Kine 2850 Exam 1 Study guide 1/2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Structural:
anatomical elements, building blocks of a system
Kinesiology:
study of human movement
Axial Skeleton
Trunk, spine, neck, head
Appendicular Skeleton
upper and lower extremities
5 major functions of skeletal system
provide basic framework
movement by serving as pointrs of attachment for muscles and acting as levers
protection to internal organs
storage for minerals
blood formation
6 major types of joints in the body:
Hinge, ball and socket, pivot, saddle, gliding, condyloid
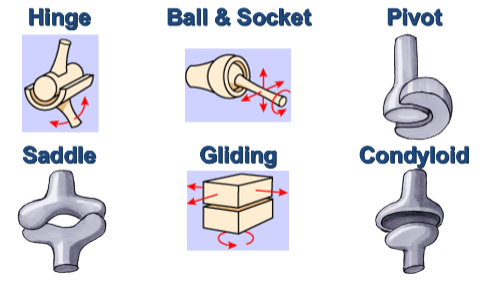
6 major types of joints in the body:
hinge, ball and socket, pivot, saddle, gliding, condyloid
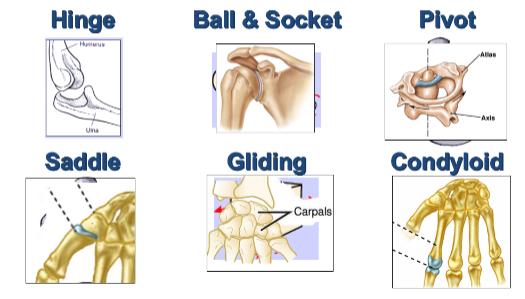
Muscle system function:
exert force through contraction
3 types of muscular contractions:
Isometric, concentric, eccentric
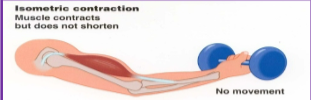
Isometric contraction:
same length (stabilizes joints)
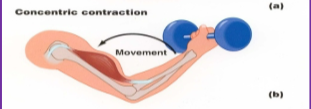
Concentric Contraction:
shortening (starts movement)
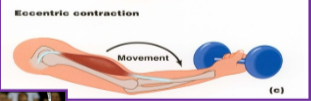
Eccentric contraction:
Lengthening (Stops movement)
Tendon:
Attaches muscle to bone (how muscles move bone)
Ligaments:
attaches bone to another bone (forms and stabilizes joints)
Anatomical position:
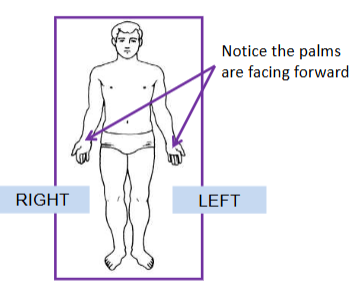
Fundamental Position
Anterior:
front of the body
Posterior:
back of the body
Medial:
toward the middle, center or midline of the body
Lateral:
toward the side, away from center or midline of body
Superior:
toward the head, above in relation to another structure
Inferior:
away from head, below in relation to another structure
Proximal:
nearest to the truck/point of origin
Distal:
away from the trunk/point of origin
Superficial:
near the surface
Deep:
beneath/below the surface
Prone:
face downward
Supine:
face upward
Contralateral:
relating to the opposite side
ipsilateral:
relating to the same side
biarticular:
a muscle that crosses and acts directly on 2 different joints
uniarticular:
a muscle that crosses and acts directly on the joint it crosses
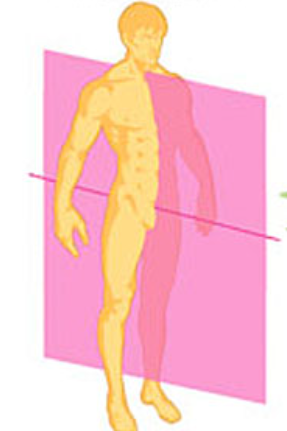
Sagittal plane:
splits the body into right and left halves
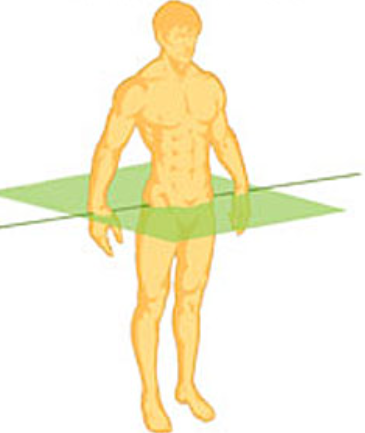
Transverse (axial) Plane:
splits body into top and bottom halves
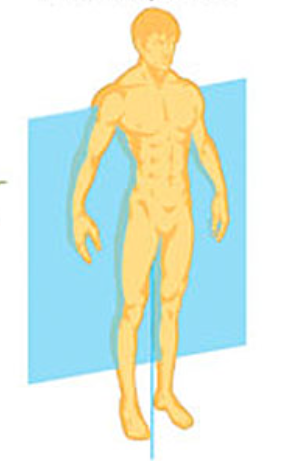
Frontal (coronal) plane:
splits body into front and back halves
Axes of rotation: Anteroposterior
(FRONTAL) movement occurring in the frontal plane rotate about this axis
Axes of rotation: Mediolateral
(SAGITTAL) Movements occurring in the sagittal plane rotate about the axis
Axes of rotation: Longitudinal Movements
(TRANSVERSE) occurring in the transverse plane rotate about this axis
Primary movements: Sagittal
flexion & extension
Primary movements: Transverse
External rotation & internal rotation
Primary movements: Frontal
Abduction & Adduction
More Primary movements: sagittal
dorsiflection & plantarflextion
More Primary movements: Frontal
Depression & Elevation
More Primary movements: Transverse
Pronation & Supination // Protraction & Retaction
More Primary movements: Multi-plane
Circumduction
The ___________ connects the lower limbs to the trunk & supports the weight of the trunk
Pelvic Girdle
How many Degrees of freedom does the Hips have?
3 Degrees of freedom
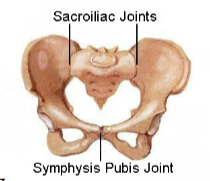
Fused Joint: Pubic Symphysis
fairly stable, widens for childbirth
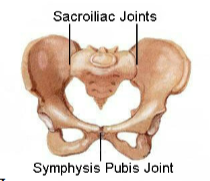
Fused joint: Sacroiliac joint
transmits weight of trunk to hips
Head of femur (navy)

Neck of femur (purple)
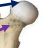
Greater trochanter (red)

Lesser Trochanter (Sky blue)

Hip flexor muscles: Iliacus
HFM: 1
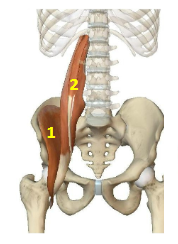
Hip flexor muscles: Psoas
HFM: 2
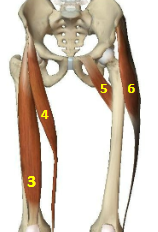
Hip flexor muscles: Rectus Femoris
HFM: 3
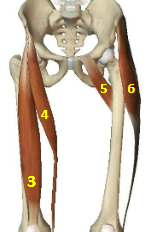
Hip flexor muscles: Sartorius
HFM: 4
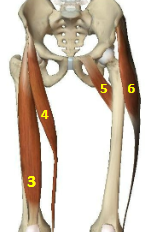
Hip flexor muscles: Pectineus
HFM: 5
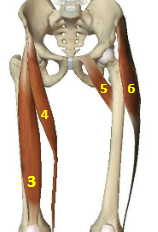
Hip flexor muscles: Tensor Fascia Latae
HFM: 6
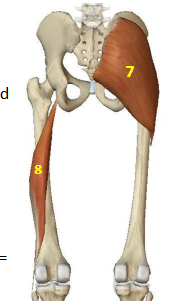
Hip Extensor Muscles: Gluteus Maximus
HEM: 7
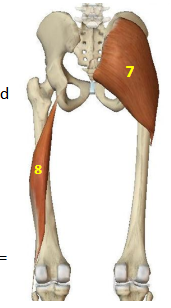
Hip Extensor Muscles: Biceps Femoris Long Head
HEM: 8
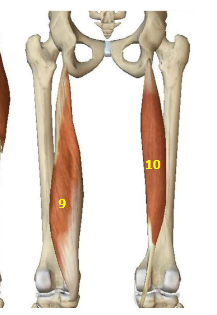
Hip Extensor Muscles: Semimembranosus
HEM: 9
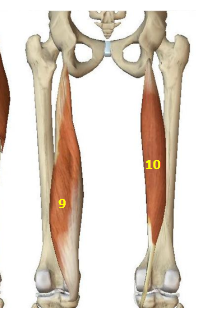
Hip Extensor Muscles: Semitendinosus
HEM: 10
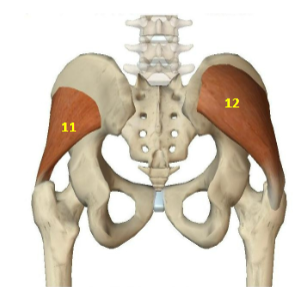
Hip Abductor Muscles: Gluteus Minimus
HAbM: 11
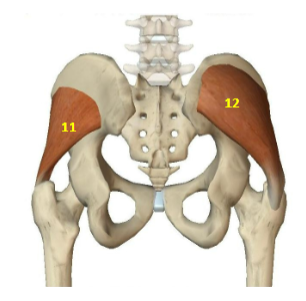
Hip Abductor Muscles: Gluteus Medius
HAbM: 12
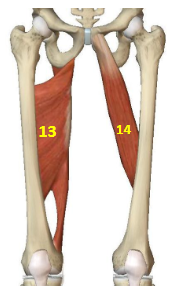
Hip Adductor Muscles: Adductor magnus
HAddM: 13
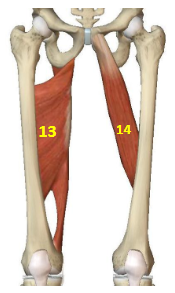
Hip Adductor Muscles: Adductor longus
HAddM: 14
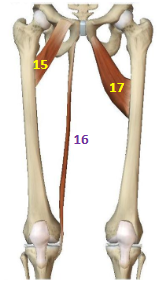
Hip Adductor Muscles: Pectineus
HAddM: 15
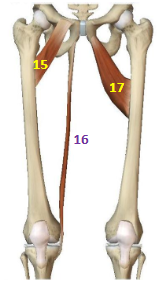
Hip Adductor Muscles: Gracilis
HAddM: 16
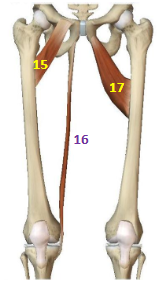
Hip Adductor Muscles: Adductor Brevis
HAddM: 17
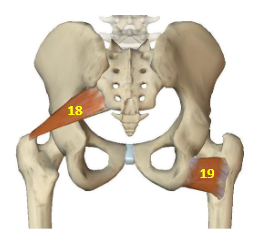
Hip External Rotators: Piriformis
HER: 18
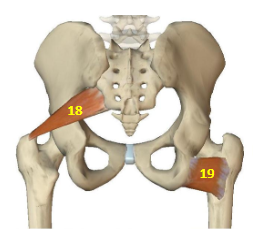
Hip External Rotators: Quadratus Femoris
HER: 19
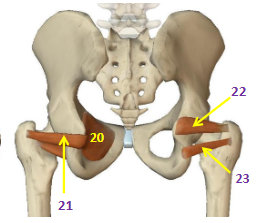
Hip External Rotators: Obturator Internus
HER: 20
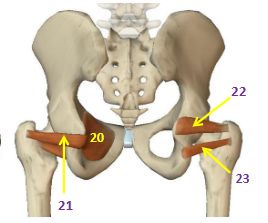
Hip External Rotators: Obturator Externus
HER: 21
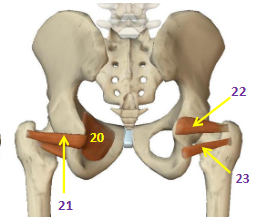
Hip External Rotators: Superior Gemellus
HER: 22
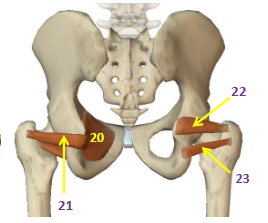
Hip External Rotators: Inferior Gemellus
HER: 23
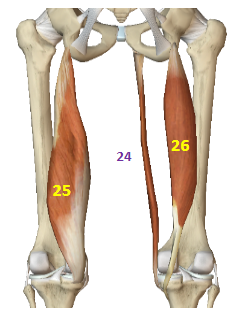
Hip Internal Rotators: Gracilis
HIR: 24
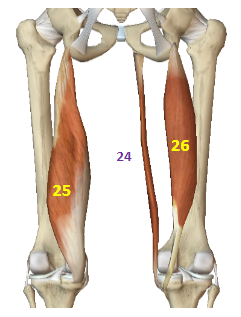
Hip Internal Rotators: Semimembranosus
HIR: 25
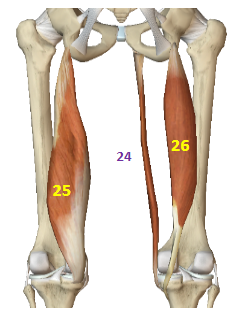
Hip Internal Rotators: Semitendinosus
HIR: 26
Hip joint fractures are common in old adults (over age 65), where do these fractures usually occur?
Typically occur the femoral neck