510 Week 2 Advocacy, Stress, Sensory Processing, and Executive Functioning
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Advocacy
Efforts directed toward promoting occupational justice and empowering clients to seek and obtain resources to fully participate in daily life occupations
Therapeutic Mode (Advocacy)
Disability is a result of environmental barriers; therapist responds to physical, social, and environmental barriers
Advocating for the Client
Helping a student list strengths and needs prior to an IEP meeting
Advocating for Community/Population
Speaking to local officials regarding policies or laws affecting individuals with disabilities
Advocating for the Profession
Providing handouts at a health fair about OT services and how to access support
Self-Advocacy
Advocacy for oneself including decision-making, obtaining information, developing support networks, knowing rights and responsibilities, reaching out for help, and self-determination
Self-Advocacy for Client
Encouraging client participation in IEP or care meetings to express wants and needs
Self-Advocacy as a Clinician
Advocating for position, using research to back choices, workload vs caseload awareness, knowing limits
Stress
Tension when demands are beyond perceived abilities
Physiological Stress effects which system
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system (controls adpative system, signals regulation of cortisol)
Cortisol
Stress hormone affecting mood, motivation, fear, insulin release, blood glucose, HR, and BP
Chronic High Cortisol Effects
Impacts brain development, EF, mood and emotional regulation, memory, and health conditions
Physical Dysregulation
Disrupted homeostasis leading to disrupted thinking and feeling overwhelmed or out of control
Emotional Dysregulation
Anxiety, panic, agitation, fearfulness, angry outbursts, sleeplessness, fatigue, numbness, withdrawal
Tina Champagne OTP
Uses sensory approaches to create therapeutic environments
Sensory Modulation (DESNOS Model)
Tina champagne, Sensory input influences hormonal secretion and brain regions involved in attention and memory
Sensory Modulation Benefits
Increased safety, security, and therapeutic relationship
OTP Role During Heightened Stress
Safe place, lower voice, empathetic facial cues, calming sensory strategies
Calming Sensory Strategies
Oral motor activities, ball tossing, deep breathing, humming, music
Types of sensory modulation approaches
grounding and calming
Grounding Strategies
Weighted blankets, joint compression, body socks, wrist/ankle weights, aerobic exercise, sour/hot candies
Calming Approaches
Hot showers, drumming, decaf tea, yoga
Sensory Rooms
Calm, quiet spaces to remove stimuli and support emotional regulation
Sensory Integration Rooms
Not meant to be calming; serve a specific sensory purpose
Snoezelen Rooms
Less stimulating environments
Executive Functioning (EF)
High-order cognitive processes supporting goal-directed behavior, self-regulation, and problem solving
Core EF Components
Inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, planning, organization, self-monitoring
Adolescent Brain Development
Ongoing PFC maturation, synaptic pruning, myelination, increased efficiency but not full maturity
Limbic System Influence
Heightened emotional influence over PFC in adolescence
EF Development Trajectory
Develops into mid-20s; varies by context; affected by stress and emotion
Risk-Taking
Limbic system dominance over PFC, emotion-driven decisions, peer influence
EF Impact on Occupations
Supports routines, roles, responsibilities, and participation
School Occupations (EF)
Organization, time management, homework completion, participation
Social Participation (EF)
Impulse control, perspective taking, conflict resolution
ADLs and IADLs (EF)
Sleep routines, personal care organization, money management, prevocational skills
MOHO (EF)
Volition, habituation, performance capactiy; Ef supports competence; Environment influences EF
Cognitive-Based Approaches
Metacognitive strategy training, self-monitoring, reflection, GPDC
General EF Strategies
Environmental structuring, visual supports, task analysis, graded practice
Group-Based Interventions
Peer-based EF skill building supporting generalization
Acquisitional Theory
Behavior is response from environment, how the children interact with the environment and determine behaviors
Social Participation FOR
Supports social pragmatics, language, and EF to participatin ni occupation
what are the skills in the Social Participation FOR that are needed for adolescents to participate in occupations
Process info, Understand others, Consider alternatives, Anticipate consequences, evaluate outcomes
EF Challenges in Social Skills
Impulse control, flexibility, initiation, planning, monitoring self , emotion regulation
Dynamic Interactional Model (DIM)
Cognition modified through activity, environment, strategies, and self-awareness. Assess. w/ interviews, rating scales, performance analysis, weekly calender planning activity Ori. TBI
Multi-Context Approach
Metacognitive strategy-based intervention promoting self-monitoring and evaluation with the goals to enhance occupational performance . Baed on Dynamic intercation theory
Public Health Model
Enriches life through meaningful engagement in everyday activities
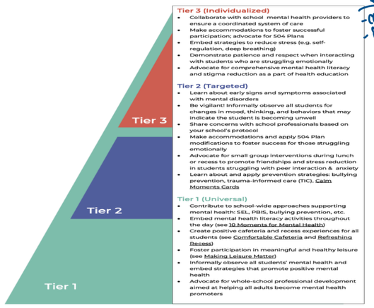
Tiered Mental Health Framework
OTP collaboration with families, schools, and communities to support adolescents