacco a cash crop
Triangular Trade
New England ship goes to West Africa with rum for enslaved Africans who go through Middle Passage and get sugar from West Indies.
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought. Major economic policy in early Europe.
Metacom's War (1675-1676)
Also known as King Philip's War. A military conflict in which the Wampanoag and Narragansett tribes of southern New England joined together to fight against English colonists' westward expansion. Thousands were killed on both sides before the English forces won the war, effectively ending most Native American resistance in New England.
Bacon's Rebellion
organized a group of angry farmers who attacked large plantation farmers in Chesapeake.
Pueblo Revolt in 1680
An uprising of Indians in Santa Fe against Spanish colonization. The Pueblo killed 400 Spanish and drove the remaining 2,000 settlers out of the province. Twelve years later the Spanish returned and were able to reoccupy New Mexico with little opposition. However, the Spanish were more accommodating of Indian culture afterwards
indentured servants
was under control of master for 4-7 years in exchange for passage to the colonies. Usually after they finished they got some land. It stopped mainly in the Chesapeake after Bacon's rebellion.
French and Indian War (1754-1763)
The name for the North American theater of the Seven Years War & was a successful attempt to move the French out of the Ohio Valley & to stop Indian raids on frontier settlements.
Historical Significance:
Colonists gained pride in their own military strength, felt more disconnected from Britain, & were left without fear of French a invasion.
Proclamation of 1763
forbid British colonist from settling West of the Appalachian Mountains.
Quartering Act (1765)
Act forcing colonists to house and supply British forces in the colonies; created more resentment; seen as assault on liberties.
Sugar Act
law passed by the British Parliament setting taxes on molasses and sugar imported by the colonies. Was repealed in 1766.
Currency Act of 1764
Forbade colonists from printing their own currency & instead required them to use hard currency (gold & silver) which was in short supply in the colonies.
Stamp Act of 1765
This act required colonists to pay for an official stamp, or seal, when they bought paper items. Was repealed in 1766.
Stamp Act Congress (1765)
27 delegates from 9 colonies and petitioned Parliament to repeal Stamp Act based on what they understood as rights of British citizens.
Declaratory Act
After repealing Stamp and Sugar Act, Parliament said that they had the right to pass any law they wanted for the colonies.
Townshend Act (1767)
British law that established new duties on tea, glass, lead, paper, and painters' colors imported into the colonies. The Townshend duties led to boycotts and heightened tensions between Britain and the American colonies.
Boston Massacre 1770
An incident in which British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists who were teasing and taunting them; five colonists were killed.
Historical Significance:
Boston's radicals used to incident to wage an Anti-British propaganda war.
Boston Tea Party 1773
British ships carrying tea sailed into Boston Harbor and refused to leave until the colonials took their tea. Boston was boycotting the tea in protest of the Tea Act and would not let the ships bring the tea ashore. Finally, on the night of December 16, 1773, colonials disguised as Indians boarded the ships and threw the tea overboard.
Coercive/Intolerable Acts (1774)
passed by Parliament because of the Boston Tea Party.
Boston Port Act: Closed Boston harbor until the tea was paid for
Quartering Act: made royal governors find homes for British soldiers.
Massachusetts Government Act: replaced elected officials in Massachusetts with royal officials.
Impartial Administration of Justice Act: gave change of judgement place for British officials because of enforcement of law.
First Continental Congress (1774)
response to Intolerable Acts and met in Philadelphia.
Adopted Suffolk Resolve which rejected Massachusetts Government Act and boycotted imported goods from Britain until Intolerable Acts got repealed.
Second Continental Congress (1775)
response to Lexington and Concord and met in Philadelphia. Forced the United States and declared independence
Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine that claimed the colonies had a right to be an independent nation
Republican Motherhood
The idea that American women had a special responsibility to cultivate "civic virtue" in their children
Articles of Confederation
Adopted in 1777 and ratified in 1781. Made central government with one legislative branch with each state getting one vote. Congress could wage war and make treaties but couldn't collect taxes.
Land Ordinance of 1785
policy for selling western land and established Rectangular Survey System
North West Ordinance of 1787
A plan for selling and governing the new lands west of the App Mts. and North of the Ohio River. Prohibited slavery in the area.
Shay's Rebellion (1786)
Armed uprising of western Massachusetts debtors seeking lower taxes and an end to property foreclosures. Though quickly put down, the insurrection inspired fears of "mob rule" among leading Revolutionaries.
Great Compromise
Compromise that there would be a bicameral legislature with one represented by population and the other by equal representation. Came out of the Virginia and New Jersey plan.
Virginia Plan: strong centralized government with representatives based on population.
New Jersey Plan: unicameral legislature with equal representation for every state.
Three fifths compromise
3/5's of a state's slave population would be counted for representation purposes and national ban on international slave trade couldn't happen until 1808
Federalist
A term used to describe supporters of the Constitution during ratification debates in state legislatures.
Democrat-Republican Party
This political party was organized in the 1790s and became the first opposition party in US history. Following the ideas of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison, this party was opposed to a strong central government and a central bank and supported strict construction of the Constitution and the predominance of agriculture in the economy. Jefferson was their first president
Louisiana Purchase
territory in western United States purchased from France in 1803 for $15 million
Lewis and Clark
Sent on an expedition by Jefferson to gather information on the United States' new land and map a route to the Pacific. They kept very careful maps and records of this new land acquired from the Louisiana Purchase.
John Marshall
American jurist and politician who served as the chief justice of the U.S. Supreme Court (1801-1835) and helped establish the practice of judicial review.
Judicial Review
Allows the court to determine the constitutionality of laws
Marbury vs Madison
Case in which the supreme court first asserted the power of Judicial review in finding that the congressional statue expanding the Court's original jurisdiction was unconstitutional
Implied Powers
Powers inferred from the express powers that allow Congress to carry out its functions.
Era of Good Feelings
Popular name for the period of one-party, Republican, rule during James Monroe's presidency. The term obscures bitter conflicts over internal improvements, slavery, and the national bank.
Monroe Doctrine
A statement of foreign policy which proclaimed that Europe should not interfere in affairs within the United States or in the development of other countries in the Western Hemisphere.
Gabriel's Rebellion
A planned slave rebellion in Richmond led by Gabriel, a slave. The plan leaked out just before the march, and authorities rounded up the participants and executed thirty-five of them, including Gabriel.
Embargo Act of 1807
This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral vessels by depriving them of American trade.
Red Jacket
Native American Seneca orator, British message runner in Revolution. He negotiated with the US for the Seneca as well.
Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa
Two Shawnee brothers who called for attacks on American frontier settlements.
Red Stick Creeks
Creek natives who allied with Tecumseh (and therefore the British) in the War of 1812 to try to protect their land. Lost at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend against Andrew Jackson
War of 1812
A war (1812-1814) between the United States and England which was trying to interfere with American trade with France.
Battle of Tippecanoe (1811)
U.S. forces - led by William Henry Harrison - defeated Tecumseh's confederacy then burned its headquarters at Prophetstown. Tecumseh's confederacy allied with the British during the War of 1812; Harrison emerged as a war hero.
War Hawks
Southerners and Westerners who were eager for war with Britain. They had a strong sense of nationalism, and they wanted to takeover British land in North America and expand.
Hartford Convention (1814)
A meeting of Federalist delegates from New England inspired by Federalist opposition to the War of 1812;contributed to the death of the Federalist Party during the "Era of Good Feelings"
Treaty of Ghent
December 24, 1814 - Ended the War of 1812 and restored the status quo. For the most part, territory captured in the war was returned to the original owner. It also set up a commission to determine the disputed Canada/U.S. border.
American System
Economic program advanced by Henry Clay that included support for a national bank, high tariffs, and internal improvements; emphasized strong role for federal government in the economy.
John C. Calhoun
South Carolina Senator - advocate for state's rights, limited government, and nullification
Henry Clay
A northern American politician. He developed the American System as well as negotiated numerous compromises.
Philadelphia-Lancaster Turnpike
a broad, paved highway that was similar to the good European highways at that time. Resulted in a turnpike-building boom
National Road
The first highway built by the federal government. Constructed during 1825-1850, it stretched from Pennsylvania to Illinois. It was a major overland shipping route and an important connection between the North and the West.
Market Revolution
Major economic changes where people buy and sell goods rather than make them themselves
Panic of 1819
Economic panic caused by extensive speculation and a decline of European demand for American goods along with mismanagement within the Second Bank of the United States. Often cited as the end of the Era of Good Feelings.
Erie Canal
A canal between the New York cities of Albany and Buffalo, completed in 1825. The canal, considered a marvel of the modern world at the time, allowed western farmers to ship surplus crops to sell in the North and allowed northern manufacturers to ship finished goods to sell in the West.
Steamboats
Boats powered by steam that increased the speed of river travel. It could travel upstream
Railroads
Networks of iron (later steel) rails on which steam (later electric or diesel) locomotives pulled long trains at high speeds. The first were built in England in the 1830s. Success caused the construction of these to boom lasting into the 20th Century
Cyrus McCormick
Irish-American inventor that developed the mechanical reaper. The reaper replaced scythes as the preferred method of cutting crops for harvest, and it was much more efficient and much quicker.
John Deere
Invented the steel plow
Dartmouth vs. Woodward (1819)
weakened the power of states, forbidding the state legislature to alter the college's charter (NH wanted to make Dartmouth a public school). protects private property.
Cotton Gin
A machine for cleaning the seeds from cotton fibers, invented by Eli Whitney in 1793
Piecework
a compensation system in which employees are paid a set rate for each item they produce
Samuel Slater
He was a British mechanic that moved to America and in 1791 invented the first American machine for spinning cotton. He is known as "the Father of the Factory System" and he started the idea of child labor in America's factories.
Francis Cabot Lowell
American industrialist who developed the Lowell system, a mill system that included looms that could both weave thread and spin cloth. He hired young women to live and work in his mill
Waltham-Lowell System
A system of labor using young women recruited from farm families to work in factories in Lowell, Chicopee, and other sites in Massachusetts and New Hampshire. The women lived in company boardinghouses with strict rules and curfews and were often required to attend church.
Free labor ideology
Belief that all work in a free society is honorable and that manual labor is degraded when it is equated with slavery or bondage (so opposed slavery).
Labor Unions
An organization formed by workers to strive for better wages and working conditions
Romantic Childhood
Period in which boys and girls were sheltered within home and educated--> available to stable families not depending on child labor
Separate spheres
Nineteenth-century idea in Western societies that men and women, especially of the middle class, should have different roles in society: women as wives, mothers, and homemakers; men as breadwinners and participants in business and politics
Cult of Domesticity
idealized view of women & home; women, self-less caregiver for children, refuge for husbands in the mid to late 1800s.
Companionate marriage
marriage built on love, intimacy, and personal choice rather than social obligation
Chain migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there. For example many individuals from Europe moved to America because their family was here.
Nativist movement
Discrimination against immigrants (notably Irish and Germans), heavily anti-Catholic, sought to limit power of immigrants (Know-Nothing Party)
Know-Nothing Party
Political party of the 1850s that was anti-Catholic and anti-immigrant
Commonwealth v Hunt (1842)
a landmark ruling of the MA Supreme Court establishing the legality of labor unions and the legality of union workers striking if an employer hired non-union workers.
Ten-hour movement
Labor unions advocated a 10-hour workday. Previously workers had worked from sun up to sundown.
Sarah Bagley
organized the Lowell Female Labor Reform Association in the 1849s. The group petitoned for the state legislature that there was a 10 hours workday
Andrew Jackson
The seventh President of the United States (1829-1837), who as a general in the War of 1812 defeated the British at New Orleans (1815). As president he opposed the Bank of America, objected to the right of individual states to nullify disagreeable federal laws, and increased the presidential powers.
Missouri Compromise (1820)
over the issue of slavery in Missouri. It was decided Missouri entered as a slave state and Maine entered as a free state and all states North of the 36th parallel were free states and all South were slave states.
Denmark Vesey
United States freed slave and insurrectionist in South Carolina who was involved in planning an uprising of slaves and was hanged (1767-1822)
Tariff of 1828
A protective tariff passed by the U.S. Congress that came to be known as the "Tariff of Abominations" to its Southern detractors because of the effects it had on the Antebellum Southern economy; it was the highest tariff in U.S. peacetime and its goal was to protect industry in the northern United States from competing European goods by increasing the prices of European products.
Election of 1828
Jackson defeats John Quincy Adams in this election, becoming our 7th President