PD E1 Special tests
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
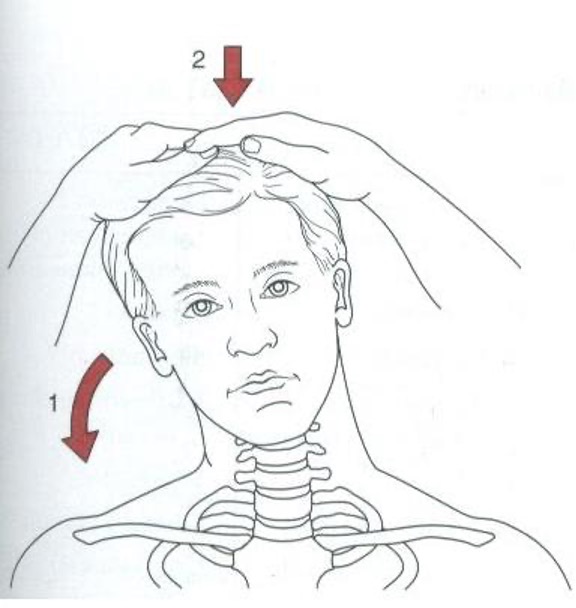
cervical test for nerve root compression/foraminal stenosis
hyperextension w/ lateral rotation and lateral flexion → apply axial compression to head
positive = pain to side of rotation
Spurling’s Test / Cervical Compression

Cervical test for cervical radiculopathy
place hands under occiput and apply upward distraction force (** don’t perform if cervical instability suspected)
positive = decreased or eliminated pain
Cervical Distraction
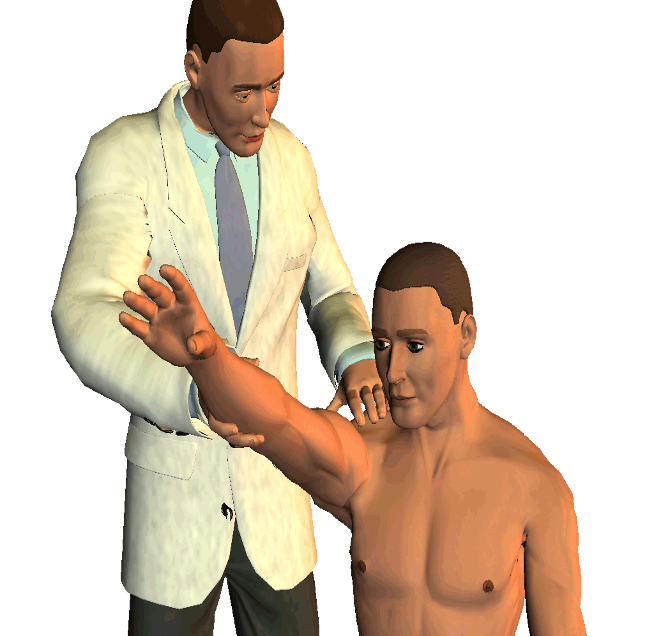
Shoulder test for impingement / rotator cuff tear
pronate and passively forward flex arm as high as possible
positive = pain
Neer’s Sign
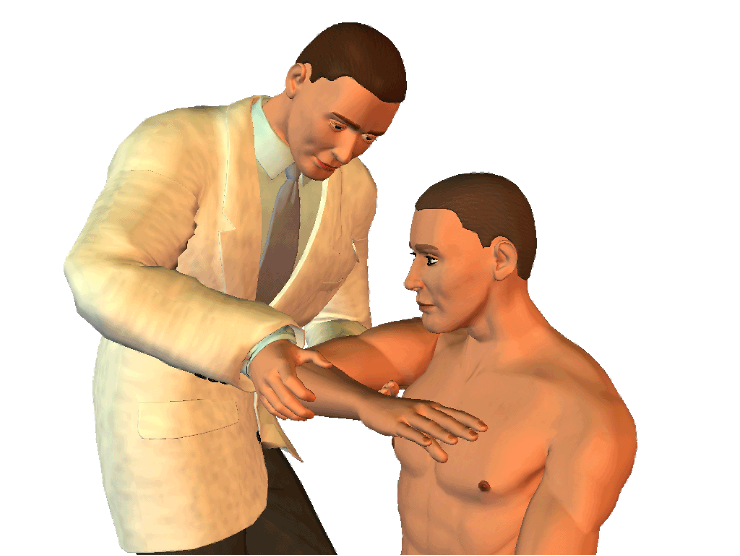

Shoulder test for impingement / rotator cuff tear
forward flex arm to 90° and bend elbow then internally rotate humerus (push down)
Hawkin’s and Kennedy test

Full thickness rotator cuff tear
test integrity of supraspinatus, teres minor & infraspinatus tendons
External rotation lag sign
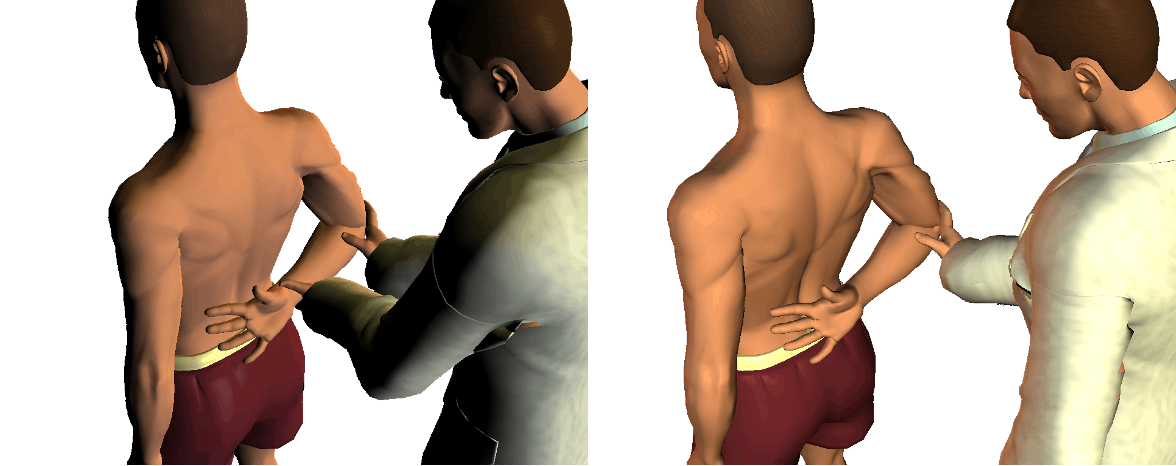
Rotator cuff tear
assesses integrity of subscapularis
Internal rotation lag sign / Liftoff test
Rotator cuff tear
assesses for supraspinatus muscle irritation, impingement, or tear
shoulder in forward flexion, 90° scapular plane & elbow fully extended→ fully pronate arm with thumb face down → resist downward pressure
positive = pain
Supraspinatus / Empty can test
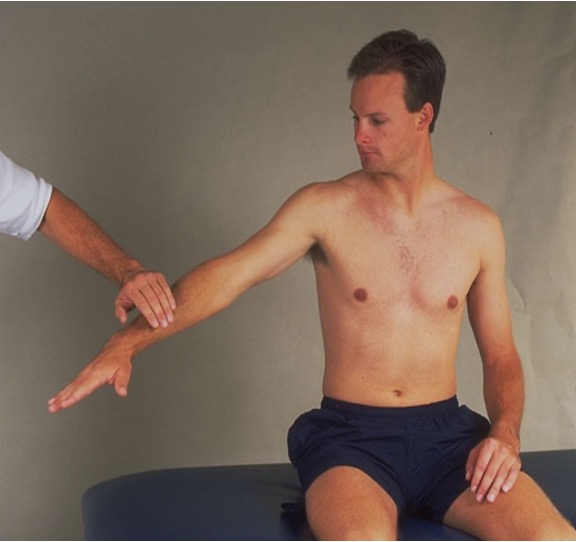
full thickness tear of supra/infraspinatus
bring arm passively to 90° abduction and external rotation → tell patient to hold and then release your hand
positive = arm drops / unable to control downward movement
Drop arm test
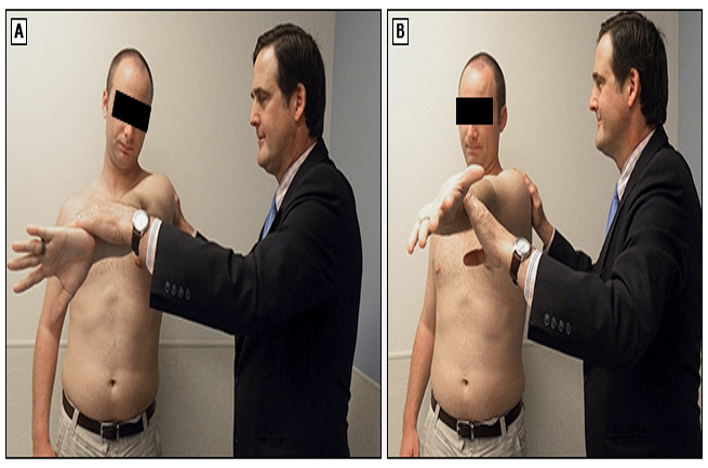
AC joint or labral tear test
shoulder flexed 90°, adducted, internally rotated, and elbow extended → resist downward force → repeat procedure in supination
positive = ACJ pain or deep clicking in GHJ
O’brien’s test
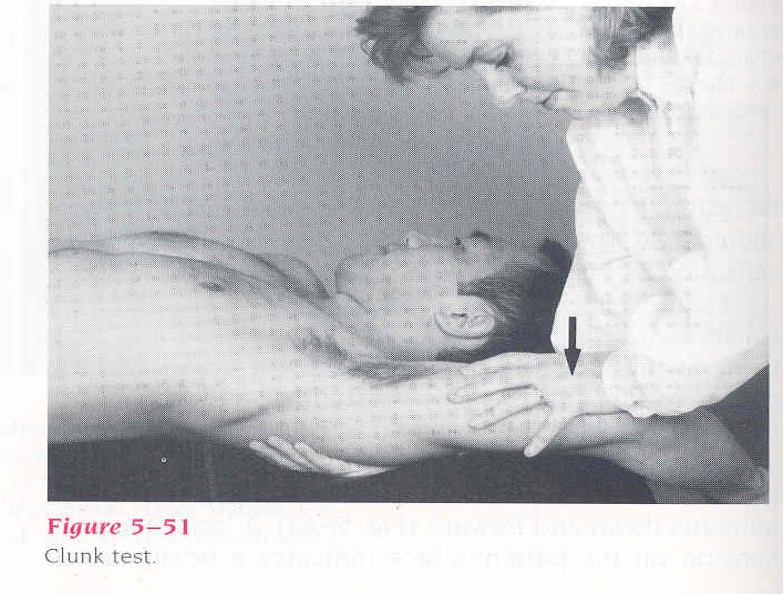
tests for labral lesions/tears
passively abduct and externally rotate shoulder overhead
positive = hear or feel a click when anteriorly translating humerus
Clunk test
SLAP lesions / Labral tears
Pt sit w/ hands on hip and thumbs pointing posteriorly → apply a forward and superior force on elbow and have pt resist
positive = click or pain increases
Anterior slide test
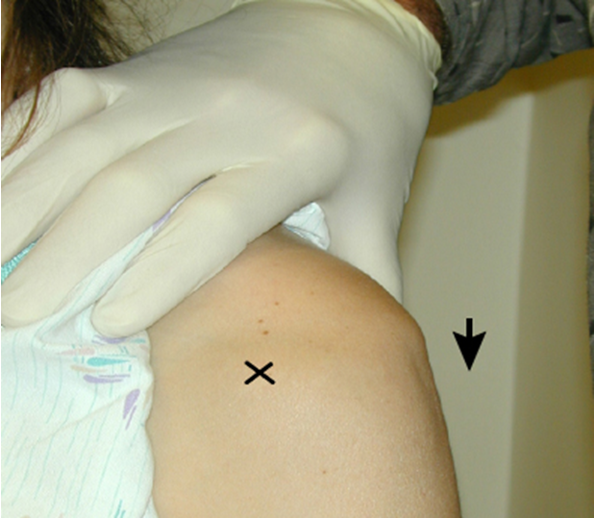
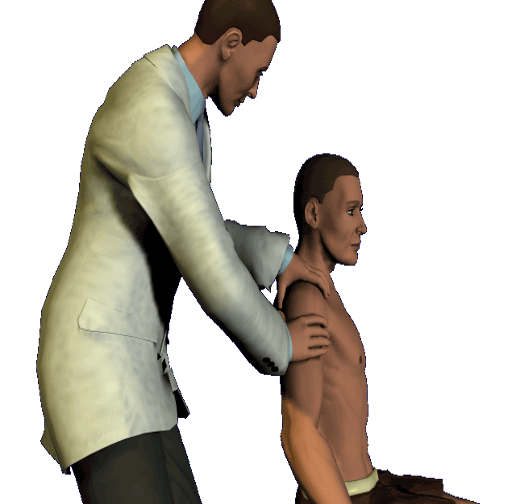
shoulder instability / inferior laxity
arm relaxed to side → palpate shoulder by placing fingers on anterior and posterior aspects of humeral head → grasp elbow and apply downward distraction
positive = depression appears bt acromion process and humeral head
Sulcus sign
detects and grades instability/laxity of shoulder /capsular mechanisms
pt supine → shoulder held at 80-120° abduction, flexion, and ER → apply force anterior or posterior
positive = relative movement / displacement
Anterior / Posterior drawer signs
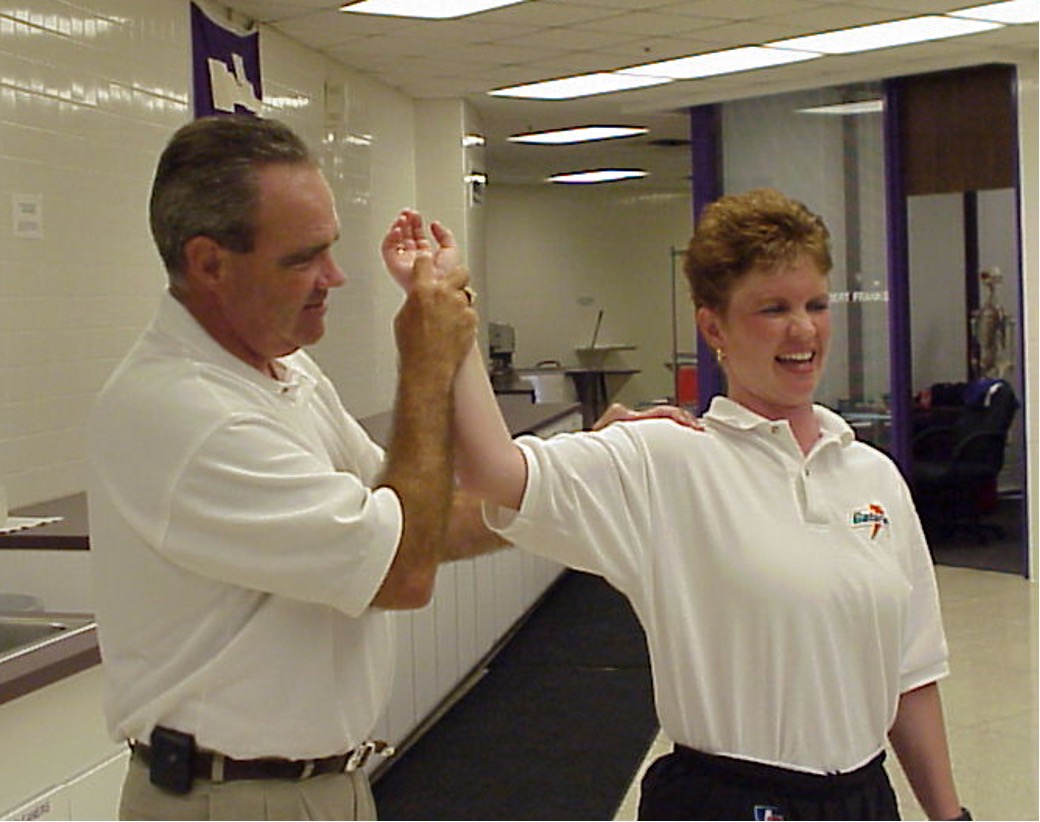

test for shoulder - anterior labrum/capsule instability
abduct and externally rate arm → apply gentle anterior force against posterior shoulder
positive = feeling of imminent subluxation / resist further motion
Anterior apprehension test
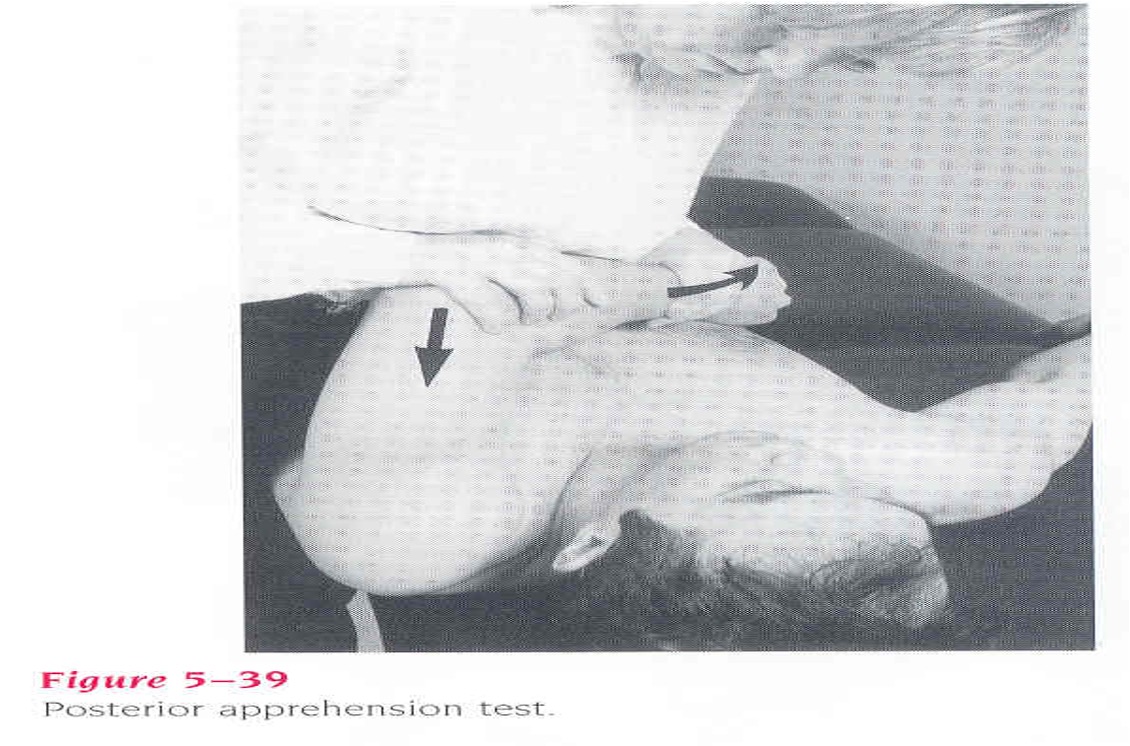
Tests for shoulder instability of posterior labrum or capsule
supine w/ shoulder and elbow flexed 90° and GHJ off table → grasp distal forearm and stabilize posterior scapula and apply downward force
positive = facial response / apprehension / resists further motion
Posterior apprehension test
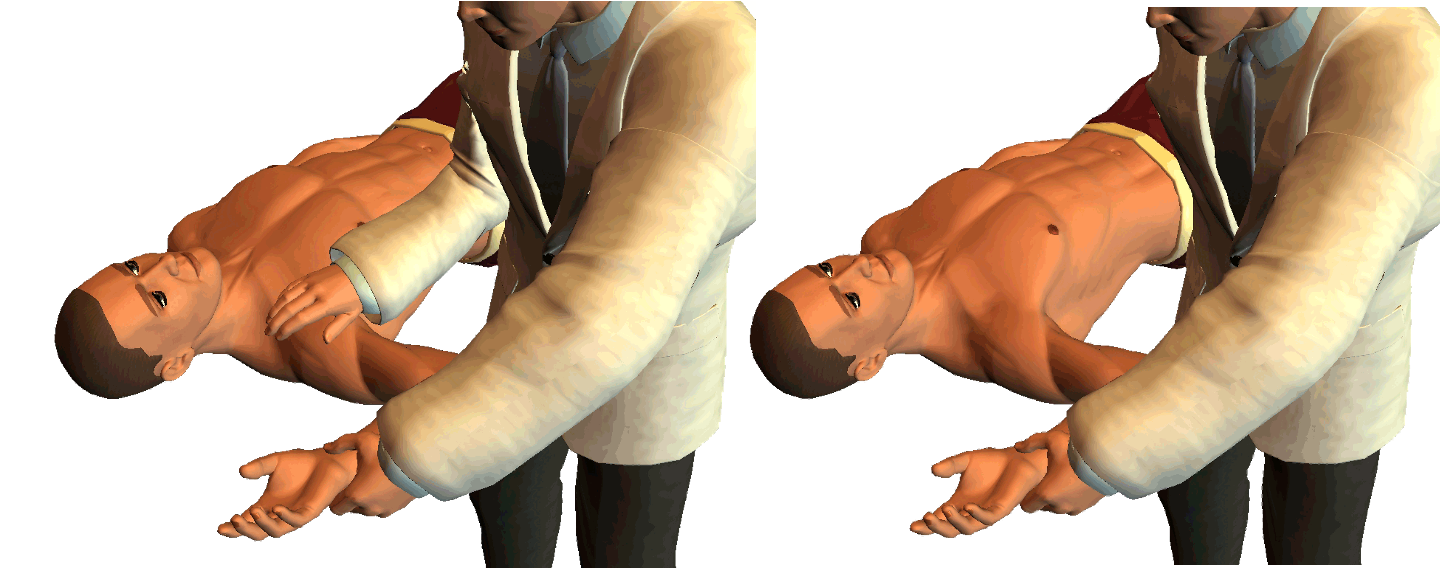
shoulder instability (anterior)
Jobe’s relocation test
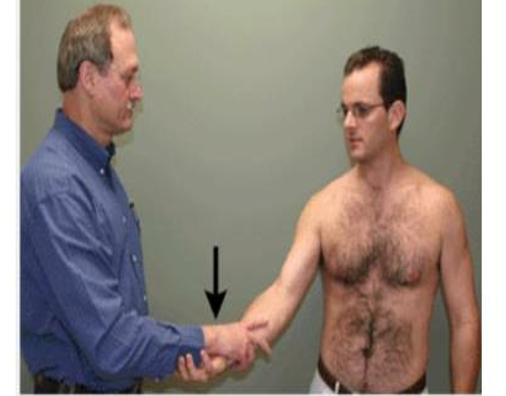
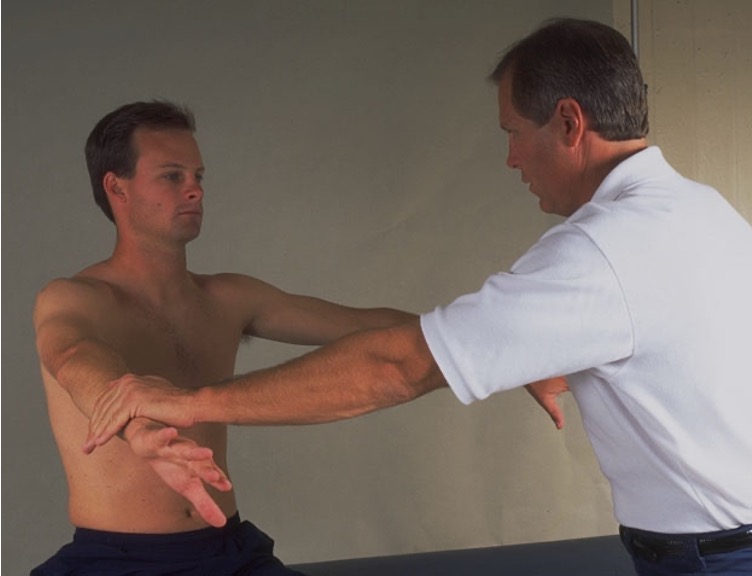
tests for bicipital tenosynovitis / pathology of bicep long head
with elbow in extension, pt flexes the shoulder against resistance from examiner
positive = pain in bicipital groove
Speed’s test
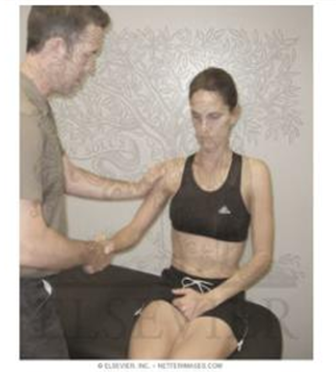
assess for pathology in long head of biceps tendon in its sheath
pt attempts to supinate wrist against resistance (with elbow flexed at side)
positive = pain in bicipital groove
Yergason’s test
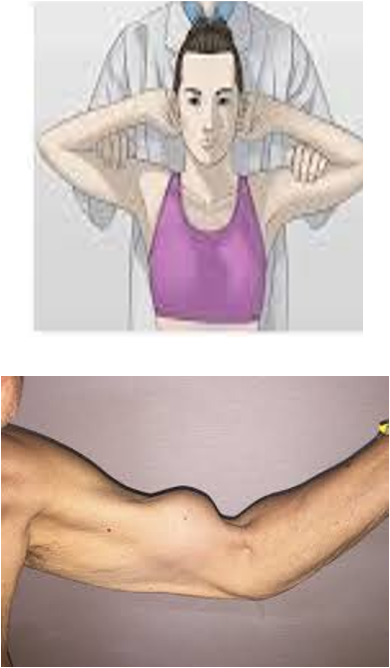
test for torn head of biceps
pt sitting, clasp hands behind head → ask pt to contract biceps
positive = no contraction is palpable
Ludington’s test
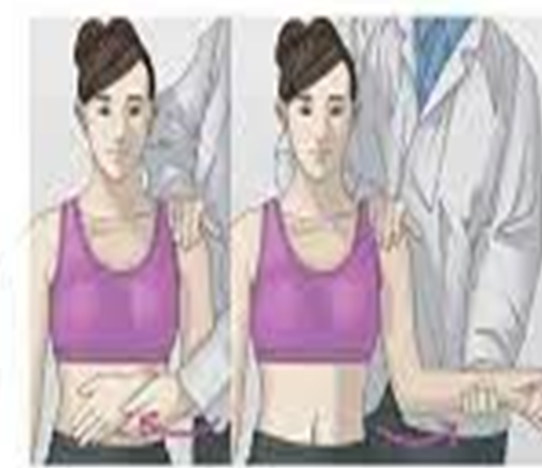
test for bicipital tendonitis or long head biceps tendon subluxation
hold pts arm and flex to 90° → palpate biceps tendon 8cm below GHJ then move tendon side to side
postive = sharp pain on bicipital groove
Lippman’s test
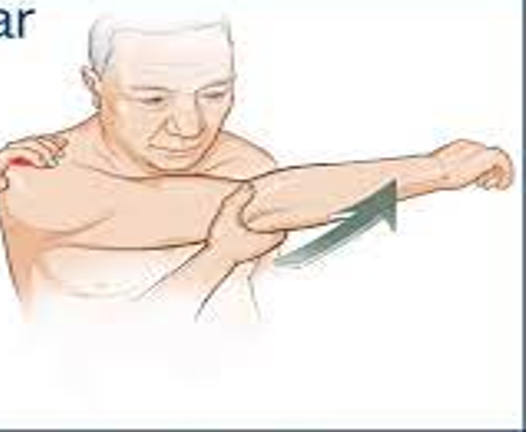
special test for AC joint
elevate arm to 90° flexion then maximum horizontal adduction
positive = pain on top of shoulder near AC joint
Crossover/Adduction test
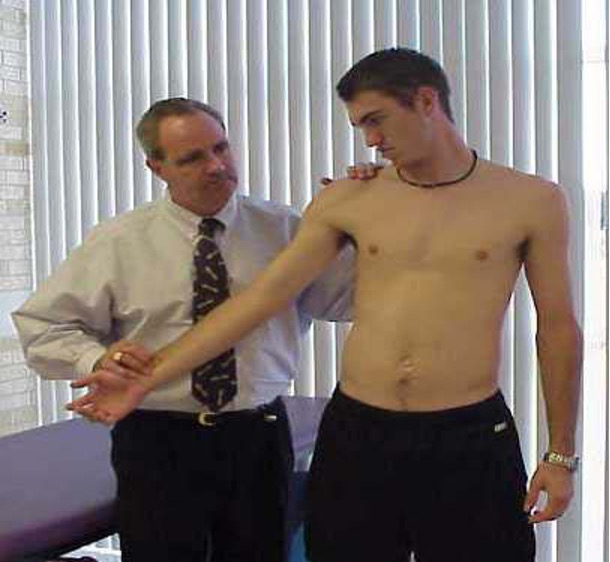
thoracic outlet syndrome
arm slightly abducted and extended → extend and rotate neck toward arm → inspire & palpate radial pulse
Adson’s or Scalene maneuver
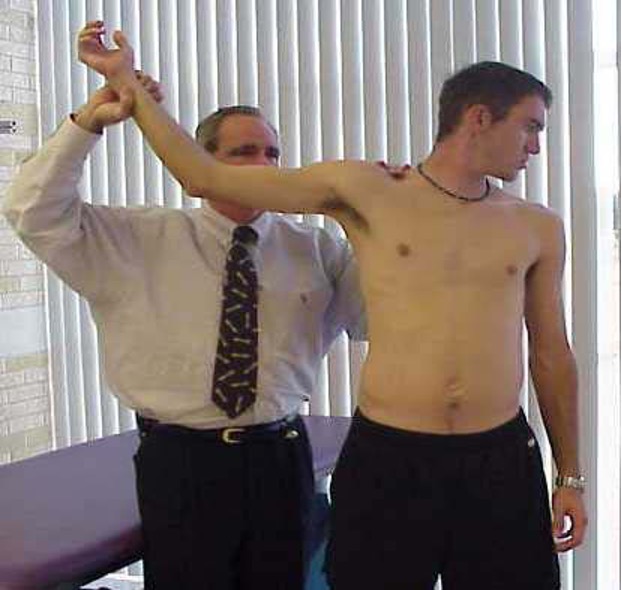
thoracic outlet syndrome
arm abducted and elbow flexed → turn head away from arm → externally rotate arm and palpate radial pulse
Allen’s test
special test for thoracic outlet syndrome
stand behind pt → passively extend and abduct arm to 30° → hyperextend head and neckline→ palpate radial pulse
Military brace
special test for thoracic outlet syndrome
pt sitting & hold both elbows at shoulder height while pushing shoulders back → repeatedly opens and close hand for several minutes
Roos Test
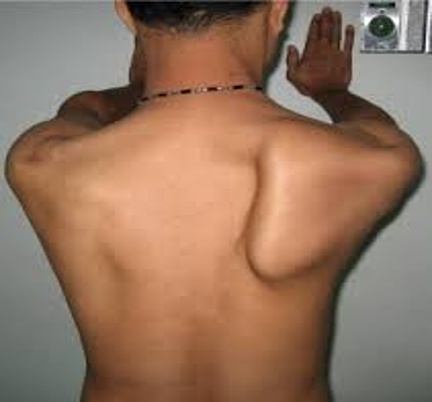
CN XI dysfunction
have pt perform a wall pushup → scapular instability makes inferior border of scapula move medially or laterally
medial- serrates anterior muscle weakness
lateral- trapezius muscle weakness
Winged scapula
Radial collateral ligament (LCL) damage
hold elbow slightly bent and apply pressure to inside of elbow → places lateral ligaments under stress
positive = pain and instability
Varus stress test
Ulnar collateral ligament (MCL) damage
hold elbow slightly bent and apply pressure to outside of elbow → placed medial ligament under tress
positive = pain and instability
Valgus stress test
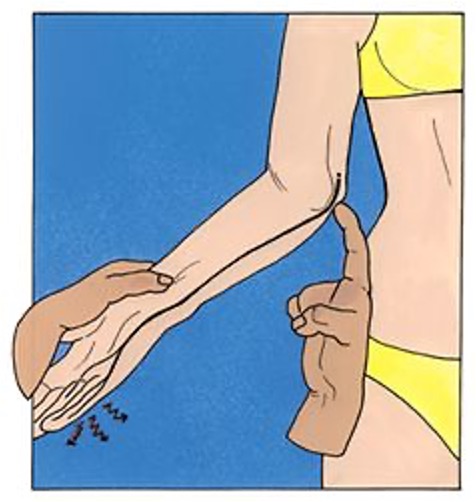
Ulnar nerve compression or entrapment (cubital tunnel syndrome)
repeated tapping over ulnar nerve where it passes behind and underneath medial epicondyle of elbow
positive = pain and tingling
Tinel’s sign of elbow
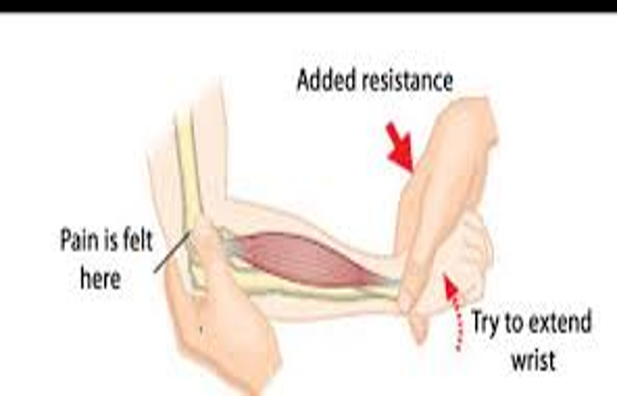
lateral epicondylitis / tennis elbow
palpate just below lateral epicondyle of elbow; apply pressure w/ hand to dorsum of pt’s fist forcing it into flexion
positive = pain on outside of elbow when hand is extended at wrist against resistance
Cozen test
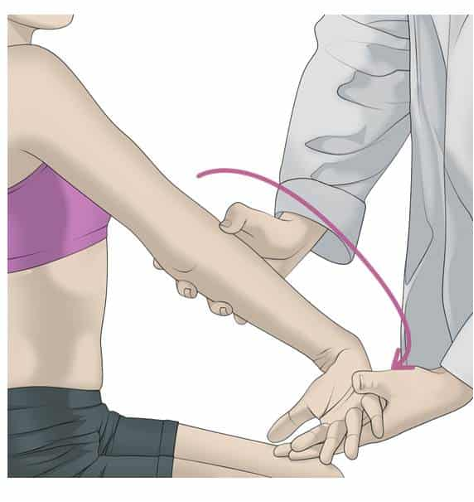
lateral epicondylitis / tennis elbow
stabilize elbow in one hand and ask pt to pronate forearm and extend and radially deviate wrist against manual resistance
positive = pain at lateral epicondyle
Mill’s test
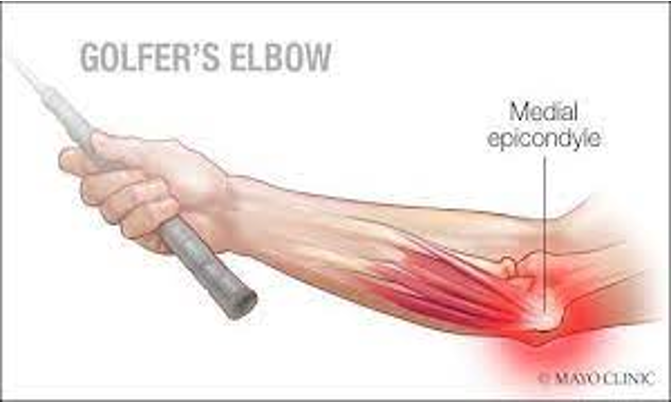
golfer’s elbow
pronate and flex wrist and forearm at same time while examiner resists in opposite direction
positive = pain isolated over attachment of wrist flexor muscles on inside of elbow
Medial epicondylitis test
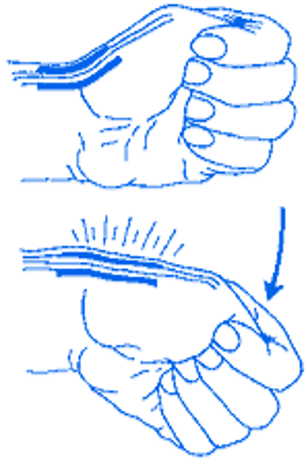
Dequervain’s tenosynovitis (abductor polices longus and/or extensor polices brevis tendon sheaths)
adduct and flex thumb and make a fist → stabilize wrist with one hand and apply varus force (or ulnar deviate)
positive = sharp pain on lateral aspect of wrist
Finkelstein test
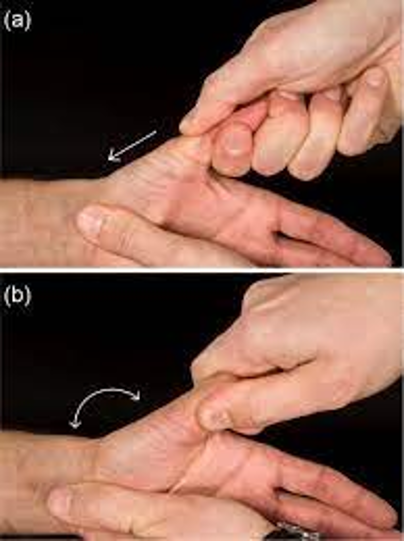
CMC arthritis
apply longitudinal axial load and rotate CMC joint
positive = pain and crepitus
Thumb grind test
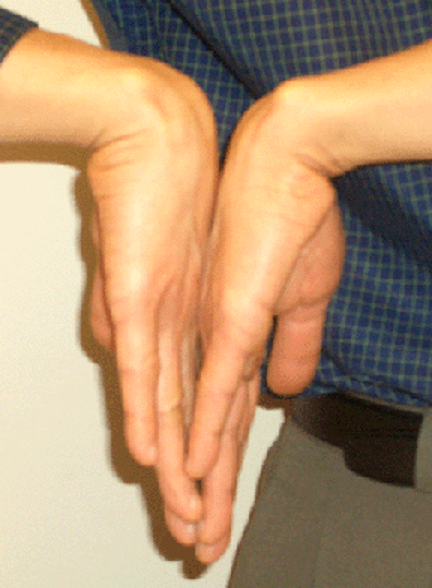
Carpal tunnel / median/radial nerve impairment
dorsal aspect of both hands in full contact w/ wrists maximally flexed → hold for 1 minute
positive = tingling/numbness radiation to fingers & palmar surface
Phalen’s test
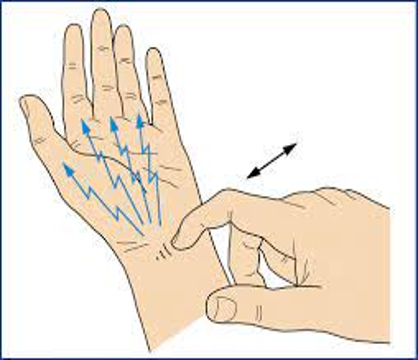
carpal tunnel syndrome
tap lightly over pt’s transverse carpal ligament
positive = paresthesia along distal most distribution of median nerve
Tinel’s sign at wrist
ulnar nerve impairment/paralysis
hold piece of paper b/t 1st and 2nd digits by forcefully opposing digits → attempt to pull paper out
positive = inability to hold contraction or weak contraction
Froment’s sign
UCL detachment
valgus force on MCP joint of thumb → stretching or rupture of UCL
MCP joint painful swollen, thumb feels weak to pinch, possible bruise discoloration
Valgus stress test / Gamekeeper’s thumb / Skier’s thumb
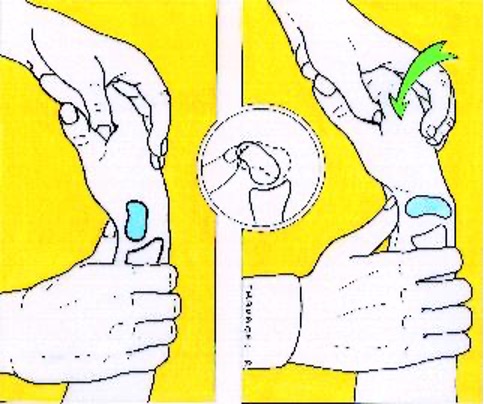
scaphoid instability
attempt to translate scaphoid anteriorly and posteriorly
positive = dislocation/subluxation
Watson clunk test
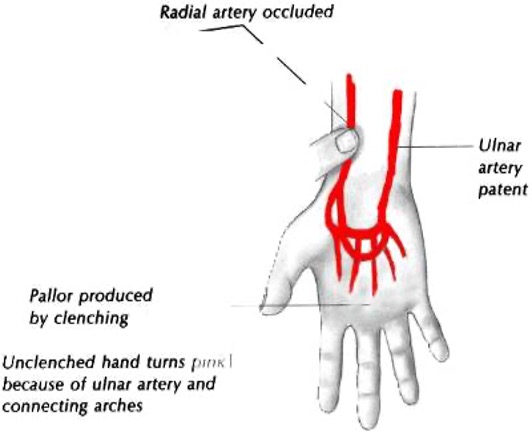
arterial compromise- assess hand circulation
rapidly open and close hand 15 times → place thumbs over radial and ulnar arteries → have pt open hand; should be pale → release one artery and hand should flush
positive = hand remains cyanotic
Digital allen test
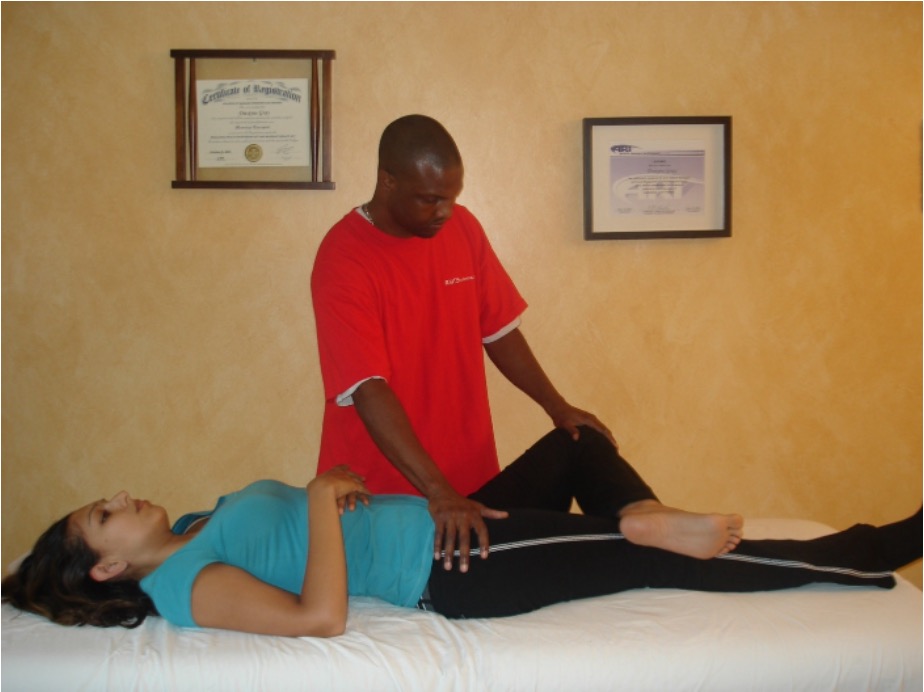
pathology of hip or sacrum
pt supine and flex, abduct, and externally rotate hip (put foot on opposite knee) → slowly press down on superior aspect of knee joint lowering leg into further abduction
positive = pain
FABER / Patrick / Figure 4 test
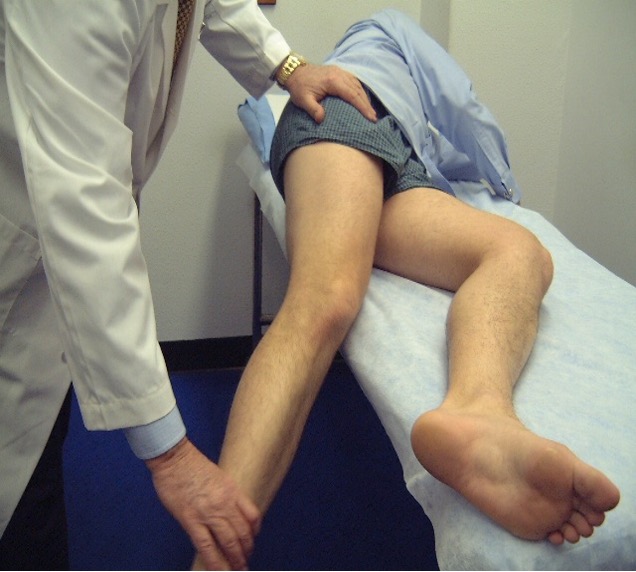
ITB or tensor fascia latae contracture
pt lie on unaffected side → abduct and extend hip to allow IT band to move posteriorly over greater trochanter then lower leg
positive = hip remains abducted
Ober test
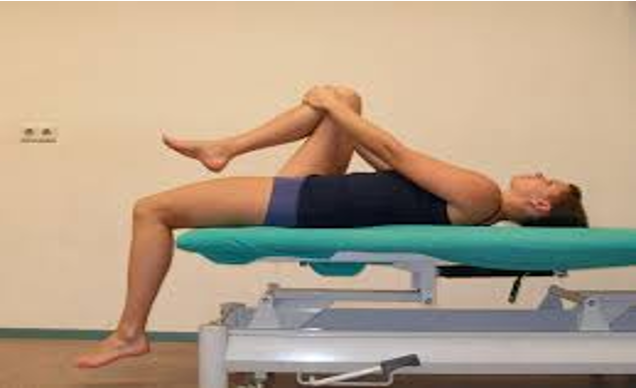
Hip flexor tightness
pt supine, bring unaffected leg to chest (flex hip&knee) → observe if other leg is slightly elevated off exam table
Thomas test
Piriformis muscle pain or pinched sciatic nerve
pt foot lateral to C/L knee → resist abduction or adduction against examiners hand
positive = pain
Piriformis syndrome test
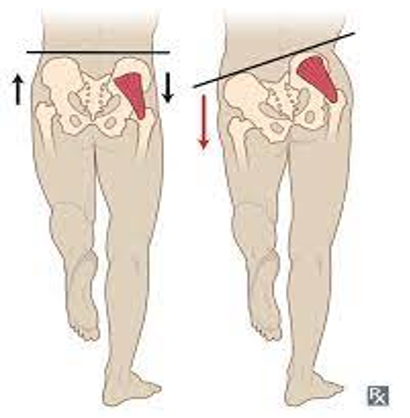
weakness of hip abductors, gluteus medius & minimus
pt stand on one leg
positive = pelvis of lifted leg tilts downward or drops
Trendelenburg test
congenital hip dysplasia - attempt to sublet unstable hip
infant supine w/ hips flexed to 90° → adduct the hip while applying downward / posterior force
positive = hip clunk
Barlow’s test
congenital hip dysplasia - attempt to relocate hip into acetabulum
infant supine w/ hips flexed 90° → abduct hip while applying upward force → push upward w/ greater trochanter (away from bed)
positive = clunk (relocated femoral head)
Ortalani’s test
moderate-severe knee effusion
pt lies supine while examiner “milks” knee capsule
positive = patella moves downwardly and then rebounds once pressure is removed (appearance of floating or ballotable patella)
Ballotable patella test
Patellofemoral syndrome (PFS)
pt supine → push patella distally in trochlear groove → quadriceps tighten against patella resistance
positive = pain or crepitus
Clarke’s sign / Patellar grind
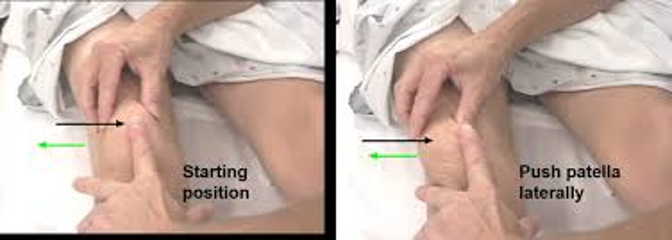
pt supine w/ legs flat on table and quads relaxed → try to dislocate patella laterally
positive = apprehensive or asks to stop (prone to patellar dislocations)
Patellar apprehension test
Knee MCL instability / tear
apply inward pressure to outer thigh and move lower limb outward
positive = pain and laxity
Valgus stress test
LCL instability / tear
apply outward pressure to inner thigh and move lower limb outward
positive = pain and laxity
Varus stress test
ACL tear
pt supin w/ hip and knee flexed → sit on pt’s foot and grasp tibia at joint line → pull tibia anteriorly
positive = inc anterior tibial translation and pain
Anterior drawer test
ACL tear
pt supine and knee flexed at 30° → femur stabilized w/ one hand and tibia pulled anterior w/ other
Lachman’s test
PCL tear
pt supine w/ hip and knee flexed → sit on pts foot and grasp tibia at joint line → push tibia posteriorly
positive = inc posterior tibial translation and pain
Posterior drawer test / Sag sign
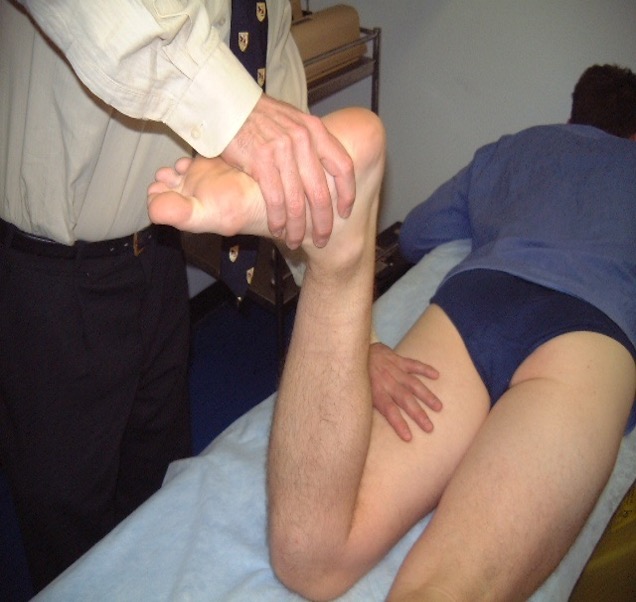
Meniscus tear
pt prone w/ knee flexed 90° → apply pressure to plantar aspect of heel, applying axial load to tibia while simultaneously IR & ER the tibia
positive = pain, clicking
Apley’s compression test
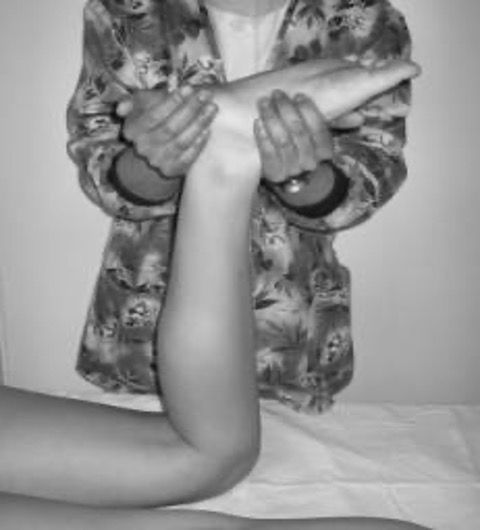

meniscus tear or ligament sprain
pt prone w/ knee flexed 90° → grasp lower leg and stabilize knee proximal to femoral condyles → distract tibia away from femur while IR and ER tibia
positive = dec pain (meniscus tear) or inc pain (ligament sprain)
Apley’s distraction test
Meniscus tear
pt supine w/ knee flexed (foot to buttocks) → internally rotate tibia and fully flex/extends knee (lateral) OR externally rotate (medial)
positive = palpable, audible, or painful click
McMurray’s test
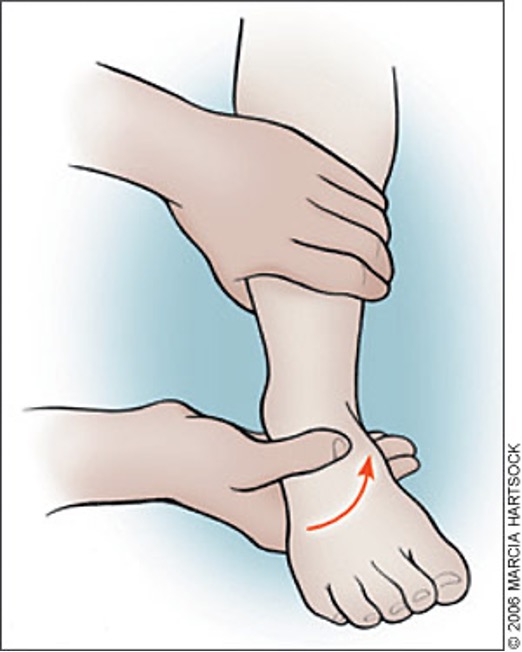
grasp calcaneus and stabilize lower leg → provide inversion or eversion stress rolling calcaneus inward or outward while ankle is in neutral
inversion = LCL injury
eversion = medial aspect of ankle (deltoid ligament)
Talar tilt test
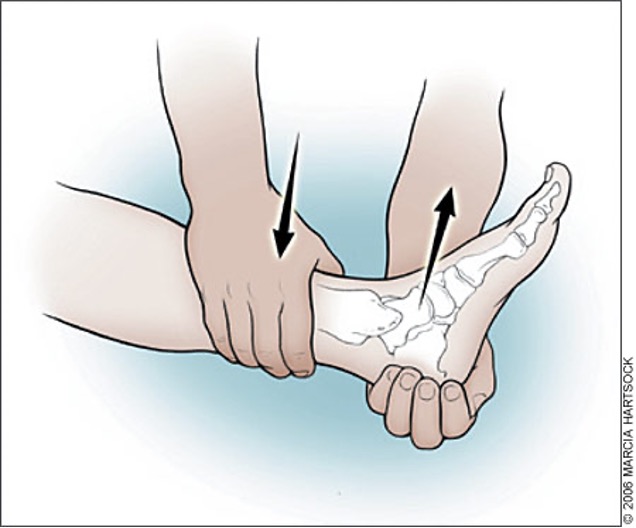
anterior taolfibular ligament tear
stabilize leg above ankle and pull up on heel or forefoot
Anterior drawer test- ankle
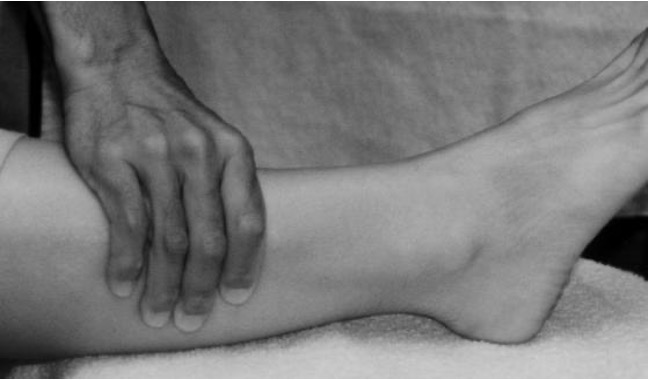
high ankle sprain or possible fx
pt sitting or lying w/ knee extended → cup hands behind the tibia and fibula, away from site of pain, compress gradually adding more pressure
Syndesmosis squeeze test
tarsal tunnel syndrome / compression of posterior tibial n.
pt supine w/ hip externally rotated and foot slightly everted → tap over tarsal tunnel
Tinel’s sign of ankle
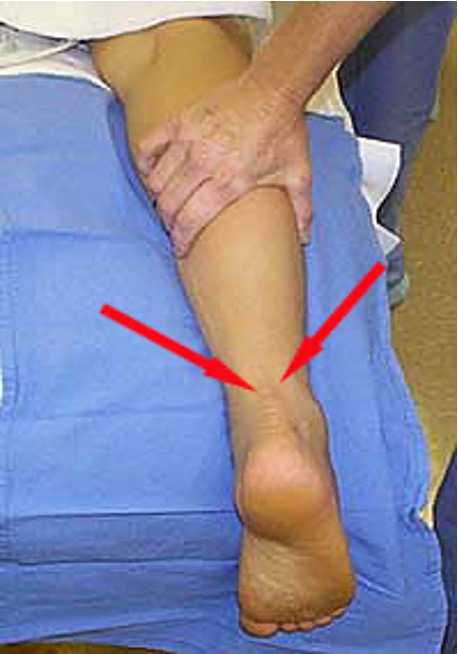
Torn achilles tendon
squeeze calf
positive = no motion
Thompson test
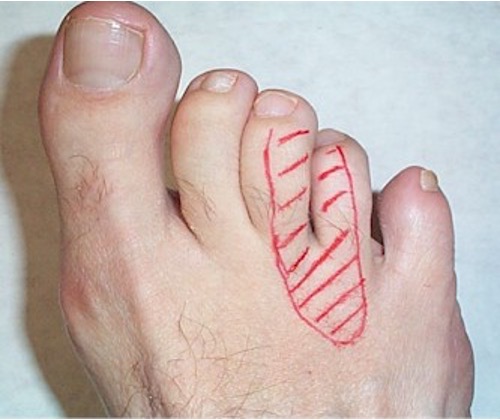
Morton’s neuroma
apply pressure between 3rd and 4th metatarsals
positive = pain
Morton’s test
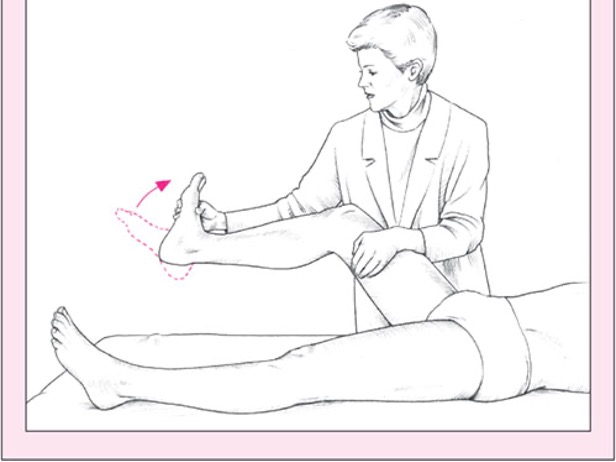
DVT
pt sitting or supine w/ knee extended → passively dorsiflex foot while knee extended → palpate calf
positive = pain
Homan’s sign
UMN lesion
stroke lateral-plantar aspect of foot and move across MTPs w/ handle of reflex hammer to provoke a cord (CNS) sign
positive = dorsiflexion of great toe w/ fanning of other toes
Babinski sign
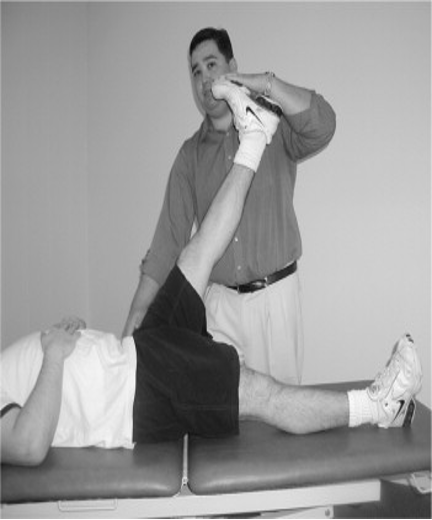
lumbosacral nerve root irritation (sciatic nerve)
pt supine → raise leg w/ hips flexed and keeping knee straight
positive = pain
Straight leg raise
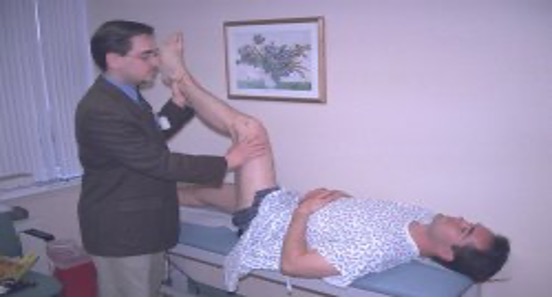
meningitis or SAH
pt supine w/ hip and knee in flexion 90° → exend knee
positive = pain or inability to extend past 135°
Kernig’s sign
meningeal irritation
pt supine → place hands behind pts head then raise head or flex neck
positive = involuntary flexion of hips/knees due to pain
Brudzinski’s sign