Introduction to Ecology (Bio 2e Chapter 44-45)
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Ecology
is the scientific study of the distribution and abundance of organisms, and their interactions with the environment.
ecology etymology
comes from the Greek words “oikos”, meaning house, and “logos”, to study
Different Levels of Organization in Ecology
Individuals Populations Communities Ecosystems
Ecology is establishing its central_______
scientific paradigms
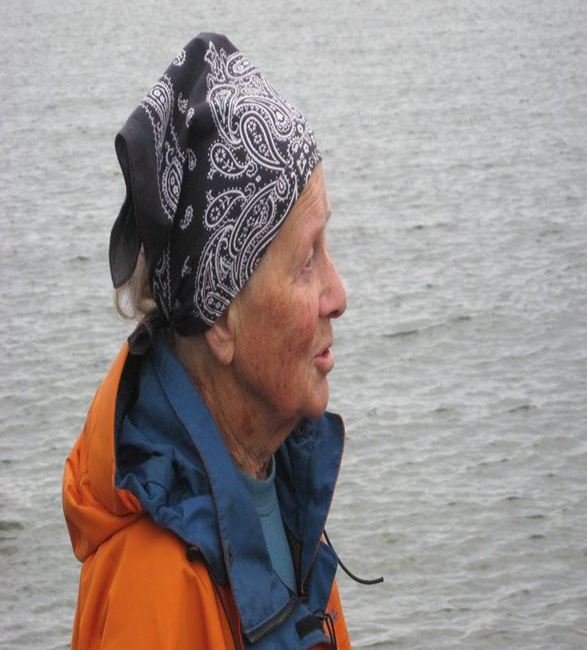

Who is this?
Evelyn Pielou an influential ecologist that brought a mathematical modeling approach to the study of ecology
Individuals
single, discrete organisms
Would a stand of aspen trees which are all interconnected be an individual or many individuals?
Since they are all interconnected they count as one indivual.
A fungus mycellium that occupies tens of square kilometers is a single or many individuals
Single, its only fungus; distance doesn’t matter
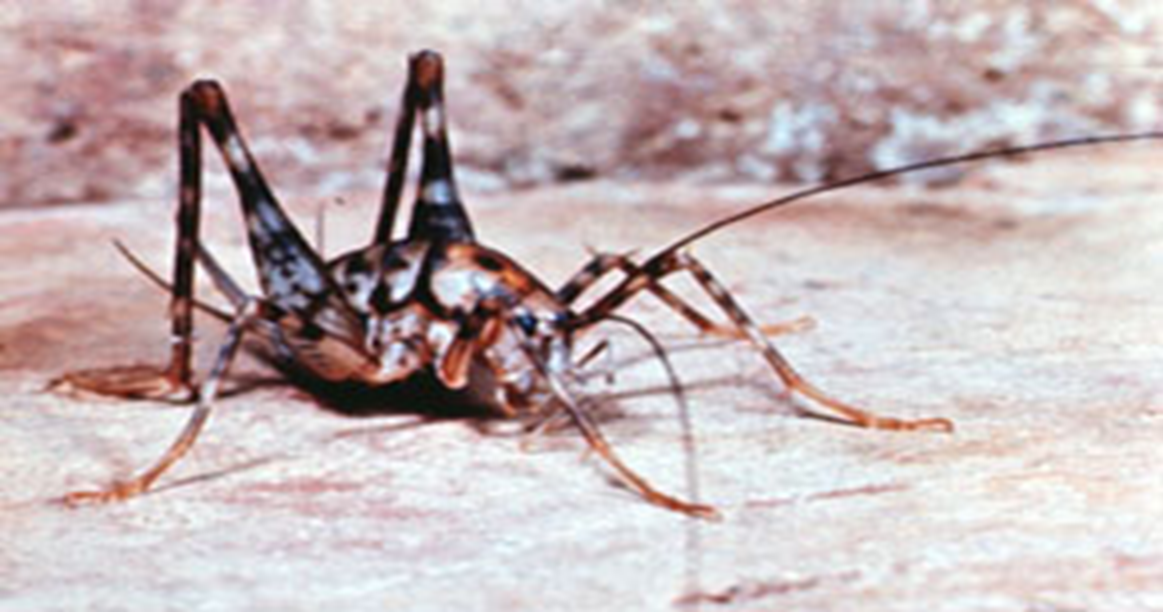

What is this an example of?
Organismal ecology: Studying how cave crickets find its entrance and exit from caves
Populations
are groups of organisms of the same species living in the same place.
most interaction among members of a given species occurs within a_______
population
a herd of wildabeast ...all the bullhead catfish living in a midwestern lake …all of the tropicbirds nesting on a single oceanic island ….the E. coli population in a single person’s gut
Are all examples of what?
populations
Population ecologists ask what kind of questions and at what ecology level?
They ask questions about abundance, density, population growth, and limits to growth and ask at the population level
Communities
are assemblages of populations of different species living in the same place.
Different species have different “_______” in a biological community
Functions, this may includes decomposers, producers,
Community Ecologists asks what kind of questions?
the structure of natural communities and the role of biodiversity in ecosystem integrity
Ecosystems
are interacting assemblages of living things living in a particular area, and the nonliving components (Water, Light, soil etc)
Ecosystems Ecologists asks what kind of questions?
ask how living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components interact to affect energy flow, nutrient cycling, and overall ecosystem function.
What did Robert Marquis and Chris Whelan study?
the role of birds in limiting the density of herbivorous insects
—> Conclusion-birds are an important potential agent of herbivore control.
One of the most important attributes of a good experiment is that its results be____
reproducible
What are ecosystems ecologists interested in?
interactions between living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components
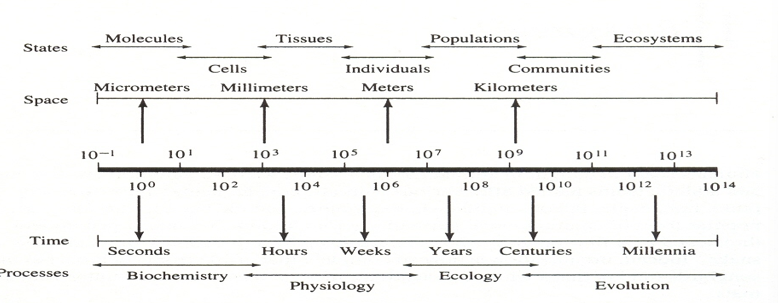
What is this?
A representation of the time-space scaling of various biological phenomena
Weather
is the particular set of abiotic conditions, such as rainfall, sunlight, temperature, and humidity, affecting a particular area at a particular time.
Climate
is the overall pattern of weather in that area.
Weather changes_________
daily
climate changes________
over decades, hundreds, or thousands of years
A fundamental theme in the study of ecology is the
interconnectedness of components.
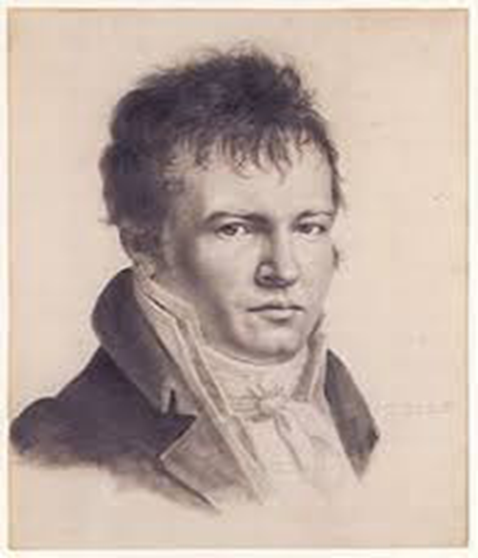

Who is this
Right-Alexander von Humboldt - He saw the living world as a connected system, with species as interacting parts.
Biomes
are Broad groups of plant and animal communities, usually defined by the dominant vegetation.
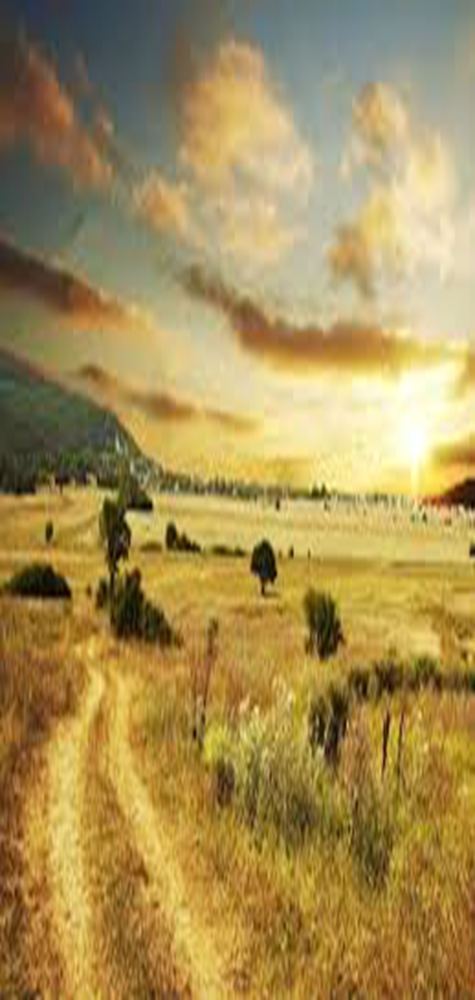

What is this
The veldt is a South African community dominated by grasses and shrubs in a semiarid region. Intense grazing and fire prevent trees from establishing. It is an example of the grassland biome.
Major Terrestrial Biomes
Tundra Taiga or Coniferous Forests Desert Chaparral Grasslands Temperate Deciduous Forests Tropical Rain Forests
Major Physical Factors Influencing Terrestrial Biomes
Rainfall, and its timing Sunlight Disturbance
How does the shape of the Earth affect climate?
It makes high latitudes colder than the tropics. Sunlight strikes the poles at an angle, spreading over a larger area, so less energy is received per unit ground.
What are Hadley cells and how do they affect climate?
Warm air rises at the equator, sheds moisture, and descends at ~30° latitude, creating dry zones (deserts).
What are Ferrel cells and how do they affect climate?
Circulation in mid-latitudes between Hadley and Polar cells; mix warm and cold air, producing temperate climates.
What are Polar cells and how do they affect climate?
Cold air descends at the poles, creating cold, dry regions.
What determines the vegetation and structure of terrestrial biomes?
Water availability (amount & timing) Sunlight Temperature
Vegetation gives __________creating _______for different organisms.
spatial structure, micro-environments
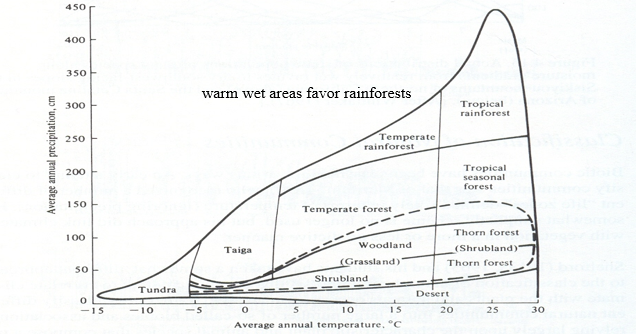
What is this
Representation of the correlation between climate and average annual rainfall
What characterizes the tundra biome?
No trees; dominant vegetation includes lichens, annual grasses, and specially adapted shrubs and woody plants.
Where does tundra occur and what is its climate like?
Found in polar regions and high elevations. Short growing season; most precipitation falls as snow
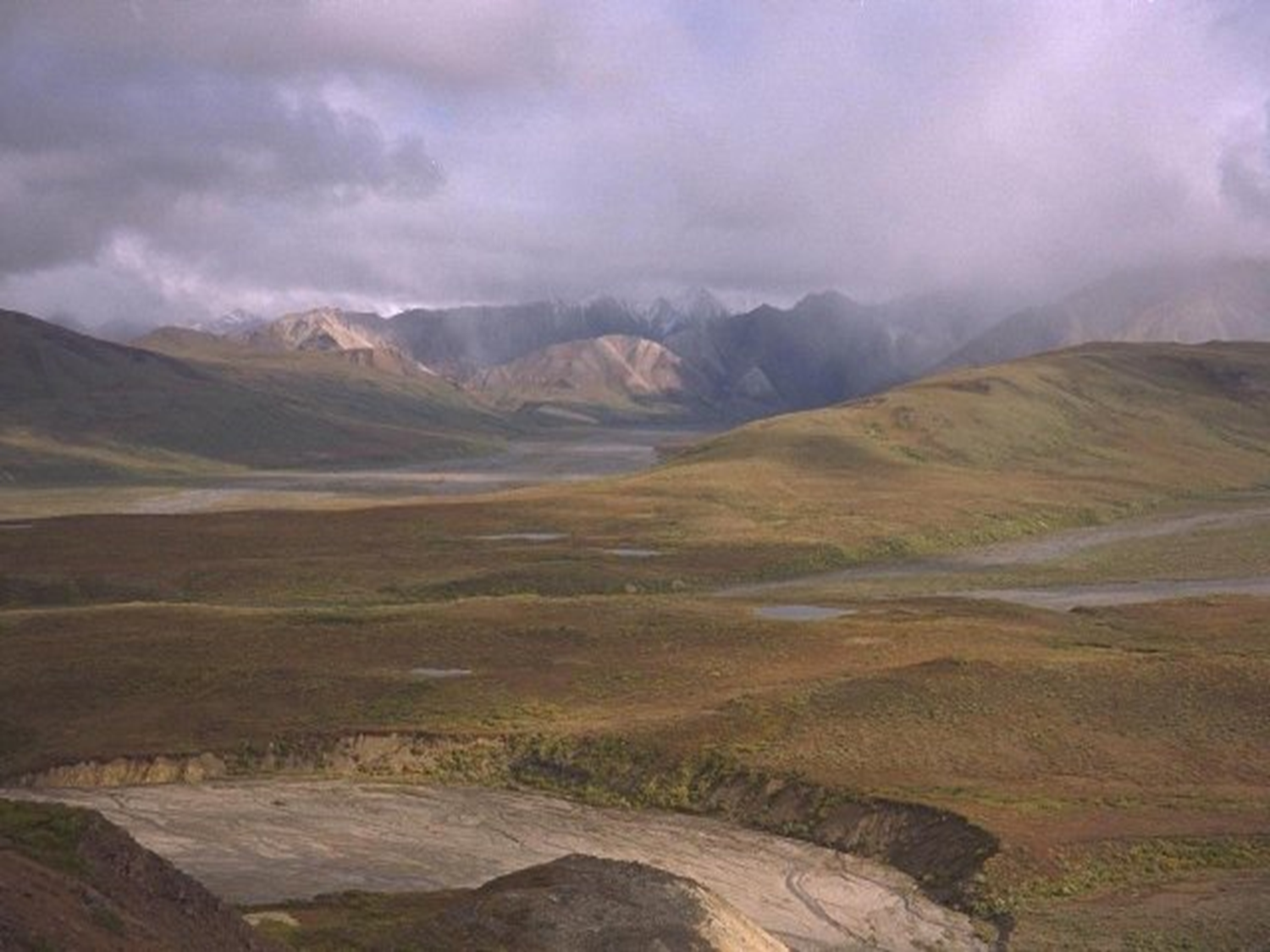

What biome is this and why?
Tundra —→ lack of trees, shubbery, dry, high mountatins,
What characterizes the taiga (coniferous forest) biome?
Dominated by cone-bearing trees like pine, spruce, and fir, usually one or a few species. Common at high latitudes and elevations, covering vast areas.
Where is the taiga biome commonly found?
It is very common, covering huge areas at high latitudes or high elevations.(Canada)
When is the growing season in the taiga?
During cool to warm summers; plants are dormant in winter because temperatures are too low for photosynthesis.
How does precipitation occur in the taiga and why is it important?
Much of the precipitation falls as snow. Snowmelt releases water that supports the communities in the taiga.
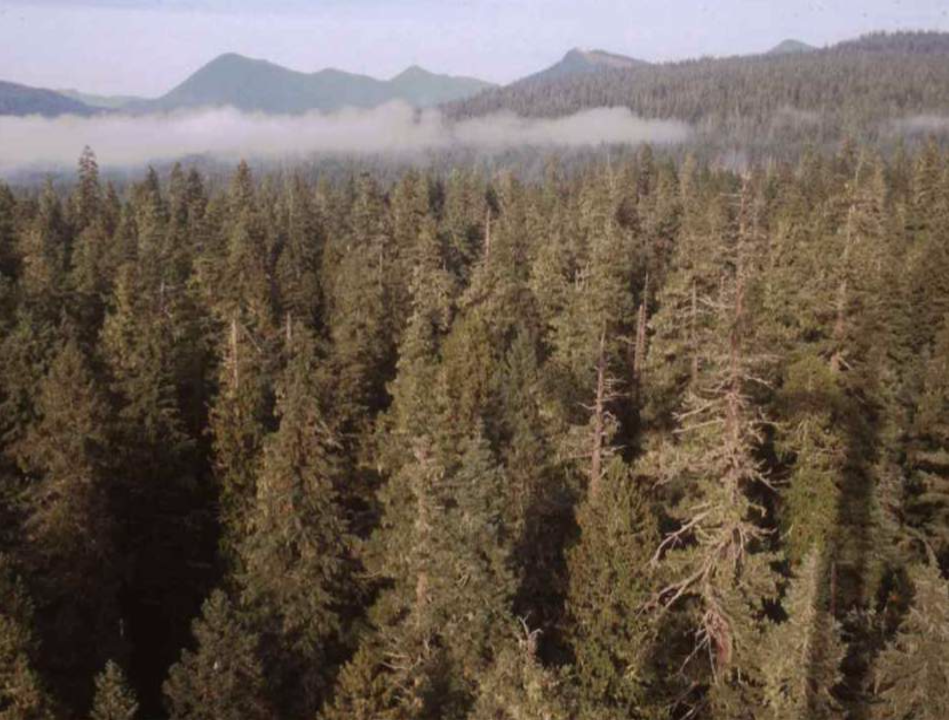

What biome is this and why?
taiga(coniferous forest), lots of trees, big area, high elevation
What is the main characteristic of deserts?
Low rainfall, generally less than 30 cm per year.
What are the temperature conditions in deserts?
very hot during the day, but some (Great Basin, Gobi) are cold most of the year. Large temperature swings between day and night are common.
What plants are found in deserts?
Grasses(when water is available) Succulents (cacti)
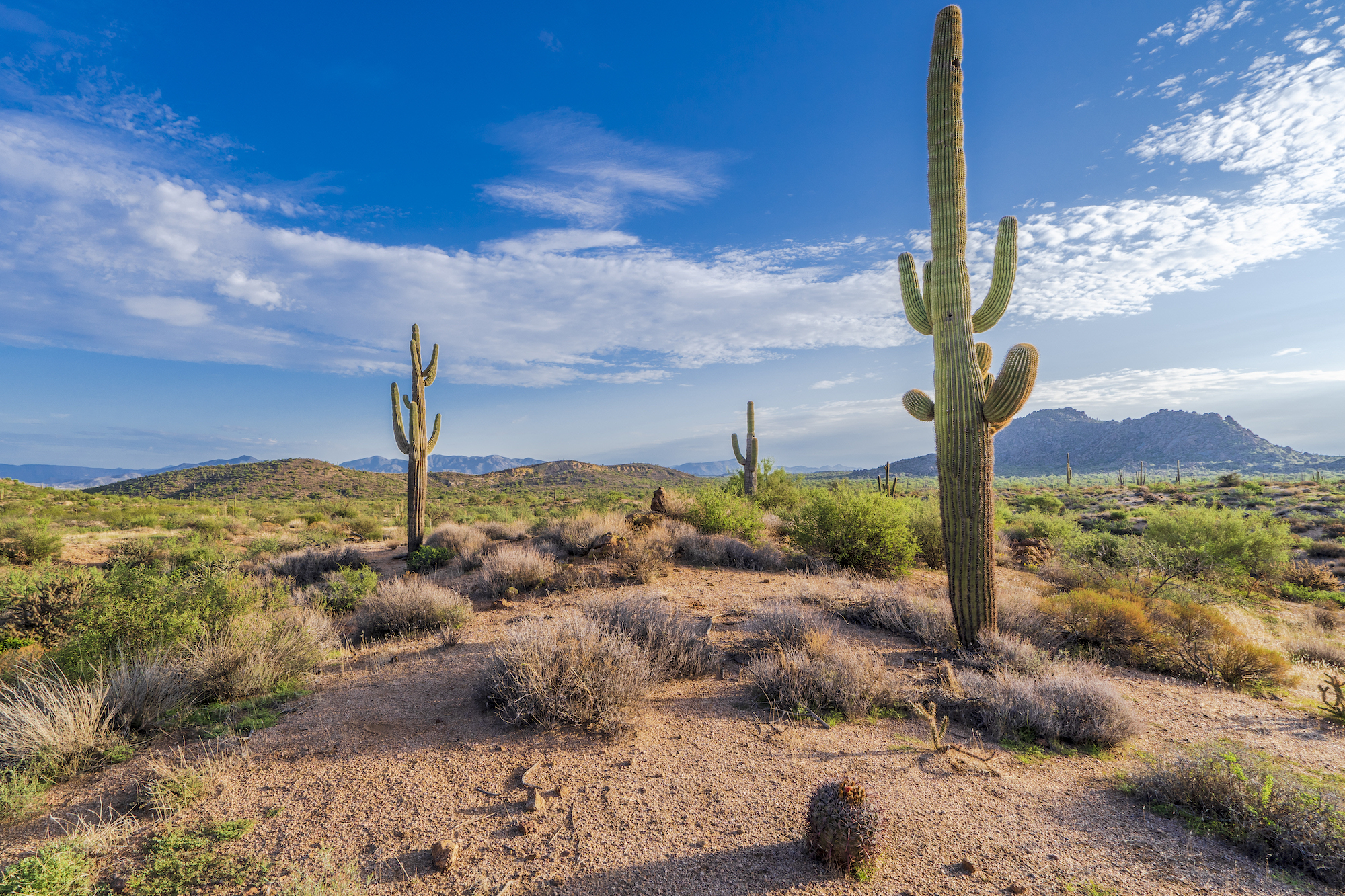

What biome is this and why?
Desert, succelents, dry, little rainfall,
What is the main characteristic of grasslands?
Grasses and forbs dominate. Fire and grazing prevent the establishment of shrubs and trees.
What climate conditions allow grasslands to exist?
Moderate to low rainfall and a wide range of temperatures
What prevents trees from becoming the dominant vegetation in grasslands?
Seasonal drought, occasional fires, and grazing by herbivores
Where are grasslands found around the world?
They are widespread. Examples include the Prairies of North America, Steppes of Asia, Pampas of Argentina, Veldts of South Africa, and Puszta of Hungary.
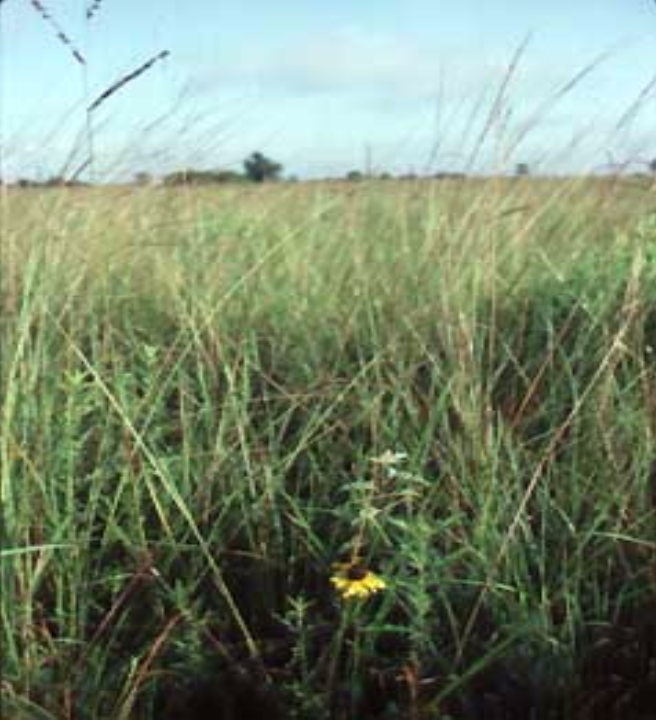

Which biome is this and why
Grasslands; The landscape is dominated by dense, tall —> Trees and large shrubs are noticeably absent
What climate characterizes temperate deciduous forests?
Moderate rainfall and mild to warm summers with cool to cold winters.
Where do temperate deciduous forests occur?
At mid-latitudes, where moisture is sufficient to support the growth of large trees.
How do organisms cope with winter in temperate deciduous forests?
Winters are cold enough to prohibit photosynthesis; most organisms go dormant or hibernate.
What is the vegetation structure in temperate deciduous forests?
Dense stands of deciduous trees predominate. Trees have distinct vertical layers, including one or two strata of trees and an understory of shrubs.
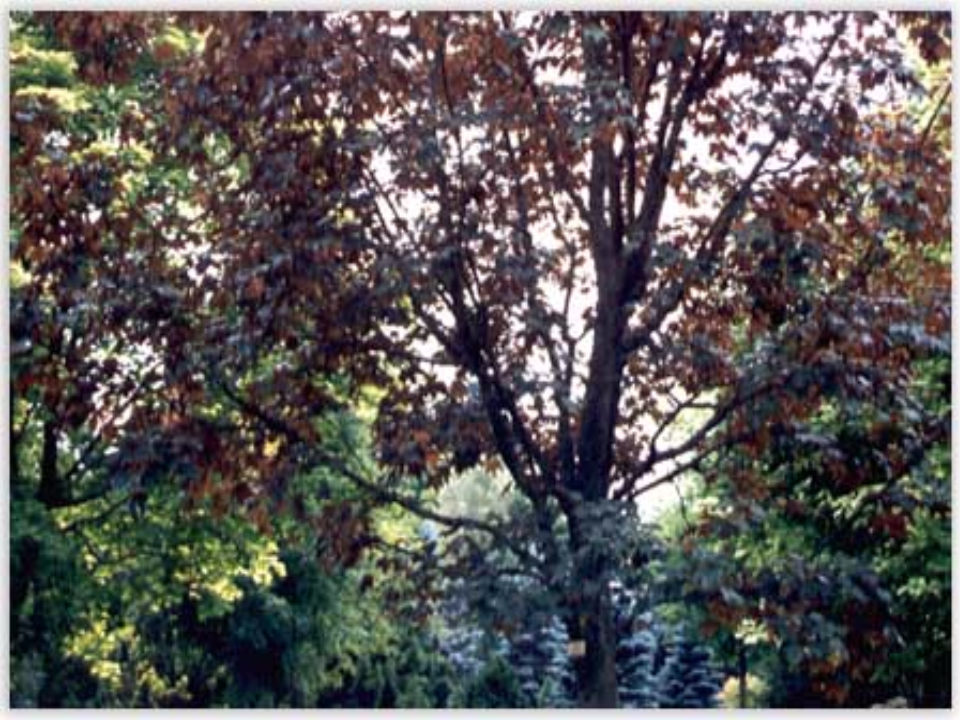

What biome is this and why?
temperate deciduous forests —> trees havee distinct vertical layers***
What is notable about tropical rain forests in terms of productivity and biodiversity?
They are the most productive biome on the planet and harbor the most biodiversity.
Where are tropical rain forests typically found?
Near the equator, where temperatures are warm and relatively constant year-round.
What types of plants are found in tropical rain forests?
Broad-leafed evergreen trees, shrubs, woody vines, and epiphytes. Epiphytes are plants that live on other plants (e.g., orchids and mistletoe).
What is the rainfall pattern in tropical rain forests?
High rainfall, often with a pronounced rainy season and a dry season.
How is competition for light structured in tropical rain forests?
Competition for light is intense. There is pronounced stratification with several layers of trees.
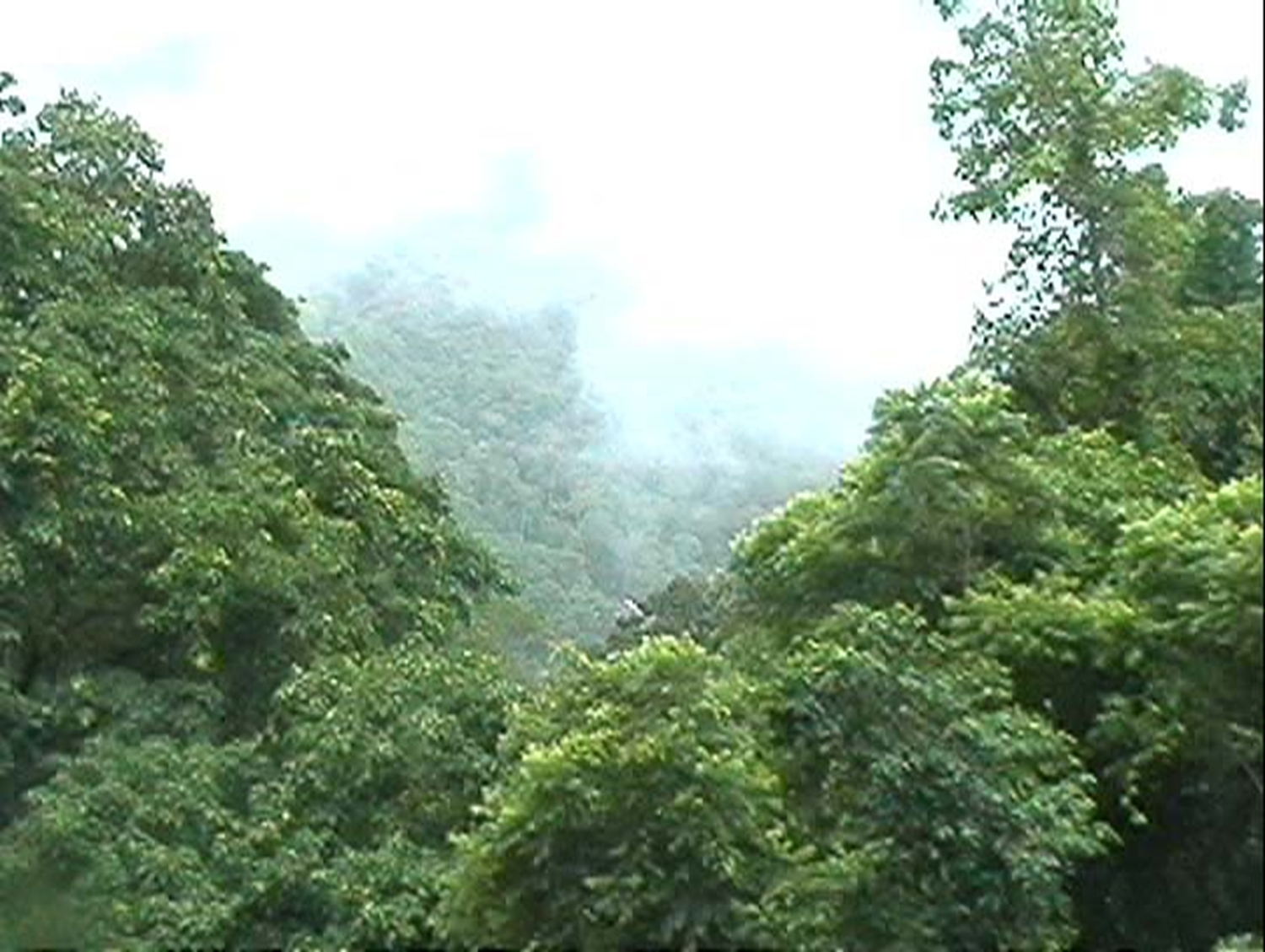

Which biome is this and why?
Tropical rainforests, dense grouping —> competition for light
What primarily structures and defines aquatic communities?
Availability of sunlight and nutrients.
Is the term “biome” commonly used for aquatic environments?
No, though oceans are sometimes divided into oceanic regions.
How are aquatic environments similar to terrestrial ones?
They include large volumes of habitat defined by a few basic factors, like light and nutrients.
How is spatial structure provided in aquatic communities?
The water column provides spatial structure. Communities within an oceanic region are stratified spatially.
Where does the intertidal zone occur?
Where ocean meets land, in the area between high and low tide, inhabited by many specially adapted organisms.
How is the intertidal zone structured?
It is stratified: upper areas experience different abiotic factors and host different organisms than lower areas.
What are wetlands?
Areas covered in water that support aquatic plants.
How do wetlands vary in water coverage?
They range from periodically flooded regions, to soil saturated during the growing season, to permanently flooded areas.
What are some typical types of wetlands?
Estuaries Swamps Marshes Bogs and Fens
What is an estuary?
A wetland that occurs at the mouths of rivers, where freshwater meets the ocean.
What is a swamp?
A wetland that is flooded and dominated by trees.
What is a marsh?
A wetland that is flooded and dominated by sedges and grasses.
What are bogs and fens?
Wetlands with distinctive vegetation due to soil chemistry: bogs are very acidic, fens are very alkaline.
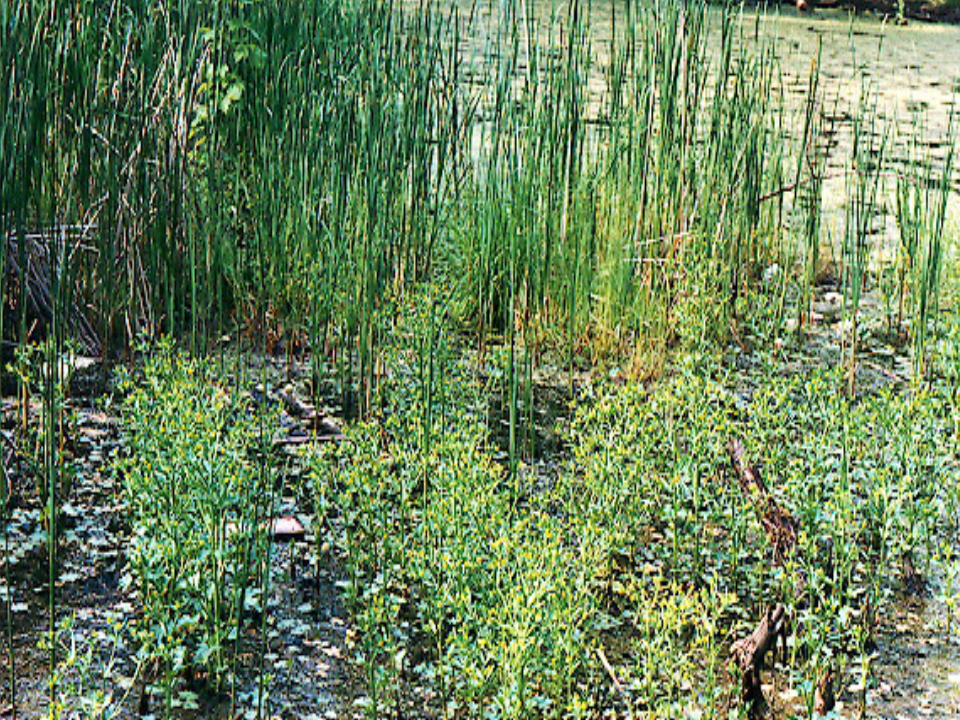

What biome is this and why
Wetlands: dense growth of low-lying plants and tall reeds, Visible water surface with algae or duckweed Shallow, standing water
What is the pelagic zone in the open ocean?
The upper layer of the ocean where light penetrates the top few meters. Nutrient concentrations are generally low (except in upwelling areas). Organisms are floating or free-swimming (nekton). Major producers are photosynthetic algae.
What is the abyssal zone in the open ocean?
The deep ocean where light is absent. Nutrients arrive by falling from above, and it supports a variety of specially-adapted organisms.
What are anthromes?
Human-dominated ecosystems that replace or modify natural biomes.
How do anthromes reflect previous biomes?
They always reflect the original biome to some extent, but the degree of modification varies: from moderate (grazed grassland, logged forest), to considerable (cropland), to extreme (cityscape).
Give an example of a highly modified anthrome.
A palm oil plantation in Southeast Asia is a virtual monoculture, often planted on cleared rainforest.
What are open ocean gyres?
Areas in the middle of ocean basins where photosynthesis is limited to the top layer due to low nutrient availability. Productivity and biodiversity are generally low.
Which statement about the scientific method is accurate?
A scientifically valid hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable—some data could theoretically invalidate it. Other statements about “proving hypotheses,” all experiments, or laws are incorrect.