AP Bio Unit 1 - Chemistry of Life
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
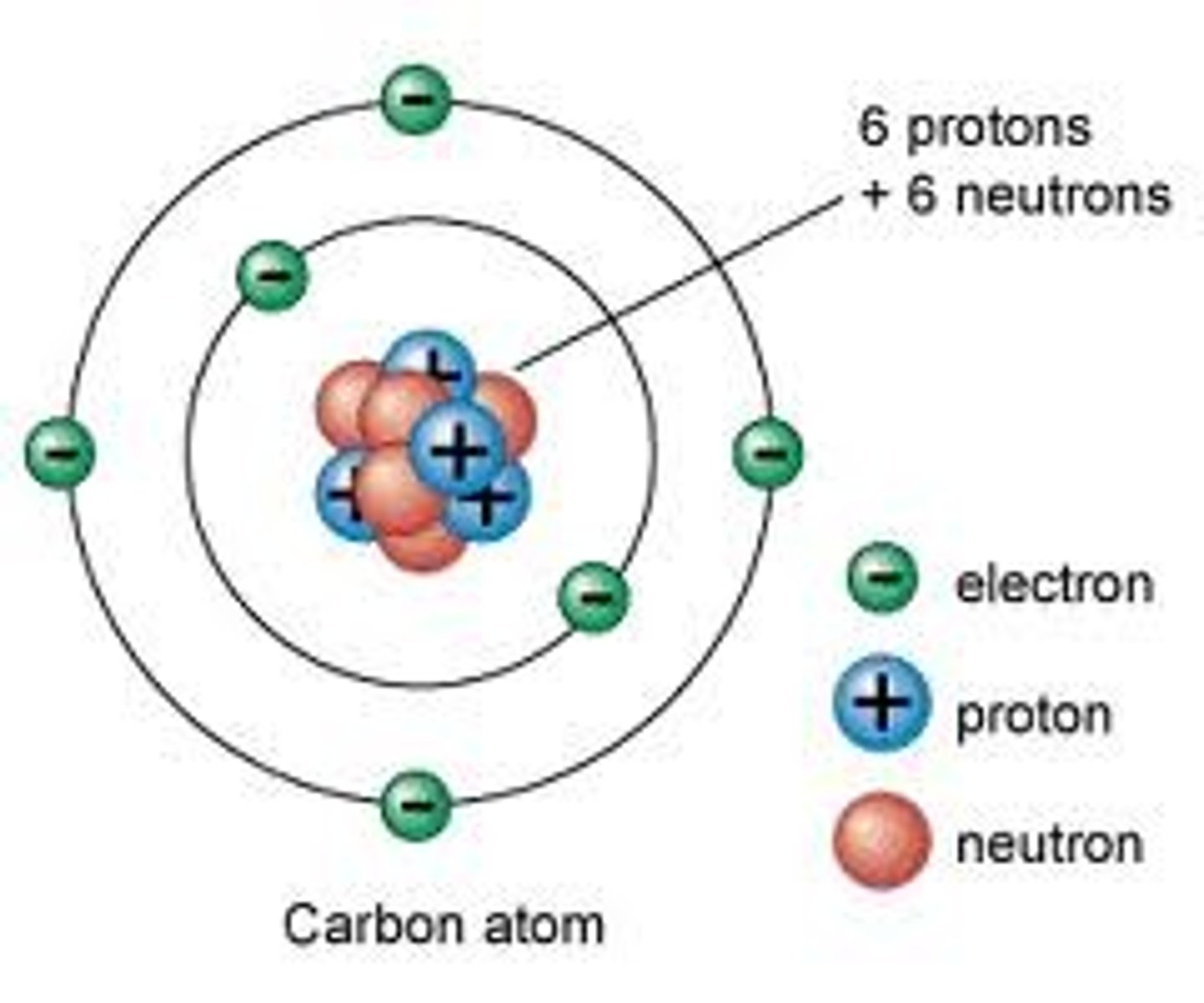
Atom
Basic unit of matter
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
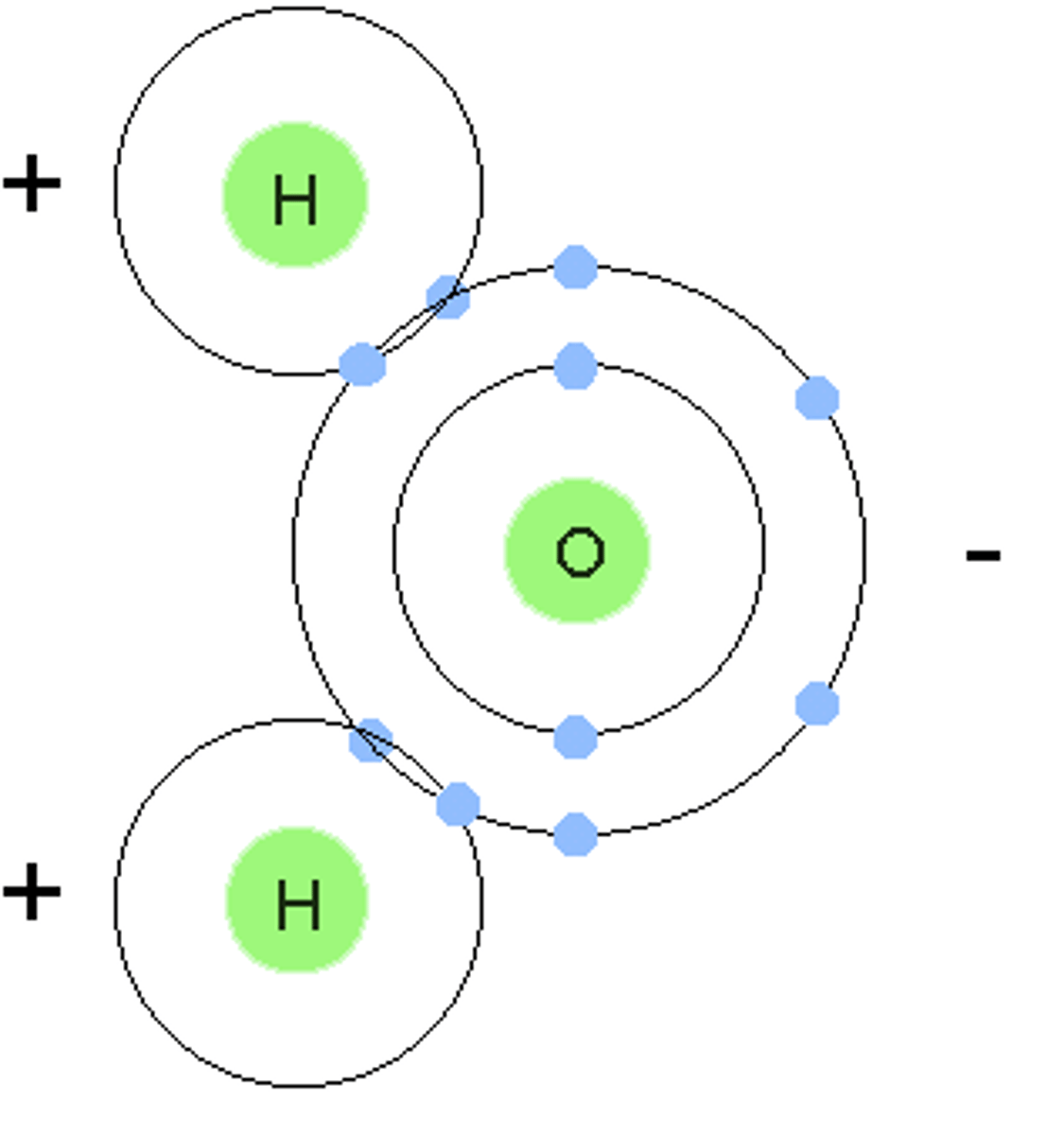
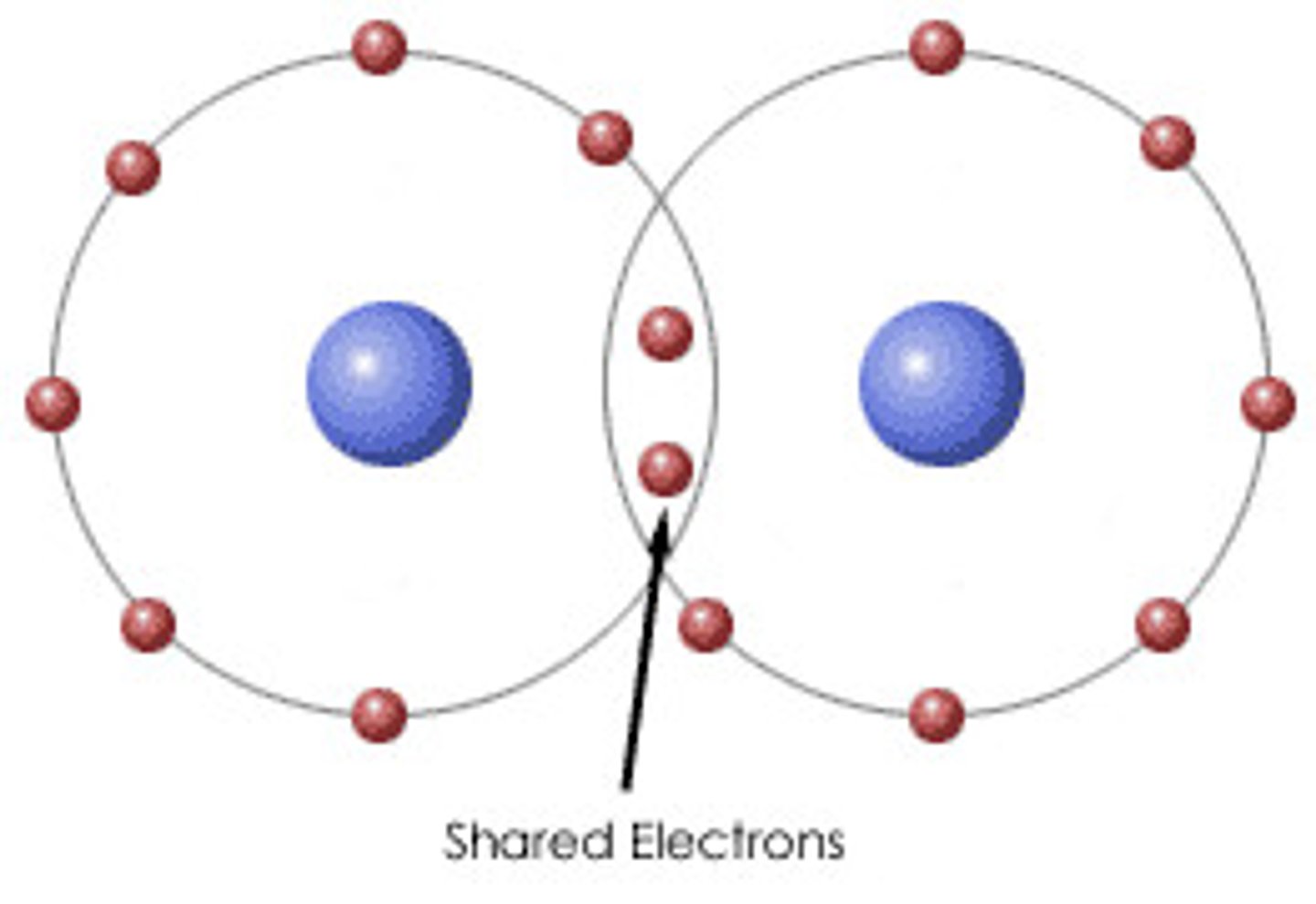
Covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
Ionic bond
Chemical bond that occurs when an atom transfers an electron to another atom
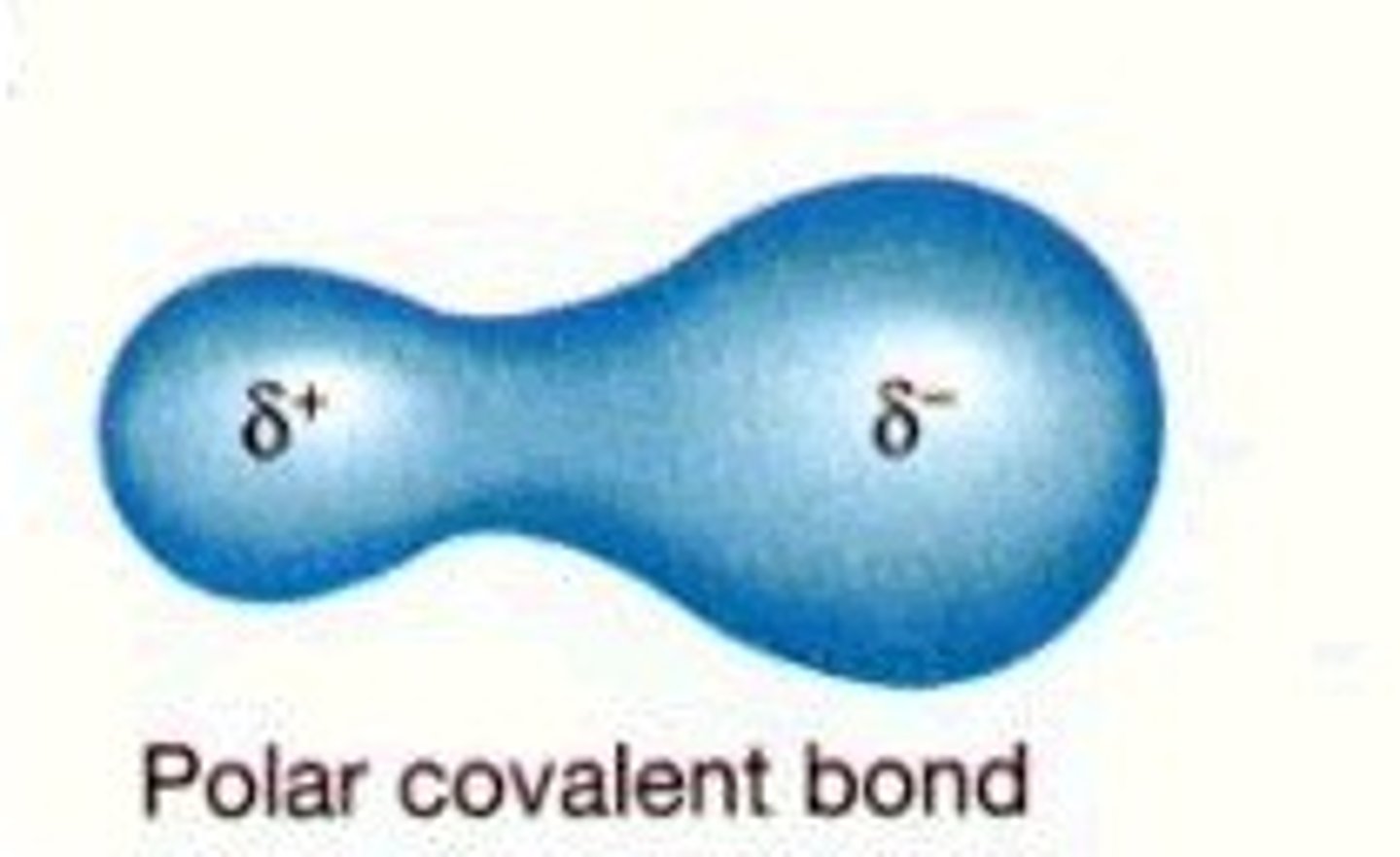
Polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
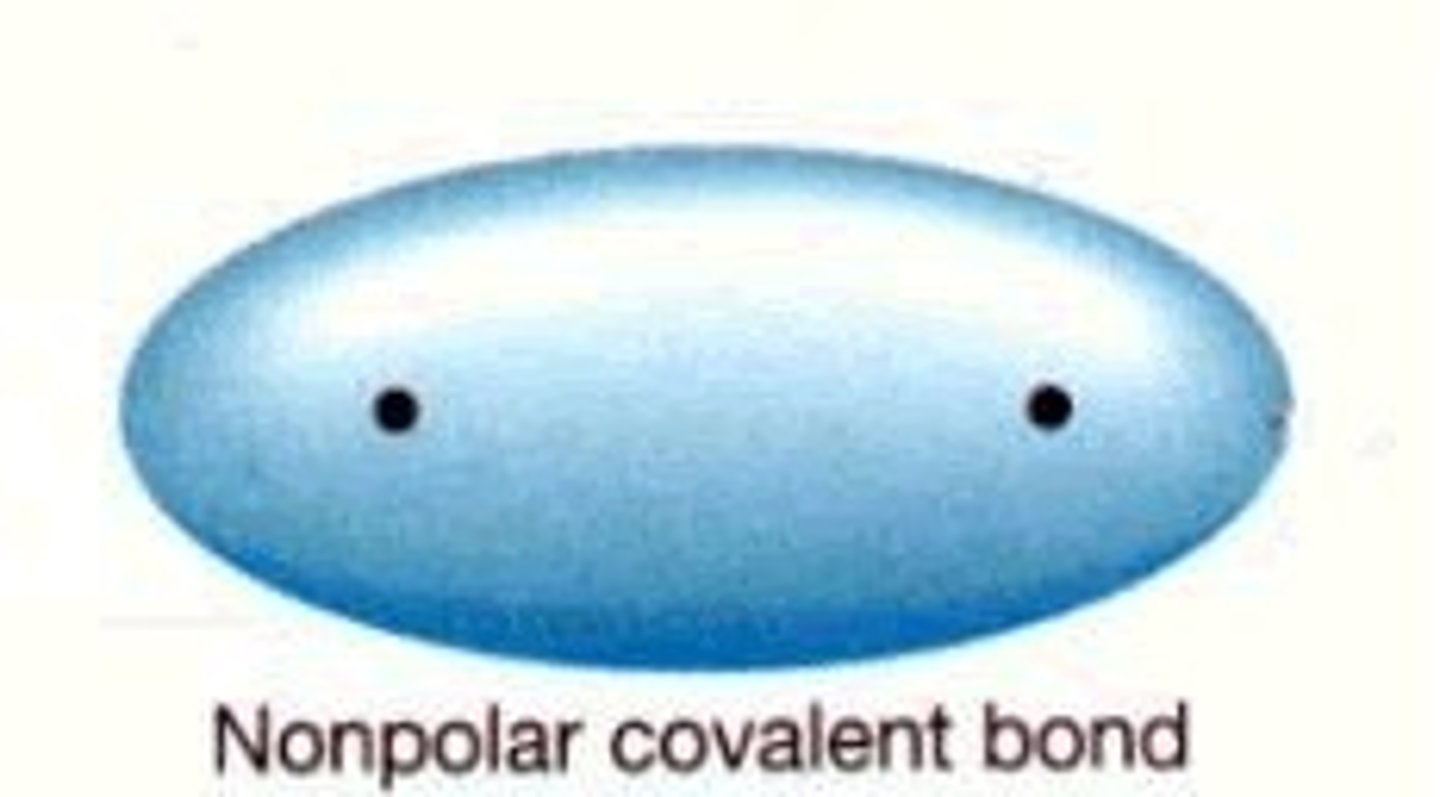
Nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water.
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
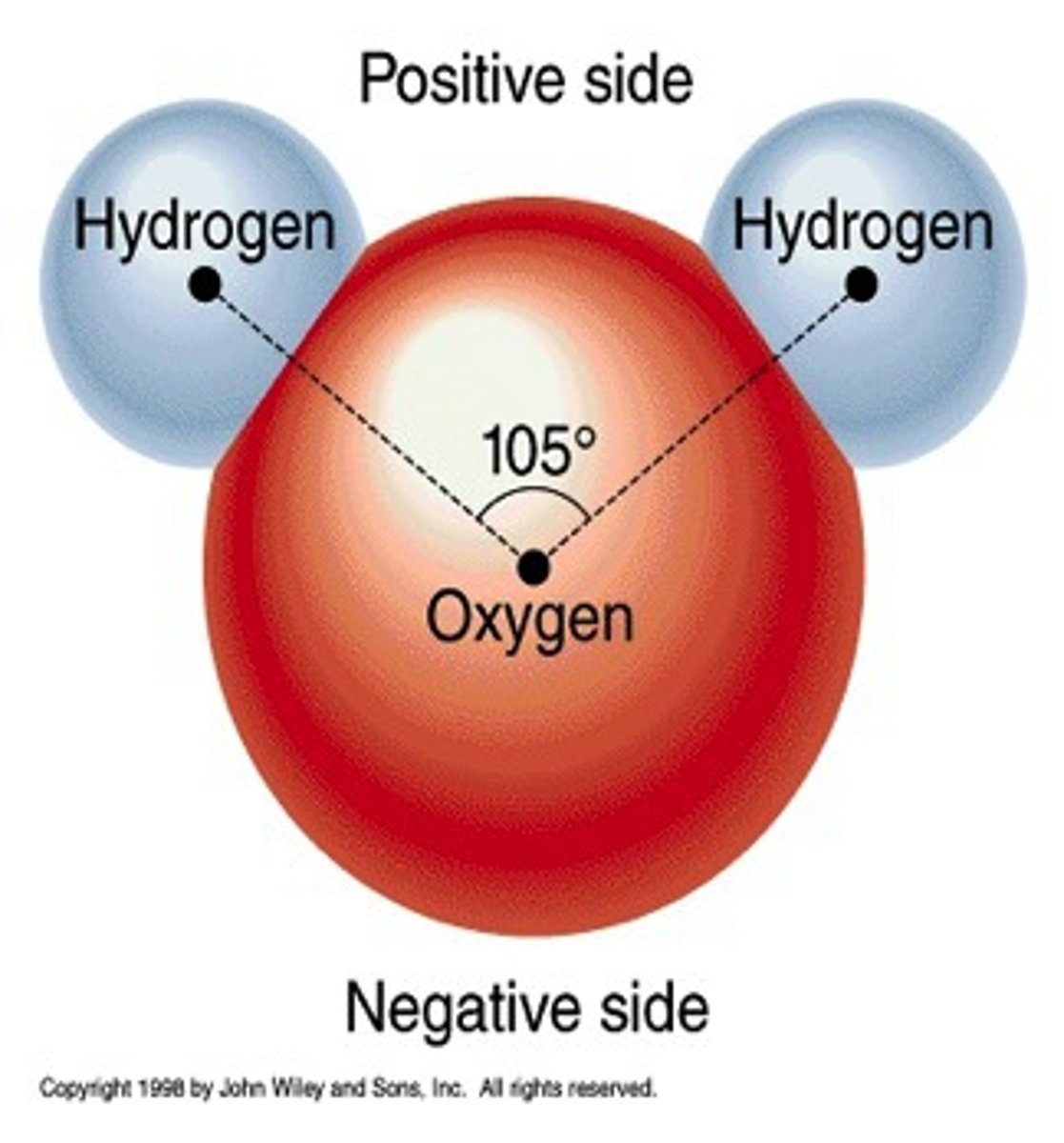
Oxygen and Nitrogen
Most common highly electronegative elements that are important in biology; will form partial negative charges in polar covalent bonds
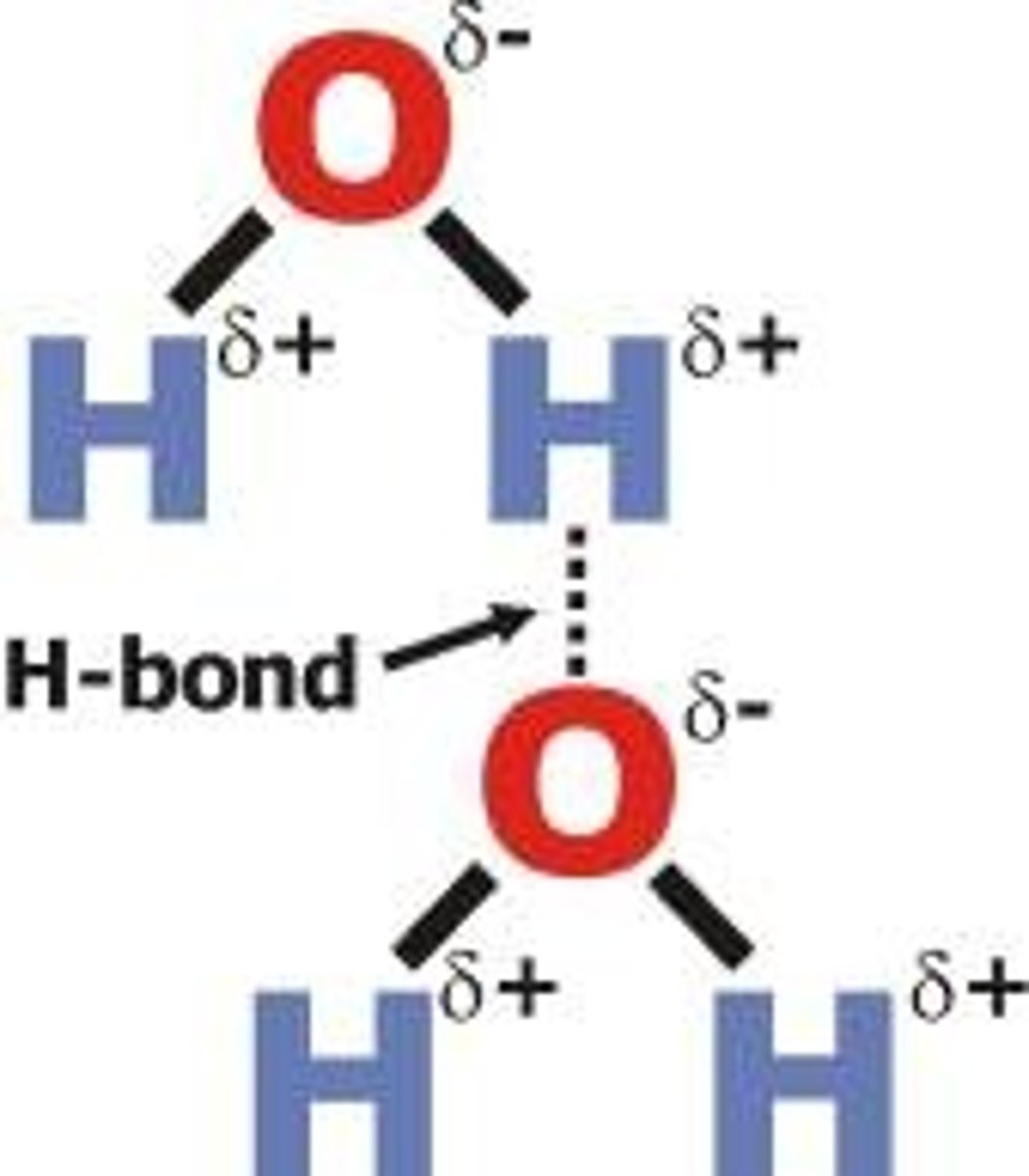
Hydrogen bonding
Interaction between partially positive hydrogen atom from one molecule and partially negative oxygen atom of another molecule
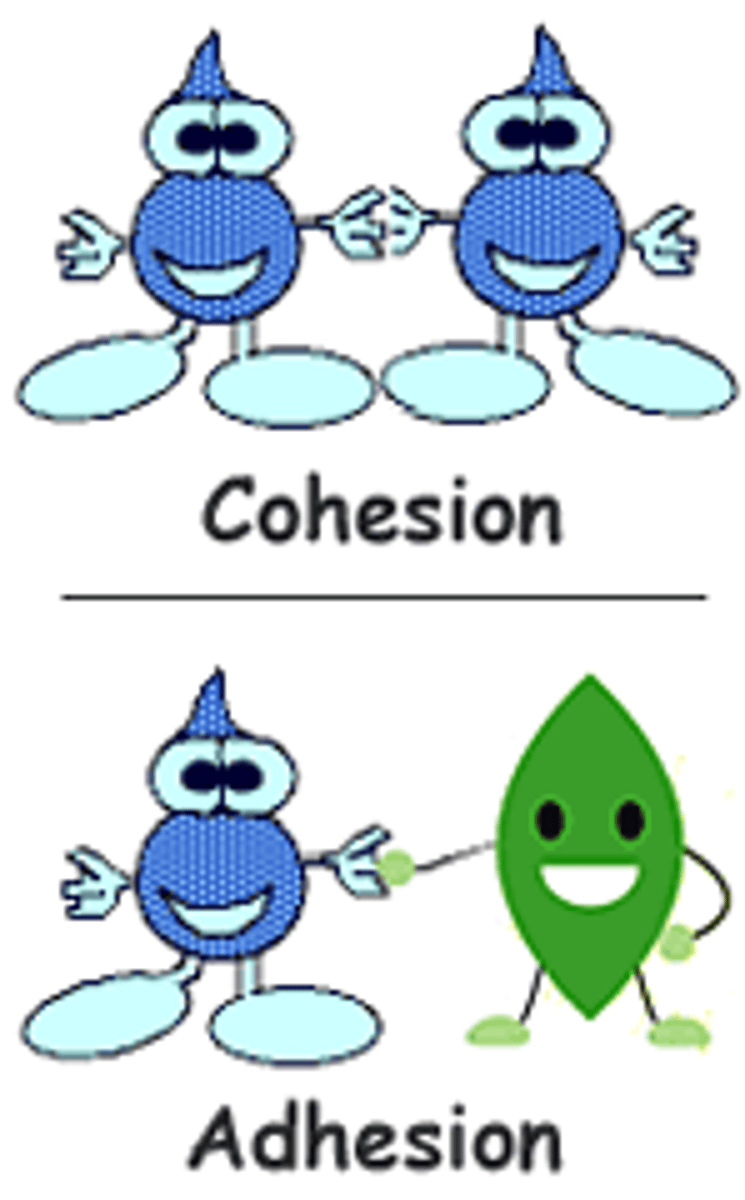
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
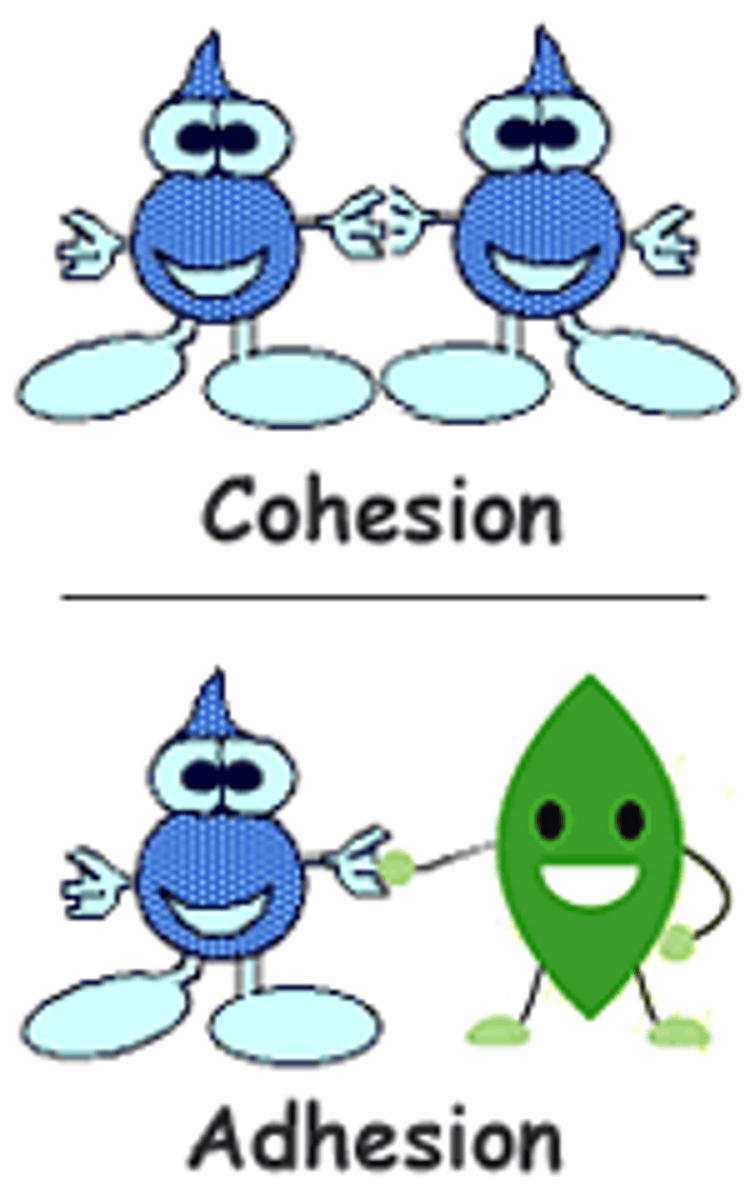
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
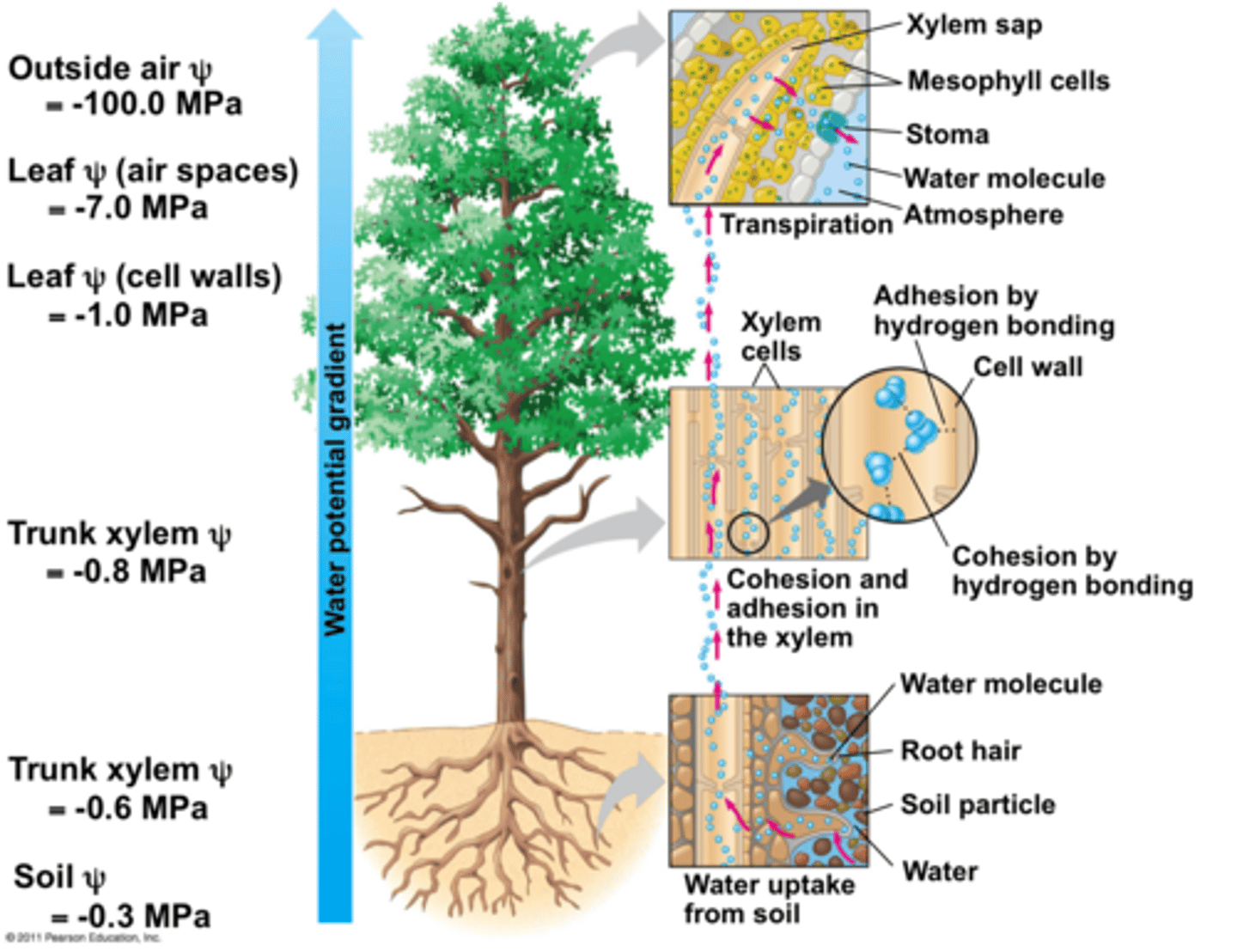
Transpiration
Movement of water from roots through the stems and leaves of plants.
Surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid

Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
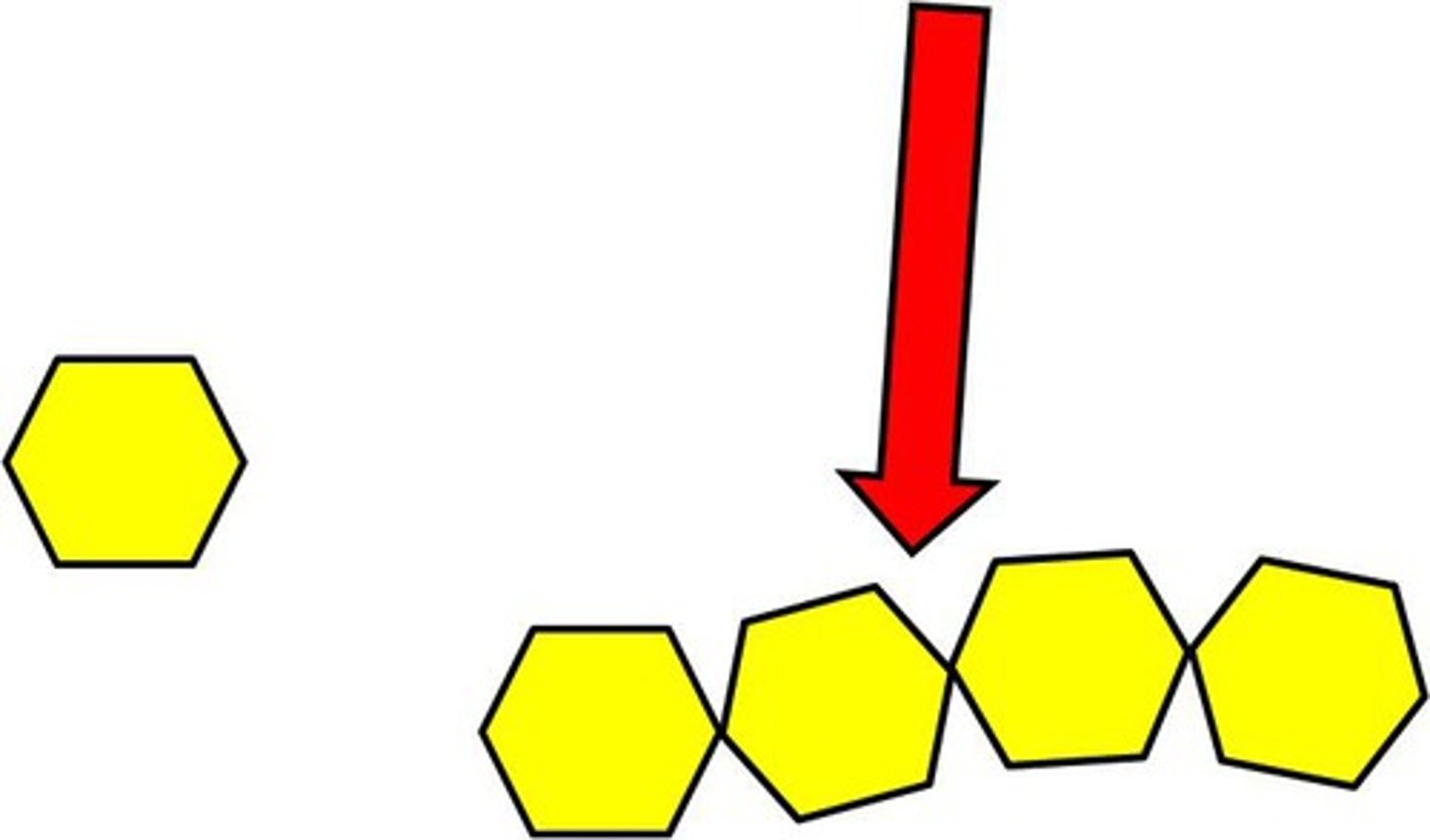
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
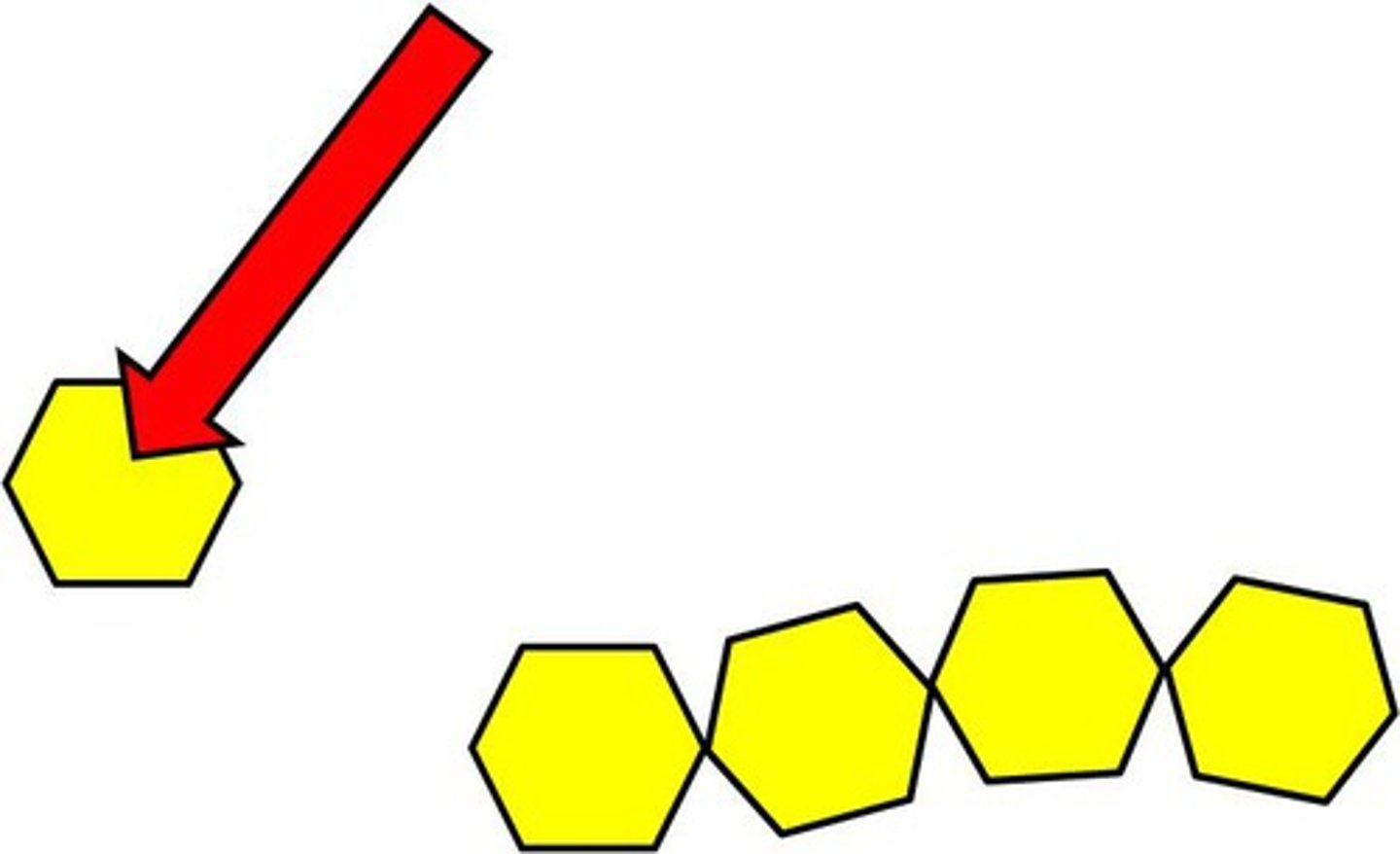
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together by covalent bonds
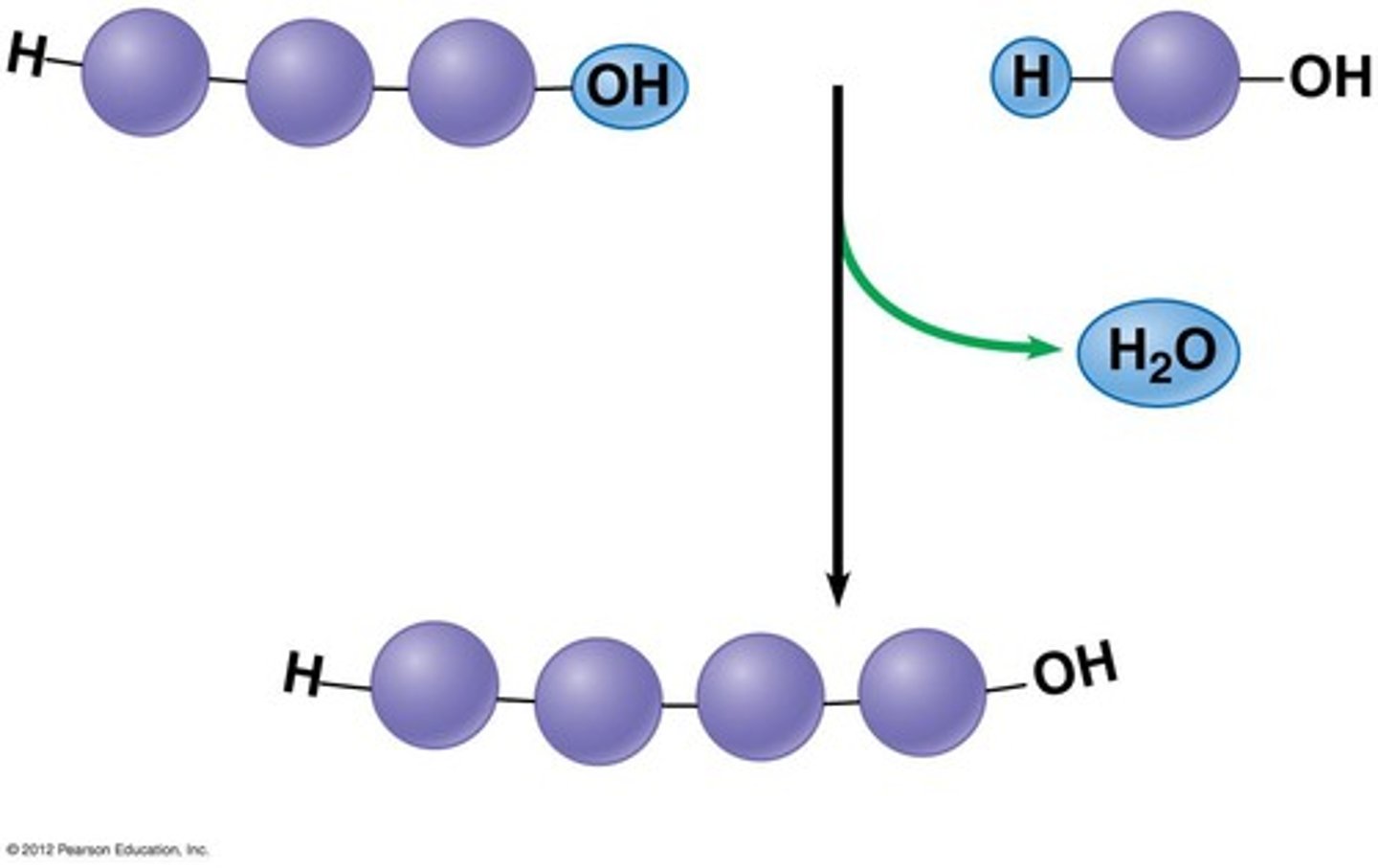
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
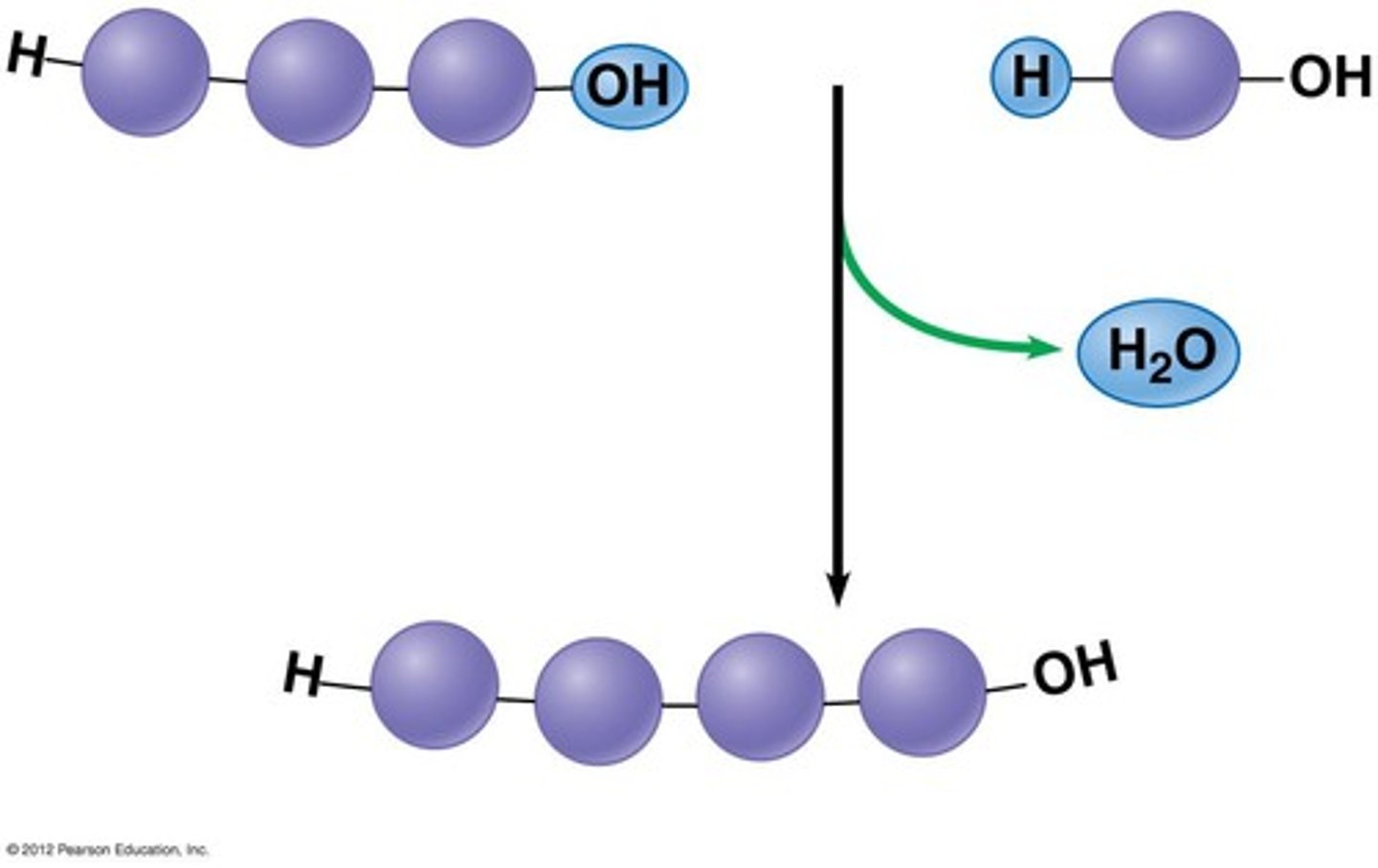
Condensation reaction
A reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water; also called dehydration reaction.
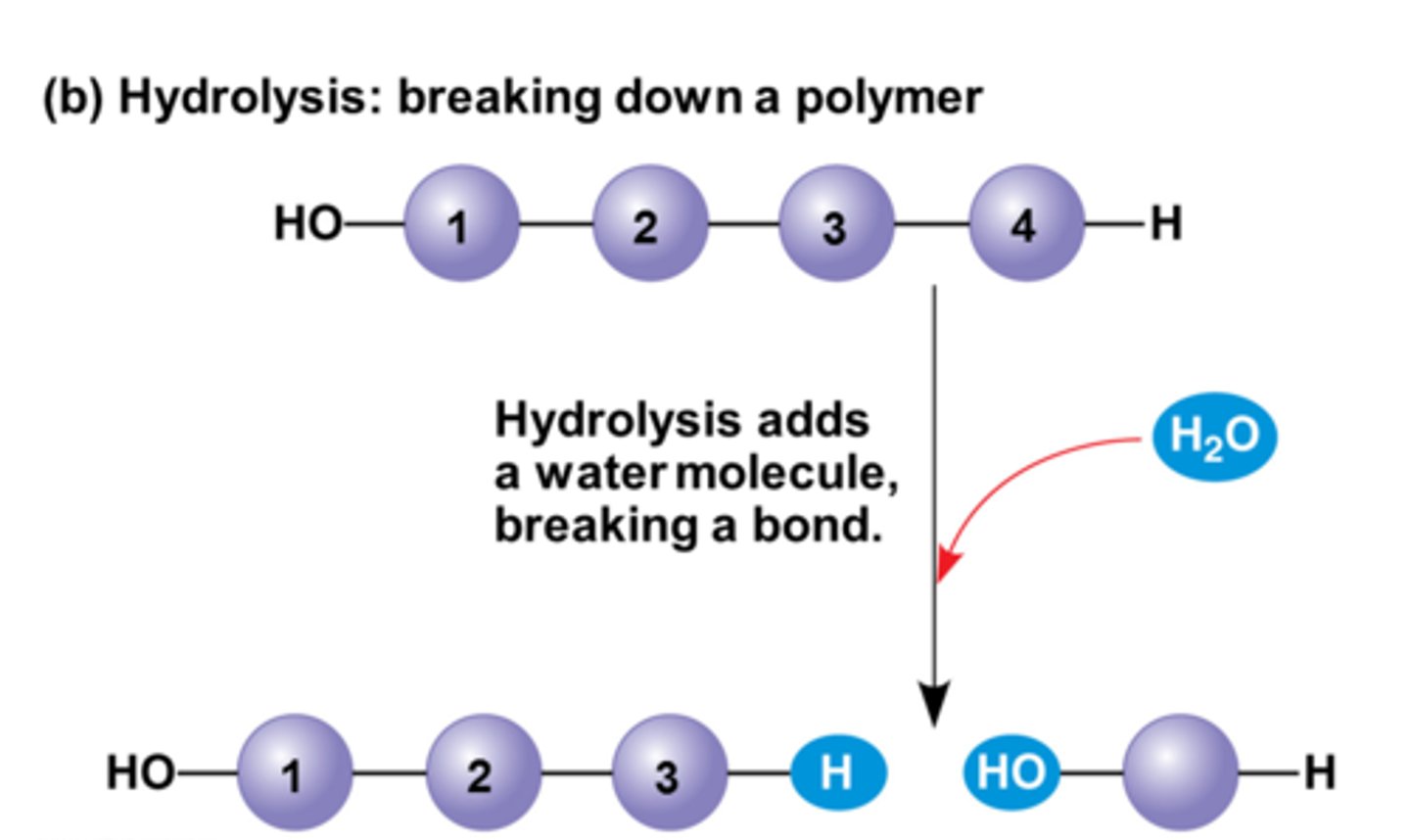
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
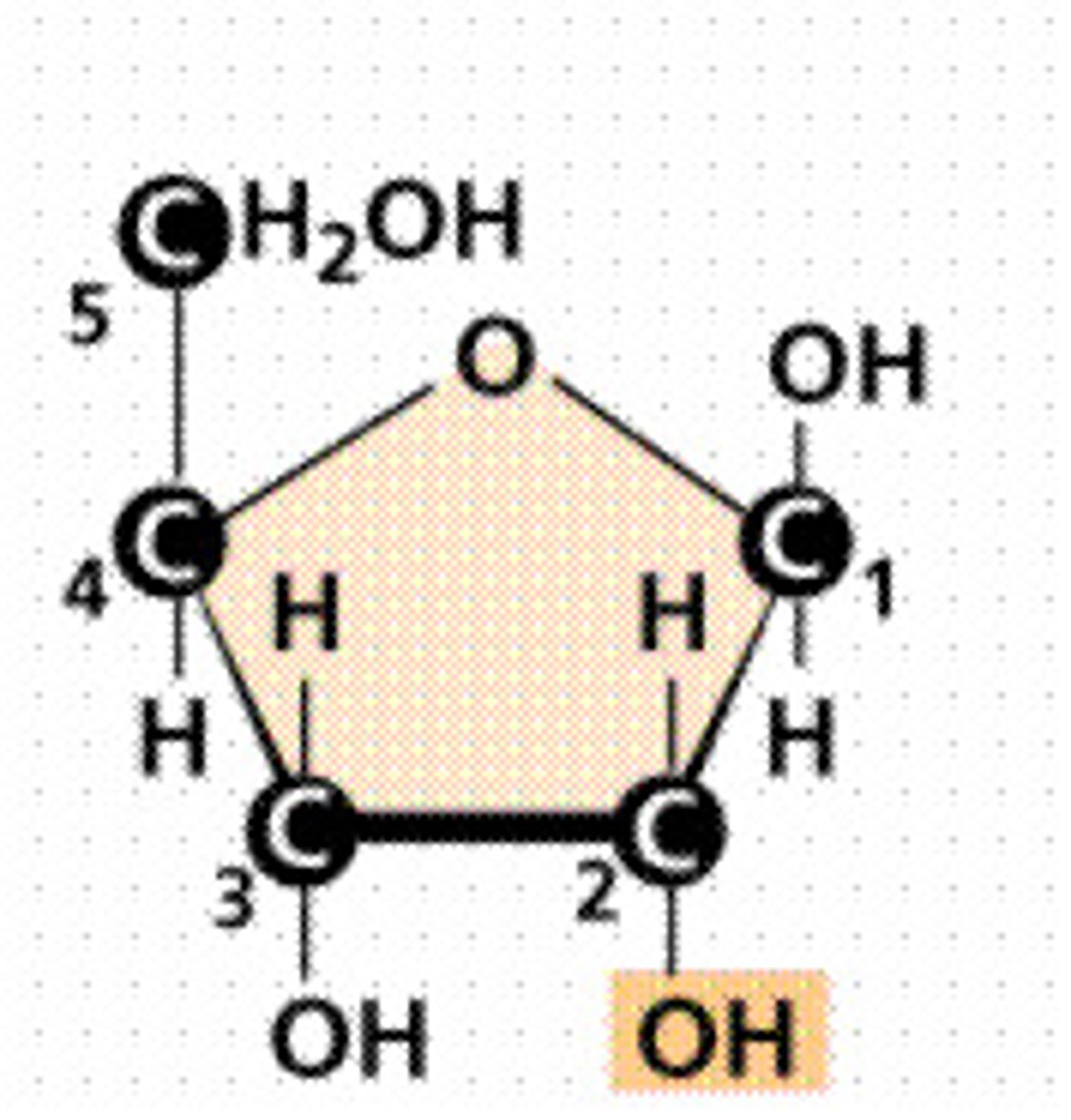
Monosaccharide
the monomer of carbohydrates (ex: glucose)
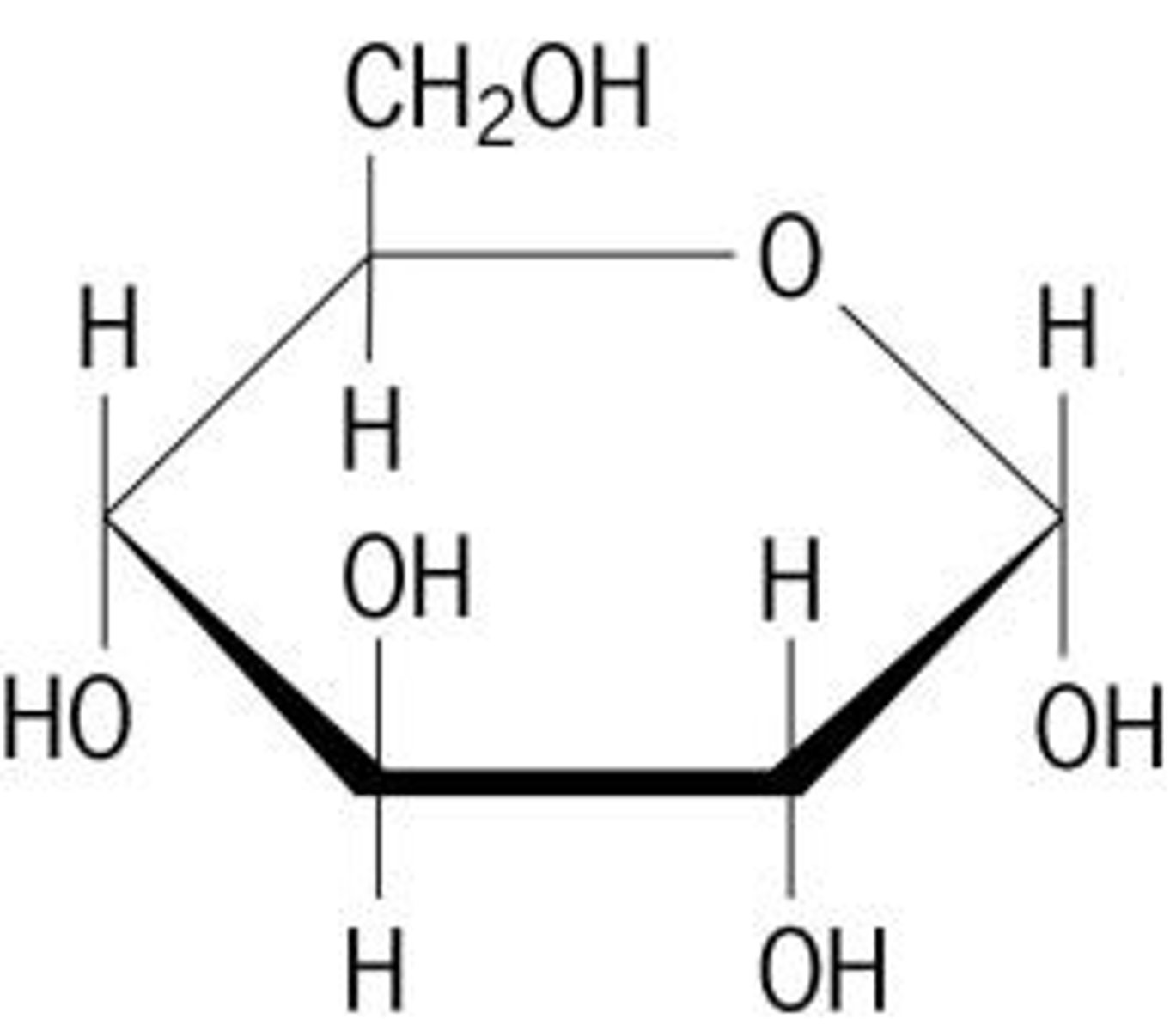
Polysaccharide
carbohydrate polymer (ex: starch, glycogen)
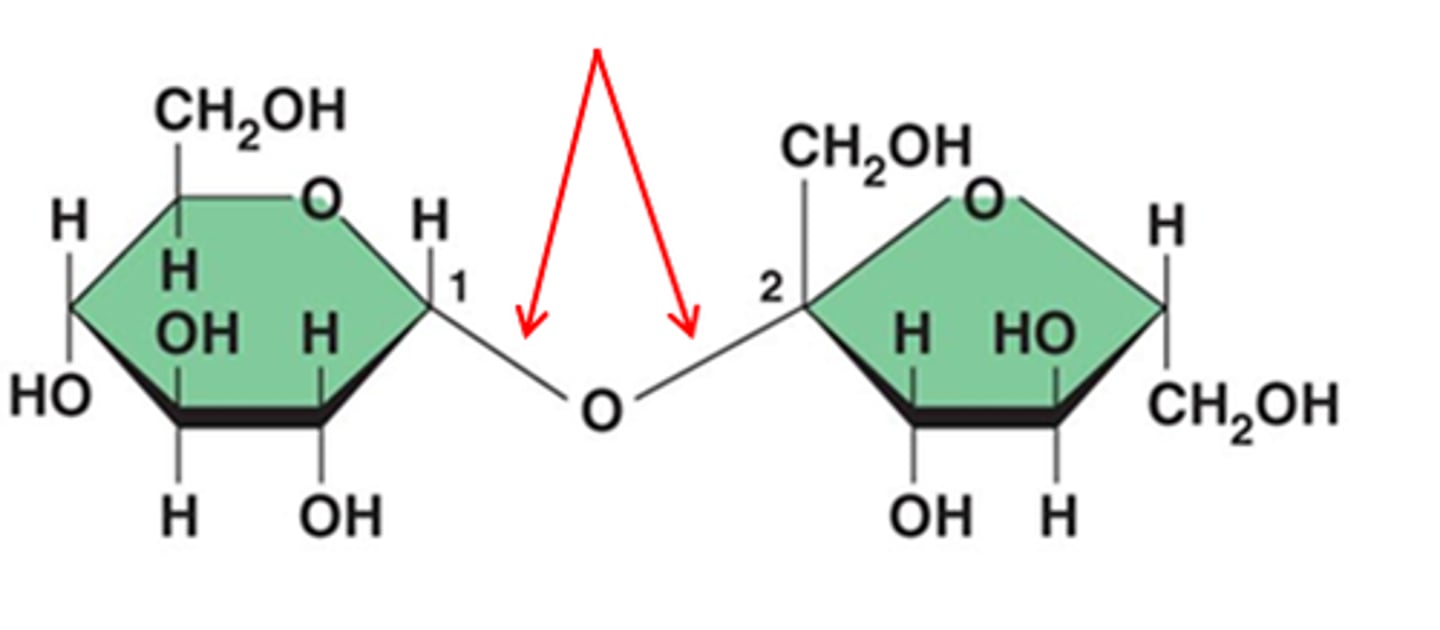
Glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
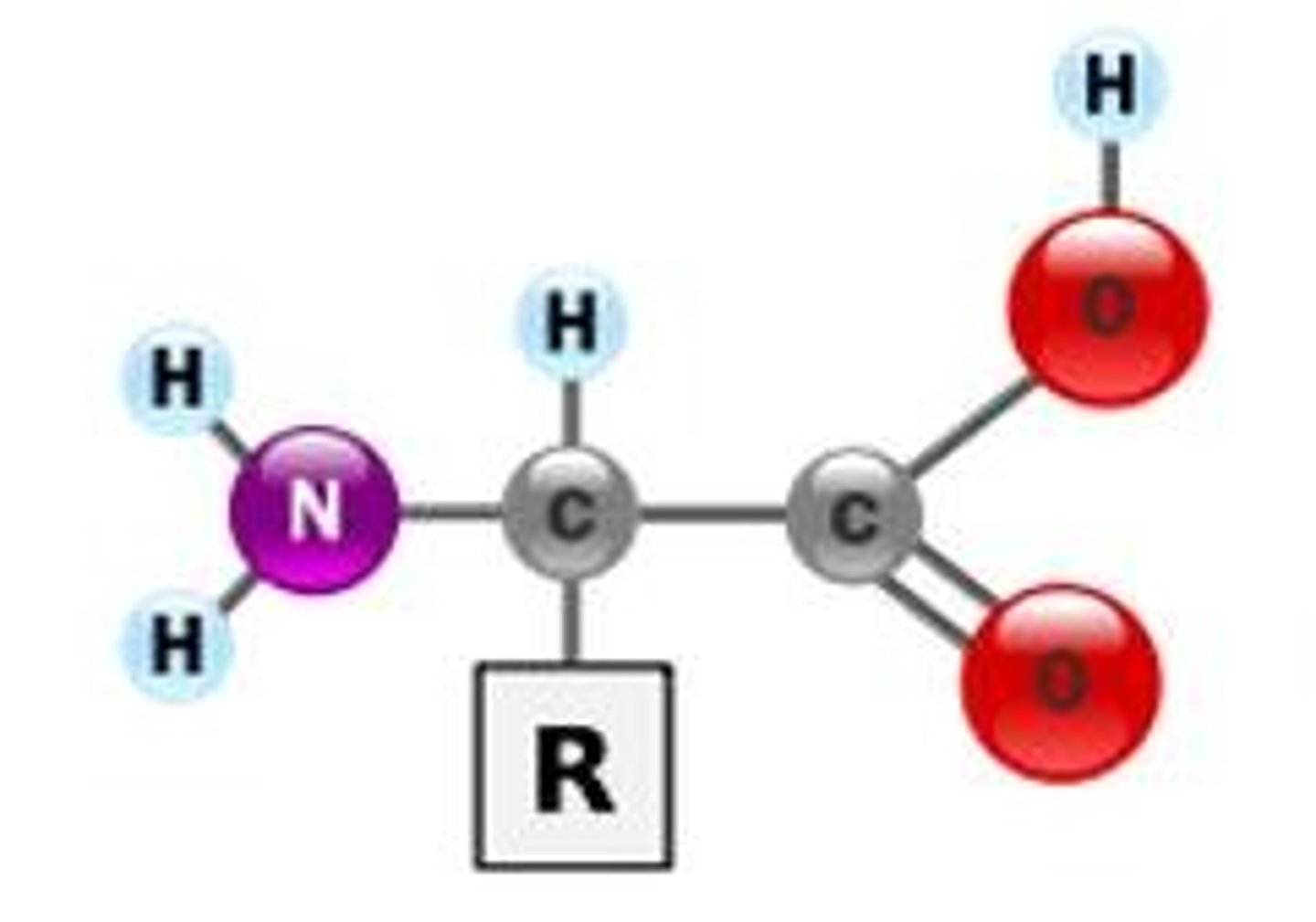
Amino acid
Building blocks of protein
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
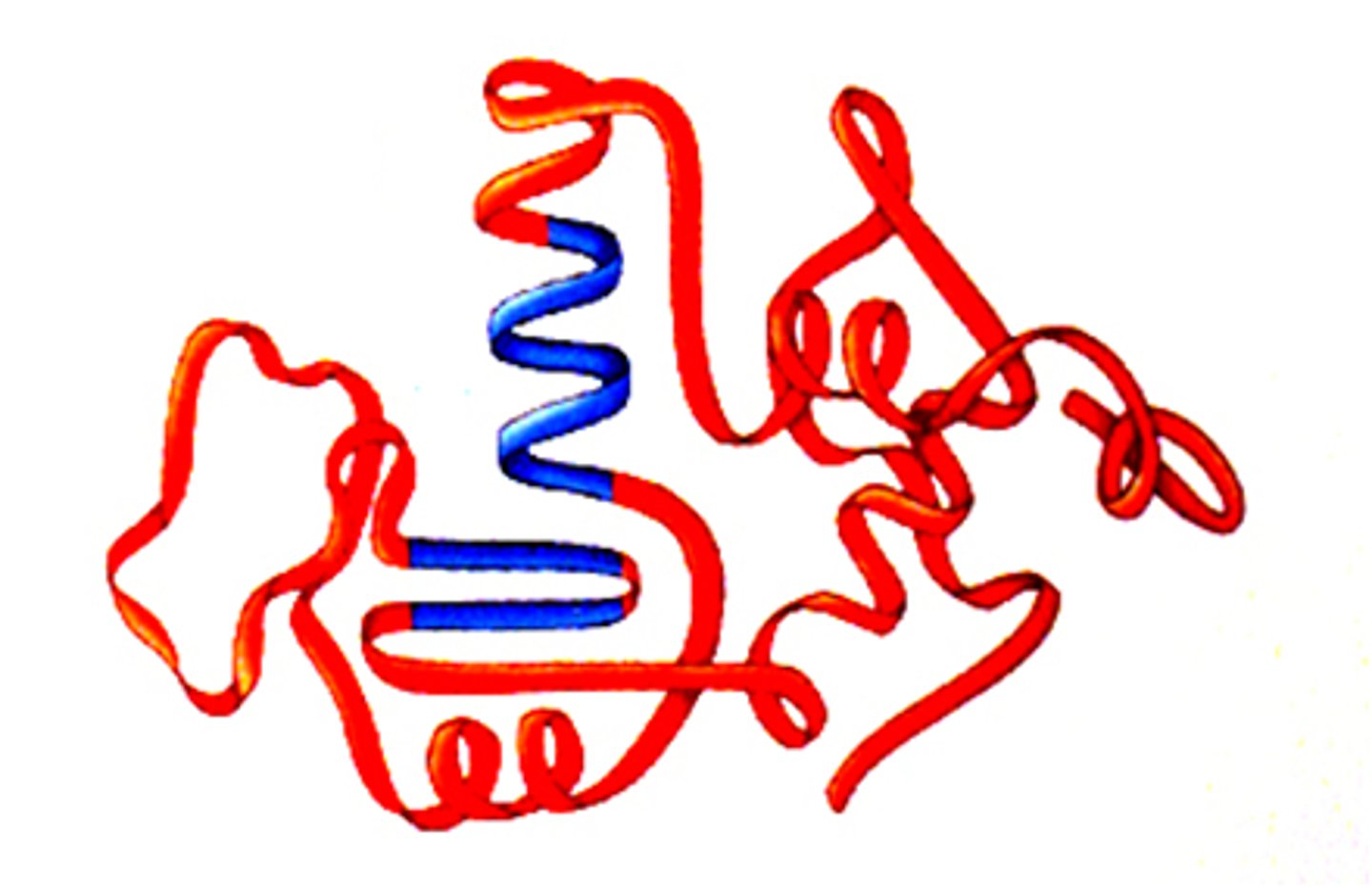
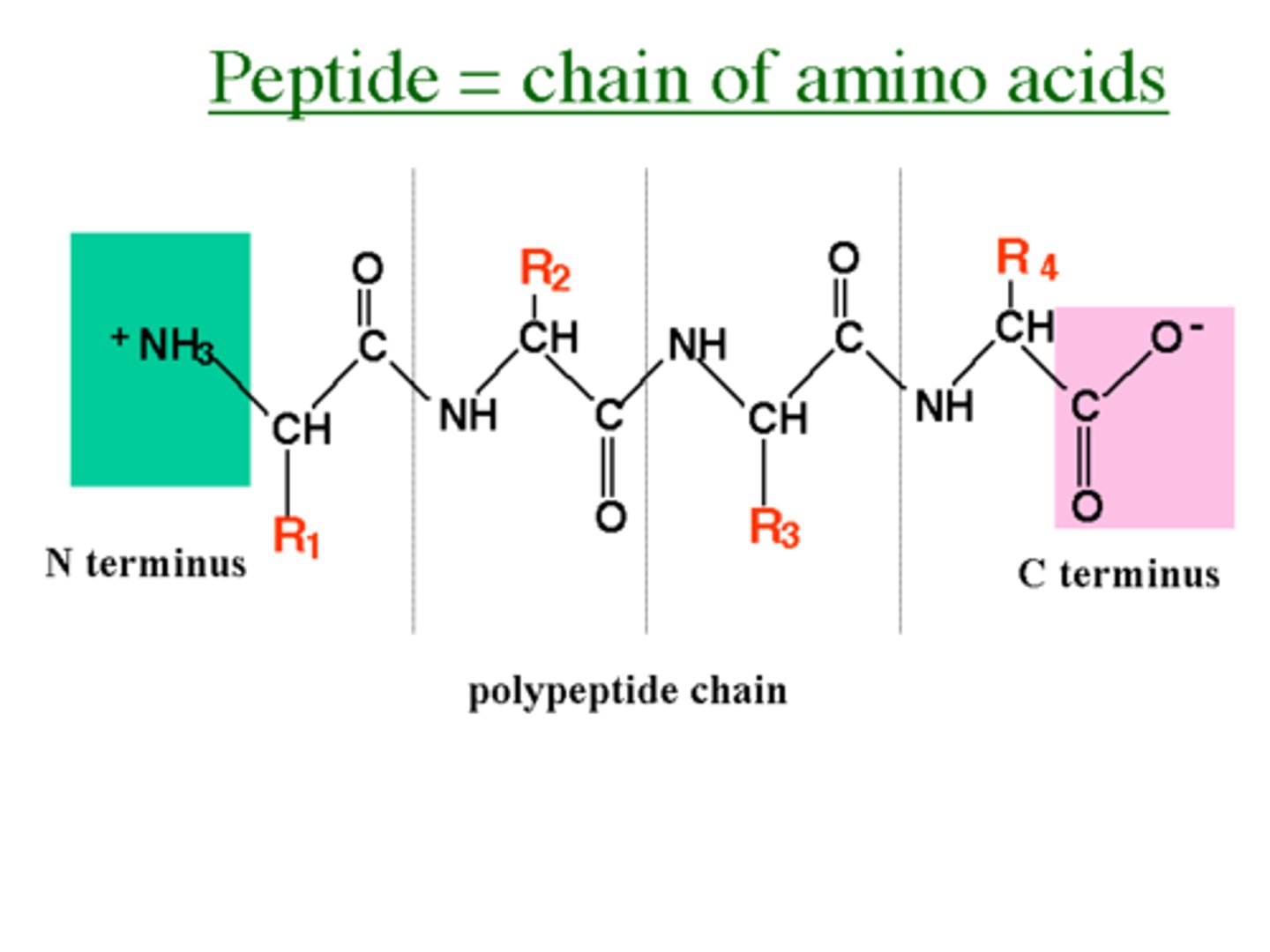
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
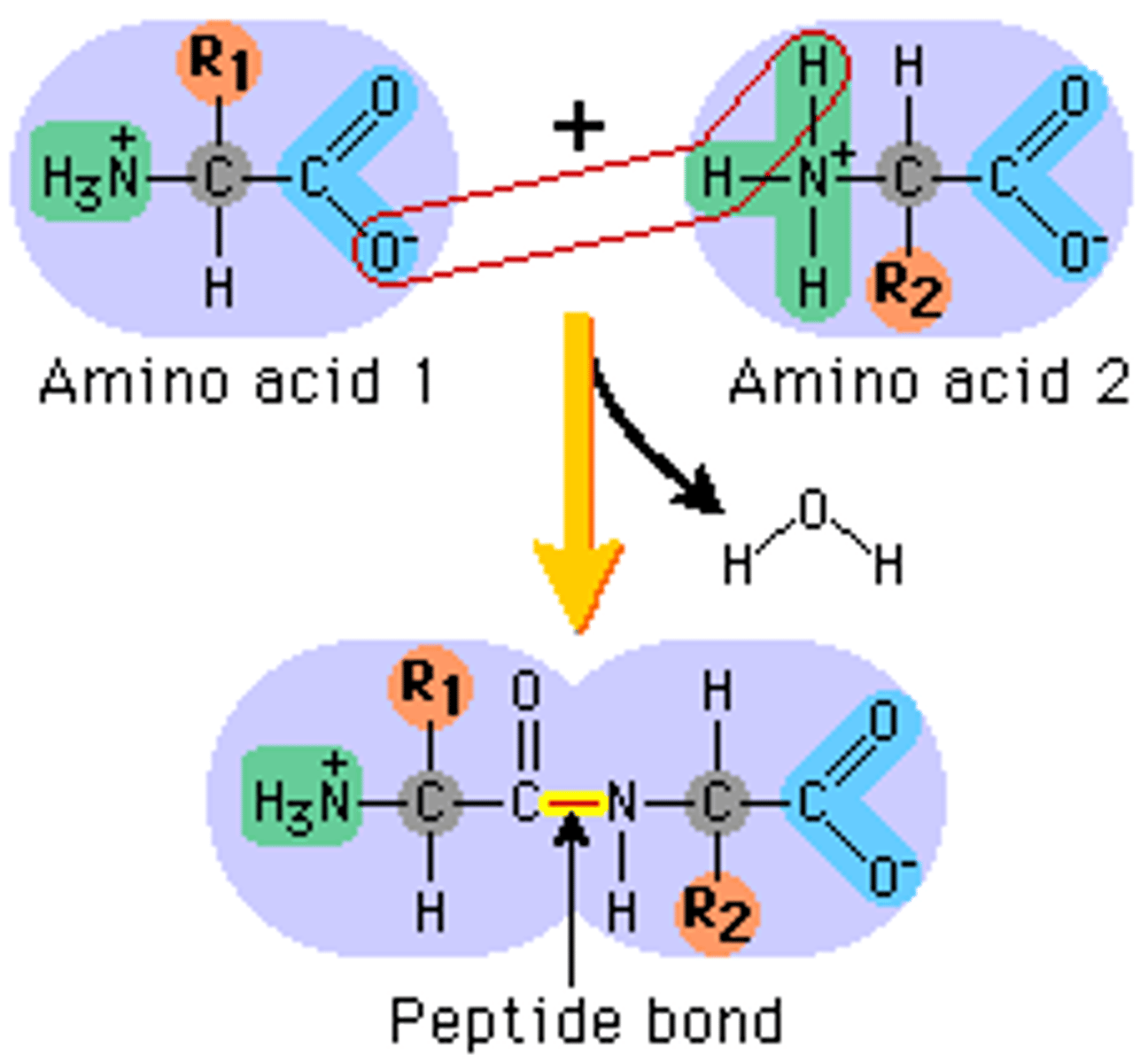
Peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
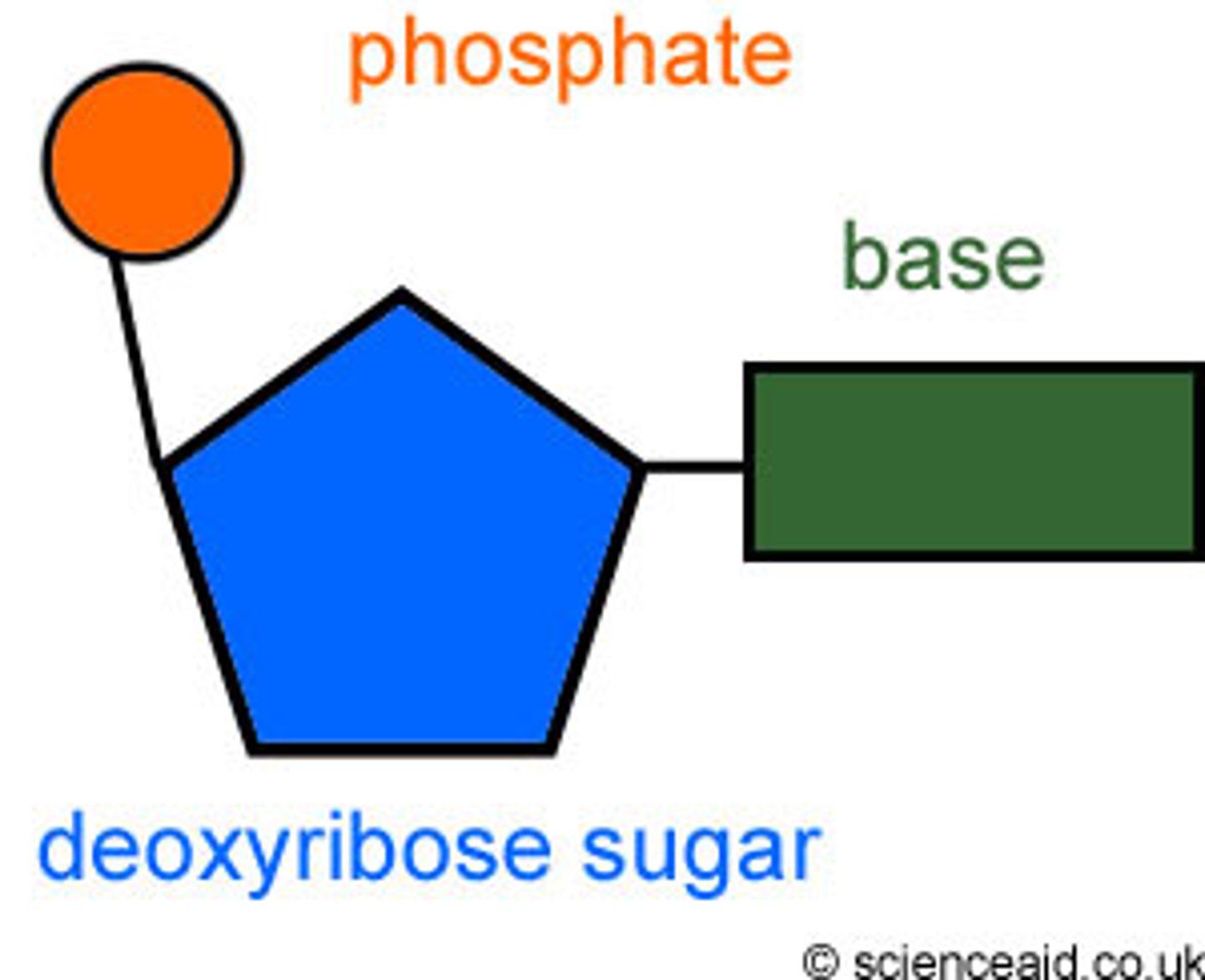
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Phosphodiester bond
a covalent bond that is responsible for the polymerization of nucleic acids by linking sugars and phosphates of adjacent nucleotides
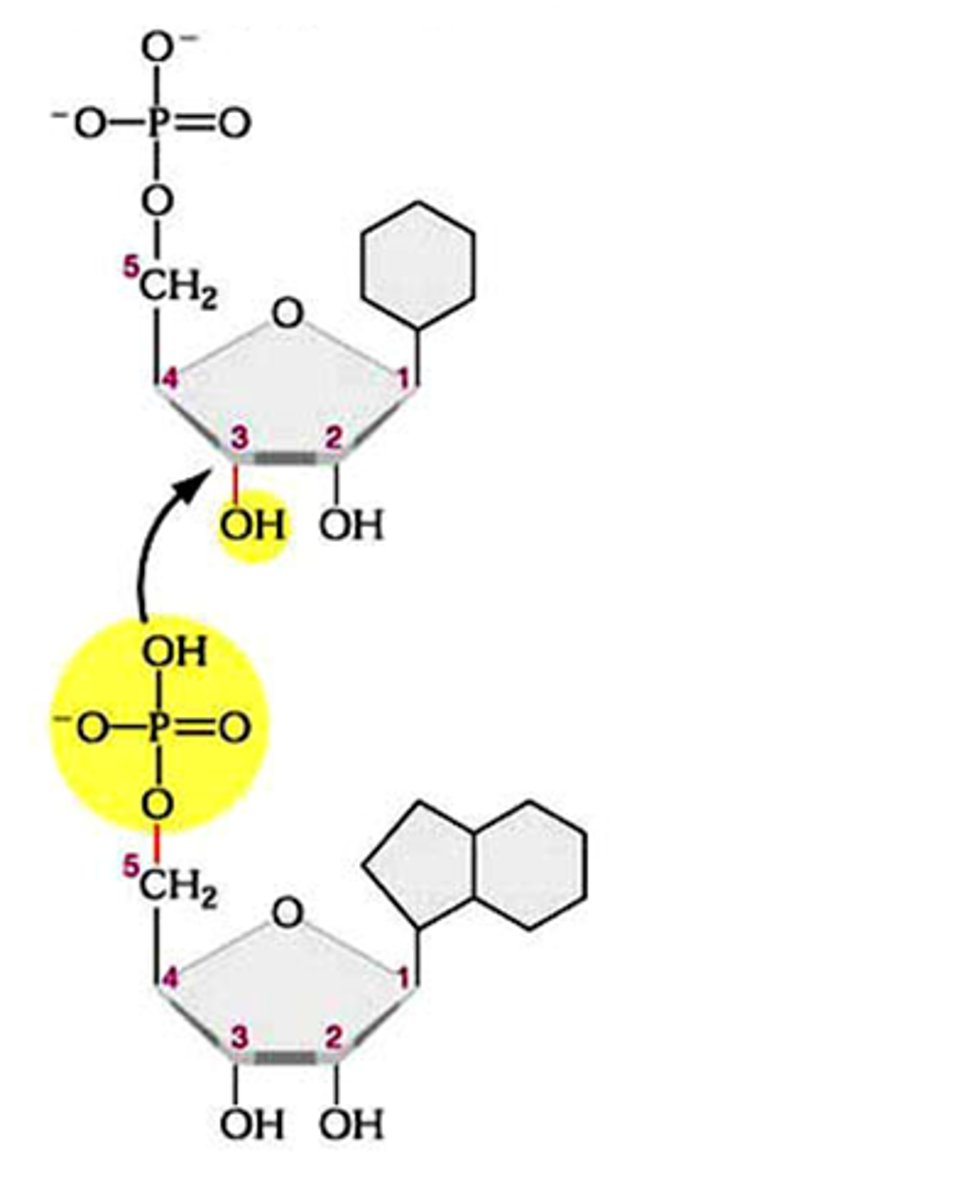
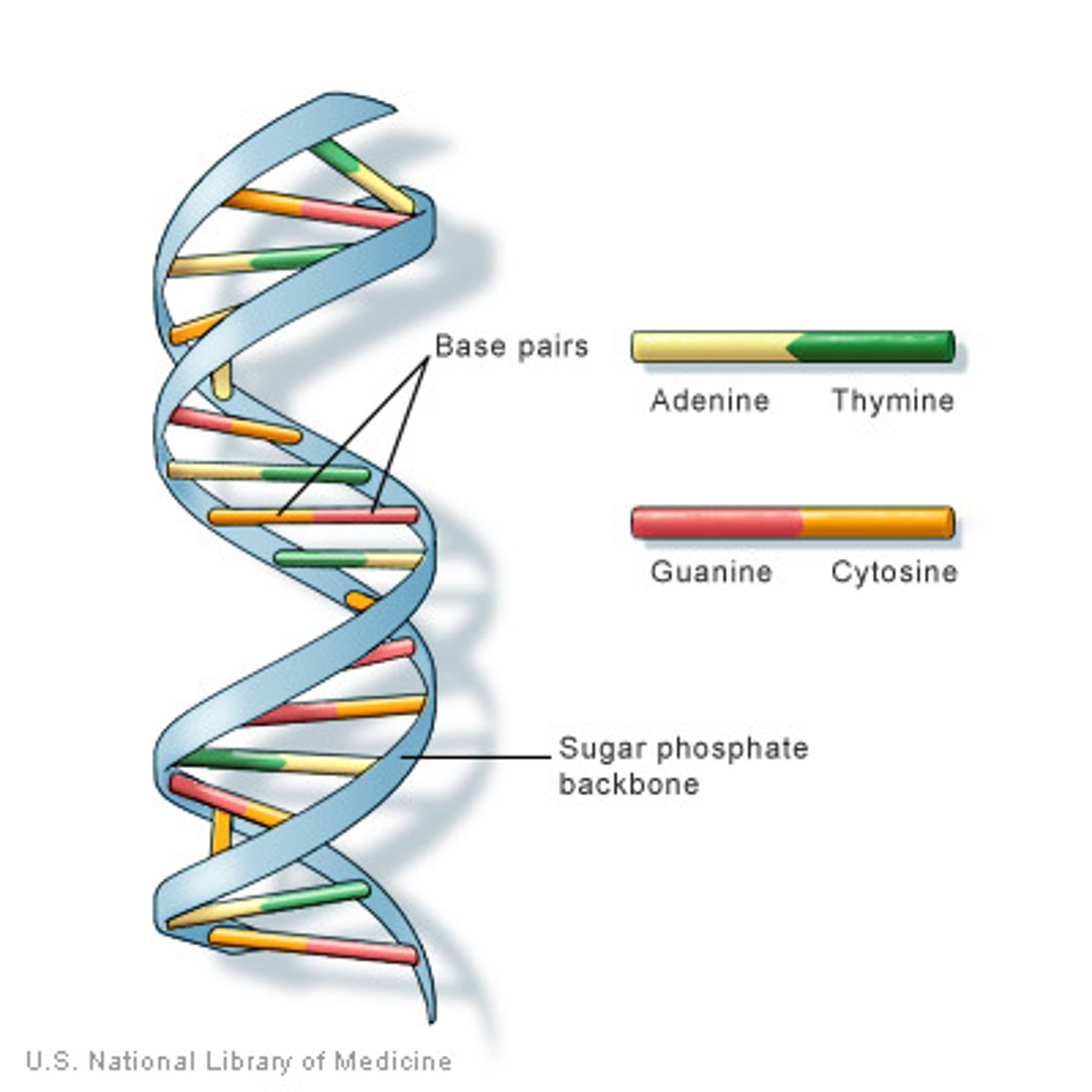
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid; a polymer of nucleotides
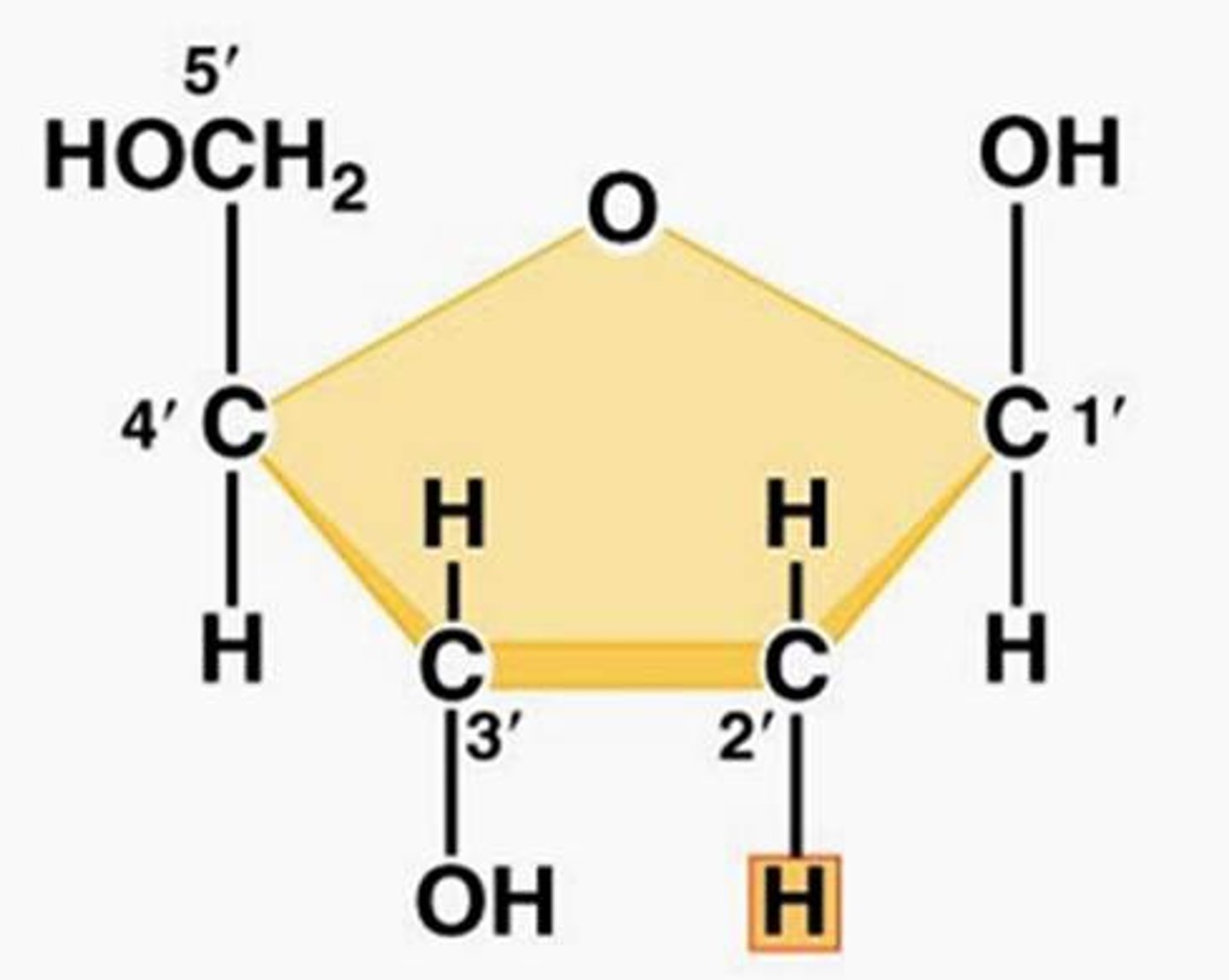
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
RNA
ribonucleic acid; a polymer of nucleotides
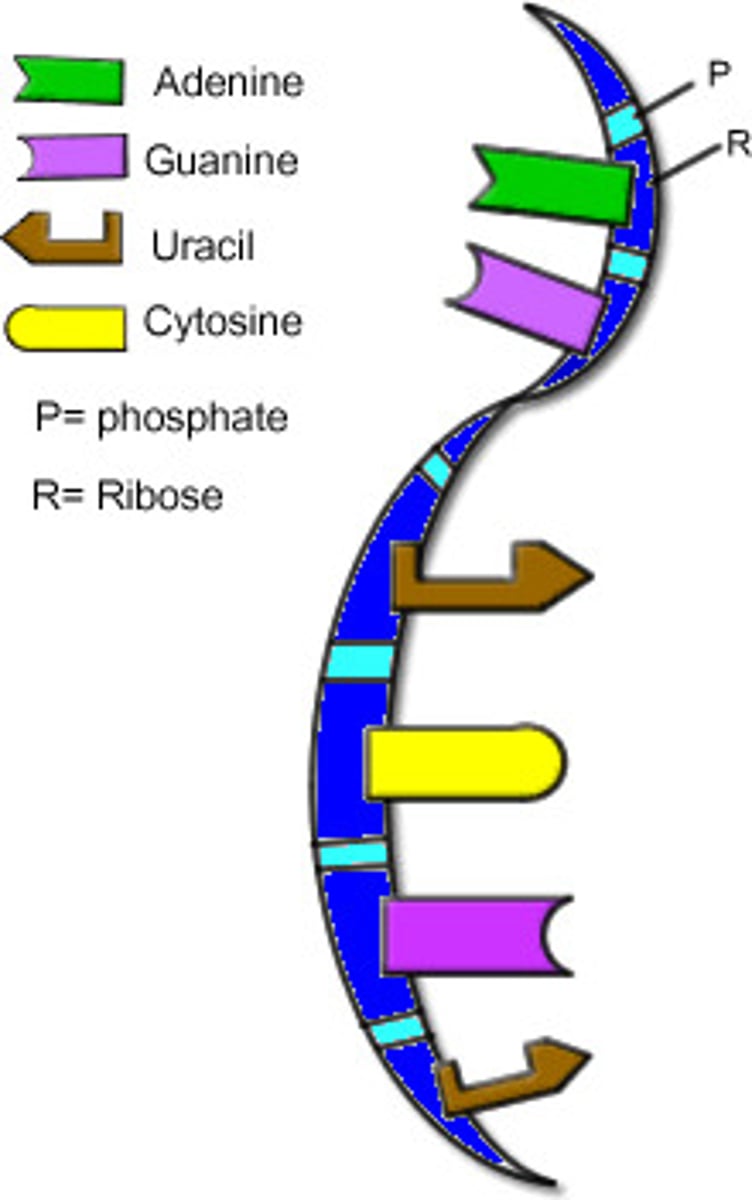
Ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
Phospholipid
a lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule
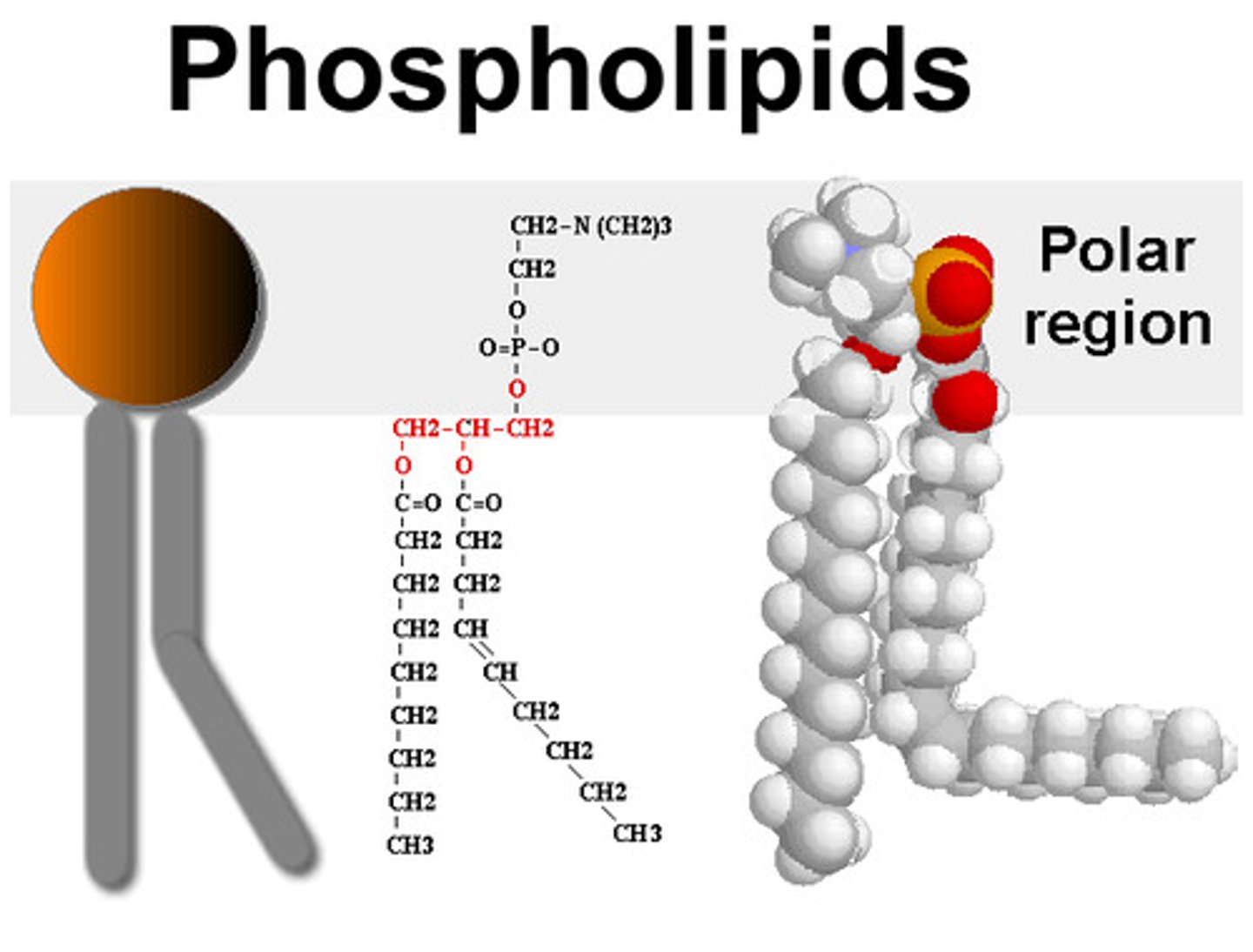
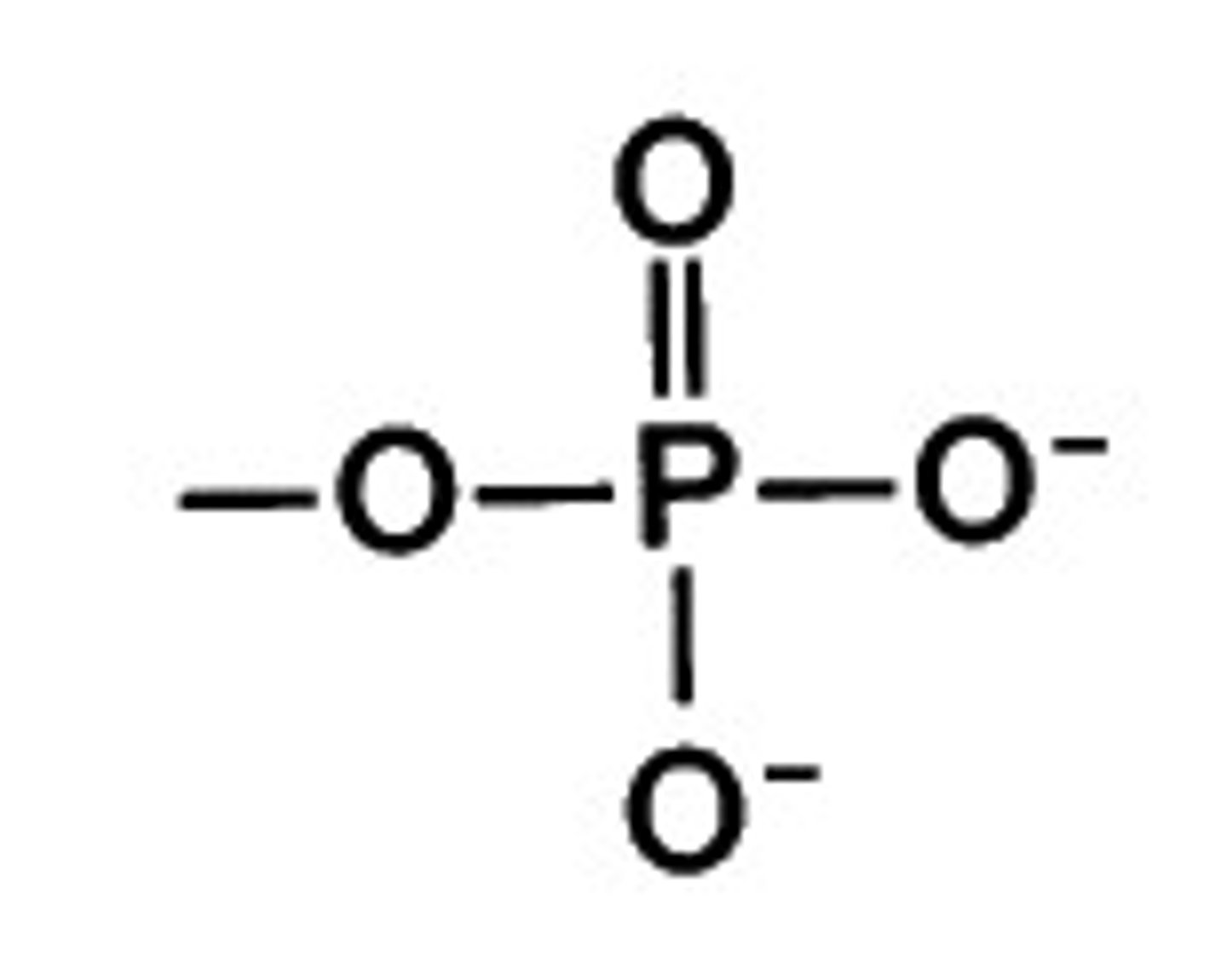
Phosphate group
A negatively charged chemical group consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms.
Hydrocarbon chain
A chain of carbon atoms bonded together with hydrogen atoms bonded onto the carbons; nonpolar.
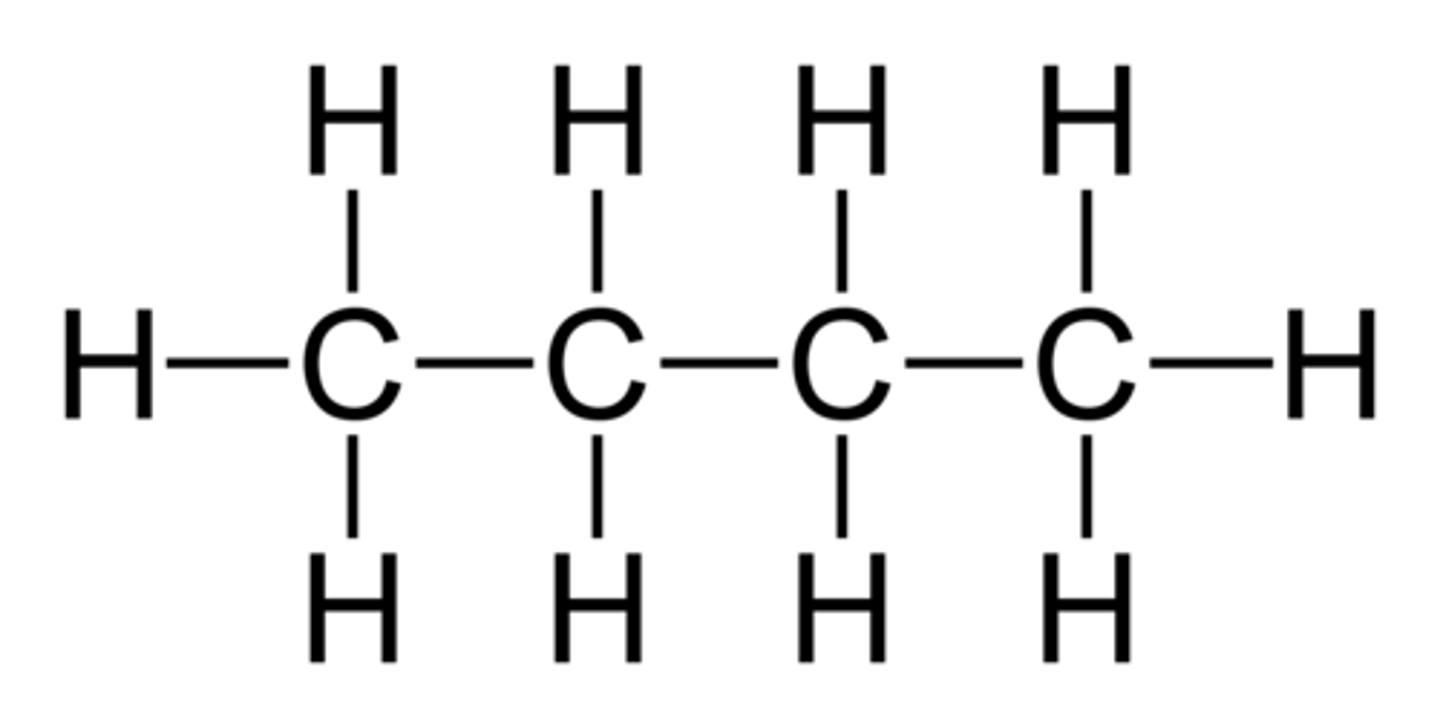
Fatty acid
Building blocks of lipids; long, nonpolar hydrocarbon chains.
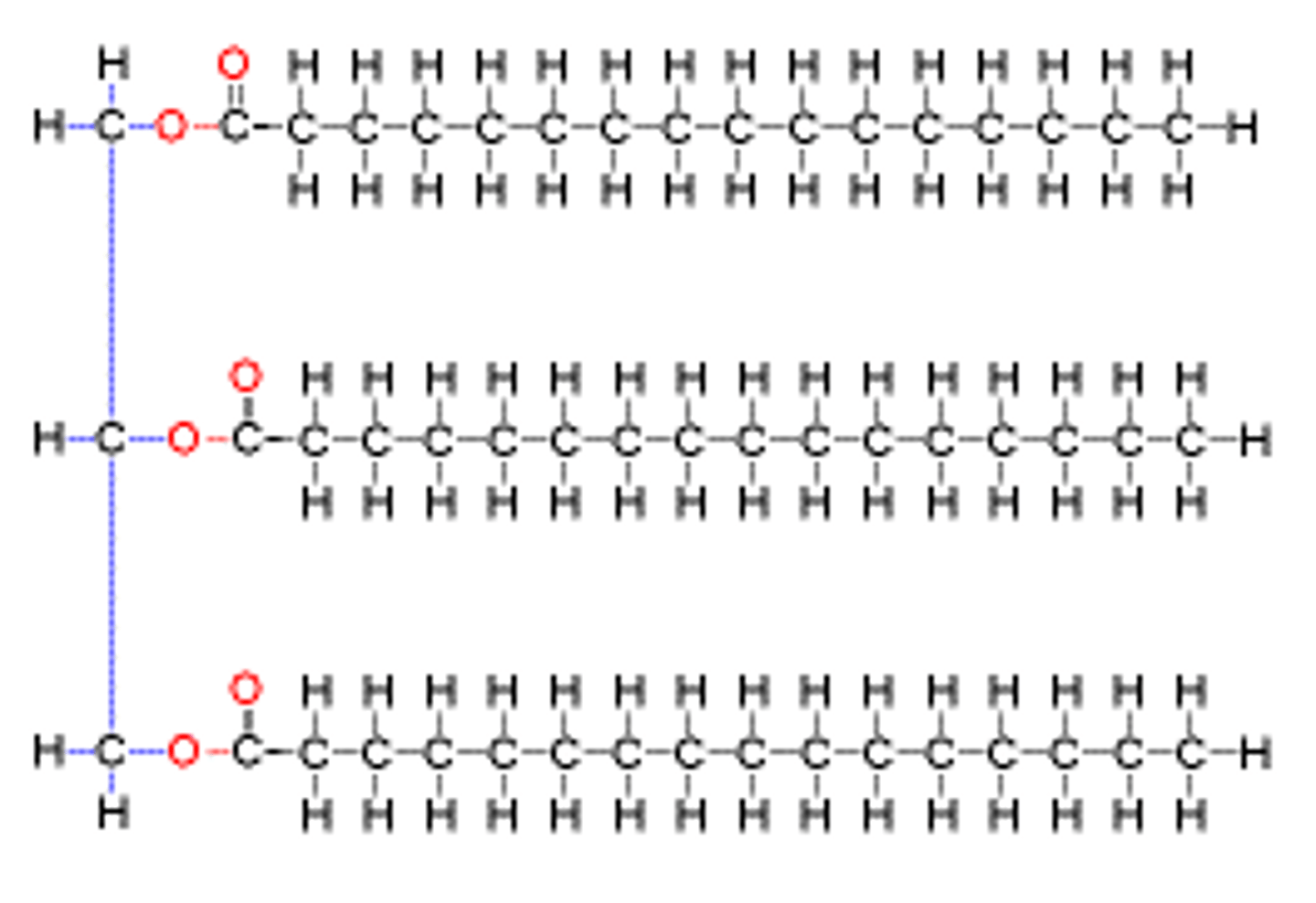
Triglyceride
Commonly called "fats"; a lipid made of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule
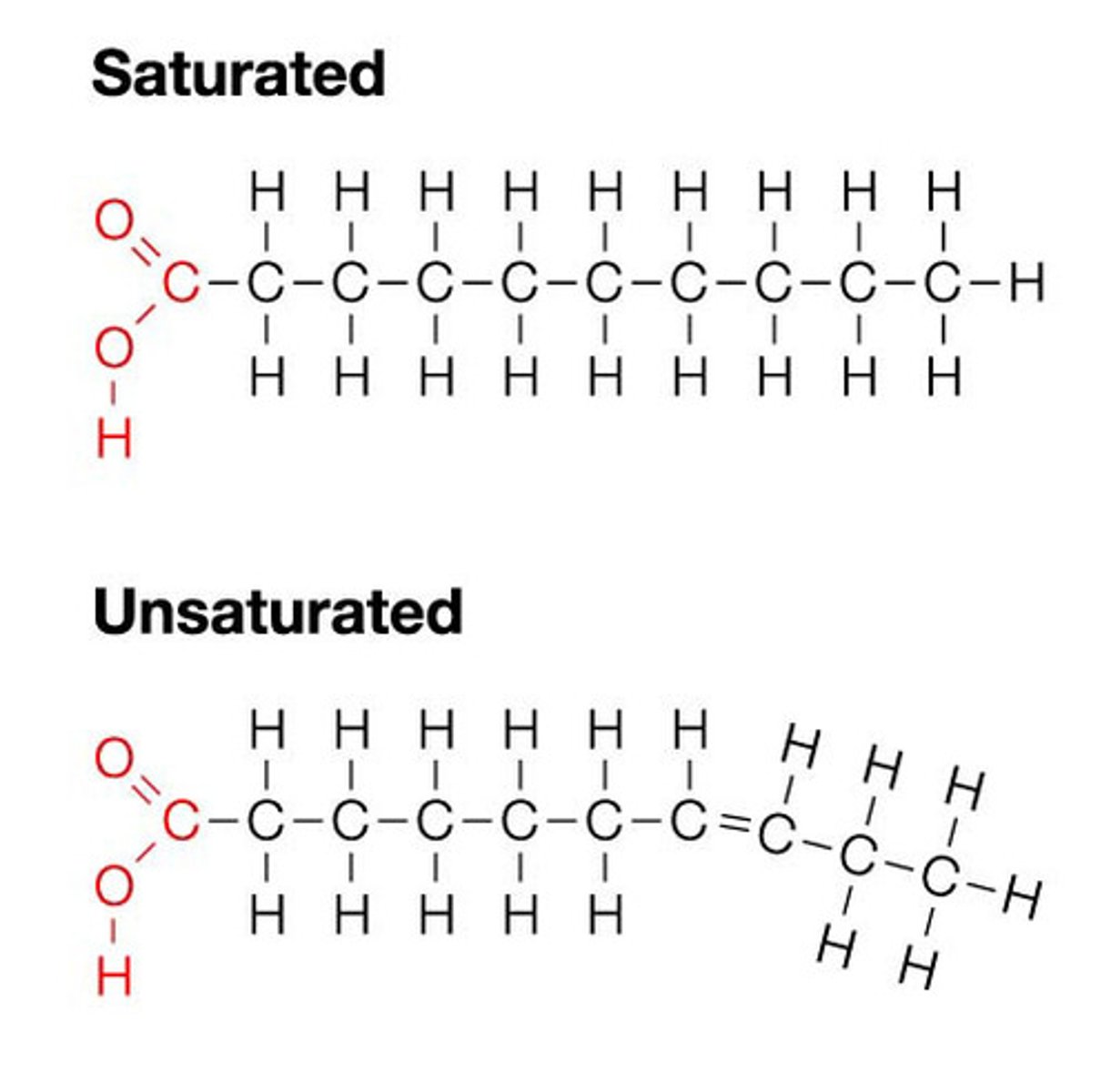
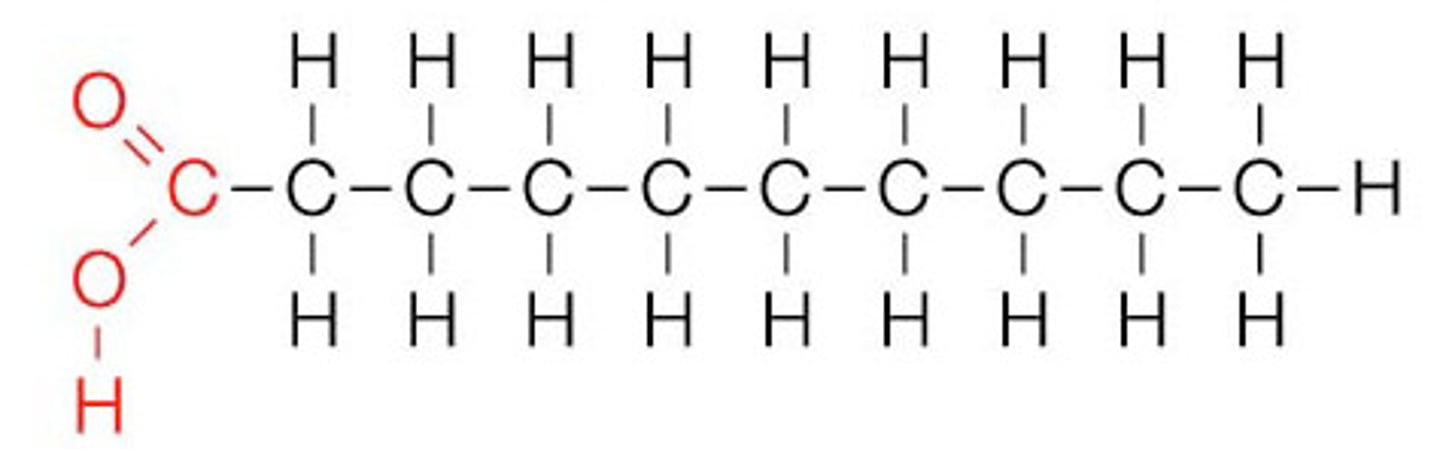
Saturated fats
Fatty acids (lipids) that are:
Solid at room temperature
Single C-C bonds only
Straight hydrocarbon chains
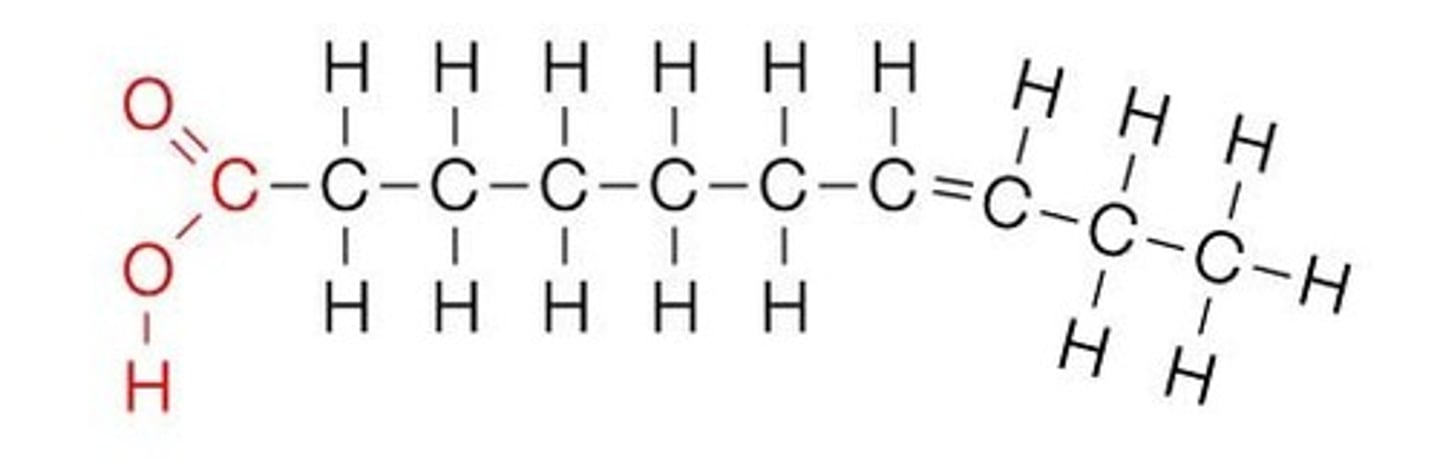
Unsaturated fats
Fatty acids (lipids) that are:
Liquid at room temperature
Have one or more double C-C bonds
Bent hydrocarbon chains
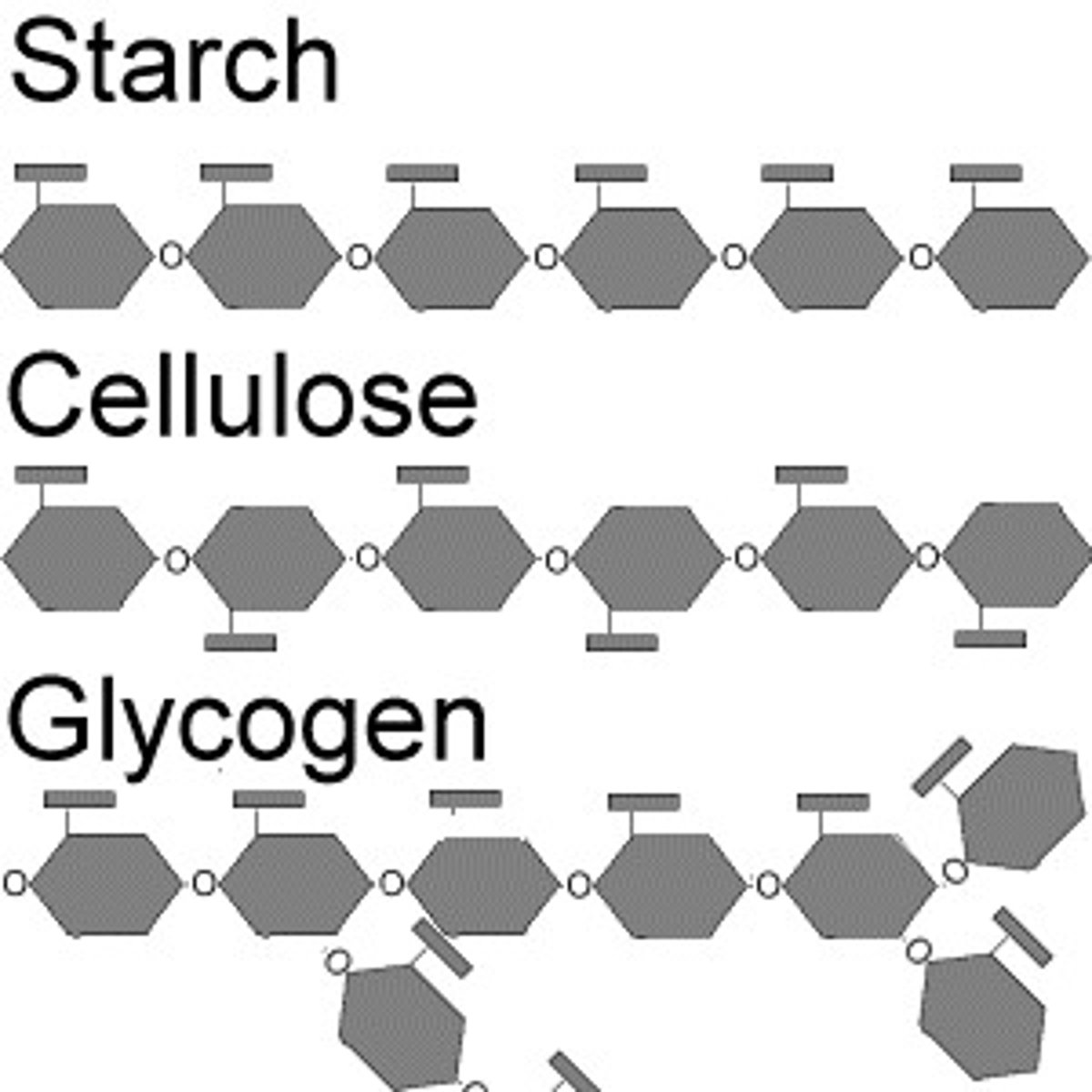
Starch
A storage polysaccharide (carbohydrate) in plants consisting entirely of glucose.

Cellulose
A structural polysaccharide (carbohydrate) consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls

Glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide (carbohydrate) found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
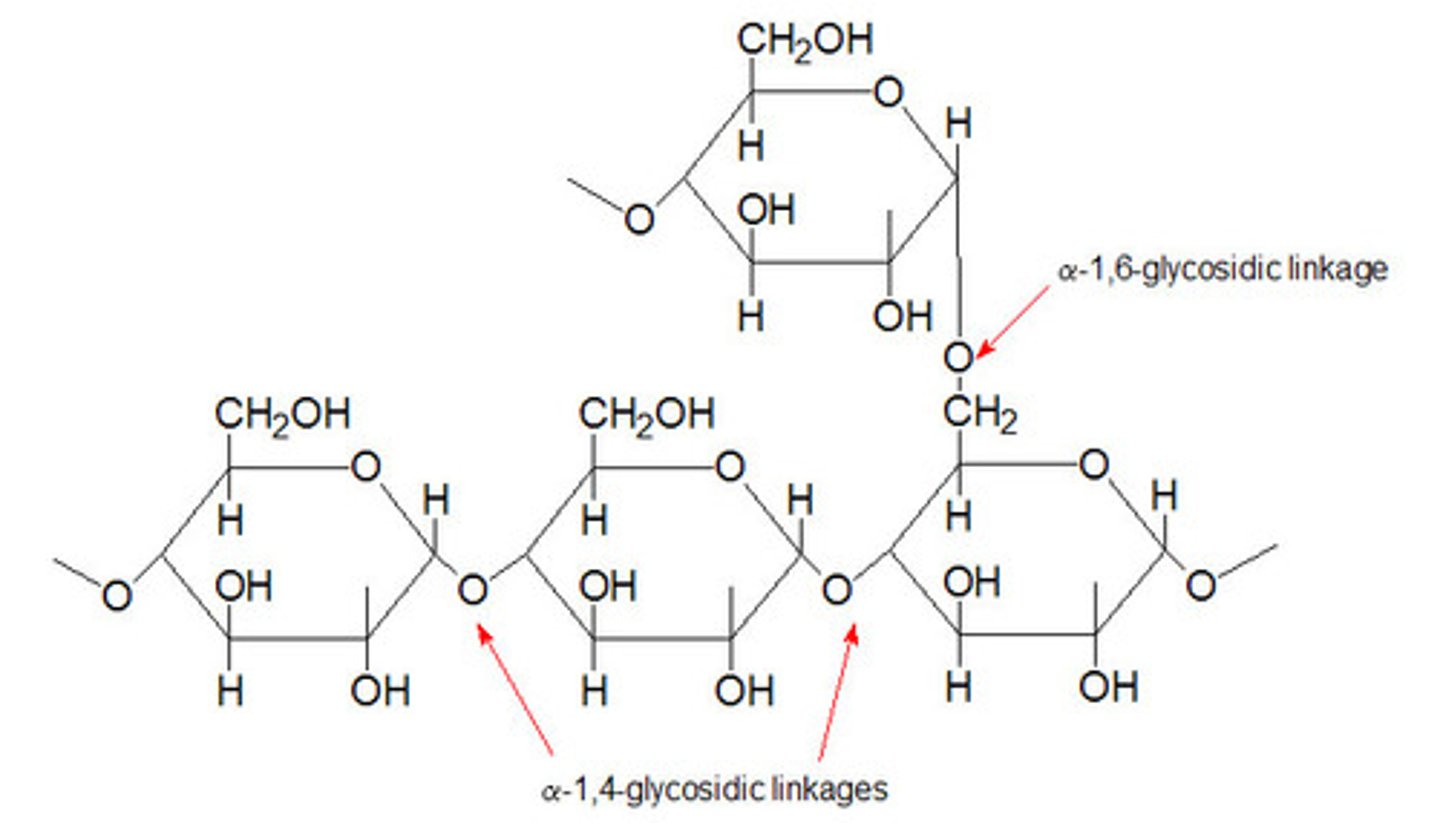
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide (carbohydrate), found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods.

Enzyme
A type of protein catalyst that speeds up a chemical reaction in cells
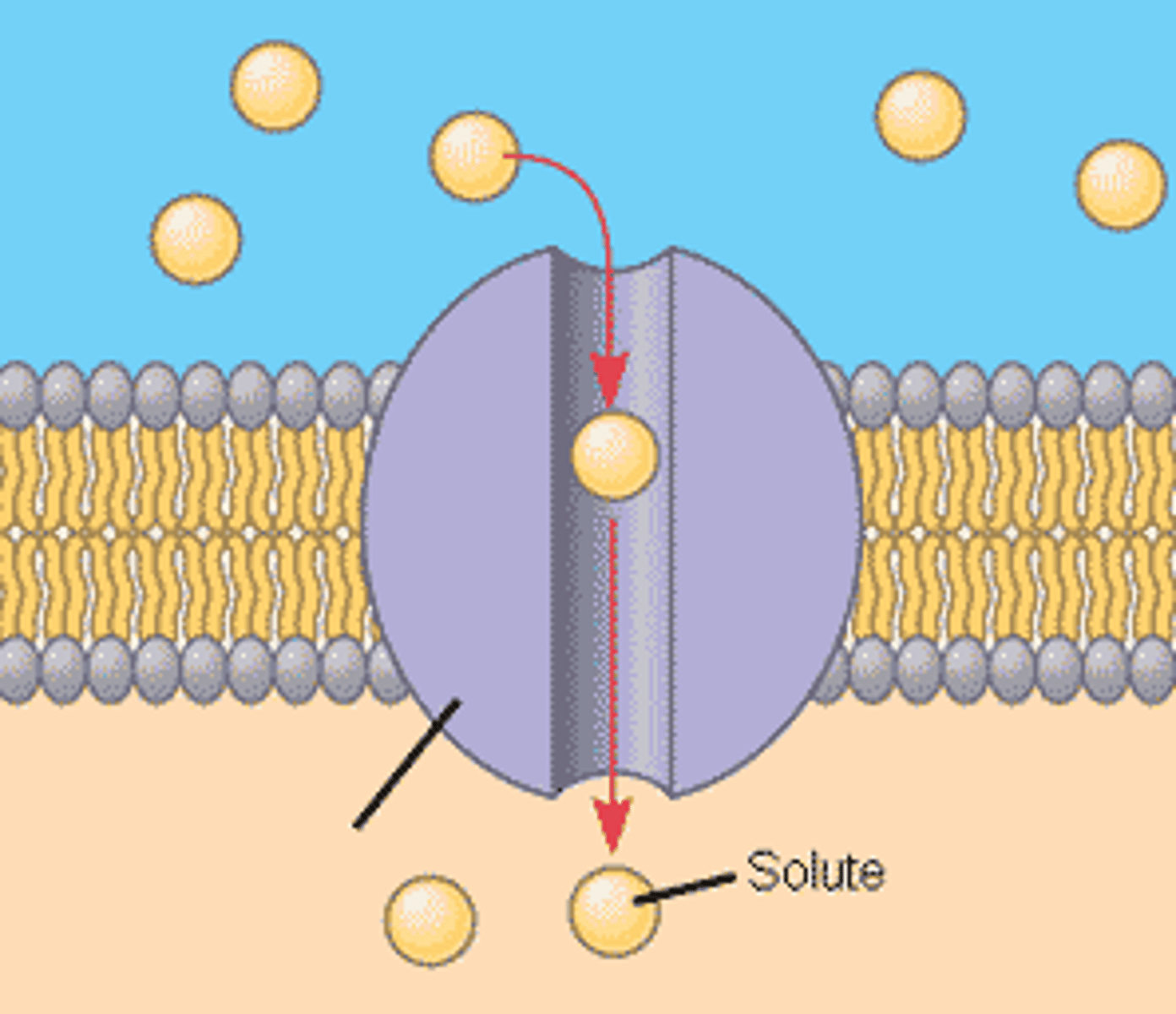
Protein channel
a protein that allows the transport of specific substances across a cell membrane
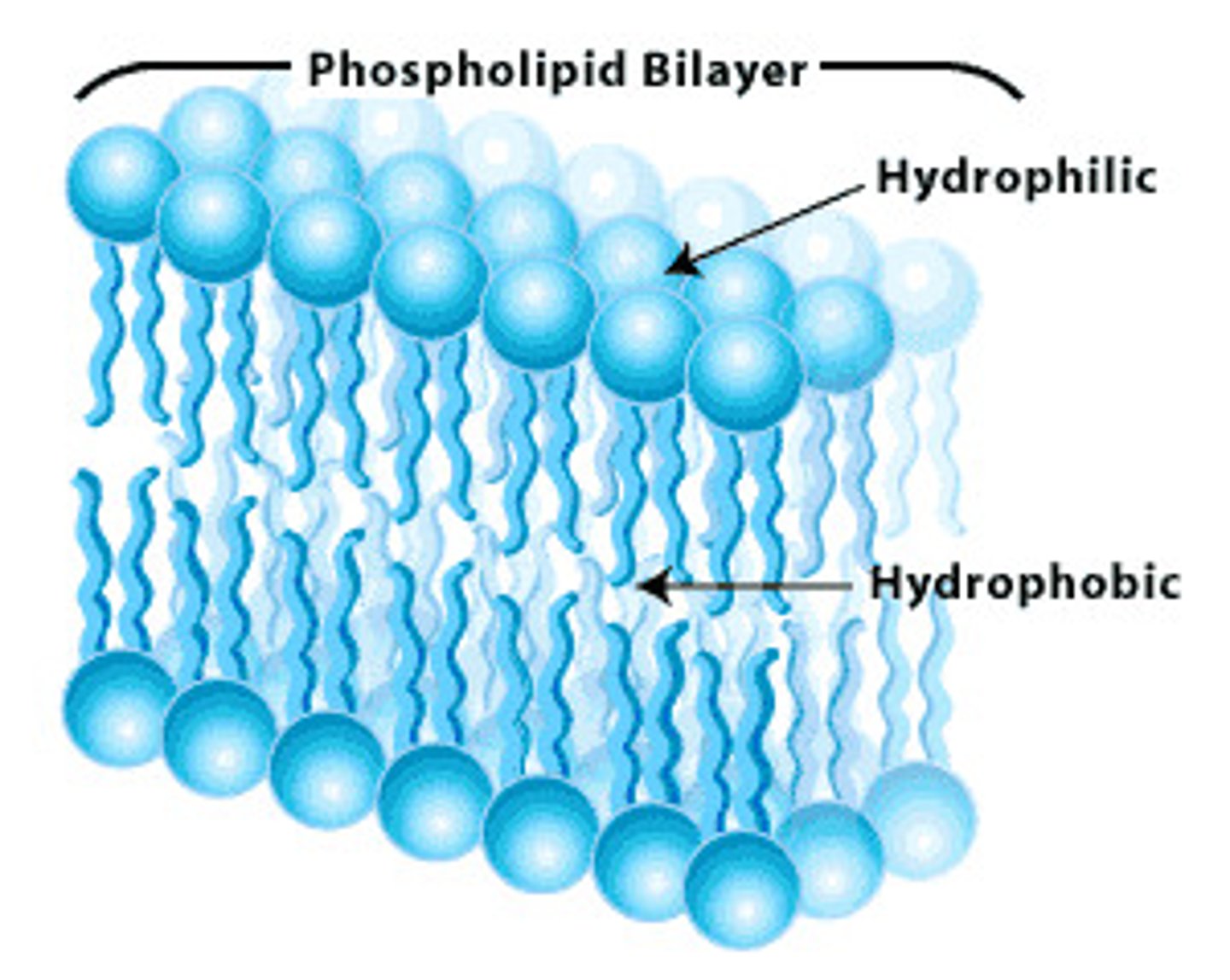
Phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes.
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
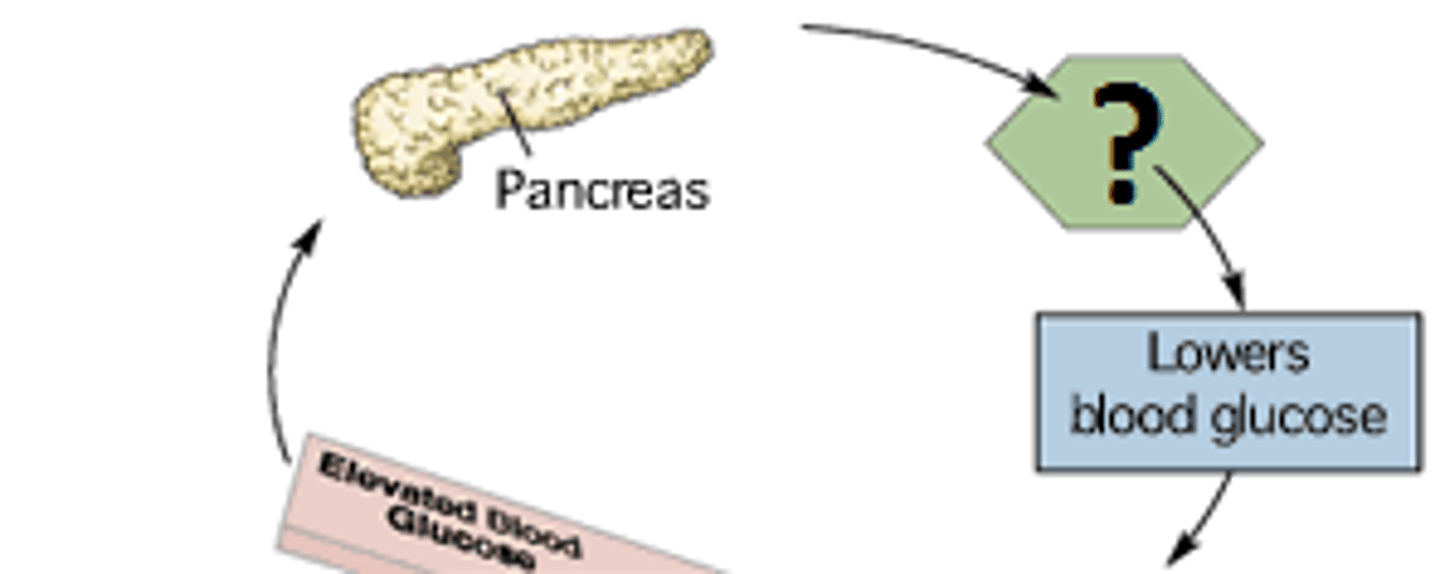
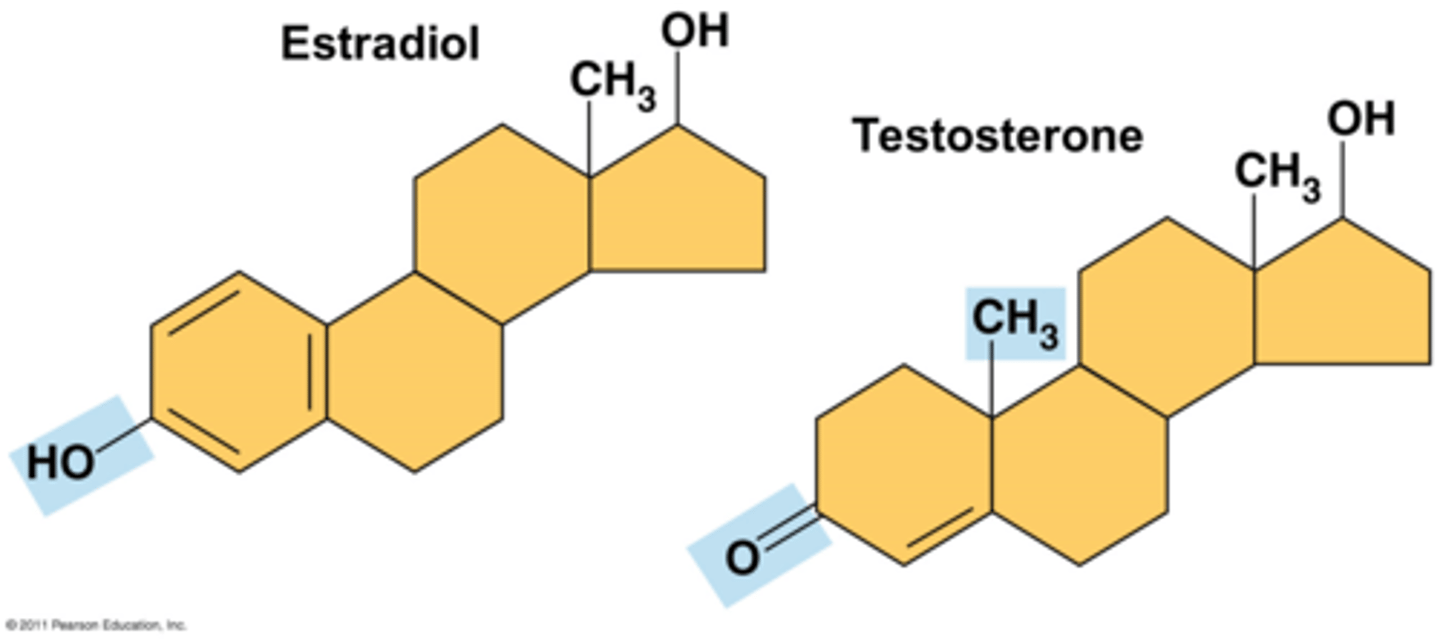
Steroids
A lipid hormone that includes testosterone and estrogen (sex hormones)
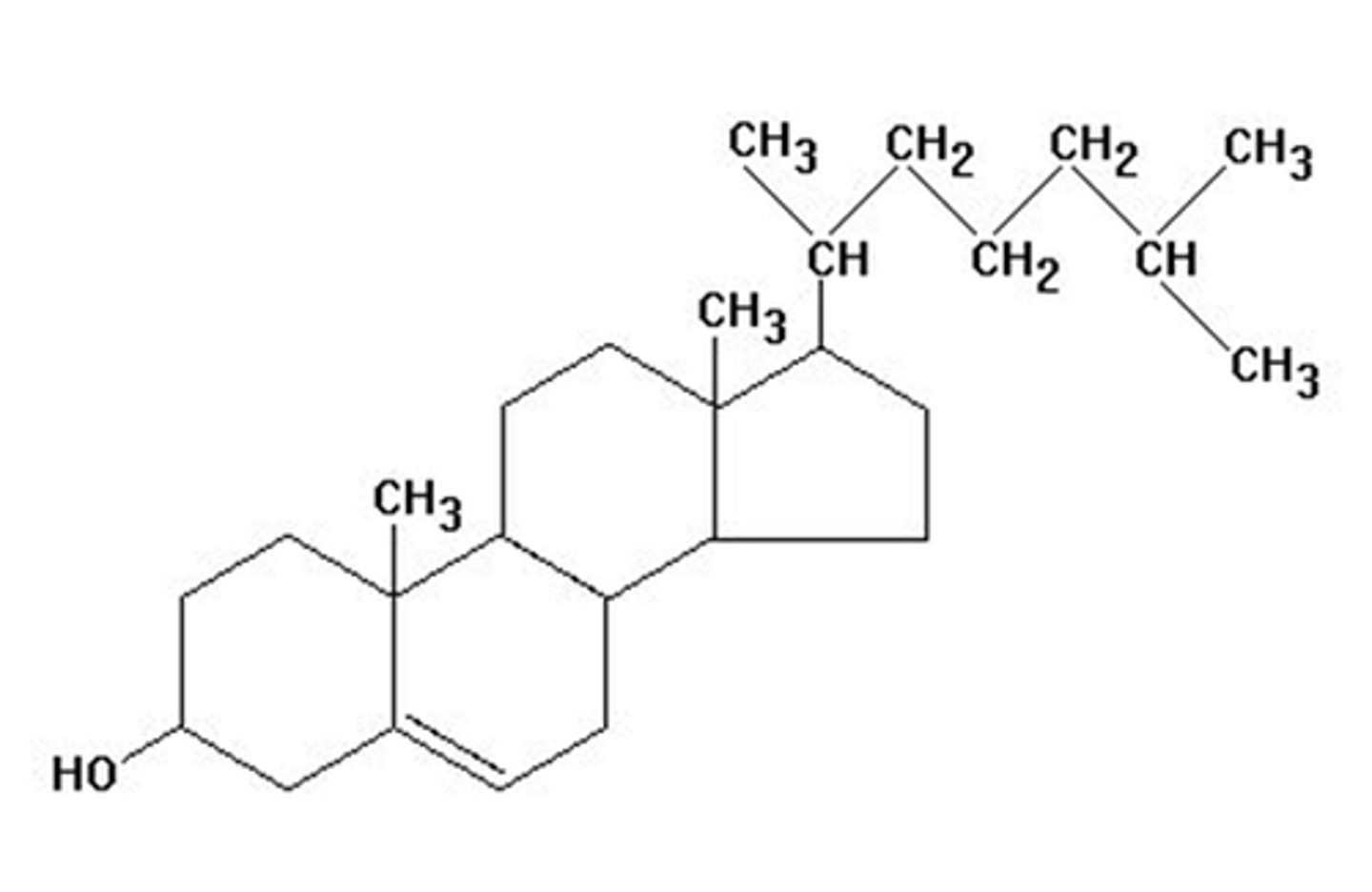
Cholesterol
A lipid that regulates the fluidity of the cell membrane
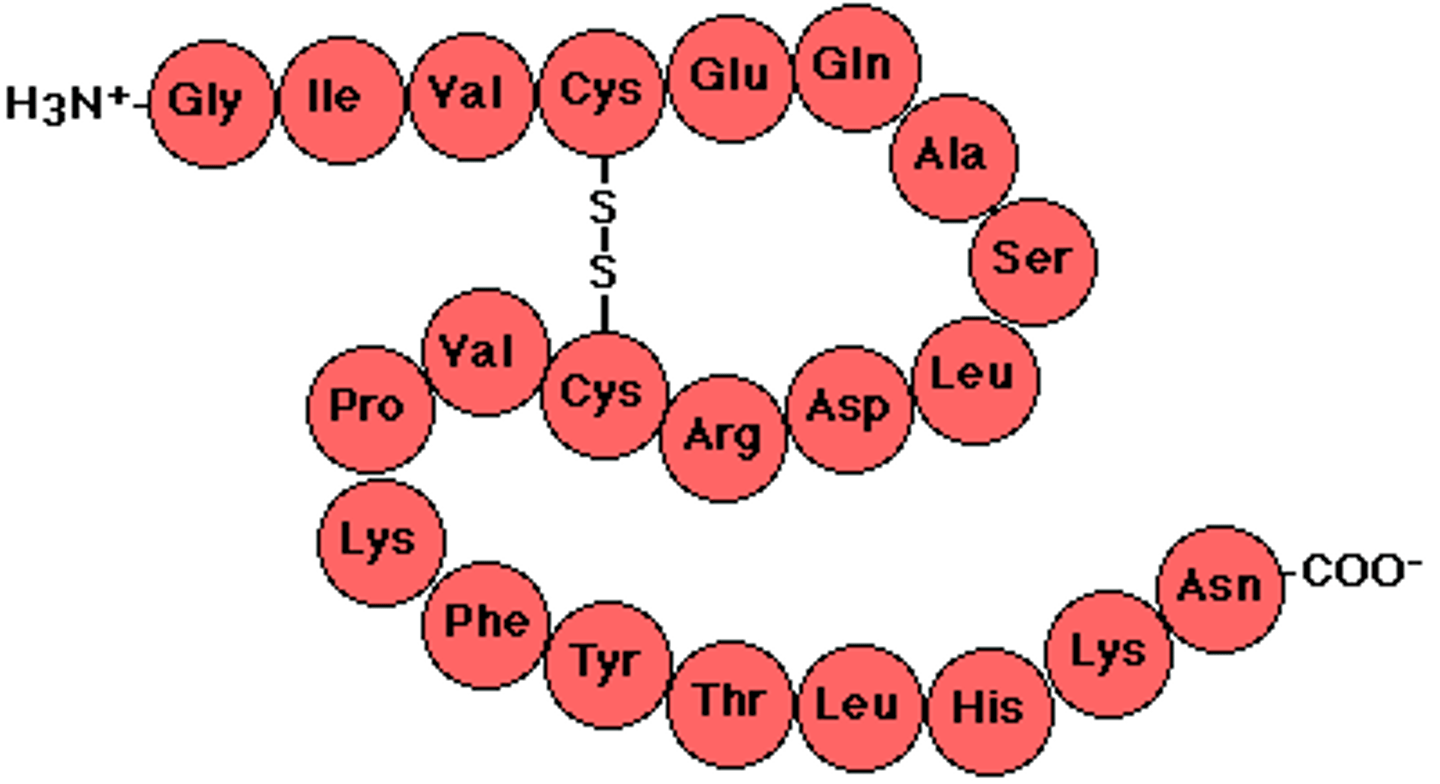
Primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
Secondary protein structure
coiling or folding of a polypeptide due to H-bonding between amino acids; forms alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets
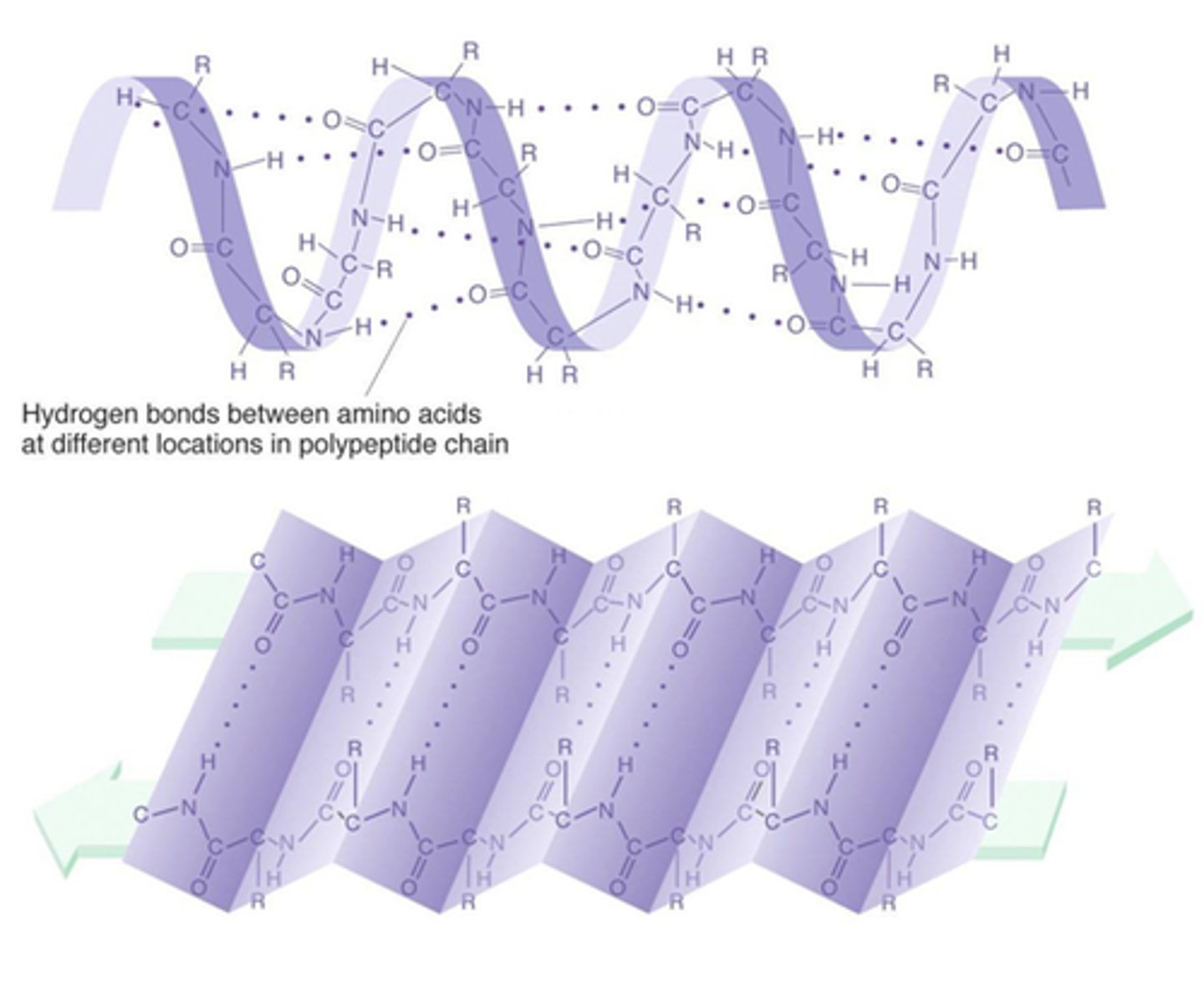
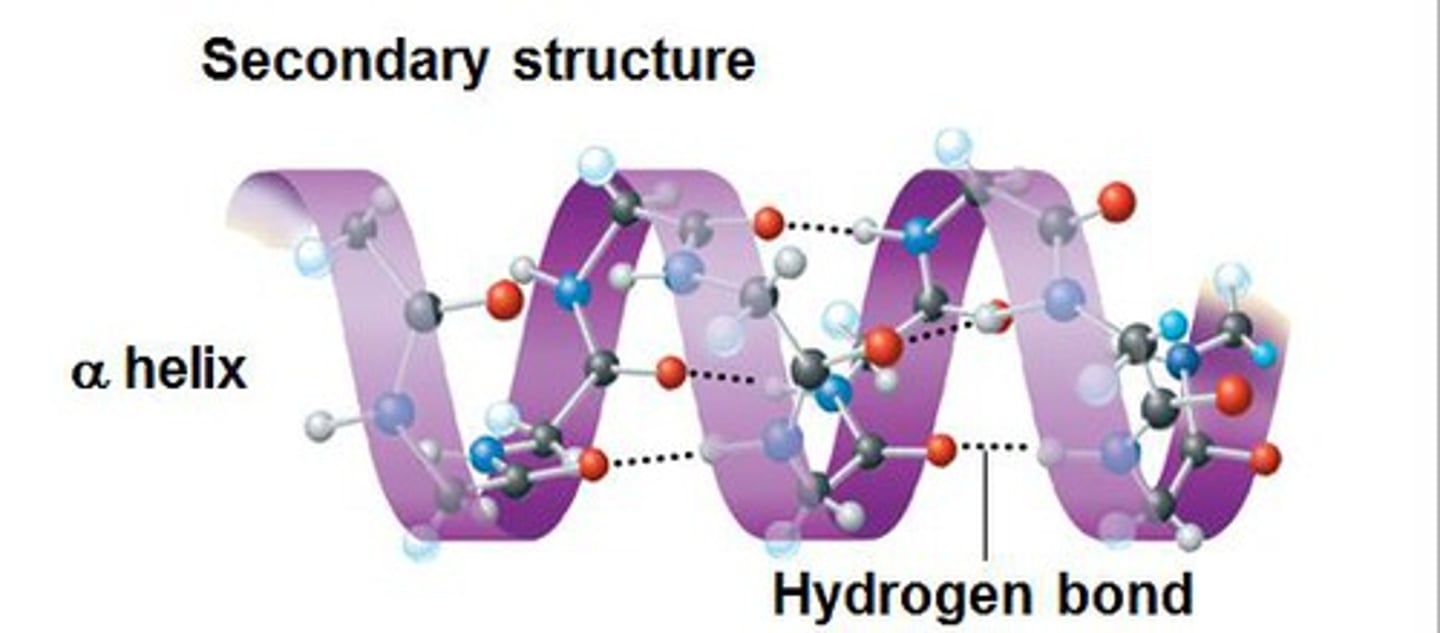
Alpha-helix
A spiral shape that is one form of the secondary structure of proteins; arising from a specific hydrogen-bonding structure.
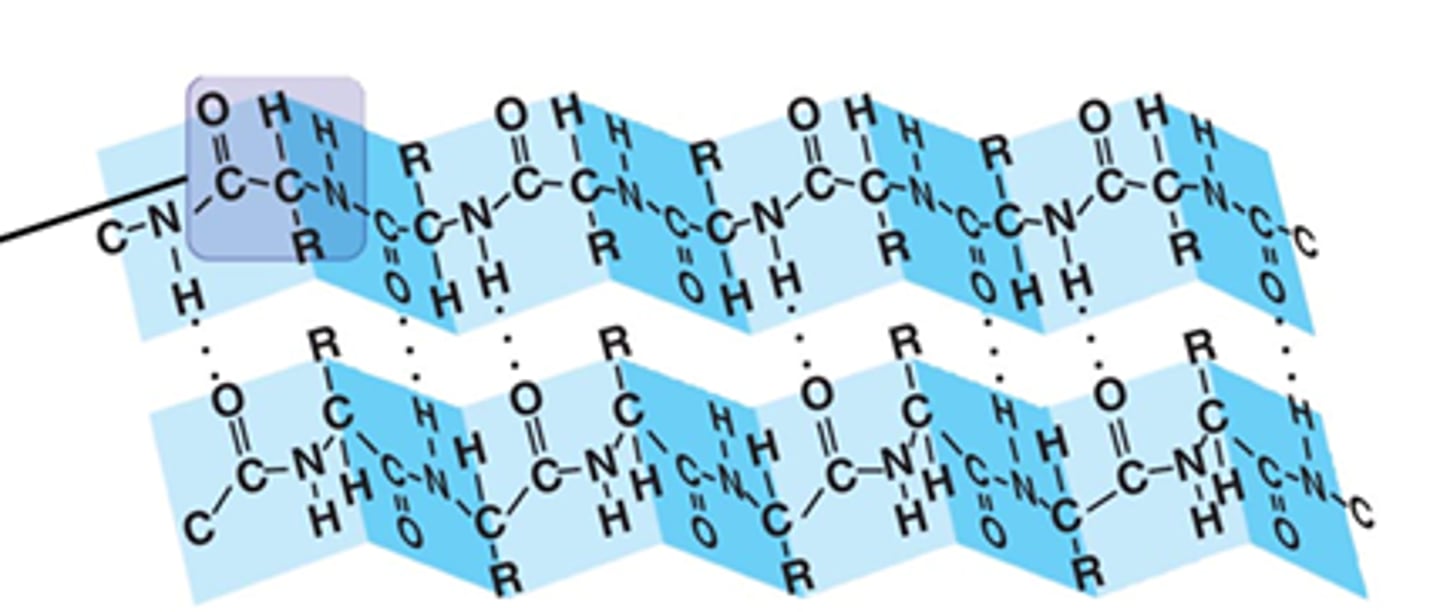
Beta-pleated sheet
A zig-zag shape that is one form of the secondary structure of proteins; arising from a specific hydrogen-bonding structure.
Tertiary protein structure
3D folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
Quaternary protein structure
2+ protein chains forming functional protein
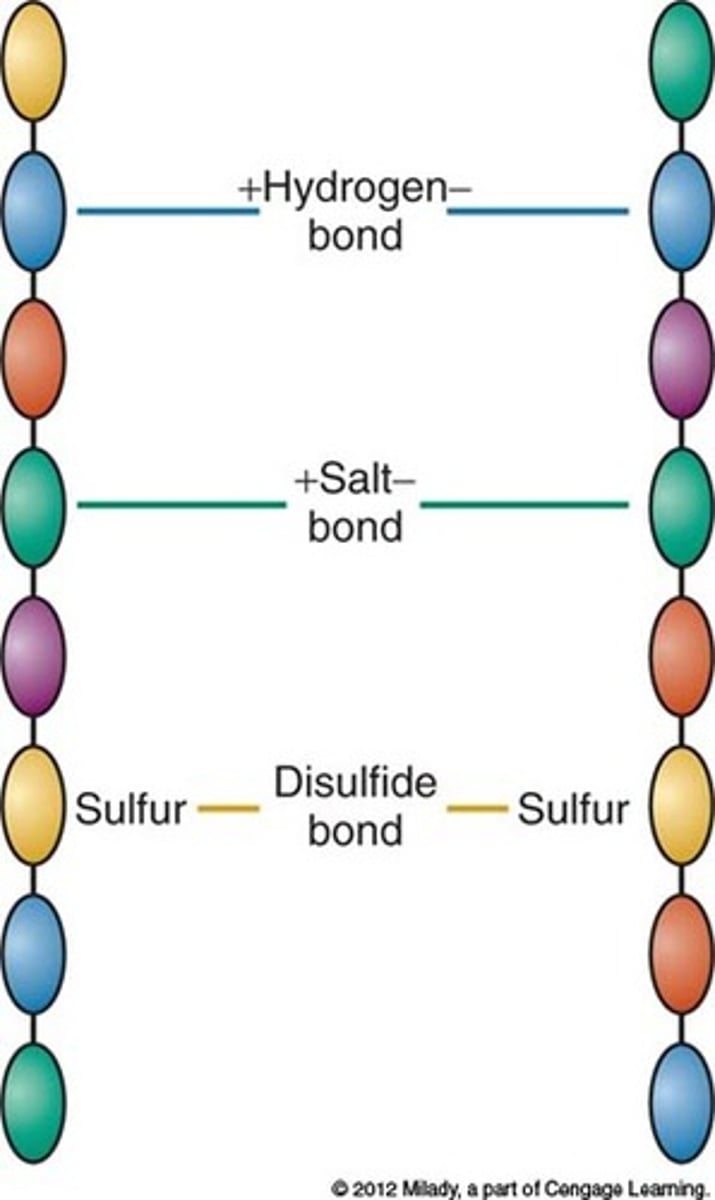
Disulfide bond
Covalent bond formed between the sulfur atoms of two cysteines in a protein; part of tertiary/quaternary protein structure