Linkage and Mapping
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What generation must you look at to see if there was a cross over event?
you have to look at the F2 generation to see what happened during meiosis because you can’t look directly at meiosis itself in the F1 generation
What is unique about neurospora?
they grow in haploid
they can mate under certain conditions even though they are haploid and when this mating happens a fusion occurs between the two mating types creating a diploid cell → it goes though meiosis and then it goes through mitosis again → the spores produced are kept in a sac called the ascus
you get an tetrad → mitosis occurs creating an octad
Does crossing over happen before or after DNA replication?
we now know that it happens after DNA replication
if it happened BEFORE DNA replication… you wouldn’t get any parental types in the progeny within a single ascus → they would all be recombinant OR all parental if recombination didn’t occur
if it happened AFTER DNA replication… you get half parental types and half recombinant in the progeny within a single ascus
What produces a higher chance of recombination?
being further apart
how to calculate recombination frequency
(recombinant 1 + recombinant 2) / total mitotic events x100
the percentage achieved = distance between the two genes
Why can’t the recombination frequency of two genes exceed 50%?
because of independent assortment and the fact that re result will always be a 50-50 chance of getting the parental type or recombinant type
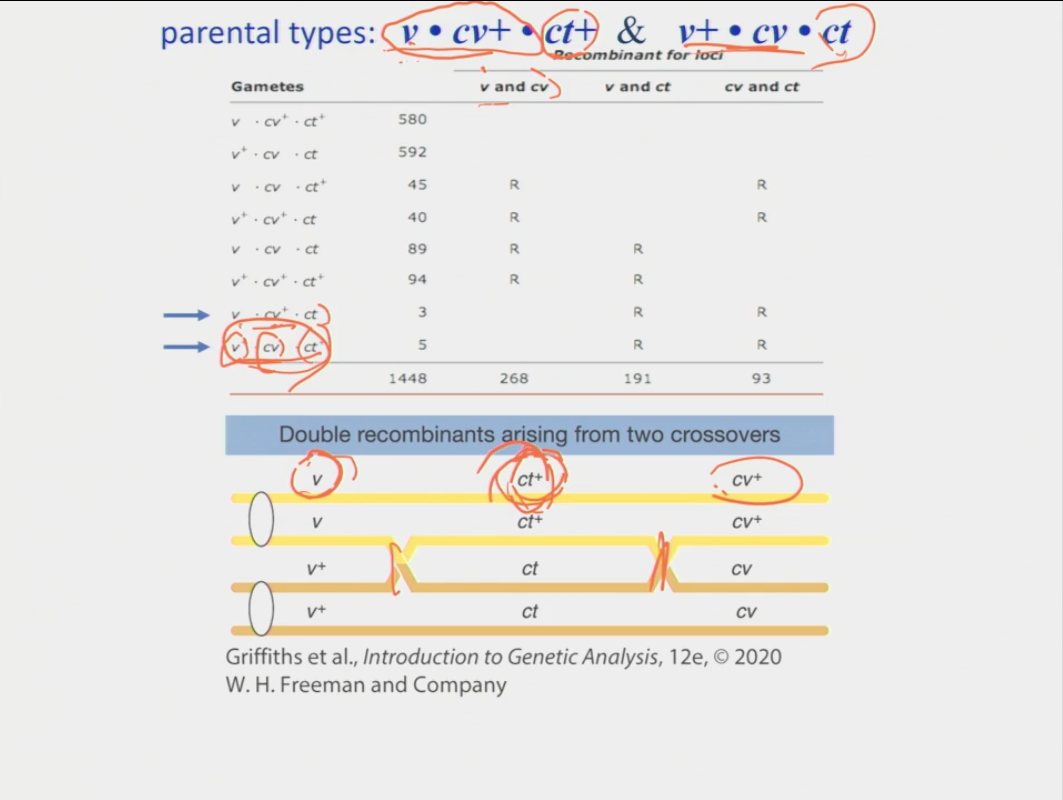
describe the 3 point cross
cross between double mutant and single mutant → the F1 resulting in the wild-type again because the genes are haplosufficient
then an F1 heterozygous female is crossed with a tester male
how many possible gamete genotypes can be produced? → 2×2×2 =8
How do you determine the distances each gene is from one another?
once you have the recombinant frequency values → the percentages represent the cM distance between each gene so you can map them to see the order of the genes

Why is there a discrepancy between the positioning of the genes and the distance between the two that are furthest apart?
it means that there are two recombinants that were the result of a double crossover event
calculation: 2 (the addition of the two double recombinants) + the original number with the highest percentage/ total x 100