Yeasts
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are considered true yeasts?
Those who reproducing sexually by forming ascospores or basidiospores
What are considered yeastlike fungi?
Isolates that are not capable of sexual reproduction
What is the primary sp that causes yeast infection?
Candida albicans
What are characteristics of Candida albicans?
Thrush
An indicator of immunosuppression
Can evolve into serious infection in patients receiving long-term antibiotics
What are the characteristic of Candida glabrata?
May account for 21% of all urinary yeast isolates
Tend to be aggressive and difficult to treat w/ traditional antifungal therapy
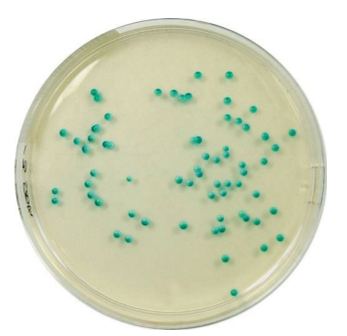
Which sp is this? On what plate?
C. albicans on chrome agar
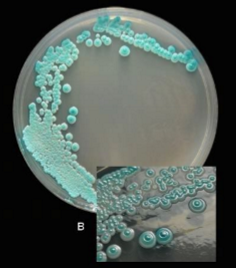
Which sp is this?
C. dubliniensis
How can you tell the difference between Candida albicans vs Canadia dubliniensis?
Candida dubliniensis does NOT grow at 42C while Candia albicans CAN grow at 42C
What are the other notable species of Candida?
Candida krusei
Candida tropicalis
Candida parapsilosis
Why is Candida auris a concering species?
Emerging multidrug-resistant yeast linked to high mortality rates
Hospital setting, likely transmitted patient to patient
What is the pathology of Cryptococcus?
Opportunistic infection
Meningitis, pneumonia and septicemia
What are the characteristics of Cryptococcus?
Mucoid due to capsule
India ink test —> Results in clear halos around organism
Blastocondia only
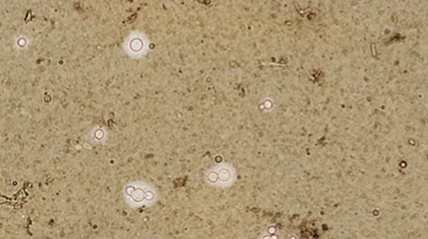
Which sp is this? Which test is being done on this slide?
Cryptococcus; India Ink
What are the characteristics of Rhodotorula?
noted for its bright salmon-pink color
Capsulated and urea-positive
Some species are nitrate-positive
What are characteristics of Trichosporon?
Causes invasive localized and disseminated disease
Some sp causes white piedra
What are the colony characteristics of Trichosporon?
At first cream-colored, most and soft —> As it aged, it becomes wrinkled, powdery and crumb-like
What is the microscope morphology of trichosporon sp?
True and pseudohyphae formation
Blastocondia singly or in chains
Arthoconidia on older cultures

Which sp is this?
Trichosproron sp (Colony)
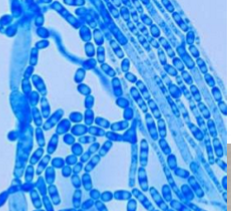
Which sp is this?
Trichosporon sp (Micro)
What is P. jirovecii?
Formerly considered a protozoa but now its considered a Pneumocystis fungi
Non-filamentous fungus
What is the life cycle of Pneumocystis?
1) Trophozoite —> Multiply via binary fission
2) Precyst
3) Cyst —> Infective stage
How would you diagnose Pneumocystis?
1) Biopsy and aspirates of the lung via Giemsa and Grocott’s methenamine silver (GMS)
2) Calcofluor white —> Blue-white color when stained and viewed under ultraviolet (UV) light
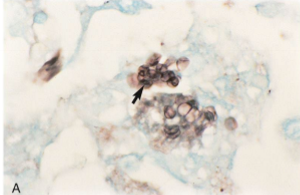
Which sp is this? Which stain is it in?
Pneumocystis Cysts in silver stain
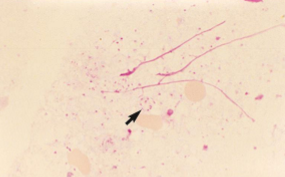
Which sp is this? Which stain is it in?
Pneumocystis in Giemsa stain
What are some clinical disease cause by yeasts / yeast-like fungi?
Candidiasis
White piedra
Pityriasis
Crypotococcosis
Onychomycosis
Vulvovaginal
UTI
How much is required for blood specimen?
8-10 mL of whole blood
How much is required for Bone Marrow?
0.5 mL
Pediatric blood culture bottle or inoculate media bedside
How much is required for Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)?
2 mL
Inoculate directly to media; centrifuge and make smears from sediment
How much is required for Sputum?
3-5 mL
Must split specimen before decontamination for AFB testing
How much is required for Sterile Body Fluids?
10-50mL
Heparin may be used to prevent clotting
How much is required for Tissues?
Place in sterile gauze wetted with sterile saline
Must be grounded / minced prior to media inoculation
How much is required for Urine?
10-40 mL (Use early morning for concentration)