Human Anatomy - Chapter 7
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
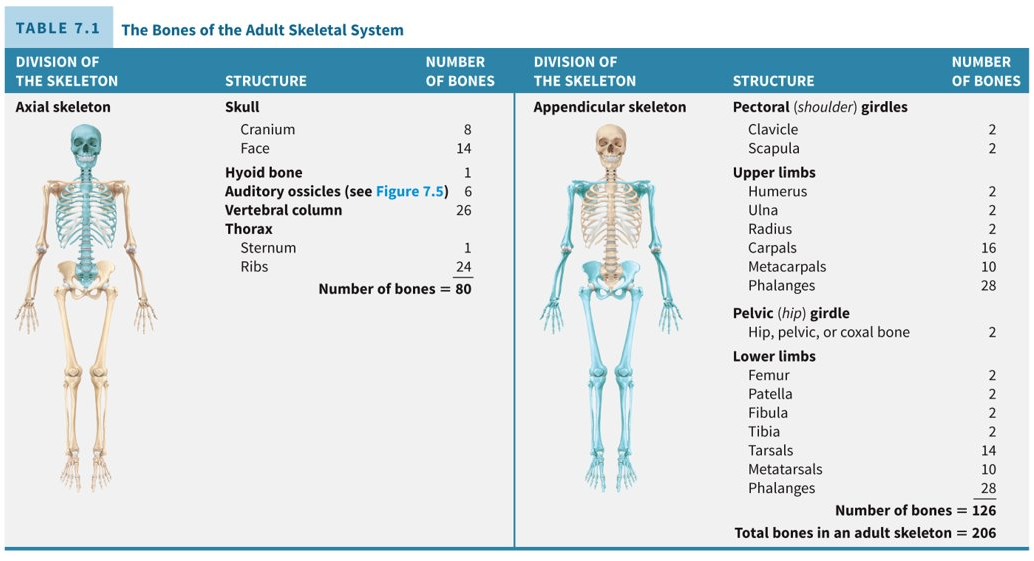
How many bones does the adult have?
two hundred and six; eighty in the axial skeleton and one hundred and six in the appendicular skeleton
2
New cards
What does the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis?
protects many of the body’s organs; support the storage and release of calcium
3
New cards
What are the five main shapes of bone?
long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid
4
New cards
What are sutural bones?
small, extra bone plates located within the sutures of cranial bones
5
New cards
What are the two major types of surface markings?
depressions/openings (passage of soft tissue, form joints) and processes (projections that form joints, attachment points for ligaments and tendons)
6
New cards
What are the five types of depressions and openings and their description?
fissure: narrow slit between bones for passage of blood vessels or nerves
foramen: hole for passage of blood vessels, nerves or ligaments
fossa: shallow depression
sulcus: furrow on a bone for passage of blood vessel, nerve or tendon
meatus: tube-like opening
foramen: hole for passage of blood vessels, nerves or ligaments
fossa: shallow depression
sulcus: furrow on a bone for passage of blood vessel, nerve or tendon
meatus: tube-like opening
7
New cards
What are the eleven types of processes and their description?
condyle: rounded projection with a smooth articular surface
facet: rounded articular process supported on a neck
head: smooth, flat, slightly concave articular surface
crest: prominent ridge or elongated process
epicondyle: roughened projection on a condyle
line: long, narrow ridge or border
spinous process: sharp, slender projection
trochanter: large projection found only on the femur
tubercle: variably sized rounded projection
tuberosity: variably sized projection with rough, bumpy surface
facet: rounded articular process supported on a neck
head: smooth, flat, slightly concave articular surface
crest: prominent ridge or elongated process
epicondyle: roughened projection on a condyle
line: long, narrow ridge or border
spinous process: sharp, slender projection
trochanter: large projection found only on the femur
tubercle: variably sized rounded projection
tuberosity: variably sized projection with rough, bumpy surface
8
New cards
How many bones are in the skull?
twenty-two (not including the three middle ear bones in both ears)
9
New cards
What are the groups of the skull bones?
cranial bones (8) and facial bones (14)
10
New cards
What is a paranasal sinus?
skull bones containing mucous membrane-lined cavities
11
New cards
What is the only moveable bone of the skull?
mandible
12
New cards
What is the function of the cranial bones?
protect the brain; stabilize the positions of the brain, blood vessels, and nerves; protect and support the special sense organs
13
New cards
What is the function of the facial bones?
protect and support the nerves and blood vessels in the area; protect and support the special sense organs
14
New cards
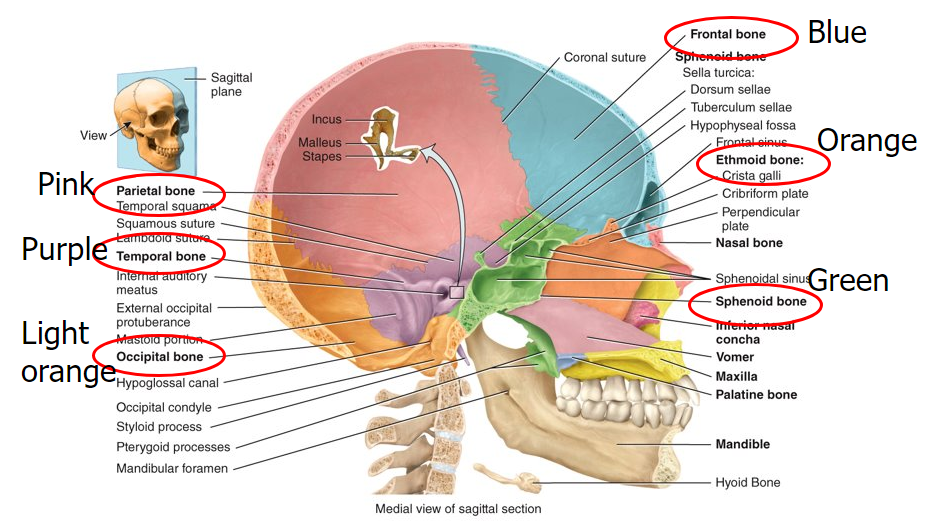
What are the six cranial bones?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid
15
New cards
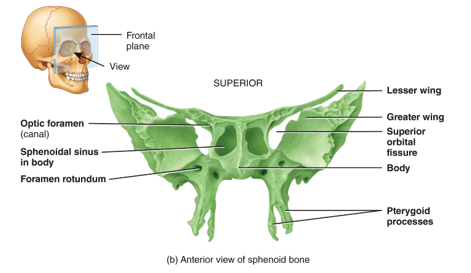
What is the sphenoid bone?
keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with all the other cranial bones
16
New cards
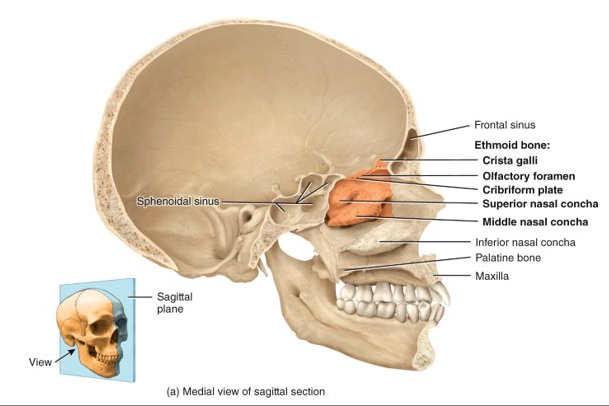
What is the ethmoid bone?
forms part of the anterior portion of the cranial floor, the medial wall of the orbits, the superior portion of the nasal septum, and most of the superior side walls of the nasal cavity; major superior supporting structure of the nasal cavity
17
New cards
What are the 14 facial bones?
two nasal bones, two maxillae, two zygomatic, mandible, two lacrimal, two palatine, two inferior nasal conchae, and vomer
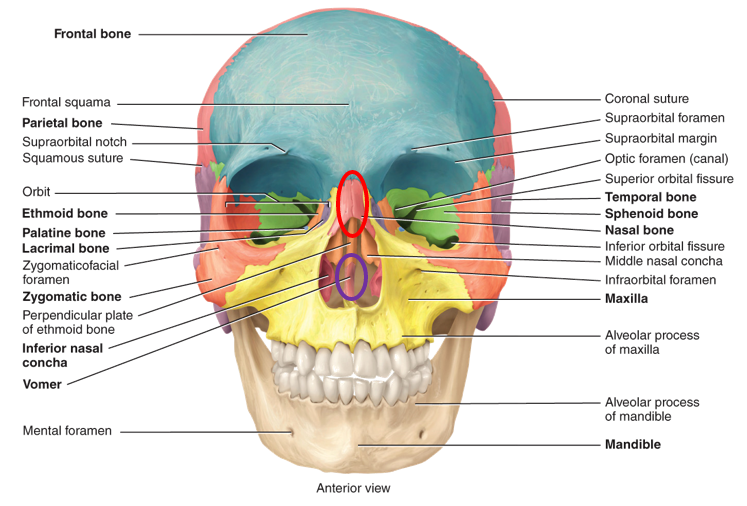
18
New cards
What does the maxillae articulate with?
every bone in the face except for the mandible
19
New cards
What is the largest and strongest facial bone?
mandible
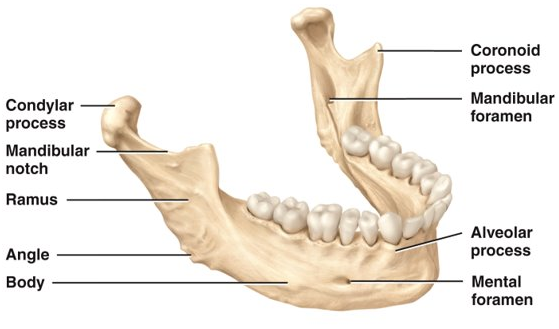
20
New cards
What is the nasal septum?
a vertical partition that divides the nasal cavity into right and left sides
21
New cards
What bones form the orbit?
frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, maxilla, palatine, ethmoid, and lacrimal
22
New cards
What are sutures?
immovable joints found only between skull bones and hold skull bones together
23
New cards
What are the four sutures of the skull?
coronal, lambdoidal, squamosal, and sagittal
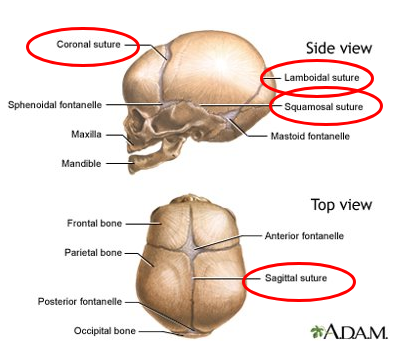
24
New cards
What are fontanels?
dense connective tissue membrane-filled spaces between the cranial bones of fetuses and infants
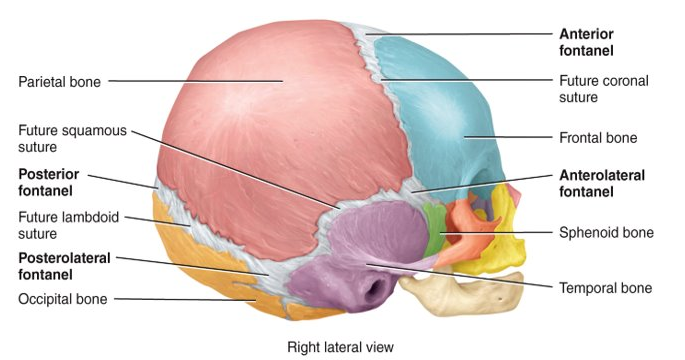
25
New cards
What are the two major functions of fontanels?
enable the fetal skull to modify its size and shape as it passes through the birth canal and permits rapid growth of the brain during infancy
26
New cards
What is the hyoid bone?
supports the tongue and provides an attachment site for some muscles of the neck and pharynx; does not articulate with any other bone
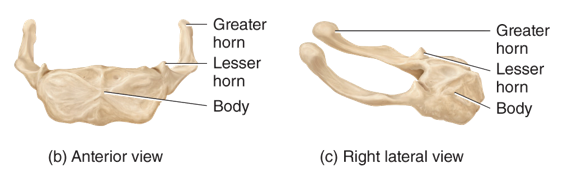
27
New cards
How many vertebrae does the vertebral column?
twenty-six; seven in the cervical, twelve in the thoracic, five in the lumbar, one as the sacrum (5 fused), and one as the coccyx (4 fused)
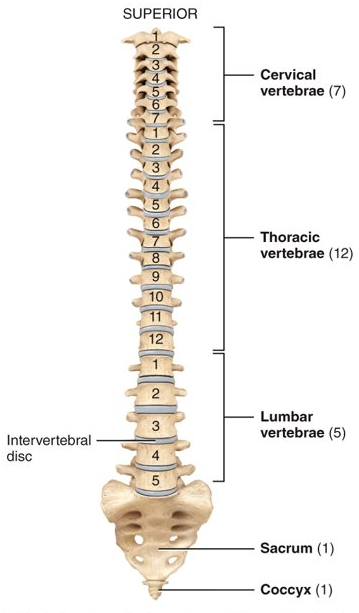
28
New cards
What are the four normal vertebral curves?
cervical and lumbar (anteriorly convex curves) and thoracic and sacral (anteriorly concave curves)
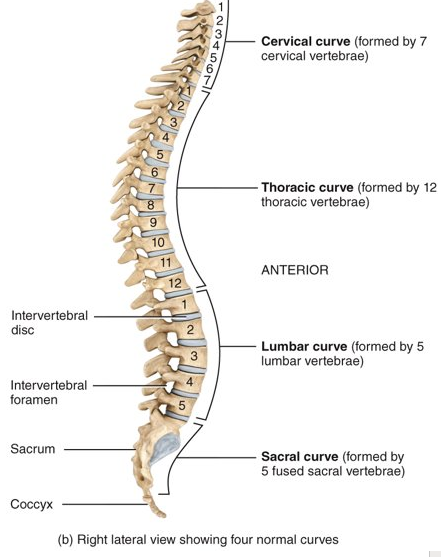
29
New cards
How does the spine develop as we age?
fetus: one single, anteriorly, concave curve
child: develops cervical curve to hold head up
child: lumbar curve develops to begin walking
child: develops cervical curve to hold head up
child: lumbar curve develops to begin walking
30
New cards
What are intervertebral discs?
located between the bodies of the vertebrae from the second cervical to the sacrum
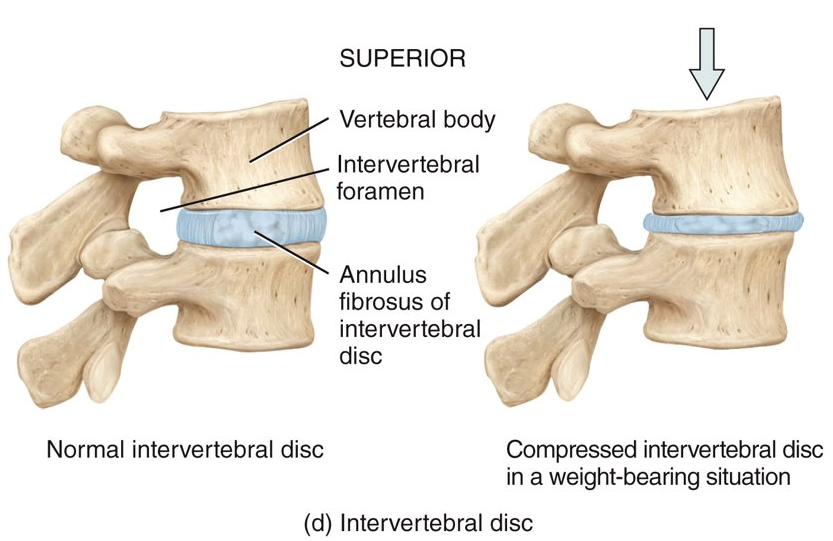
31
New cards
What are intervertebral discs made of?
an outer ring of fibrocartilage and an inner, soft nucleus with a layer of hyaline cartilage
32
New cards
what do intervertebral discs do?
Absorb shock and separate the vertebrae
33
New cards
What are the first and second cervical vertebra?
atlas (supports the skull) and axis (side-to-side rotation)
34
New cards
What are the largest and strongest vertebrae?
lumbar
35
New cards
Picture of difference of vertebra.
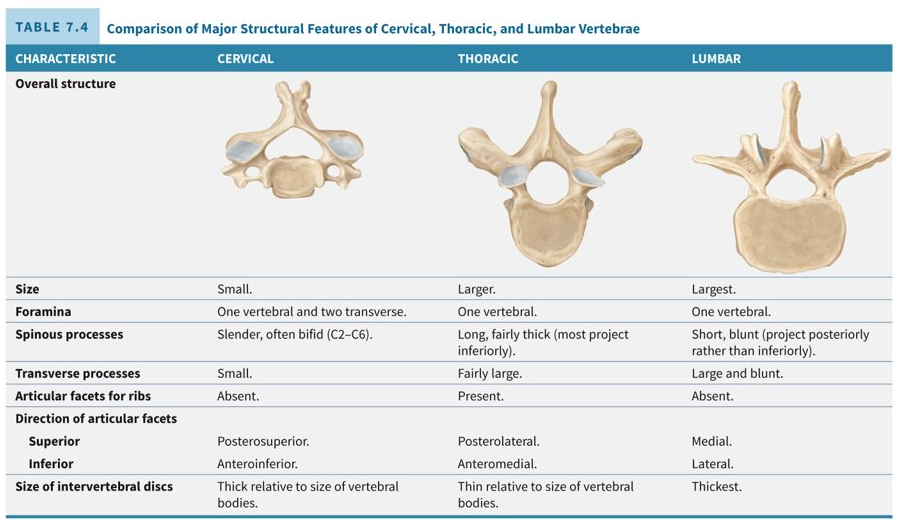
36
New cards
Picture with vertebra diagram.
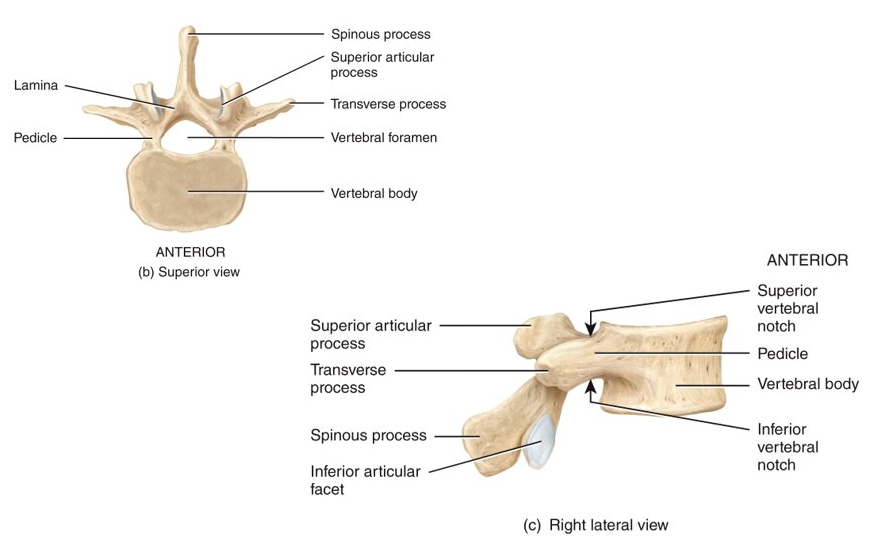
37
New cards
What makes up the bones of the thorax?
ribs, sternum, and costal cartilage
38
New cards
What is the purpose of the thoracic cage?
protects the organs in the thoracic and superior abdominal cavities; provides support for the bones of the shoulder girdle and upper limbs
39
New cards
What are the three segments of the sternum?
manubrium, sternal body, and the xiphoid process
40
New cards
How are the 12 ribs divided?
first seven (vertebrosternal) are true ribs, next five (vertebrochondral) are false ribs, and the last two of the false ribs are called floating ribs
41
New cards
Picture of rib diagram.
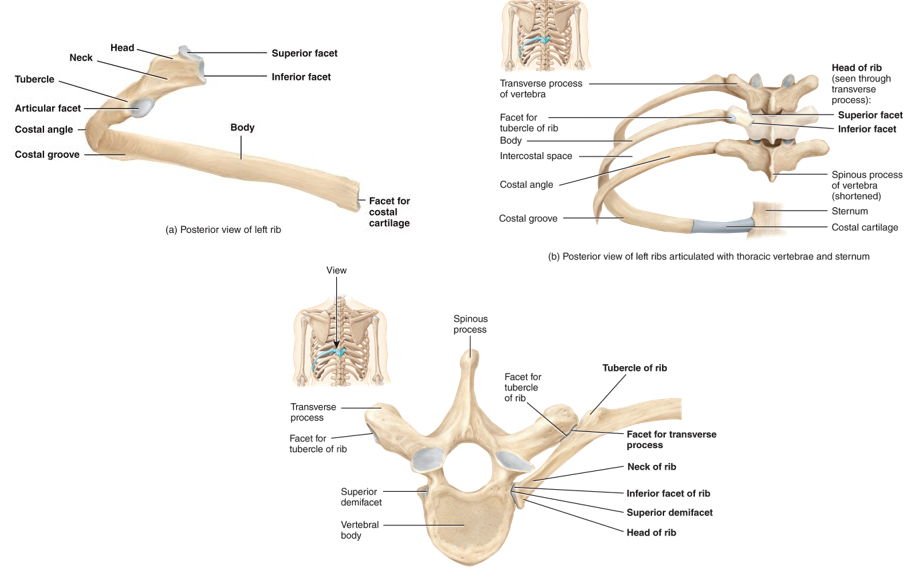
42
New cards
What causes a herniated disc?
may occur due to trauma or sometimes is simply associated with aging
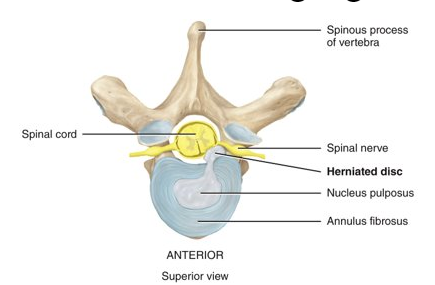
43
New cards
What are the three curve-related pathologies of the spine?
scoliosis (lateral curvature), kyphosis (thoracic curve), and lordosis (lumbar curve)
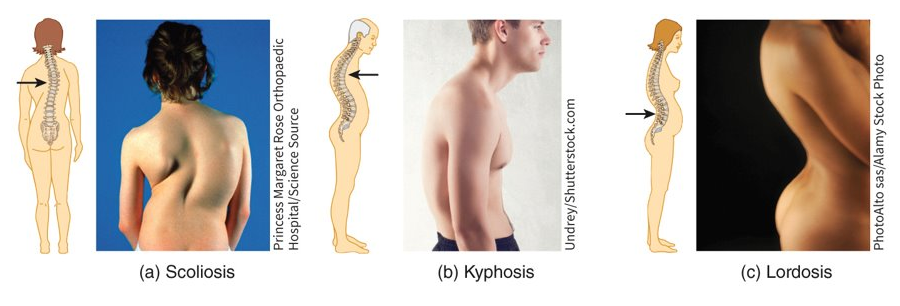
44
New cards
What is spina bifida?
a congenital defect caused by failure of the vertebral laminae to unite at the midline
45
New cards
What vertebra are most commonly fractured?
C1, C2, C4-T, and T12-L2