CHEM - ICE Tables + Acid-Base Equilibria
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Initial
Use given initial concentrations of reactants
Always start with zero products
Change
Use stoichiometric coefficients to subtract mX from reactants or add nX to products
Equilibrium
If given Keq: solve for X and equilibrium concentrations
If given equilibrium concentration, determine concentrations for all and calculate Keq
When K<5%
assume x is small and ignore it in the denominator
How to check 5% rule?
(X/initial concentration) x 100
how to get rid of ln?
ex
Bronsted-Lowry says that acids are proton donors and bases are proton…
acceptors
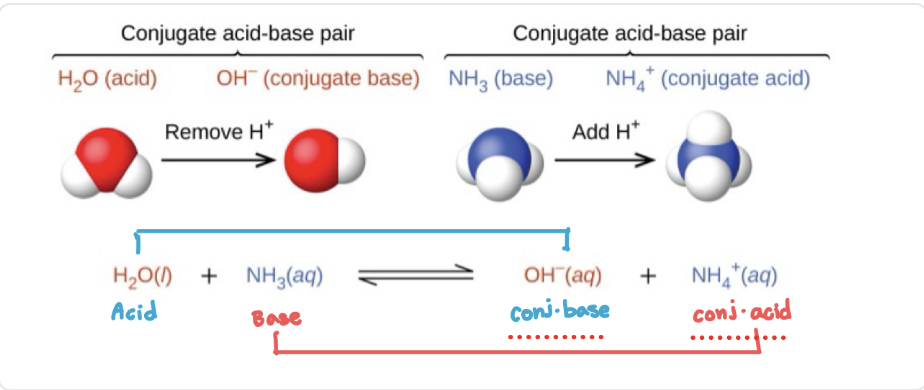
Conjugate acids and bases act as the…
acid or base in the reverse reaction
Ka =
products/reactants
If Ka >> 1 that means its a
strong acid
K is the equilibrium constant and it is __________ dependent
temperature
On the pH scale, the red side is lower pH and the middle (green) is neutral and the purple is higher pH. Where do acids and bases lie on the scale?
Acids on red side (smaller pH), base on purple side (larger pH)
Acidic
< 7
Basic
> 7
pOH scale is the opposite of pH scale
7 neutral
< 7 basic
> 7 acidic
pH + pOH =
14
Significant figures for pH and pOH =
#of decimal places
HA =
Acid
A =
Base
What is a polyprotic acid?
An acid that can donate multiple protons (H+)
A strong acid has a Ka _____ 1
much greater than
What’s the trend for Ka of polyprotic acids?
As protons are removed, the Ka decreases and the acids become weaker
The stronger the acid, the _________ the conjugate bases
weaker
Kw =
Ka x Kb
Ka and Kb are ______ proportional
inversely
Lower ionization =
weaker acid
Higher Ka =
stronger
K2CO3
Basic
CaCl2
neutral
KCN
Basic
NaCl
neutral
KNO₃
neutral
NH₄Cl
acidic
Na₂CO₃
Basic
Monoprotic
1 proton to give up (H+)
Diprotic
2 protons to give up
Triprotic
3 H+
Each proton given up =
weaker
Strong acid + strong base =
neutral salt
Strong acid + weak base =
acidic salt
Weak acid + strong base
basic salt
→ Or ←
completely ionized
<->
not completely ionized
Strong acids and bases react with water =
completely ionized
Weak acids and bases react =
only partially ionize
Larger Ka = more acidic and
lower pH
Larger Ka =
more product and stronger acid
Smaller Ka =
more reactants and a weaker acid
A buffer is a solution that has the ability to…
resist changes in pH when limited amounts of acids or bases are added to it
Buffers are made by combining
a weak acid or base with its conjugate
Strong acid = readily lose a
proton
A strong acid has a stable but weak conjugate base
not dying to pick up a proton
Weak acid is not very willing to _____ a proton
lose
increase [H3O+]
increase acidity
decrease pKa
increase acidity
[H3O+] > 10-7
acidic solution
[H3O+] < 10-7
basic solution
[H3O+] = 10-7
neutral solution
Strong acids deprotonate
completely
weak acids deprotonate
partially
pH = pKa when buffer has equal amounts of
HA and A-
more base than acid =
higher pH than pKa
more acid than base =
higher pKa than pH