Neuropsychology Key Terms Exam 1
1/294
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1 - 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
295 Terms
Alexia
the loss of the ability to read
Amnesia
partial or total loss of memory
Apraxia
inability to make sequences of movement that results from the disconnection of motor areas from sensory areas
Ataxia
a neurological condition characterized by a lack of muscle coordination, resulting in clumsy, unsteady movements due to damage to the cerebellum or nervous system.
Symptoms include gait imbalance, poor hand coordination, speech issues (dysarthria), and eye movement abnormalities
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiological processes, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal
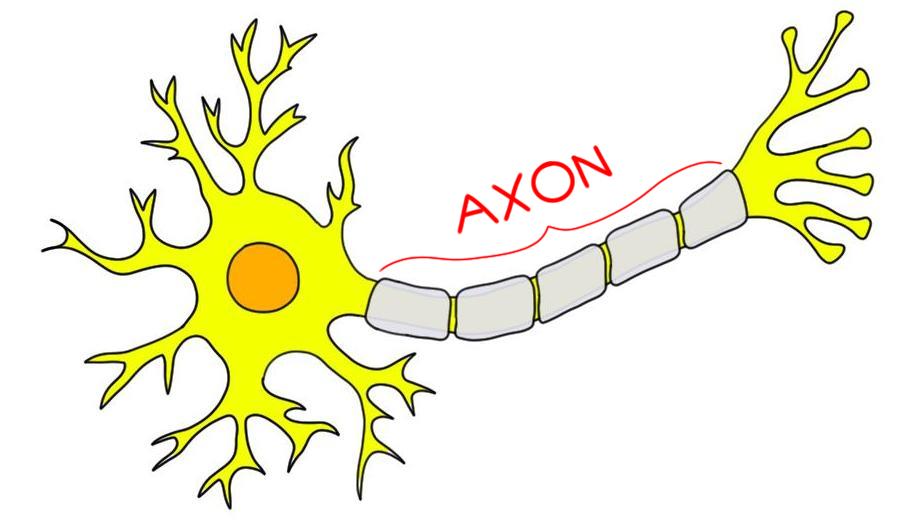
axon
usually long and single nerve-cell process that usually conducts impulses away from the cell body
binding problem
the challenge of explaining how the brain integrates disparate features (such as color, shape, motion, and location) processed in separate brain regions into a single, cohesive, and unified perception of an object
The essence of the puzzle: although the brain analyzes sensory events through multiple parallel channels that do not converge on a single brain region, we perceive a unified experience, such as a memory.
brain
The part of the central nervous system that is responsible for processing sensory information and coordinating movements.
brain theory
states that the brain is the source of behavior
brainstem
The hypothalamus, midbrain, and hindbrain. (Some authorities also include the thalamus and basal ganglia
broca’s aphasia
An inability to speak fluently despite the presence of normal comprehension and intact vocal
mechanisms; results from a lesion to Broca’s area. Also called expressive aphasia, or nonfluent aphasia.
Broca’s area
An anterior speech area in the left hemisphere (frontal operculum) that functions with the motor cortex
to produce movements needed for speaking. Damage to this area results in Broca aphasia.
cell assemblies
A hypothetical group of neurons that become functionally connected because they receive the same
sensory inputs; proposed by Donald Hebb to be the basis of perception, memory, and thought.
cell body (soma)
A core region of the cell that contains the nucleus and other organelles for making proteins. Also called
the soma
central nervous system (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord that are encased in bone — the skull and vertebrae, respectively — and cannot regrow after damage
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
A clear solution of sodium chloride and other salts that cushions the brain and may play a role in
removing metabolic waste. CSF fills the ventricles inside the brain and circulates around the brain,
beneath the arachnoid layer in the subarachnoid space
clinical trial
A consensual experiment directed toward developing a treatment
computed tomography (CT)
An X-ray technique that produces a static, three-dimensional image of the brain in cross section — a CT
conduction aphasia
A type of fluent aphasia resulting from severing fiber connections between anterior and posterior speech zones; speech sounds and movements are retained, but speech is impaired because it cannot be conducted from one region to the other.
corpus callosum
A commissure (fiber system) that connects homotopic areas in the two hemispheres. A split-brain
patient is one whose corpus callosum has been severed.
dendrite
A branching extension of a neuron’s cell membrane that greatly increases the surface area of the cell
and collects information from other cells.
dorsal stream
A visual processing pathway from the primary visual cortex to the parietal lobe; guides movements
relative to objects
dualism
The philosophical position that two distinct entities underlie human consciousness: one is mind (or
soul), the other is the body
epigenetics
Differences in gene expression related to environment and experience
epilepsy
A condition caused by spontaneous, abnormal discharges of brain neurons as a result of scarring from
injury, infections, or tumors and characterized by recurrent seizures associated with a disturbance of
consciousness.
fluent aphasia
A speech disorder in which a person articulates words in a languagelike fashion, but what is said actually makes little sense; usually results from damage to the left posterior cortex
forebrain
The cerebral hemispheres, basal ganglia, thalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and septum
frontal lobe
All the neocortex and connections forward of the central sulcus.
functional brain imaging
A method of imaging that determines the relative contribution of different brain regions to behavior
glia
Nervous-system cells that provide insulation, nutrients, and support and aid in repairing neurons and
eliminating waste products.
gyri
A convolution (bump) in the neocortex produced by folding
hemispheres
On the left and right sides of the cerebrum and cerebellum, either of the pair of structures constituting
the telencephalon.
hierarchical organization
A principle of cerebral organization in which information is processed serially, with each level of
processing assumed to represent the elaboration of some hypothetical process.
intelligence quotient (IQ)
Defined originally as the ratio of mental age to chronological age multiplied by 100. On contemporary
intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned a value of 100, and a person’s IQ score is expressed relative to 100.
lateral fissure
A deep cleft in the cortical surface of the brain that separates the temporal and parietal lobes. Also called Sylvian fissure
lateralization
A process by which functions become located primarily on one side of the brain
localization of function
The theory that different brain regions have different functions
longitudinal fissure
ma
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A technique that produces a static, three-dimensional brain image by passing a strong magnetic field
through the brain, followed by a radio wave, and then measuring the radiation emitted from hydrogen
atoms
materialism
A philosophical position which holds that behavior can be explained as a function of the nervous system without explanatory recourse to the mind.
mind-body problem
A quandary in explaining how a nonmaterial mind and a material body interact.
minimally conscious state (MCS)
A condition in which a person can display some rudimentary behaviors but is otherwise not conscious.
motor pathways
Nerve fibers that connect the brain and spinal cord to the body’s muscles through the somatic nervous system
natural selection
Darwin’s theory explaining how new species evolve and how existing species change over time; states
that differential success in the reproduction of characteristics (phenotypes) results from the interaction
of organisms with their environment.
neocortex
The newest layer of the brain, forming the outer layer, or “new bark”; has four to six layers of cells; in this book, synonymous with cortex
neural tube
A structure in the early stage of brain development from which the brain and spinal cord develop
neuron
A nerve cell that transmits and stores information: the basic unit of the nervous system; includes the cellbody (soma), many processes (dendrites), and an axon.
neuron theory
the idea that the unit of brain structure and function is the neuron, or nerve cell
neuroplasticity
The nervous system’s potential for physical or chemical change that enhances its adaptability to
environmental change and its ability to compensate for injury. Also called plasticity or brain plasticity.
neuropsychology
Study of the relationships between brain function and behavior.
occipital lobe
A general area of the cortex that lies in the back part of the head
parietal lobe
A general region of the brain lying behind the frontal lobe, beneath the parietal bone
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The collective name for all the neurons in the body that are located outside the brain and spinal cord and can regrow after damage.
persistent vegetative state (PVS)
A condition in which a person is alive but unable to communicate or to function independently at even
the most basic level.
phenotype
Individual characteristics that can be seen or measured
phrenology
The long-discredited study of the relationship between mental faculties and the skull’s surface features.
positron emission tomography (PET)
An imaging technique that detects changes in blood flow by measuring changes in the uptake of
compounds such as oxygen or glucose; used to analyze the metabolic activity of neurons.
psychometrics
The science of measuring human abilities.
sensory pathways
Nerve fibers that convey sensory information to the brain
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Nerve fibers that are extensively connected to sensory receptors on the body’s surface and to muscles
and that carry information to the CNS. A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system.
species
A group of organisms that can interbreed
spinal cord
Part of the central nervous system that is enclosed within the vertebral column.
Structural brain imaging
A method of brain imaging that describes the structure, cells, and fibers of the brain.
sulci
A cleft in the cortex produced by folding
temporal lobe
An area of the cortex and connections below the lateral fissure, adjacent to the temporal bones.
topographic organization
A neural–spatial representation of the body or areas of the sensory world a sensory organ detects
traumatic brain injury (TBI)
A wound to the brain that results from a blow to the head
trephining
Removing a disc of bone, chiefly from the skull.
ventral stream
A visual processing pathway from the primary visual cortex to the temporal cortex for object
identification and perception of related movements
visual-form agnosia
An inability to see the shapes of objects or to recognize objects or drawings of them
Wernicke aphasia
An inability to comprehend or to produce meaningful speech even though the production of words
remains intact.
Wernicke’s area
Secondary auditory cortex (part of the planum temporale, roughly equivalent to Brodmann’s area 22),
which regulates language comprehension. Also called posterior speech zone.
Mind
The psyche; the faculty, or brain function, by which one is aware of one’s surroundings and by which one
experiences feeling, emotions, and desires and is able to attend, reason, and make decisions.
Wernicke-Geshwind Model
A theoretical model of the neurological organization of language that involves a serial passage of
information from the auditory cortex to the posterior speech zone to the anterior speech zone.
alleles
An alternative form of a gene; a gene pair contains two alleles.
cladogram
A phylogenetic tree that branches repeatedly, suggesting a classification of organisms based on the time sequence in which evolutionary branches arise.
critical period
A developmental window during which some event has a long-lasting influence on an individual. Also called sensitive period
culture
Complex learned behaviors passed from generation to generation through teaching and experience.
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A long, complex macromolecule consisting of two interconnected helical strands; contains an organism’s genetic information
down syndrome
A chromosomal abnormality that results in intellectual disability and other deficits, usually caused by
an extra chromosome 21. Also called trisomy 21.
dystonia
An imbalance in muscle tone, usually excessive muscle tone.
encephalization quotient (EQ)
The ratio of actual brain size to expected brain size for a typical mammal of a particular body size.
epigenetic
Differences in gene expression related to environment and experience.
gene methylation (DNA Methylation)
A process in which a methyl group attaches to the DNA sequence, suppressing gene expression.
genotype
An individual’s genetic makeup
heterozygous
Having two different alleles for the same trait.
hominins
A term referring to the human family, the primate species that include modern human, extinct human
species, and immediate ancestors, but not apes.
homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait.
huntigton disease
A hereditary disorder characterized by chorea (ceaseless, involuntary, jerky movements) and
progressive dementia, ending in death
meme
An idea, a behavior, or a style that spreads from person to person within a culture.
mutation
An alteration of an allele that yields a different version of the allele.
parkinson’s disease
A disorder of the motor system that is correlated with a loss of dopamine in the brain and characterized
by tremors, muscular rigidity, involuntary movements (akathesia), and changes in emotion and
memory.
phenotypic plasticity
An individual’s capacity to develop into more than one phenotype.
species-typical behaviors
Behavior that is characteristic of all members of a species. Also called species-specific behavior.
Tay-Sachs disease
An inherited birth defect caused by the loss of genes that encode the enzyme necessary for breaking
down certain fatty substances; appears 4 to 6 months after birth and results in seizures, blindness,
degenerating motor and mental abilities, and death by about age 5.
transgenic animals
A product of technology in which numbers of genes or a single gene from one species is introduced into
the genome of another species, passed along, and expressed in subsequent generations
wild-type
The allele that is most common in a population.
afferent
Conducting toward a central nervous system area.
amygdala
An almond-shaped collection of nuclei in the base of the temporal lobe; the part of the limbic system
that participates in emotional and species-typical behaviors.
anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
A vessel originating from the carotid artery that irrigates the medial and dorsal parts of the cortex,
including the orbitofrontal and dorsolateral frontal regions, anterior cingulate cortex, corpus callosum,
and striatum.